Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Financial Econometrics Introduction
Transféré par
Prabath Suranaga Morawakage0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
142 vues13 pagesEconometric for financial markets
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentEconometric for financial markets
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
142 vues13 pagesFinancial Econometrics Introduction
Transféré par
Prabath Suranaga MorawakageEconometric for financial markets
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 13
FINANCIAL ECONOMETRICS:
SCOPE AND METHODS
By Prabath. S. Morawakage
Financial Econometrics
Concerns
A mission for models that describe financial
time series such as prices, returns, interest
rates, financial ratios, defaults etc.
Reason for the existence of such subject?
Main Question in Financial Econometrics
Its a multi discipline
Finance
Economics
Mathematics
Statistics
The universe cannot be read until we have
learnt the language and become familiar with
the characters in which it is written. It is
written in the language of mathematics; the
letters are triangles, circles, and other
geometrical figures, without which it is
humanly impossible to comprehend a single
word.
Galileo -1623
It was only in the second half of the 20th
century that a quantitative description of
economics became a mainstream discipline:
econometrics (i.e., the quantitative science of
economics) was born.
Data Generating Process
We write mathematical models, that is, relationships
between different variables and/or variables in
different moments and different places.
The basic tenet of quantitative science is that there
are relationships that do not change regardless of
the moment or the place under consideration
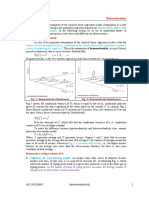
sea waves - random movement
in every moment and location the basic laws of hydrodynamics
hold without change
asset price - random movement
but econometric laws should hold in every moment and for
every set of assets
Econometric models model the economy or
financial markets
Information efficiency today Vs yesterday
Because the economy and financial markets are
artifacts subject to change, econometric models
are not unique representations valid throughout
time; they must adapt to the changing
environment.
financial econometrics uses both continuous
time and discrete time models
Derivatives Pricing
CAPAM
What is Data generating Process
In a discrete dynamic model the mathematical relation ship
between variables at different time is called the data
generating process
E.g. p
t + 1
= + p
t
+
t
+ 1
if we consider any two consecutive instants of time,
there is a combination of prices that behave as random
noise
E.g. p
t+ 1
pt
=
t + 1
an econometric model can be regarded as a
mathematical device that reconstructs a noise sequence
from empirical data.
Static models (i.e, models that involve only
one instant) are used to express relationships
between different variables at any given
time.
Static models are used, for example, to
determine exposure to different risk factors.
However, because they involve only one instant,
static models cannot be used to make forecasts;
forecasting requires models that link variables in
two or more instants in time.
Financial Econometrics at
Work
Applying financial econometrics involves thre
key steps:
1. Model selection
2. Model estimation
3. Model testing
Modeling issues
How do we apply statistics given that there is only one realization of
financial series?
Given a sample of historical data, how do we choose between linear
and nonlinear models, or the different distributional assumptions or
different levels of model complexity?
Can we exploit more data using, for example, high-frequency data?
How can we make our models more robust, reducing model risk?
How do we measure not only model performance but also the ability
to realize profits?
Important factors to be
considered
Time horizon
Model Riskiness
Model Robustness
APPLICATIONS
There has been a greater use of econometric
models in investment management since the
turn of the century. Application areas include:
Portfolio construction and optimization
Risk management
Asset and liability management
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 01 Introductory Econometrics 4E WoolridgeDocument13 pages01 Introductory Econometrics 4E WoolridgeKrak RanechantPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Test Bank Questions No Feedback - Chapter 3: y + X + X + X + UDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Test Bank Questions No Feedback - Chapter 3: y + X + X + X + Uimam awaluddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Linear Regression: y BX BX BXDocument14 pagesMultiple Linear Regression: y BX BX BXPalaniappan SellappanPas encore d'évaluation
- Agcv2012 SeptDocument12 pagesAgcv2012 SeptSimon MehariPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3Hope Knock100% (1)
- Chapt 2 MICDocument13 pagesChapt 2 MICAkkamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Econometrics Notes PDFDocument8 pagesEconometrics Notes PDFumamaheswariPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Value at Risk (Var) Models, Methods & Metrics - Excel Spreadsheet Walk Through Calculating Value at Risk (Var) - Comparing Var Models, Methods & MetricsDocument65 pages1-Value at Risk (Var) Models, Methods & Metrics - Excel Spreadsheet Walk Through Calculating Value at Risk (Var) - Comparing Var Models, Methods & MetricsVaibhav KharadePas encore d'évaluation
- SEM 4 - 10 - BA-BSc - HONS - ECONOMICS - CC-10 - INTRODUCTORYECONOMETRI C - 10957Document3 pagesSEM 4 - 10 - BA-BSc - HONS - ECONOMICS - CC-10 - INTRODUCTORYECONOMETRI C - 10957PranjalPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical t and F values for hypothesis testingDocument5 pagesCritical t and F values for hypothesis testingvisu009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Dummy Variable AssignmentDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Dummy Variable Assignmentharis100% (1)
- AEconometricAnalysisofQualitativeVariablesDocument21 pagesAEconometricAnalysisofQualitativeVariablesClaudio AballayPas encore d'évaluation
- Multicollinearity Among The Regressors Included in The Regression ModelDocument13 pagesMulticollinearity Among The Regressors Included in The Regression ModelNavyashree B MPas encore d'évaluation
- Estimating Demand: Regression AnalysisDocument29 pagesEstimating Demand: Regression Analysissamer abou saadPas encore d'évaluation
- Homoscedastic That Is, They All Have The Same Variance: HeteroscedasticityDocument11 pagesHomoscedastic That Is, They All Have The Same Variance: HeteroscedasticityNavyashree B M100% (1)
- 3 Multiple Linear Regression: Estimation and Properties: Ezequiel Uriel Universidad de Valencia Version: 09-2013Document37 pages3 Multiple Linear Regression: Estimation and Properties: Ezequiel Uriel Universidad de Valencia Version: 09-2013penyia100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Scope and Methods of EconomicsDocument59 pagesChapter 1 Scope and Methods of EconomicsMuhammad Maaz RashidPas encore d'évaluation
- Ordinary Least Square EstimationDocument30 pagesOrdinary Least Square Estimationthrphys1940Pas encore d'évaluation
- Econometrics Exam.Document4 pagesEconometrics Exam.Shayan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Theories of Dualism: (1) Social Dualism or Sociological DualismDocument9 pagesTheories of Dualism: (1) Social Dualism or Sociological DualismsheglinalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 7 PDFNarutoLLNPas encore d'évaluation
- Econometrics Solutions for Finance PanelsDocument4 pagesEconometrics Solutions for Finance PanelsNazim Uddin MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Econometrics ARMA GARCH ModelsDocument5 pagesFinancial Econometrics ARMA GARCH ModelsVANDITA MISHRA Economics BGR CampusPas encore d'évaluation
- Econ Assignment AnswersDocument4 pagesEcon Assignment AnswersKazımPas encore d'évaluation
- Two-Variable Regression Interval Estimation and Hypothesis TestingDocument36 pagesTwo-Variable Regression Interval Estimation and Hypothesis TestingOliver Tate-DuncanPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam 1Document4 pagesFinal Exam 1HealthyYOU50% (2)
- Dev't PPA I (Chap-4)Document48 pagesDev't PPA I (Chap-4)ferewe tesfaye100% (1)
- AutocorrelationDocument172 pagesAutocorrelationJenab Peteburoh100% (1)
- Stationarity and Unit Root TestingDocument21 pagesStationarity and Unit Root TestingAwAtef LHPas encore d'évaluation
- Introductory Econometrics For Finance Chris Brooks Solutions To Review - Chapter 3Document7 pagesIntroductory Econometrics For Finance Chris Brooks Solutions To Review - Chapter 3Bill Ramos100% (2)
- General Equilibrium, Growth, and Trade II: The Legacy of Lionel McKenzieD'EverandGeneral Equilibrium, Growth, and Trade II: The Legacy of Lionel McKenziePas encore d'évaluation
- Notes and Problems in Applied General Equilibrium EconomicsD'EverandNotes and Problems in Applied General Equilibrium EconomicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Keynesian Cross Model and Fiscal Policy MultipliersDocument30 pagesUnderstanding Keynesian Cross Model and Fiscal Policy MultiplierswaysPas encore d'évaluation
- Krugman2e Solutions CH13Document12 pagesKrugman2e Solutions CH13amw4011100% (1)
- MGMT331 Practice ProblemsDocument11 pagesMGMT331 Practice ProblemsSvetlana PetrosyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Econometrics 2010-2011Document483 pagesFinancial Econometrics 2010-2011axelkokocur100% (1)
- EconometricsDocument25 pagesEconometricsLynda Mega SaputryPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Business Statistics: Simple Linear Regression and CorrelationDocument50 pagesComplete Business Statistics: Simple Linear Regression and Correlationmallick5051rajatPas encore d'évaluation
- Econometrics Chapter Two-1Document41 pagesEconometrics Chapter Two-1haile ethioPas encore d'évaluation
- Nature of Regression AnalysisDocument22 pagesNature of Regression Analysiswhoosh2008Pas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Econometrics AutocorrelationDocument36 pagesApplied Econometrics AutocorrelationBarep Adji Widhi0% (1)
- Introduction to Regression Models for Panel Data Analysis WorkshopDocument42 pagesIntroduction to Regression Models for Panel Data Analysis WorkshopAnonymous 0sxQqwAIMBPas encore d'évaluation
- SM Basic Econometrics Gujarati Porter 5th EditionDocument10 pagesSM Basic Econometrics Gujarati Porter 5th EditionMuhammad Mohab83% (6)
- Economics Text BooksDocument4 pagesEconomics Text BooksKevin Andrew100% (1)
- Weil GrowthDocument72 pagesWeil GrowthJavier Burbano ValenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- 007 - Buku Basic Econometric Damodar N Gujarati 4th Solution-15-25Document12 pages007 - Buku Basic Econometric Damodar N Gujarati 4th Solution-15-25Kurniawan ArikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Econometrics II-1Document56 pagesEconometrics II-1Teneshu HorsisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Econometrics Intro CLRM PDFDocument46 pagesAdvanced Econometrics Intro CLRM PDFMarzieh RostamiPas encore d'évaluation
- For Chapter 2, Statistical Techniques in Business & EconomicsDocument61 pagesFor Chapter 2, Statistical Techniques in Business & EconomicsVic SzePas encore d'évaluation
- Harvard Economics 2020a Problem Set 3Document2 pagesHarvard Economics 2020a Problem Set 3JPas encore d'évaluation
- FIN 5309 Homework 5Document2 pagesFIN 5309 Homework 5Slaine JiaoPas encore d'évaluation
- EconometricsDocument1 pageEconometricsJessica SohPas encore d'évaluation
- The Economics of Inaction: Stochastic Control Models with Fixed CostsD'EverandThe Economics of Inaction: Stochastic Control Models with Fixed CostsPas encore d'évaluation
- Wooldridge 7e Ch01 SM-1Document5 pagesWooldridge 7e Ch01 SM-1Carlos Ignacio CidPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex08 PDFDocument29 pagesEx08 PDFSalman FarooqPas encore d'évaluation
- ArimaDocument4 pagesArimaSofia LivelyPas encore d'évaluation
- 178.200 06-4Document34 pages178.200 06-4api-3860979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 02 - The Structure of Economic Data and Basic Data HandlingDocument12 pagesChapter 02 - The Structure of Economic Data and Basic Data HandlingMuntazir HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Real Estate Financing Notes MortgageDocument15 pagesReal Estate Financing Notes MortgagePrabath Suranaga Morawakage100% (1)
- Relationship Between Macro - Economic Variables andDocument14 pagesRelationship Between Macro - Economic Variables andPrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- Leverage, Corporate FinanceDocument15 pagesLeverage, Corporate FinancePrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument21 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisPrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- Emerging Markets and L'Oreal MarketingDocument16 pagesEmerging Markets and L'Oreal MarketingPrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- Capital BudgetingDocument32 pagesCapital BudgetingPrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- Leverage, Financial and OperatingDocument15 pagesLeverage, Financial and OperatingPrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- Cost of CapitalDocument33 pagesCost of CapitalPrabath Suranaga Morawakage100% (1)
- Capital BudgetingDocument30 pagesCapital BudgetingPrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- SynoRise and Fall of BaanpsisDocument2 pagesSynoRise and Fall of BaanpsisPrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics: Basic Concepts, Data Collection and PresentationDocument19 pagesStatistics: Basic Concepts, Data Collection and PresentationPrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To LimitsDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To LimitsPrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- Integrating Processes To Build RelationshipsDocument42 pagesIntegrating Processes To Build RelationshipsPrabath Suranaga MorawakagePas encore d'évaluation
- Movie Segment: InstantaneousDocument18 pagesMovie Segment: InstantaneousAwishka ThuduwagePas encore d'évaluation
- Homogenous Coordinate System: Unit 1Document52 pagesHomogenous Coordinate System: Unit 1Sanand MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: Trigonometry Main Topic: Solving Logarithmic Equation Containing Logarithms. Sample QuestionDocument2 pagesSubject: Trigonometry Main Topic: Solving Logarithmic Equation Containing Logarithms. Sample Questioncathline austriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Solid MechanicsDocument469 pagesApplied Solid MechanicsMd AmirulPas encore d'évaluation
- Add Subtract FractionsDocument1 pageAdd Subtract FractionsKnight, Mason C StudentPas encore d'évaluation
- Regression Analysis GuideDocument37 pagesRegression Analysis GuideAbderrhman ErPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra Skills For Grade 10 PDFDocument35 pagesAlgebra Skills For Grade 10 PDFTeeranun NakyaiPas encore d'évaluation
- C03 P001 P010Document10 pagesC03 P001 P010何凱翔Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Pencil-and-Paper Algorithm For Solving Sudoku Puzzles: (Reduced From Paper by JF Crook)Document3 pagesA Pencil-and-Paper Algorithm For Solving Sudoku Puzzles: (Reduced From Paper by JF Crook)Brian Paul Taboada CheroPas encore d'évaluation
- Math8Q2F DoneDocument40 pagesMath8Q2F Donedream king100% (2)
- F Matrix CalculusDocument9 pagesF Matrix CalculusedwarzambranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Paper - Grade-V - MathsDocument8 pagesModel Paper - Grade-V - Mathsmaqbool ur rehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Srinivasa Ramanujan - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesSrinivasa Ramanujan - Britannica Online EncyclopediaEvariste MigaboPas encore d'évaluation
- OOP - I - GTU - Study - Material - Lab Manual - Object Oriented Programming - I (3140705) - 08052020070602AM PDFDocument129 pagesOOP - I - GTU - Study - Material - Lab Manual - Object Oriented Programming - I (3140705) - 08052020070602AM PDFRakesh Venkatesan100% (1)
- Note Aug 8 2023 5Document17 pagesNote Aug 8 2023 5Noha NabilPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimization Methods (MFE) : Elena PerazziDocument28 pagesOptimization Methods (MFE) : Elena Perazziddd huangPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Project Work: Made By: Aashish, Harinder, Rajat Anuj Sati, Navam, ArjunDocument12 pagesMathematics Project Work: Made By: Aashish, Harinder, Rajat Anuj Sati, Navam, ArjunJ Singh AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 6-1Document7 pagesLesson 6-1api-260352449Pas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Paper Class 3Document6 pagesMaths Paper Class 3sastryPas encore d'évaluation
- Direction. Encircle The Letter of Your Best Answer.: Name: - DateDocument3 pagesDirection. Encircle The Letter of Your Best Answer.: Name: - DateИан ЦомаиасPas encore d'évaluation
- Core Maths Extended Project and FSMQ Grade Boundaries June 2023Document1 pageCore Maths Extended Project and FSMQ Grade Boundaries June 2023penPas encore d'évaluation
- Vogal's Approximation MethodDocument12 pagesVogal's Approximation MethodRishab Jain 2027203Pas encore d'évaluation
- Game Theory WSC PDFDocument297 pagesGame Theory WSC PDFHoracioCastellanosMuñoaPas encore d'évaluation
- 62f896029b19ea001261ce5f-1660465185-Math 8 - Q2W1Document15 pages62f896029b19ea001261ce5f-1660465185-Math 8 - Q2W1Elmer HabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Tolerance AnalysisDocument5 pagesTolerance Analysisdeepakgr79Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tricks For Speed MathDocument3 pagesTricks For Speed MathSourav ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Improving Numeracy Performance Through Peer TutoringDocument14 pagesImproving Numeracy Performance Through Peer TutoringJomar Gasilla NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Cse2012 PPS3 w2022Document3 pagesCse2012 PPS3 w2022Lazer TronPas encore d'évaluation
- Pole-Zero Plots StabilityDocument9 pagesPole-Zero Plots StabilityNaveen SaiPas encore d'évaluation