Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Oil Outline: - A. History of Use
Transféré par
VishalIndrapuriTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Oil Outline: - A. History of Use
Transféré par
VishalIndrapuriDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Oil Outline
A. History of Use
B. Formation of Oil
C. Oil Refining
D. What are the environmental Concerns?
History of Use
1858: first oil drilled in Canada
1859: Edwin Drake!
Who is he?
He was the first person in the U.S. to drill for oil
Where?
Titusville, Pennsylvania
Initial cost: $20 per barrel, within three years
dropped to 10 cents
Now why do we measure oil in barrels?
History of Use
1901: Texas! Spindletop gushed 60m
high and gave 100,000 bbl a day
Name:
Petro means rock
Oleum means oil
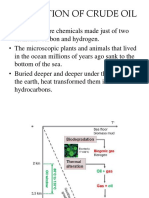
B. Formation of Oil
Oil usually occurs with natural gas:
mixture of hydrocarbons of light molecular
weight
Forms almost exclusively from organic
matter in marine sedimentswhereas
natural gas forms in both marine and
terrestrial rocks
? Remember coal? What is that?
B. Formation of Oil
Marine Realm
Remains of free-floating planktonic organisms
Plankton are rich in lipids
Terrestrial plant has cellulose and lignin
B. Formation of Oil
Depth represents
Increase in time
Increase in temperature
Increase in pressure
B. Formation of Oil
Diagenesis
Surface to about km, T , 50C; CH
4
Catagenesis
50 to 150C, P about 1.5 kb
Compaction of sediment, expulsion of water
Organic matter becomes kerogen and liquid
petroleumbiogenic gas decreases, however
some formed by thermal cracking of kerogen
Wet gas: methane+ethane+propane+butane
B. Formation of Oil
Metagenesis
Greater than 4 km, and 150C
Dry gas
C rich residue
Graphite developed
C. Oil Refining
Method by which crude oil converted to
petroleum products
(I think that a barrel (42 galproduces 44 gal
of petroleum products)
Distillation (fractionation)
At high temperature the lightest fractions rise
to the top of a tower, heavier fractions
condense at bottom
C. Oil Refining
Typical Oil
Gasoline C
4
to C
10
27%
Kerosene C
11
to C
13
13%
Diesel C
14
to C
18
12%
Heavy gas oil C
19
to C
25
10%
Lubricating oil C
26
-C
40
20%
Residue >C
40
18%
C. Oil Refining
What we get out of oil now with modern
refineries:
50% gas
30% fuel oil
7.5% jet fuel
HOW??
C. Oil Refining
Thermal Cracking
Catalytic Cracking
adds H, hydrogenation and thus increase the
gas productions
Contaminants
Sulphur, Vanadium, Nickel
D. What are the environmental
concerns?
Oil Spills
Pollution
According to 1992 Worldwatch breathing in
Bombay is equivalent to smoking 10
cigarettes/day
Global warming
Transportation infrastructure
Burning gasoline in cars/trucks
Produces the following
95% of CO
58% of hydrocarbons
32% of nitrous oxides
2% of sulphur dioxide
11.3% of the particulates
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 001lecture Petroleum Refinery History and Intro B&W 001Document50 pages001lecture Petroleum Refinery History and Intro B&W 001Ahmed MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Lesson 2 Petroleum Processing (Upto Mid Semester)Document22 pagesUnit 2 Lesson 2 Petroleum Processing (Upto Mid Semester)Green JeskPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Discussed The Crude Formation-06-01-2022 (06-Jan-2022) Material - I - 06-01-2022 - LECTURE - 1 - Crude - OilDocument36 pages1-Discussed The Crude Formation-06-01-2022 (06-Jan-2022) Material - I - 06-01-2022 - LECTURE - 1 - Crude - Oilish guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding the Oil & Gas IndustryDocument29 pagesUnderstanding the Oil & Gas Industrypintu ramPas encore d'évaluation
- Origin and Migration of PetroleumDocument46 pagesOrigin and Migration of PetroleumHaziq YussofPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Conversion ES 832a: Eric SavoryDocument38 pagesEnergy Conversion ES 832a: Eric SavoryBetty GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument35 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionDeniz AkoumPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Texts About Petroleum For Reading ComprehensionDocument4 pages2 Texts About Petroleum For Reading ComprehensionEmmanuel Tartagal100% (2)
- Lecture 19: Energy and Fossil Fuels: Learning ObjectivesDocument48 pagesLecture 19: Energy and Fossil Fuels: Learning ObjectivesjparanotiPas encore d'évaluation
- APES Chapter 10 Final PPT For Dec 2004Document43 pagesAPES Chapter 10 Final PPT For Dec 2004Cristy Mae Parol JandayanPas encore d'évaluation
- FORMATION OF CRUDE OIL: HOW ORGANIC MATTER TRANSFORMS INTO PETROLEUMDocument36 pagesFORMATION OF CRUDE OIL: HOW ORGANIC MATTER TRANSFORMS INTO PETROLEUMmuneeb tahirPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum IndustryDocument49 pagesPetroleum IndustryQueenie BalisongPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 161115070923 PDFDocument39 pagesModule 1 161115070923 PDFSafwan NasirPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum CHE252 Industrial ProcessDocument31 pagesPetroleum CHE252 Industrial ProcessdaabgchiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Chemical IndustryDocument45 pagesThe Chemical IndustryYantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Processes and Sustainability: PetroleumDocument32 pagesChemical Processes and Sustainability: PetroleumMohd Shahrul Nizam SallehPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To The Oil Gas IndustryDocument71 pagesIntroduction To The Oil Gas IndustryTamunodein WestPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit7 MAL PDFDocument23 pagesUnit7 MAL PDFSudhanvaDesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Crude Oil Characterization - IntroDocument26 pages1 - Crude Oil Characterization - Introvijetakumari.201ch059Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oil & GasDocument27 pagesOil & GasCiprian HarliscaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuels & Combustion (MEE322) NotesDocument17 pagesFuels & Combustion (MEE322) NotessheenPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Nonrenewable EnergyDocument56 pages10 Nonrenewable Energyabbicox.stlPas encore d'évaluation
- PetroleumDocument92 pagesPetroleumBabyPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Chemistry - Liquid Fuels and Cracking ProcessesDocument84 pagesEngineering Chemistry - Liquid Fuels and Cracking ProcessesL PircyPas encore d'évaluation
- Refinery 1Document45 pagesRefinery 1makramPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Oil and Gas BusinessDocument27 pagesUnderstanding Oil and Gas BusinessAdnan ShakirPas encore d'évaluation
- PetroDocument28 pagesPetroErma FatihaPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum RefiningDocument28 pagesPetroleum RefiningAdityaPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon, Climate, & Energy Resources: Unit 4 Fossil Fuel FormationDocument46 pagesCarbon, Climate, & Energy Resources: Unit 4 Fossil Fuel FormationPatricia NikolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Crude OilDocument25 pagesCrude OilBipin AryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Coal & PetroleumDocument31 pagesCoal & PetroleumRarunbe Ram0% (1)
- Natural Gas Engineering: An SEO-Optimized TitleDocument79 pagesNatural Gas Engineering: An SEO-Optimized TitleSamPas encore d'évaluation
- Crude Oil 32Document11 pagesCrude Oil 32Muneer Basha BashaPas encore d'évaluation
- Agrees On Its Origin, They Differ On The Issues Related To: - Even Though Believer of Organic Origin of PetroleumDocument52 pagesAgrees On Its Origin, They Differ On The Issues Related To: - Even Though Believer of Organic Origin of PetroleumSumanth Reddy0% (2)
- Fossil FuelsDocument38 pagesFossil FuelsrhiPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTERDocument26 pagesCHAPTERNesi HafilaPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Oil Industry & Crude Oil CompositionDocument21 pagesHistory of Oil Industry & Crude Oil CompositionNuman KhawajaPas encore d'évaluation
- GasolineDocument41 pagesGasolineRaphael SebucPas encore d'évaluation
- Raw Material Petrochemical IndustriesDocument13 pagesRaw Material Petrochemical Industriesabdul rehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum explained: Why we use oil and what it's made ofDocument65 pagesPetroleum explained: Why we use oil and what it's made ofOmer KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Mesin Konversi Energi 1: I Gede Eka LesmanaDocument38 pagesMesin Konversi Energi 1: I Gede Eka LesmanaPrayogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Crudeoilpetrolium 2022Document30 pagesCrudeoilpetrolium 2022Ndapiwa KengaletswePas encore d'évaluation
- General Introduction To Oil and Gas IndustryDocument23 pagesGeneral Introduction To Oil and Gas IndustryRialgong Chuol DuokPas encore d'évaluation
- Chevron EverythingYouNeedToKnowAboutFuels v3 1a DESKTOPDocument32 pagesChevron EverythingYouNeedToKnowAboutFuels v3 1a DESKTOPNamal FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy CrisesDocument79 pagesEnergy CrisesRana Zafar Arshad100% (1)
- OriginDocument8 pagesOriginAkashShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Industries Part 2 1Document23 pagesChemical Industries Part 2 1Yasir MukhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil Refinary Dr Adndn 2016-مهمةDocument234 pagesOil Refinary Dr Adndn 2016-مهمةHmid AljbrePas encore d'évaluation
- MCB 410Document33 pagesMCB 410oluwaleye victorPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum Refinery Engineering: Dr. M. Saif Ur RehmanDocument37 pagesPetroleum Refinery Engineering: Dr. M. Saif Ur RehmanMahi FatimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Crude Oil Refinery-Short VersionDocument14 pagesCrude Oil Refinery-Short Versionligia hancuPas encore d'évaluation
- Heavy-Oil ReservoirsDocument72 pagesHeavy-Oil ReservoirsCostelPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum Processing: From Exploration to RefiningDocument58 pagesPetroleum Processing: From Exploration to RefiningGreen JeskPas encore d'évaluation
- Shale Oil Impacts on RefiningDocument24 pagesShale Oil Impacts on RefiningAnonymous NmOXutCKPas encore d'évaluation
- C1 RevisionDocument42 pagesC1 Revisionsophie harePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture - 1DM1 PETROLEUM CHE, YDocument59 pagesLecture - 1DM1 PETROLEUM CHE, YAlhaj MassoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum and Natural Gas Geology - Prof.Dr. Nam─▒k ├Зa─ЯatayDocument45 pagesPetroleum and Natural Gas Geology - Prof.Dr. Nam─▒k ├Зa─ЯatayStephen FortisPas encore d'évaluation
- Liquid Fuels: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Metallurgy DivisionD'EverandLiquid Fuels: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Metallurgy DivisionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Crude Petroleum analysis handbook: Crude oil Quality control, #1D'EverandCrude Petroleum analysis handbook: Crude oil Quality control, #1Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Optimization of Pulsed TIG Welding Process Parameters On Mechanical Properties of AA 5456 Aluminum Alloy WeldmentsDocument10 pagesOptimization of Pulsed TIG Welding Process Parameters On Mechanical Properties of AA 5456 Aluminum Alloy Weldmentsnofrian akbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Genapol PF 10Document2 pagesGenapol PF 10Mohamed HalemPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumables Accessories DMA 80 PDFDocument4 pagesConsumables Accessories DMA 80 PDFwillwPas encore d'évaluation
- Diffusivity Formula Chart (Infographic)Document3 pagesDiffusivity Formula Chart (Infographic)Safayet AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure Covalumine PigmentsDocument3 pagesBrochure Covalumine PigmentsMamadou Lamine FallPas encore d'évaluation
- Hombright S-Id (WD)Document6 pagesHombright S-Id (WD)何恭彥Pas encore d'évaluation
- Creep and Failure of Lead-Free Solder AlloysDocument77 pagesCreep and Failure of Lead-Free Solder AlloysTamara KhasimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Glucose Solution ViscosityDocument13 pagesGlucose Solution ViscosityThomas Teh Qian Hua100% (1)
- Rock Failure under Confined Brazilian TestDocument9 pagesRock Failure under Confined Brazilian TestMichel SartoPas encore d'évaluation
- Is 8147 PDFDocument170 pagesIs 8147 PDFMangesh GajbhiyePas encore d'évaluation
- Niosh SHO Exam Notes - Module 3 Question and Answer PDFDocument19 pagesNiosh SHO Exam Notes - Module 3 Question and Answer PDFExcellentdeals4all94% (51)
- Book 72902Document43 pagesBook 72902Latest sports updatesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 10: Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA)Document13 pagesLecture 10: Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA)Binoni Laja EndongPas encore d'évaluation
- Spintronics Based Random Access Memory: A ReviewDocument19 pagesSpintronics Based Random Access Memory: A ReviewAgtc TandayPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane Potential MCQ-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesMembrane Potential MCQ-WPS OfficeFavourPas encore d'évaluation
- Greener One-Pot Synthesis of Chromeno Oxazin and Oxazin Quinoline Derivatives and Their Antibacterial ActivityDocument5 pagesGreener One-Pot Synthesis of Chromeno Oxazin and Oxazin Quinoline Derivatives and Their Antibacterial ActivityIJAERS JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- RMS 6th 2019Document14 pagesRMS 6th 2019angelgupta2303Pas encore d'évaluation
- Coconut OilDocument12 pagesCoconut OilAniruddh KhalatkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Parker SizeTempratureApplicationMediaPressureDocument40 pagesParker SizeTempratureApplicationMediaPressuretrilemmaPas encore d'évaluation
- HEAT TRANSFERDocument28 pagesHEAT TRANSFERSayantan ChakrabortyPas encore d'évaluation
- 780HT - Catalytic Gas DetectorDocument48 pages780HT - Catalytic Gas DetectorinelecstarPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 A5 Amiya Kumar SahuDocument7 pages6 A5 Amiya Kumar SahuChandan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Document2 pagesPNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Nickson KomsPas encore d'évaluation
- HW Proteins EnzymesDocument2 pagesHW Proteins Enzymesapi-524061079Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kate Coleen D. Galera BS in Chemistry II May 4, 2017 Experiment 11 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and DetergentsDocument5 pagesKate Coleen D. Galera BS in Chemistry II May 4, 2017 Experiment 11 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and DetergentsKatePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy & Physiology Made Incredibly Visual!Document412 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Made Incredibly Visual!Cereal KillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Cocaine in Blood of Coca ChewersDocument10 pagesCocaine in Blood of Coca ChewersKarl-GeorgPas encore d'évaluation
- Metallurgy For Non Metallurgist - Module-2Document65 pagesMetallurgy For Non Metallurgist - Module-2ajaysharma_1009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Protocols Cleaning Disinfection SterilizationDocument23 pagesProtocols Cleaning Disinfection SterilizationGeneSegoviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Iit Model Paper 10Document13 pagesIit Model Paper 10studysteps.in100% (1)