Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Segmentation, Target and Positioning: Prashant@iimcal - Ac.in
Transféré par
senadi14Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Segmentation, Target and Positioning: Prashant@iimcal - Ac.in
Transféré par
senadi14Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Segmentation, Target and
Positioning
prashant@iimcal.ac.in
The Substance of Marketing
Want To Enter the Watch Business!!!
You Must Make A Set Of Important
(Marketing Related) Decisions!!!
WHAT ARE THESE DECISIONS???
The Probable Decisions are!!!
To which consumer should I sell my
watches?
How should I define the consumer I hope to
serve?
Should I think in terms of geography,
perhaps the country in which my consumer
lives?
Or may be the consumers income or sex or
fashion orientation is more important?
The Probable Decisions are!!!
What Product or Products should I offer?
For example should I offer digital or analog,
ornate or simple, multifunction or single
function?
How much should I charge for each watch?
Should I offer discounts to people who pay
cash or who buy in large amounts?
The Probable Decisions are!!!
Should I sell direct to consumers or through
stores, and if through stores, what type of
stores?
Do I want to offer my product in several
types of outlet or only in one type?
How do I select and service the particular
outlets I Chose?
Finally, How do I convince the store to carry
my brand?
The Probable Decisions are!!!
How should I communicate to the
consumers to whom I wish to sell?
Do I use advertising, and if so in what
media?
How do I reach the stores? Do I use sales
people?
Should the salespeople visit the stores or
should they just telephone them?
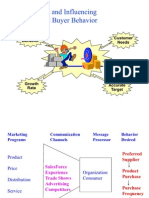
Views on the Marketing Processes
5-C Analysis
Customer
Competitor
Company
Collaborators
Context
S-T-P Marketing
Segmentation
Targeting
Positioning
4 Ps Marketing Plan
Product
Pricing
Promotion
Place
The Functional View
Views on the Marketing Processes
Understanding
Customer
Value
Creating
Customer
Value
The Process View
Capturing
Customer
Value
Delivering
Customer
Value
Sustaining
Customer
Value
Understanding Customer Value
Psychological
Functional
Economic
Steps in Market Segmentation,
Targeting,and Positioning
1. Identify
segmentation
variables and
segment the
market
2. Develop
profiles of
resulting
segments
Market
Segmentation
3. Evaluate
attractiveness
of each
segment
4. Select the
target
segment(s)
Market
Targeting
5. Identify
possible
positioning
concepts for
each target
segment
6. Select,
develop, and
communicate
the chosen
positioning
concept
Market
Positioning
Why Segmentation ?
Not all buyers alike
Subgroups may be identified
Subgroups smaller and more
homogeneous
Easier to satisfy smaller groups
How to Segment & Target?
1.
Break
market
down
2.
Group
into
segments
TARGET MARKET
3.
Choose
target
market
Basic Market-Preference
Patterns
(a) Homogeneous
preferences
Quality
E
c
o
n
o
m
y
(c) Clustered
preferences
E
c
o
n
o
m
y
Quality
(b) Diffused
preferences
E
c
o
n
o
m
y
Quality
Bases for Segmenting
Consumer Markets
Demographic
Sociographic
Lifestyle
Geographic
Behavior
Consumption
Predispositions
Bases for Segmenting
Business Markets
Geography
Organizational charateristics
Purchase behavior
Usage patterns
Organizational predispositions
Size, purchasing power, profiles
of segments can be measured.
Segments can be effectively
reached and served.
Segments are large or
profitable enough to serve.
Measurable
Accessible
Substantial
Differential
Actionable
Segments must respond
differently to different marketing
mix elements & programs.
Effective programs can be
designed to attract and serve
the segments.
Step 1. Market Segmentation
Requirements for Effective Segmentation
Segment 1
Segment 2
Segment 3
Segment 1
Segment 2
Segment 3
Company
Marketing
Mix
Company
Marketing
Mix
Company
Marketing Mix 1
Company
Marketing Mix 2
Company
Marketing Mix 3
Market
A. Undifferentiated Marketing
B. Differentiated Marketing
C. Concentrated Marketing
Step 2. Market Targeting
Market Coverage Strategies
Company Resources
Product Variability
Products Stage in the Life Cycle
Market Variability
Competitors Marketing Strategies
Step 2. Market Targeting
Choosing a Market-Coverage
Strategy
Step 3. Choosing a Positioning
Strategy
Products Position - the way the product is
defined by consumers on important
attributes - the place the product occupies
in consumers minds relative to competing
products.
Marketers must:
Plan positions to give their products the
greatest advantage in selected target markets,
Design marketing mixes to create these
planned positions.
Positioning
The way consumers perceive the brand
relative to its competition
ID competitive advantage
Stress salient characteristics
Differentiate
Services
Differentiation
i.e. Delivery, Installation,
Repair Services, Customer
Training Services
Product
Differentiation
i.e. Features,
Performance, Style &
Design, or Attributes
Image
Differentiation
i.e. Symbols,
Atmospheres, Events
Personnel
Differentiation
i.e. Hiring, Training
Better People Than
Competitors Do
Identifying Possible Competitive
Advantages
Five Patterns of Target Market
Selection
Single-segment
concentration
Product
specialization
M1 M2 M3
P1
P2
P3
Selective
specialization
M1 M2 M3
P1
P2
P3
M1 M2 M3
Full market
coverage
P1
P2
P3
Market
specialization
M1 M2 M3
P1
P2
P3
P1
P2
P3
M1 M2 M3
P = Product
M = Market
Gender
F
M
Age
14 - 21 22 - 29
G
e
o
g
r
a
p
h
y
Japan
Western
Europe
U.S.
Segment Cross-Classification:
Aerobic Shoes
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Scottish Gaelic 2nd EditionDocument117 pagesScottish Gaelic 2nd EditionMila Akimova-LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Journal of Management Education 2001 Comer 430 6Document8 pagesJournal of Management Education 2001 Comer 430 6senadi14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing PlanDocument27 pagesMarketing PlanKartheek AldiPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Product Positioning?Document11 pagesWhat Is Product Positioning?Mohit Rana100% (1)
- Marketing Management for Beginners: How to Create and Establish Your Brand With the Right Marketing Management, Build Sustainable Customer Relationships and Increase Sales Despite a Buyer’s MarketD'EverandMarketing Management for Beginners: How to Create and Establish Your Brand With the Right Marketing Management, Build Sustainable Customer Relationships and Increase Sales Despite a Buyer’s MarketPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3-Usp, Service Segmentation, Targeting & PositioningDocument55 pagesChapter 3-Usp, Service Segmentation, Targeting & PositioningAngelica AbajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Compulsory CounterclaimDocument4 pagesCompulsory CounterclaimAlexandria FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Customer-Driven Marketing StrategyDocument66 pagesCustomer-Driven Marketing Strategyswatiskhuraniya100% (3)
- Cosmology NotesDocument22 pagesCosmology NotesSaint Benedict Center100% (1)
- Chapter 08 Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning For Competitive AdvantageDocument22 pagesChapter 08 Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning For Competitive AdvantageHarini MuraliPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 15 STPDocument24 pagesLesson 15 STPdjokouwm100% (1)
- Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning NotesDocument7 pagesSegmentation, Targeting, and Positioning NotesSavannah Simone Petrachenko100% (2)
- Targeting and PositioningDocument25 pagesTargeting and PositioningMandeep Raj100% (1)
- Back To Basics MRODocument5 pagesBack To Basics MROrstein666Pas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing For Beginners: The key conceptsD'EverandMarketing For Beginners: The key conceptsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- The Tourist Market SegementationDocument24 pagesThe Tourist Market SegementationRylyn Isabel100% (1)
- p2 Process Model 2017Document1 pagep2 Process Model 2017Miguel Fernandes0% (1)
- STPDocument22 pagesSTPzakirno19248Pas encore d'évaluation
- MM Lecture 4 AMDocument28 pagesMM Lecture 4 AMArun Mishra100% (1)
- Lesson 15: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningDocument24 pagesLesson 15: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningManu SehgalPas encore d'évaluation
- Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning (STP)Document18 pagesSegmentation, Targeting, Positioning (STP)Tanvir AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing STPDocument23 pagesMarketing STPshivgupta_132Pas encore d'évaluation
- Market SegmentationDocument16 pagesMarket SegmentationMohammad Rafeeq BhatPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Phone Company Market Segmentation Plan0Document35 pagesCell Phone Company Market Segmentation Plan0Shamsul ArefinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Environ STPDocument40 pages2 Environ STPAnirban KunduPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Marketing: Lecture-18Document50 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: Lecture-18Maqbool HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- STP Market Segmentation Targeting PositioningDocument34 pagesSTP Market Segmentation Targeting PositioningJaymss MirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- SegmentationDocument51 pagesSegmentationajmeerMBAPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - Market Segmentation - Targeting - PositioningDocument28 pagesChapter 3 - Market Segmentation - Targeting - PositioningFarrah SokriPas encore d'évaluation
- IM1019 L4 Customer Value-Driven Marketing StrategyDocument44 pagesIM1019 L4 Customer Value-Driven Marketing StrategyDƯƠNG NGUYỄN THÁI BÌNHPas encore d'évaluation
- Building BrandsDocument21 pagesBuilding BrandsSHREYASH DESHPANDEPas encore d'évaluation
- STPDDocument28 pagesSTPDJayRavasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 5 Chap 7Document24 pagesLec 5 Chap 7Fahad RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapt-4 EdtdDocument12 pagesChapt-4 EdtdTeketel chemesaPas encore d'évaluation
- STP AnalysisDocument5 pagesSTP AnalysissutharshanlkPas encore d'évaluation
- Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Prepared To Accompany The Lecture at Karachi University Business SchoolDocument29 pagesCustomer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Prepared To Accompany The Lecture at Karachi University Business Schoollakhan Muhammad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- STP Iims ASDocument34 pagesSTP Iims ASraja380Pas encore d'évaluation
- STP: Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning: Presented By: Ravi RamoliyaDocument35 pagesSTP: Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning: Presented By: Ravi RamoliyaRavi RamoliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning: Ankita SrivastavaDocument18 pagesSegmentation, Targeting and Positioning: Ankita SrivastavaAbhishek KulkarniPas encore d'évaluation
- Market Analysis and Planning and SegmentationDocument59 pagesMarket Analysis and Planning and SegmentationShailendra ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Segmentation, Targeting & PositioningDocument34 pagesSegmentation, Targeting & PositioningMd Tabish RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Segmentation, Target Marketing & PositioningDocument53 pagesSegmentation, Target Marketing & PositioningVIKRANTPas encore d'évaluation
- Market Segmentation Targeting Positioning: Vu THN Ngocvth@uel - Edu.vnDocument43 pagesMarket Segmentation Targeting Positioning: Vu THN Ngocvth@uel - Edu.vnKhanh Trương Lê MaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical PromotionDocument25 pagesPharmaceutical PromotionZisan Ahmed ZikoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Business ManagementDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Business ManagementrliritisPas encore d'évaluation
- Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning: Building The Right Relationships With The Right CustomersDocument21 pagesSegmentation, Targeting, and Positioning: Building The Right Relationships With The Right CustomersSahan MPPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7Document34 pagesChapter 7Nurul Athirah GhazaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Segementatiion Targeting PositiongDocument41 pagesSegementatiion Targeting PositiongVishal MalhotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Management: UNIT-2Document15 pagesMarketing Management: UNIT-2Tanya GrewalPas encore d'évaluation
- C6 - Segment Target M LMSDocument43 pagesC6 - Segment Target M LMShuuhung29032003Pas encore d'évaluation
- Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDocument18 pagesSegmentation, Targeting and PositioningHussain AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10Document16 pagesMarketing: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10Ana García BarbelPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparing Effective Business Plans: An Entrepreneurial ApproachDocument21 pagesPreparing Effective Business Plans: An Entrepreneurial ApproachHafsah Ahmad najibPas encore d'évaluation
- Market Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning (STP)Document57 pagesMarket Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning (STP)Amritava Deb RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Mrktg. - Q3 Module 7Document11 pagesPrinciples of Mrktg. - Q3 Module 7Marilyn TamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- SMPDocument5 pagesSMPShaheen MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Nedzma HrvatPas encore d'évaluation
- Entrep All NotesDocument63 pagesEntrep All NotesErekha Jicah Sheibe SayonPas encore d'évaluation
- Positioning: BenefitsDocument4 pagesPositioning: BenefitsAnonymous rWn3ZVARLgPas encore d'évaluation
- Market SegmentationDocument22 pagesMarket SegmentationTony WariboPas encore d'évaluation
- Fashion Marketing Research LogDocument9 pagesFashion Marketing Research LogNaina Pradeep singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Market Segmentation: Prepared By: Ma. Anna Corina G. Kagaoan Instructor College of Business and AccountancyDocument33 pagesStrategic Market Segmentation: Prepared By: Ma. Anna Corina G. Kagaoan Instructor College of Business and AccountancyAhsan ShahidPas encore d'évaluation
- Pillers of Marketing - Segment, Target, Positioning & DifferentiationDocument26 pagesPillers of Marketing - Segment, Target, Positioning & Differentiationlalulili2367Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ibsaaa Marketing Assignment Haramaya UniversityDocument9 pagesIbsaaa Marketing Assignment Haramaya UniversityibsaashekaPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Wiki: Who Are Some 1% Product Managers?Document1 pageAnswer Wiki: Who Are Some 1% Product Managers?senadi14Pas encore d'évaluation
- CourseOutline or in Marketing OM219Document3 pagesCourseOutline or in Marketing OM219senadi14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Alshaya Project Judging, T&C's 2014Document2 pagesAlshaya Project Judging, T&C's 2014senadi14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stay FreshDocument1 pageStay Freshsenadi140% (1)
- LIME 7 Rule Book For Wild Card 2015Document8 pagesLIME 7 Rule Book For Wild Card 2015senadi14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Determining The Ductility of The BitumenDocument2 pagesDetermining The Ductility of The Bitumensenadi14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Front PageDocument1 pageFront Pagesenadi14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Beam L19Document1 pageBeam L19senadi14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Milgrim's Exp BS AssgnmntDocument3 pagesMilgrim's Exp BS Assgnmntsenadi14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ob13 Tif13Document18 pagesOb13 Tif13senadi14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Current Technique in The Audiologic Evaluation of Infants: Todd B. Sauter, M.A., CCC-ADocument35 pagesCurrent Technique in The Audiologic Evaluation of Infants: Todd B. Sauter, M.A., CCC-AGoesti YudistiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1Jerard AnciroPas encore d'évaluation
- Project RealDocument4 pagesProject RealKenneth Jay BagandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ujt and PutDocument35 pagesUjt and Putisraeljumbo100% (1)
- CHAPTER 6 - Adjusting EntriesDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Adjusting EntriesMuhammad AdibPas encore d'évaluation
- Hindu Dharma Parichayam - Swami Parameswarananda SaraswatiDocument376 pagesHindu Dharma Parichayam - Swami Parameswarananda SaraswatiSudarsana Kumar VadasserikkaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Sedition ActDocument11 pagesSedition ActYei TengPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Finance Chapter 4Document15 pagesBusiness Finance Chapter 4chloe frostPas encore d'évaluation
- Agvan DorzhievDocument7 pagesAgvan DorzhievMichael FelicianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Activity - A Lost DogDocument3 pagesReading Activity - A Lost DogGigsFloripaPas encore d'évaluation
- Firewatch in The History of Walking SimsDocument5 pagesFirewatch in The History of Walking SimsZarahbeth Claire G. ArcederaPas encore d'évaluation
- Astro ExamDocument7 pagesAstro ExamRitu DuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fairy Rebel PDFDocument2 pagesFairy Rebel PDFSamuel0% (1)
- Introduction PDFDocument7 pagesIntroduction PDFJalal NhediyodathPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Ci Sinif Word Definition 6Document2 pages6 Ci Sinif Word Definition 6poladovaaysen11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Who Di 31-4 Atc-DddDocument6 pagesWho Di 31-4 Atc-DddHenderika Lado MauPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 1108 - JKM 01 2020 0064Document23 pages10 1108 - JKM 01 2020 0064BBA THESISPas encore d'évaluation
- Handwriting Examination Lesson 4.2Document3 pagesHandwriting Examination Lesson 4.2Edrie Boy OmegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Birth and Growth of Semiotics: November 2020Document9 pagesBirth and Growth of Semiotics: November 2020Maria del Carmen Alvarado AcevedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fabric Data Science 1 150Document150 pagesFabric Data Science 1 150pascalburumePas encore d'évaluation
- Notification On Deemed Examination Result NoticeDocument2 pagesNotification On Deemed Examination Result Noticesteelage11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Script - Macbeth A La MafiosiDocument27 pagesScript - Macbeth A La MafiosiMohd Afiq Mat RazaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Academic 8 2.week Exercise Solutions PDFDocument8 pagesAcademic 8 2.week Exercise Solutions PDFAhmet KasabalıPas encore d'évaluation
- Movie Review TemplateDocument9 pagesMovie Review Templatehimanshu shuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- LTRC FInal Report 558 Development of Performance-Based Specifications For Louisiana Asphalt MixturesDocument149 pagesLTRC FInal Report 558 Development of Performance-Based Specifications For Louisiana Asphalt MixtureswalaywanPas encore d'évaluation