Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 Substructure
Transféré par
Haritharan ManiamCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 1 Substructure
Transféré par
Haritharan ManiamDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CHAPTER 1 SUBSTRUCTURE
1.1 Earthwork
INTRODUCTION
Earthwork: the processes whereby the surface of the
earth is excavated and transported to and compacted
at another location.
The introduction of the internal combustion engine,
electric power and hydraulic power have led to the
development of a wide range of earthwork plant (size,
capacity and efficiency).
Scale: ranges from small works (the excavation of
ditches and trenches for drainage and pits and trenches
for foundations) to the large earthworks (highways and
dams).
INTRODUCTION
carried out at an early stage in a construction project,
completion of the earthworks within the scheduled
time is often the key to the completion on time of the
whole project
success often depends on:
o an adequate site investigation and preparing
practical and satisfactory designs of the
earthworks.
o the choice and efficient use of the correct types
and size of plant to meet the particular
requirements of the site.
SCOPE OF EARTHWORKS
Site clearing (Pembersihan tapak)
Cutting and excavation (Pengorekan dan pemotongan)
Transport and moving (Pemunggahan,Pengangkutan
dan Penuangan)
Compaction (Pemadatan)
Sloping (Pencerunan)
Site clearing
Clearing, grubbing, demolishing, breaking up and
removing all trees, shrubs, vegetation, butts,
structures such as walls, fences and other obstruction
within the site which have been designated to be
demolished or removed
All spoils and debris shall be removed and disposed of
off-site at an approved certified construction landfill
Site clearing
Cutting and excavation
Most construction projects require the movement of
earthwork on site. This will result in altering the
existing elevation to a different or finish elevation.
To determine the amount of soil to be moved, the
estimator needs to have a plot plan or topographic
survey.
This drawing is developed by plotting the readings
(elevations) obtained from a topographic field survey
usually performed by a licensed land surveyor.
Cutting and excavation
Part of the permanent works (e.g. cuttings)
A temporary expedient in the construction of the
works (e.g. for foundations and drainage)
The sides of the excavations are required to remain
stable during their design life, can be achieved by:
excavating the material to a stable slope angle
by retaining or supporting the material.
Cutting and excavation
Cutting and excavation
Transport and moving
Trucks are used to transport excavated material,
aggregates and construction material
As the primary hauling unit provides a high degree of
flexibility.
Found in the crust of the earth
Classified as rock or soil
Soil characteristics that affect a soils behaviour for
construction purposes.
Transport and moving
Lab tests are required to fully determine a soils
physical and chemical properties which control those
characteristics.
Transport and moving
Compaction
Increased bearing capacity
Increased compressibility
Reduce permeability
Improve stability
Heavy/highway vs. building foundation compaction
operations
Compaction
Sloping
Function of the natural angle of repose, density,
surface and subsurface water flow.
Early stabilization of surfaces is critical
Eliminate points of concentrated flow using slope
drains as outlets.
Difficult slopes may require riprap, gabions, or other
measures for permanent stabilization .
Sloping
Sloping
KEYS TO SUCCESSFUL
EARTHWORK OPERATIONS
1. Control surface and subsurface water
2. Maintain optimum moisture range by drying, mixing ,
or wetting
3. Identify and monitor cut & fill quantities
4. Good layout (horizontal & vertical control)
5. Minimize handling - minimize stockpiling
KEYS TO SUCCESSFUL
EARTHWORK OPERATIONS
6. Optimize haul lengths
7. Minimize cycle time
8. Proper selection and sizing of excavators and haul
units
9. Alternate haul unit wheel paths
10. Experienced personnel in the field
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cve522 Building Technology Compact and Module 1Document22 pagesCve522 Building Technology Compact and Module 1Joshua OmolewaPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Technology Assignment 2Document5 pagesConstruction Technology Assignment 2Otee IsaacPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Soils InvestigationDocument45 pagesChapter 1 Soils InvestigationAndrian AgengPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Engineering Level 6 OSDocument161 pagesCivil Engineering Level 6 OSmatundura100% (1)
- CHAPTER 1 Substructure PDFDocument139 pagesCHAPTER 1 Substructure PDFsayqa100% (6)
- Enhancing the Climate Resilience of Africa's Infrastructure: The Power and Water SectorsD'EverandEnhancing the Climate Resilience of Africa's Infrastructure: The Power and Water SectorsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce195-2: Civil Engineering Law, Contracts, Specification and EthicsDocument13 pagesCe195-2: Civil Engineering Law, Contracts, Specification and EthicsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Crane Runway Beam Design Using CSA S16-14 CodeDocument3 pagesCrane Runway Beam Design Using CSA S16-14 CodesergiooiPas encore d'évaluation
- Windows and DoorsDocument29 pagesWindows and DoorsShayne GaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction MaterialsDocument35 pagesConstruction MaterialsShubham ChhabraPas encore d'évaluation
- Banglo Bkt. Tunku Taking-Off Schedule: Bill No. DescriptionDocument3 pagesBanglo Bkt. Tunku Taking-Off Schedule: Bill No. DescriptionAsrul Azhar Abd RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Construction Lecture Note.Document31 pagesBuilding Construction Lecture Note.Umar Bello NuhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Highway Pavement Construction 25.072023Document37 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Highway Pavement Construction 25.072023Timothy MagikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cracks - Types of Defects in BuildingsDocument19 pagesCracks - Types of Defects in BuildingsParulDhimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Roof CoveringDocument26 pagesRoof CoveringNaresh SankuruPas encore d'évaluation
- RoofDocument9 pagesRoofHakim AkemPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 2 Building ServicesDocument95 pagesCHAPTER 2 Building ServicesNur Ain ZainuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Chapter-Site InvestigationDocument9 pages2nd Chapter-Site InvestigationKalsoma CarlsPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Building ServicesDocument15 pagesManaging Building ServicesEfifi Ben DaldalPas encore d'évaluation
- Did154 Introduction BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONDocument44 pagesDid154 Introduction BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONDanishhadi100% (1)
- Masonry and AsphaltDocument106 pagesMasonry and AsphaltChelsiemea Vargas100% (1)
- Chapter 3.1 Geometric Design of HighwaysDocument85 pagesChapter 3.1 Geometric Design of HighwaysAmanuel AshenafiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-5.2 Floor SystemDocument68 pagesChapter-5.2 Floor SystemFikaduKitessa67% (3)
- Basic Components of A StructureDocument12 pagesBasic Components of A StructureBasmaI73% (11)
- SuperstructureDocument39 pagesSuperstructureaang100% (1)
- Building Technology Notes Form 4 2012-2013Document116 pagesBuilding Technology Notes Form 4 2012-2013olvernejacobs9741100% (2)
- Construction Technology - USM School of Civil Engineering ConstructionDocument65 pagesConstruction Technology - USM School of Civil Engineering ConstructionArvinthran Raja KumaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Technology and Methods Assignment 02Document18 pagesConstruction Technology and Methods Assignment 02malithPas encore d'évaluation
- Estimation of Fundamental Frequency in Dammam City, Eastern Saudi ArabiaDocument16 pagesEstimation of Fundamental Frequency in Dammam City, Eastern Saudi Arabiaansari100% (1)
- 10 - Lecture 10 - Building Materials and Construction IIDocument45 pages10 - Lecture 10 - Building Materials and Construction IIYohans EjiguPas encore d'évaluation
- Debre Markos University: College of TechnologyDocument39 pagesDebre Markos University: College of TechnologyLij Davis100% (1)
- Soil Erosion Measurement and Control TechniquesDocument12 pagesSoil Erosion Measurement and Control TechniquessezaitanyoluPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Technology B AssignmentDocument71 pagesConstruction Technology B AssignmentBihanChathuranga100% (2)
- Chapter Two Rainfall-Runoff Relationships 2.0 Runoff: Engineering Hydrology Lecture Note 2018Document46 pagesChapter Two Rainfall-Runoff Relationships 2.0 Runoff: Engineering Hydrology Lecture Note 2018Kefene GurmessaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alumni Feedback FormDocument1 pageAlumni Feedback FormjayeshjoglekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Construction EditDocument26 pagesBuilding Construction EditSami Zama100% (1)
- Component Longevity in Terms of Operation Performance and Resistance To Deleterious ForcesDocument8 pagesComponent Longevity in Terms of Operation Performance and Resistance To Deleterious ForcesPalanisamy RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Introduction To ConcreteDocument24 pages02 Introduction To ConcreteS. M. ZAHIDUR RAHMAN 1301129Pas encore d'évaluation
- Buiding Services Compass SurveyDocument578 pagesBuiding Services Compass SurveyAnonymous jphuejJIYyPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Construction I-Lecture 3 (Excavation)Document17 pagesBuilding Construction I-Lecture 3 (Excavation)sujan shresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Technology 2Document27 pagesConstruction Technology 2SamZa ChiewPas encore d'évaluation
- SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE OF TSUNAMI AND MITIGATION MEASURES FOR NATURAL DISASTERS K.L. Srilal SAHABANDU Central Engineering Consultancy Bureau (CECB)Document8 pagesSRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE OF TSUNAMI AND MITIGATION MEASURES FOR NATURAL DISASTERS K.L. Srilal SAHABANDU Central Engineering Consultancy Bureau (CECB)Srilal SahabanduPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 03-Uom 2019 - Iesl Code of Ethics-ADocument39 pagesSession 03-Uom 2019 - Iesl Code of Ethics-AAsitha RathnayakePas encore d'évaluation
- Types of PavementDocument4 pagesTypes of Pavementibrahim0007100% (1)
- 08 - Lecture 08 - Building Materials and Construction IIDocument30 pages08 - Lecture 08 - Building Materials and Construction IIYohans EjiguPas encore d'évaluation
- Retaining WallDocument7 pagesRetaining WallEdward SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 Substructure Design Foundations CompressedDocument53 pagesUnit 5 Substructure Design Foundations CompressedHundeejireenyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Handout 3 Earthwork OperationsDocument25 pagesHandout 3 Earthwork OperationsthuraiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit (2) Construction TechnologyDocument31 pagesUnit (2) Construction TechnologyNyein Chan Aung100% (1)
- Building Construction CAP 123B PDFDocument28 pagesBuilding Construction CAP 123B PDFJustin NgPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Pile Foundation of Thermal Power Plant at NelloreDocument68 pagesAnalysis of Pile Foundation of Thermal Power Plant at NelloreAmanKediaPas encore d'évaluation
- Structures and Buildings 2014 PDFDocument6 pagesStructures and Buildings 2014 PDFIvan GuerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - Site PreparationDocument12 pages5 - Site PreparationJetty CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- (24513148 - Scientific Bulletin) Design and Manufacturing Process For A Ballistic MissileDocument7 pages(24513148 - Scientific Bulletin) Design and Manufacturing Process For A Ballistic MissileDavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Multipurpose HallDocument15 pagesMultipurpose HallNieves Guardian100% (1)
- 1 - Introduction - FoundationDocument45 pages1 - Introduction - FoundationLouise LuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pavement Design Concepts-Flexible PavementsDocument3 pagesPavement Design Concepts-Flexible PavementsSuryasis DasguptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Technology Assignment 01Document13 pagesConstruction Technology Assignment 01Hashan PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Earthquake EngineeringDocument21 pagesEarthquake EngineeringAbbasabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding the Building Construction Process: Simply ExplainedD'EverandUnderstanding the Building Construction Process: Simply ExplainedPas encore d'évaluation
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985D'EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Pas encore d'évaluation
- ASTAR2011 InterVarsity ResultsDocument2 pagesASTAR2011 InterVarsity ResultsHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
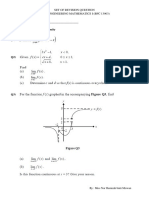
- Part 1: Limit and Continuity: Set of Revision Question Civil Engineering Mathematics I (BFC 13903)Document9 pagesPart 1: Limit and Continuity: Set of Revision Question Civil Engineering Mathematics I (BFC 13903)Haritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- How Is Reasonably Practicable' Defined?Document7 pagesHow Is Reasonably Practicable' Defined?Haritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- Alpha ZenDocument2 pagesAlpha ZenHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- FAQ UniFi LiteDocument20 pagesFAQ UniFi LiteHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- LMH SSG Gemini Ex Penang Winter Buy2free1 - Valid Till 15oct2018 PDFDocument2 pagesLMH SSG Gemini Ex Penang Winter Buy2free1 - Valid Till 15oct2018 PDFHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- Alpha Instruments Supplies & Services SDN BHDDocument2 pagesAlpha Instruments Supplies & Services SDN BHDHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- Traverse Report BearingDocument1 pageTraverse Report BearingHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Car Washes and Water QualityDocument2 pagesCommunity Car Washes and Water QualityHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- Countrat ProcedurDocument4 pagesCountrat ProcedurHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- Speaking Reading Listening Writing Easy Moderate Easy Moderate Hard HardDocument2 pagesSpeaking Reading Listening Writing Easy Moderate Easy Moderate Hard HardHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- Progress ReportDocument11 pagesProgress ReportHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- Benefits of Public TransportationDocument1 pageBenefits of Public TransportationHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- Force in A Statically Indeterminate Cantilever Beam UmmuDocument17 pagesForce in A Statically Indeterminate Cantilever Beam UmmuHaritharan ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- K Subra 1000 Solved ProblemsDocument2 pagesK Subra 1000 Solved ProblemsMat0% (1)
- Concrete Works Construction MethodologyDocument36 pagesConcrete Works Construction MethodologyJose Rowell MacabantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Esperance Tanker Jetty Structural AssesmentDocument21 pagesEsperance Tanker Jetty Structural AssesmentsgatzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Part 2Document26 pagesChapter 1 Part 2Mustafa OmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Dos Iii - Unit Iv Masonry WallDocument26 pagesDos Iii - Unit Iv Masonry WallMohamed ArzathPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis & Design of Residential Buildings Using E-TabsDocument6 pagesAnalysis & Design of Residential Buildings Using E-TabsmulualemPas encore d'évaluation
- Motivation LettreDocument2 pagesMotivation LettreViny Alen100% (1)
- Prop PantDocument29 pagesProp PantAbdalrhman MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Composite Deck EurocodeDocument99 pagesComposite Deck EurocodeĐoàn Đức PhongPas encore d'évaluation
- Engr. Richard A. Badiola, RMP, ENP, M. Eng'g, Ph.D. CEDocument7 pagesEngr. Richard A. Badiola, RMP, ENP, M. Eng'g, Ph.D. CEVincent VillabrozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudyDevagya GandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Post Tensioning DesignDocument4 pagesPost Tensioning DesignFrancisFengPas encore d'évaluation
- Roll Shit BE III Sem Ex Summer 2012Document14 pagesRoll Shit BE III Sem Ex Summer 2012Praful KakdePas encore d'évaluation
- Bi Layer Diaphragm Walls Structural andDocument8 pagesBi Layer Diaphragm Walls Structural andLuthfi NPas encore d'évaluation
- Asphalt ProcedureDocument3 pagesAsphalt Procedurekath vinluanPas encore d'évaluation
- Report1 - Study of Structural System in Architecture - Post Lintel - 5,10,15,20,24,29Document81 pagesReport1 - Study of Structural System in Architecture - Post Lintel - 5,10,15,20,24,29নূরুন্নাহার চাঁদনী100% (1)
- 20ME68 - Analysis of BarsDocument18 pages20ME68 - Analysis of BarsranjithkrajPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument53 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab ManualprashanthreddyhPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Pavement EngineeringDocument15 pagesInternational Journal of Pavement EngineeringDipendra AwasthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction TipsDocument4 pagesConstruction TipsbenmaybankPas encore d'évaluation
- DimensionsDocument11 pagesDimensionsAsavela NotshwelekaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ground Probing and Treatments in Rock TBM To Overcome Limiting ConditionsDocument18 pagesGround Probing and Treatments in Rock TBM To Overcome Limiting ConditionsLe Thuy Linh100% (1)
- UASB Upflow Anaerobic Sludg..Document2 pagesUASB Upflow Anaerobic Sludg..Devendra BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cold In-Place Recycling Using Foamed Bitumen - Step Towards Sustainable Road ConstructionDocument14 pagesCold In-Place Recycling Using Foamed Bitumen - Step Towards Sustainable Road ConstructionBijay Krishna DasPas encore d'évaluation
- EWPL - S. JayachandraDocument82 pagesEWPL - S. JayachandraNaveen Kumar Patel100% (1)
- Design CaculationsDocument14 pagesDesign Caculationsmkpasha55mpPas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages of GabionsDocument8 pagesAdvantages of GabionsAnkur DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscosity of Fluids-Newtonian and Non Newtonian Analysis As Applied To PlasticsDocument20 pagesViscosity of Fluids-Newtonian and Non Newtonian Analysis As Applied To PlasticsSushmaPas encore d'évaluation