Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
© 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Transféré par
Nishant MishraTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
© 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Transféré par
Nishant MishraDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
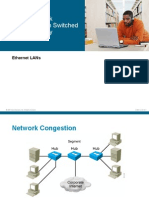
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-2 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2
Spanning-Tree Protocol
Overview
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-3
Objectives
Upon completing this lesson, you will be
able to:
Describe the purpose and operation of the STP
Explain how to implement STP to solve the
problems associated with redundant switched
or bridged topologies
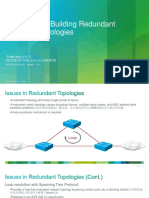
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-4
Provides a loop-free redundant network topology by
placing certain ports in the blocking state.
Spanning-Tree Protocol
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-5
One root bridge per network
One root port per nonroot bridge
One designated port per segment
Nondesignated ports are unused
Spanning-Tree Operation
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-6
Bpdu = Bridge Protocol Data Unit
(default = sent every two seconds)
Root bridge = Bridge with the lowest bridge ID
Bridge ID =
In the example, which switch has the lowest bridge ID?
Spanning-Tree Protocol
Root Bridge Selection
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-7
Spanning-tree transits each port through
several different states:
Spanning-Tree Port States
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-8
Spanning-Tree Port States (Cont.)
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-9
Spanning-Tree Path Cost
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-10
Spanning-Tree Example
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-11
Spanning-Tree Recalculation
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-12
Spanning-Tree Convergence
Convergence occurs when all the switch and
bridge ports have transitioned to either the
forwarding or the blocking state.
When the network topology changes,
switches and bridges must recompute the
Spanning-Tree Protocol, which disrupts user
traffic.
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-13
Rapid Spanning-Tree Protocol
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-14
Rapid Transition to Forwarding
2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ICND v2.03-15
Summary
STP is a bridge-to-bridge protocol used to maintain a
loop-free network.
STP establishes a root bridge, a root port, and designated
ports.
With STP, the root bridge has the lowest bridge ID, which
is made up of the bridges priority and MAC address.
With STP, ports transition through four states: blocking,
listening, learning, and forwarding.
If a change occurs to the network topology, STP
maintains connectivity by transitioning some blocked
ports to the forwarding state.
RSTP significantly speeds the recalculation of the
spanning tree when the network topology changes.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument30 pagesSpanning Tree ProtocolVo Ngoc HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Improving Performance With Spanning Tree: Medium-Sized Switched Network ConstructionDocument30 pagesImproving Performance With Spanning Tree: Medium-Sized Switched Network ConstructionĐen Vs TrắngPas encore d'évaluation
- ICND20S03L01Document15 pagesICND20S03L01api-3706840Pas encore d'évaluation
- © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument39 pages© 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedRajPas encore d'évaluation
- Improving Performance With Spanning Tree: Medium-Sized Switched Network ConstructionDocument30 pagesImproving Performance With Spanning Tree: Medium-Sized Switched Network ConstructionDuyHuynhPas encore d'évaluation
- BRK-135T CCNA Switching PDFDocument60 pagesBRK-135T CCNA Switching PDFparthasn83Pas encore d'évaluation
- 14 - Configuring A RouterDocument25 pages14 - Configuring A RouterQuan PhanPas encore d'évaluation
- STPOverviewDocument14 pagesSTPOverviewruwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Internetworking Concepts Overview: © 1999, Cisco Systems, IncDocument39 pagesInternetworking Concepts Overview: © 1999, Cisco Systems, IncIrfan Ahmed KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 - STPDocument22 pagesChapter 8 - STPchrispewePas encore d'évaluation
- 25.6 Enabling OSPFDocument54 pages25.6 Enabling OSPFQuan PhanPas encore d'évaluation
- ScaNv6 instructorPPT Chapter3Document29 pagesScaNv6 instructorPPT Chapter3sochea domjsPas encore d'évaluation
- Internetworking Concepts Overview: © 1999, Cisco Systems, IncDocument50 pagesInternetworking Concepts Overview: © 1999, Cisco Systems, IncShashi Kant RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- ICND20S07L01Document12 pagesICND20S07L01api-3706840Pas encore d'évaluation
- TECDCT-2145 Cisco FabricPathDocument156 pagesTECDCT-2145 Cisco FabricPathWeiboraoPas encore d'évaluation
- © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument19 pages© 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedVo Ngoc HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- INFO CCNA 2 Routing and Switching v5Document55 pagesINFO CCNA 2 Routing and Switching v5SabinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Switching in An Enterprise NetworkDocument42 pagesSwitching in An Enterprise NetworkSida HashimPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter1 - Part 1 SWDocument36 pagesChapter1 - Part 1 SWAsy RafPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation and Utilization of Layer 2 VPN Technologies: BRKAGG-2000Document56 pagesImplementation and Utilization of Layer 2 VPN Technologies: BRKAGG-2000Nguyen Tien HaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Switch Hardware ArchitectureDocument65 pagesSwitch Hardware ArchitecturevickygssnPas encore d'évaluation
- Brkcom 3001Document103 pagesBrkcom 3001connect2praveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Ip RoutingDocument67 pagesChapter 5 Ip RoutingWilfredo AparicioPas encore d'évaluation
- Exploration LAN Switching Chapter5Document36 pagesExploration LAN Switching Chapter5Reymond D. SePas encore d'évaluation
- CMTS OverviewDocument54 pagesCMTS OverviewAmol AmollPas encore d'évaluation
- STP PDFDocument60 pagesSTP PDFMartyn OlaPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Routing and Switching: © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation - IDDocument60 pagesCCNA Routing and Switching: © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation - IDMartyn OlaPas encore d'évaluation
- BRKSEC-3052 Troubleshooting DMVPNsDocument108 pagesBRKSEC-3052 Troubleshooting DMVPNssailubPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Center Design Power SessionDocument192 pagesData Center Design Power SessionJarod AhlgrenPas encore d'évaluation
- SS7 OverviewDocument113 pagesSS7 OverviewnicolescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Iec Material Datasheet All PDFDocument57 pagesIec Material Datasheet All PDFDelna RintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch1.RS InstructorPPT Chapter1 Final My LectureDocument7 pagesCh1.RS InstructorPPT Chapter1 Final My LectureManisara PuentePas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco CGS2520 Data Sheet c78 593672Document14 pagesCisco CGS2520 Data Sheet c78 593672Adib RahmatPas encore d'évaluation
- Establishing A WAN Connection With Frame RelayDocument22 pagesEstablishing A WAN Connection With Frame RelayL Robert BravePas encore d'évaluation
- Cgs2520 TechnicalDocument80 pagesCgs2520 Technicallinden1961Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Solving Network ChallengeDocument13 pages11 Solving Network ChallengeKeepmoving NevergiveupPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco 2 Chapter 1Document31 pagesCisco 2 Chapter 1wendellpoPas encore d'évaluation
- ZXCZXCZXDocument9 pagesZXCZXCZXDaryl BrionesPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolved EPC For LTE by CiscoDocument70 pagesEvolved EPC For LTE by Ciscotech_geekPas encore d'évaluation
- BRKDCT-2334 Real World Data Centre Deployments and Best Practice SessionDocument126 pagesBRKDCT-2334 Real World Data Centre Deployments and Best Practice SessionKevin Anel Hernández RuízPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1.2.10 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant Links ListoDocument9 pages2.1.2.10 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant Links ListoMartin SaldañaPas encore d'évaluation
- RS instructorPPT Chapter1 FinalDocument26 pagesRS instructorPPT Chapter1 Finalnovenosigno20fPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1.2.10 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant Links - ILM PDFDocument18 pages2.1.2.10 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant Links - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov84% (37)
- Catalyst 6500 ArchitectureDocument91 pagesCatalyst 6500 ArchitectureAnonymous WjkE6LPas encore d'évaluation
- IPexpert's Cisco CCIE R&S (v4) Written Exam Video On Demand SlidesDocument1 078 pagesIPexpert's Cisco CCIE R&S (v4) Written Exam Video On Demand Slidesveracespedes100% (1)
- BRKDCT 2840Document182 pagesBRKDCT 2840PankajPas encore d'évaluation
- Spanning Tree VlanDocument16 pagesSpanning Tree VlanAaron Reyes SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 3.2routingDocument27 pagesDay 3.2routingGorvam SaddarPas encore d'évaluation
- Metro Ethernet Standards: Lim Wong APAC Consulting TeamDocument56 pagesMetro Ethernet Standards: Lim Wong APAC Consulting Teamchaidar_lakarePas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Nexus 9200 Platform SwitchesDocument16 pagesCisco Nexus 9200 Platform SwitchesRobert UrquiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Switch v7 Ch08Document65 pagesSwitch v7 Ch08TheltonPas encore d'évaluation
- Completing An Isdn Bri Call: © 2000, Cisco Systems, IncDocument34 pagesCompleting An Isdn Bri Call: © 2000, Cisco Systems, IncVo Ngoc HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 LAN DesignDocument22 pagesChapter 1 LAN DesignFatah Nur AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Bridging in The Data Center With or Without Spanning Tree: BRKDCT-1927Document53 pagesBridging in The Data Center With or Without Spanning Tree: BRKDCT-1927汤源Pas encore d'évaluation
- Determining IP Routes: © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1Document39 pagesDetermining IP Routes: © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1احمد مسعودPas encore d'évaluation
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkD'EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1D'EverandCisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1Pas encore d'évaluation
- IP Encapsulation, Fragmentation, and Reassembly: Computer Science Prof. MartinsDocument26 pagesIP Encapsulation, Fragmentation, and Reassembly: Computer Science Prof. MartinsNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Google Advanced FeaturesDocument26 pagesGoogle Advanced FeaturesNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Wan Frly 12 4 BookDocument248 pagesWan Frly 12 4 BookNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Be Prepared - Getting Ready For Job InterviewsDocument97 pagesBe Prepared - Getting Ready For Job InterviewshutsupPas encore d'évaluation
- For Browse More TCY Network Engineer's Resume, Please VisitDocument1 pageFor Browse More TCY Network Engineer's Resume, Please VisitNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Iewb-Rs Technology Labs Ipv6: Brian Dennis, Ccie # 2210 (R&S / Isp Dial / Security / Service Provider)Document17 pagesIewb-Rs Technology Labs Ipv6: Brian Dennis, Ccie # 2210 (R&S / Isp Dial / Security / Service Provider)Nishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide 3.2Document106 pagesConfiguring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide 3.2skuzurov67% (3)
- CCIE Notes From ExperienceDocument27 pagesCCIE Notes From Experienceapi-3817990Pas encore d'évaluation
- Using OSPF in MPLS VPN EnvironmentDocument52 pagesUsing OSPF in MPLS VPN EnvironmentMauro Ferri100% (1)
- Configuring IP Access Lists: Document ID: 23602Document18 pagesConfiguring IP Access Lists: Document ID: 23602Srikanth ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Betwwen You and DreamDocument13 pagesBetwwen You and DreamNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Interview Questionjkndqwjks For System Engineer Net. EngDocument5 pagesInterview Questionjkndqwjks For System Engineer Net. EngNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring IP Access Lists: Document ID: 23602Document18 pagesConfiguring IP Access Lists: Document ID: 23602Srikanth ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- 001Document4 pages001Venkata Nagi ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Engineer CV TemplateDocument2 pagesNetwork Engineer CV TemplatemacumuPas encore d'évaluation
- 2523 Hub N SpokeDocument2 pages2523 Hub N SpokeNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- 026Document3 pages026frontechaslPas encore d'évaluation
- 023Document3 pages023Nishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Commn Fundamentals DATA and SIGNALDocument13 pagesData Commn Fundamentals DATA and SIGNALapi-3806586100% (1)
- Using OSPF in MPLS VPN EnvironmentDocument52 pagesUsing OSPF in MPLS VPN EnvironmentMauro Ferri100% (1)
- Neibour RelationshipDocument1 pageNeibour RelationshipNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco IOS Cisco Discovery Protocol Command Reference Cdp-Cr-BookDocument42 pagesCisco IOS Cisco Discovery Protocol Command Reference Cdp-Cr-BookNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Subnetting Course MapDocument0 pageCCNA Subnetting Course Maprick018Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2523 Full Mesh. 4 3 3Document2 pages2523 Full Mesh. 4 3 3Nishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA GlossaryDocument36 pagesCCNA GlossaryAamir KhalilPas encore d'évaluation
- 3600 Hub N SpokeDocument2 pages3600 Hub N SpokeNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW Careercert InfoDocument1 pageWWW Careercert InfoNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2523 Full Mesh. 4 3 3Document2 pages2523 Full Mesh. 4 3 3Nishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- 3600 Hub N SpokeDocument2 pages3600 Hub N SpokeNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- TosDocument3 pagesTosNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- PRP and HSR For High Availability Networks in Power Utility Automation - A Method For Redundant Frames DiscardingDocument8 pagesPRP and HSR For High Availability Networks in Power Utility Automation - A Method For Redundant Frames DiscardingashishPas encore d'évaluation
- Limit Bandwidth Using Layer 7 Protocol MarkingDocument5 pagesLimit Bandwidth Using Layer 7 Protocol Markingwawa_sygPas encore d'évaluation
- PPP and HDLCDocument8 pagesPPP and HDLCBinod RImalPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1:: FoundationDocument39 pagesTopic 1:: FoundationJalil AsifPas encore d'évaluation
- 98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 5Document19 pages98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 5cvigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Configure Site ID and Interfaces for Site ZJD286Document175 pagesConfigure Site ID and Interfaces for Site ZJD286fahadPas encore d'évaluation
- CS425: Computer Networks: Bhaskaran Raman (Braman) AT (Cse - Iitk.ac - In)Document11 pagesCS425: Computer Networks: Bhaskaran Raman (Braman) AT (Cse - Iitk.ac - In)23wingsPas encore d'évaluation
- GCCEventlog 2023-7-29Document8 pagesGCCEventlog 2023-7-29daniriveromolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalyst 8500 Configuration GuidelinesDocument32 pagesCatalyst 8500 Configuration GuidelinesApple Johnnyseed100% (1)
- Access Lists Workbook - Student Edition Ver1 - 2 PDFDocument69 pagesAccess Lists Workbook - Student Edition Ver1 - 2 PDFJuan LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Gait C 1 1 2 0Document27 pagesGait C 1 1 2 0jiri_lPas encore d'évaluation
- Nokia 99Document167 pagesNokia 99Ali HumayunPas encore d'évaluation
- Comandos Cisco, Huawei, Transition, MikrotikDocument4 pagesComandos Cisco, Huawei, Transition, MikrotikJuan Carlos Sotelo CéspedesPas encore d'évaluation
- Diameter and IMS for Call RoutingDocument1 pageDiameter and IMS for Call Routinglouie mabiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Call Type A-Party B-Party Date & Time Duration Cell ID ImeiDocument130 pagesCall Type A-Party B-Party Date & Time Duration Cell ID ImeiMohsin RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 1 v6.0 ITN Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2019 - Premium IT Exam & Certified PDFDocument1 pageCCNA 1 v6.0 ITN Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2019 - Premium IT Exam & Certified PDFZersh EthioPas encore d'évaluation
- CU-E22 Configuration For AMIDocument4 pagesCU-E22 Configuration For AMIBilal WirkPas encore d'évaluation
- IP Phone Metavoice MV100 (P)Document2 pagesIP Phone Metavoice MV100 (P)Aditya Pratama SomantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sip PSTN Call FlowDocument7 pagesSip PSTN Call FlowPrakash SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- KMPL-2143 - EVPN Migration From Legacy To Modern ArchDocument32 pagesKMPL-2143 - EVPN Migration From Legacy To Modern ArchquintaPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 - 1 RTU500 End-To-End Cyber SecurityDocument25 pages09 - 1 RTU500 End-To-End Cyber SecuritybzyPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring RADIUS: Finding Feature InformationDocument46 pagesConfiguring RADIUS: Finding Feature InformationFilipe da SilveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Nimbra 390Document2 pagesNimbra 390Karyadi DjayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna The ExamDocument3 pagesCcna The Examyatish777Pas encore d'évaluation
- An Analysis of QUIC Use On Cloud EnvironmentsDocument75 pagesAn Analysis of QUIC Use On Cloud EnvironmentsVinicius Cardoso GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- All-in-One 10G Transport Tester: Key BenefitsDocument4 pagesAll-in-One 10G Transport Tester: Key BenefitsChrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Implement Spanning Tree Protocols: LAN Switching and Wireless - Chapter 5Document14 pagesImplement Spanning Tree Protocols: LAN Switching and Wireless - Chapter 5Anand WuPas encore d'évaluation
- FortiOS-6.4.0-Ports and ProtocolsDocument80 pagesFortiOS-6.4.0-Ports and ProtocolsHari KumavatPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco-Juniper Commands ComparisonDocument2 pagesCisco-Juniper Commands Comparisonich8dich100% (5)
- Tucano PrintDocument2 pagesTucano PrintAdarsh NanaiahPas encore d'évaluation