Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sistem Limfatik
Transféré par
Vani Taah G0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
127 vues27 pagesLymphatic System Absorbs excess fluid from the tissues Returns this fluid to the circulatory system or the heart Additional function in Immunity Components of the lymphatic system. Lymphatic nodules: - Dense clusters of lymphocytes - Transient: pop up during infection lymphatic vessels Carry and Transport lymph for infectious particles SpleenScreen and Filter Blood for old, dead cells and infectious particles.
Description originale:
Titre original
Sistem Limfatik.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentLymphatic System Absorbs excess fluid from the tissues Returns this fluid to the circulatory system or the heart Additional function in Immunity Components of the lymphatic system. Lymphatic nodules: - Dense clusters of lymphocytes - Transient: pop up during infection lymphatic vessels Carry and Transport lymph for infectious particles SpleenScreen and Filter Blood for old, dead cells and infectious particles.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
127 vues27 pagesSistem Limfatik
Transféré par
Vani Taah GLymphatic System Absorbs excess fluid from the tissues Returns this fluid to the circulatory system or the heart Additional function in Immunity Components of the lymphatic system. Lymphatic nodules: - Dense clusters of lymphocytes - Transient: pop up during infection lymphatic vessels Carry and Transport lymph for infectious particles SpleenScreen and Filter Blood for old, dead cells and infectious particles.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 27
Lymphatic System
Absorbs excess fluid from the tissues
Returns this fluid to the circulatory system
or the heart
Additional function in Immunity
Components of the Lymphatic
System
Lymph
Lymphatic Tissue
Lymphatic Vessels
Thymus
Bone Marrow
Spleen
Lymph
Lymph
The clear fluid
absorbed by
the lymphatic
system
Lymphatic
Tissue
Clusters of
Lymphocytes
and
macrophages
Lymphatic Tissue
Malt: (Mucosa Associated Lymphatic Tissue)
Diffuse array of lymphocytes found along body
passages in mucous membranes.
Examples of malt: lining of the stomach and
respiratory tract
Lymph nodules:
Dense clusters of Lymphocytes
Transient: pop up during infection
Lymphatic Vessels
Carry and Transport
Lymph and proteins
Similar Structure to
veins
Tunica Interna:
Thin inner lining
and valves
Tunica Media:
Elastic fibers and
Smooth Muscle
Tunica Externa:
Thin Outer Layer
Lymphatic Filters
Lymph Nodes- Screen and Filter
Lymph for infectious particles
Spleen- Screen and Filter Blood for
old, dead cells and infectious particles
Subclavian
2 collecting Trunks
6 Lymphatic Trunks
More Collecting Vessels
Lymph Nodes
Collecting Vessels
Lymphatic Vessels
Lymphatic Movement
No pump
Rhythmic contraction of the lymph vessels
Skeletal Muscles
How is backflow prevented?
Immune Cell Generators
Bone Marrow- Makes B- Cells
Thymus- Makes T- Cells
Thymus
Break for
Dynamic Human
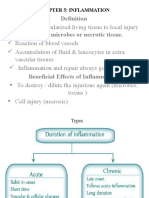
Inflammation
Non-specific response to tissue trauma or
infection
4 signs of Inflammation
Redness
Swelling
Heat
Pain
Whats the purpose of pain?
Purpose of Inflammation
Remove Invading Pathogens
Remove Debris of Damaged Tissues
Initiate Tissue Repair
Mediators of Inflammation
Chemical Messengers
Leukocyte
Chemical Messengers
Released by mast cells in response to damage
Bradykinin, Histamine, and Leukotrienes
Increases Local Blood Flow to distressed area
Stimulates Vasodilation
Increases Permeability of Capillaries
Whats Accomplished?
Chemical Messengers
Bradykinin, Histamine, and Leukotrienes
Increases Local Blood Flow
Stimulates Vasodilation
Increases Permeability of Capillaries
Whats Accomplished?
Heats area causes redness and swelling
Dilutes toxins and helps Remove waste
Supplies oxygen and nutrients for tissue repair
Pain Response
Purpose?
Causes?
Pain Response
Purpose? Prevents further injury to area.
Causes?
Direct Nerve Damage
Pressure from Swelling
Chemical Stimulation particularly bradykinin
Leukocyte Deployment
Leukocyte: any white blood cell including
T cells, B cells, granulocytes, platelets,
basophils, mast cells, monocytes and
macrophages
Leukocytes Migrate toward inflammed area
Why? TO KILL and RECRUIT
Leukocyte Deployment
Leukocytes Migrate to inflammed tissue
How?
1. Margination or pavementing: To
migrate to the wall of a capillary
2. Diapedesis: Passage of blood cells
through vessel wall into tissue
3. Chemotaxis: Movement of a cell
towards or away a chemical source
What do the leukocytes plan
to do?
Phagocytosis: release of toxic chemicals
Recruit more leukocytes
Phagocytosis
Leukocytes consume and destroy foreign
invaders and dead cells
Ejected as Pus
Break for
Dynamic Human
Selected Topics in Immunity
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lecture Overview: Lymphatic System and ComponentsDocument29 pagesLecture Overview: Lymphatic System and ComponentsElaine How YuenPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintain Balance and Protect BodyDocument94 pagesMaintain Balance and Protect Bodyistep100% (1)
- Sistem Limfatik Dan ImunitasDocument78 pagesSistem Limfatik Dan ImunitasMasna Arisah NasutionPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammation and RepairDocument34 pagesInflammation and RepairJoshua HonoridezPas encore d'évaluation
- ANP 1105 The Lymphatic SystemDocument23 pagesANP 1105 The Lymphatic SystemMathios TigerosPas encore d'évaluation
- WameedMUCLecture 2021 9274861Document36 pagesWameedMUCLecture 2021 9274861ROSE ANN JAWADPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphatic System PPT Notes SBDocument13 pagesLymphatic System PPT Notes SBnoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute InflammationDocument5 pagesAcute InflammationnsyingPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology: Topic 7 (CHP 33) The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument56 pagesBiology: Topic 7 (CHP 33) The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsIain Choong WKPas encore d'évaluation
- 700 - Wk. 2 - Inflammation, Infection & HIV LODocument10 pages700 - Wk. 2 - Inflammation, Infection & HIV LOAfPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammation and RepairDocument34 pagesInflammation and Repairanshum guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lypm Immunity SystemDocument22 pagesLypm Immunity SystemPhoenix JudgePas encore d'évaluation
- Acute InflammationDocument55 pagesAcute InflammationMohammad_Islam8790% (10)
- Basic mechanisms of inflammation and repairDocument23 pagesBasic mechanisms of inflammation and repairdhanashriPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Limfa dan Imun Mengatur Pertahanan TubuhDocument60 pagesSistem Limfa dan Imun Mengatur Pertahanan TubuhPutriantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14 - Lymph and ImmunityDocument13 pagesChapter 14 - Lymph and Immunityapi-220531452Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocument12 pagesThe Lymphatic and Immune SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- CLS224 Lecture 5 PDFDocument37 pagesCLS224 Lecture 5 PDFmike RPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutritional PathologyDocument24 pagesNutritional PathologySH MannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology On Body DefenceDocument21 pagesBiology On Body Defences2020058Pas encore d'évaluation
- What is Inflammation: The Biological Response and ProcessDocument135 pagesWhat is Inflammation: The Biological Response and Process77 Weam AliPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.3 Defence Against Infectious DiseaseDocument43 pages6.3 Defence Against Infectious DiseaseAlacrity Xenoion SpadesPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 Study GuideDocument16 pagesWeek 1 Study GuideKatePas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammation I: Early Events & TerminologyDocument35 pagesInflammation I: Early Events & TerminologySiinaan DerejePas encore d'évaluation
- Immune SystemDocument52 pagesImmune SystemDerón Asbery HolmesPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Sistem Raspuns Imun 2011 PDFDocument63 pages4 Sistem Raspuns Imun 2011 PDFGigiEnergiePas encore d'évaluation
- BIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013Document58 pagesBIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013raunak .comPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1: RBC, Anemia/Wbc, Inflammation: Page 1 of 7Document7 pagesLecture 1: RBC, Anemia/Wbc, Inflammation: Page 1 of 7lifecostPas encore d'évaluation
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemcrtgyhujikPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammation Part 1Document31 pagesInflammation Part 1Gunagold RobPas encore d'évaluation
- inflammation and tissue repairDocument55 pagesinflammation and tissue repairSingitan SiyoumPas encore d'évaluation
- SISTEM LIMFATIK DAN IMUNITASDocument72 pagesSISTEM LIMFATIK DAN IMUNITASAisya Alya RahmadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Week 2 p1-18Document18 pagesPathology Week 2 p1-18zeroun24100% (1)
- Lymphatic System ExplainedDocument22 pagesLymphatic System ExplainedKim, Seyoung Cristine G.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acute and Chronic InflammationDocument69 pagesAcute and Chronic InflammationJac mswimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundations in Microbiology: TalaroDocument35 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: Talaromertx013Pas encore d'évaluation
- Immune ResponseDocument41 pagesImmune ResponseRIMI SALOUMPas encore d'évaluation
- Anp2001 Week 3 Lymph To RespDocument125 pagesAnp2001 Week 3 Lymph To RespJerilee SoCute WattsPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemBasant karn100% (6)
- Mekanisme Pertahanan Tubuh (Sistem ImunDocument34 pagesMekanisme Pertahanan Tubuh (Sistem ImunSeptian PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- InflammationDocument93 pagesInflammationbekaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Compliment-Mediated Immune Responses: Response EffectsDocument12 pagesCompliment-Mediated Immune Responses: Response EffectsbiancameePas encore d'évaluation
- 07 InflammationDocument69 pages07 InflammationSangameswaran B.BPas encore d'évaluation
- LymphomaDocument37 pagesLymphomaMohammed T. Abdul Razak100% (2)
- Lymphatic System: By-Victor BawiahDocument42 pagesLymphatic System: By-Victor BawiahTheophilus BaidooPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3Document56 pagesLecture 3w2tz2qrqxdPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 5 InflammationDocument51 pagesCHAPTER 5 Inflammationyeshita yonasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 22 Summary Chapter 22 SummaryDocument13 pagesChapter 22 Summary Chapter 22 SummarytinecastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphatic SystemDocument25 pagesLymphatic Systemumar khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphatics BD BloodDocument10 pagesLymphatics BD BloodIchokwu VivianPas encore d'évaluation
- Study-Notes - Inflammation-And-Repair (1) 88Document17 pagesStudy-Notes - Inflammation-And-Repair (1) 88jjjkkPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Features of Gingivitis & Gingival Inflammation: Pathogenesis.Document9 pagesClinical Features of Gingivitis & Gingival Inflammation: Pathogenesis.Prince AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- MRSM Biology Notes TransportDocument16 pagesMRSM Biology Notes TransportAhmad Hafize100% (2)
- Inflammation. Part 1. Fall 2022.Document60 pagesInflammation. Part 1. Fall 2022.Mirleyka GonzálezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphatics and BloodDocument9 pagesLymphatics and BloodIchokwu VivianPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphatic System Functions and Immune ResponseDocument6 pagesLymphatic System Functions and Immune ResponseGlenn Arjay BataraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Inflammation: Causes, Types, and ResolutionDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Inflammation: Causes, Types, and ResolutionAnonymous ftGUywTJPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisD'EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisPas encore d'évaluation
- Transplant ImmunologyD'EverandTransplant ImmunologyXian C. LiPas encore d'évaluation
- Everyday 3d ShapesDocument14 pagesEveryday 3d ShapesVani Taah GPas encore d'évaluation
- FriendshipDocument1 pageFriendshipVani Taah GPas encore d'évaluation
- 21st Century Skills for SuccessDocument22 pages21st Century Skills for Success9w2zlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Urinari EDocument36 pagesSistem Urinari EVani Taah GPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem IntegumentariDocument42 pagesSistem IntegumentariVani Taah GPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Rangka Sendi - PergerakanDocument36 pagesSistem Rangka Sendi - PergerakanVani Taah GPas encore d'évaluation
- Rangka Aksial at Rangka TubuhDocument54 pagesRangka Aksial at Rangka TubuhVani Taah GPas encore d'évaluation
- FriendshipDocument1 pageFriendshipVani Taah GPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf 1 EDocument53 pagesSistem Saraf 1 EVani Taah GPas encore d'évaluation
- Five Minute Adding Frenzy Math WorksheetsDocument20 pagesFive Minute Adding Frenzy Math Worksheetseb1rcsPas encore d'évaluation
- Five Minute Adding Frenzy Math WorksheetsDocument20 pagesFive Minute Adding Frenzy Math Worksheetseb1rcsPas encore d'évaluation
- Five Minute Adding Frenzy Math WorksheetsDocument20 pagesFive Minute Adding Frenzy Math Worksheetseb1rcsPas encore d'évaluation
- Adding 4-Digit Numbers Worksheet with AnswersDocument20 pagesAdding 4-Digit Numbers Worksheet with Answerseb1rcsPas encore d'évaluation
- Adding 4-Digit Numbers Worksheet with AnswersDocument20 pagesAdding 4-Digit Numbers Worksheet with Answerseb1rcsPas encore d'évaluation
- Five Minute Adding Frenzy Math WorksheetsDocument20 pagesFive Minute Adding Frenzy Math Worksheetseb1rcsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Kulit FungsiDocument36 pagesSistem Kulit FungsiVani Taah GPas encore d'évaluation
- Adding 4-Digit Numbers Worksheet with AnswersDocument20 pagesAdding 4-Digit Numbers Worksheet with Answerseb1rcsPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesLecture Notesapi-523871352Pas encore d'évaluation
- FY 2018 Self Identified Generic Drug Facilities Sites and OrganizationsDocument175 pagesFY 2018 Self Identified Generic Drug Facilities Sites and OrganizationsDavid Paul HensonPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Biology The Essentials 3rd EditionDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Biology The Essentials 3rd EditionKristi Markus100% (34)
- BPak's MI40-X - CEP Training BlueprintDocument22 pagesBPak's MI40-X - CEP Training BlueprintJose Rincon75% (8)
- Cell JunctionDocument63 pagesCell JunctionsphuyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture-Cell Membranes and SignalingDocument64 pagesLecture-Cell Membranes and SignalingDiabyPas encore d'évaluation
- Wilson, R. A. - Species - New Interdisciplinary EssaysDocument326 pagesWilson, R. A. - Species - New Interdisciplinary EssaysMaria Eduarda100% (2)
- Vishram Singh AnatomypdfDocument6 pagesVishram Singh Anatomypdfnanda kishorePas encore d'évaluation
- AI May Help Fight Future Disease OutbreaksDocument2 pagesAI May Help Fight Future Disease OutbreaksYESWANTH SPas encore d'évaluation
- Swamed DiareDocument10 pagesSwamed DiaredhikaPas encore d'évaluation
- moduleLESSON Genes and BehaviorDocument11 pagesmoduleLESSON Genes and BehaviorRecxs Baludio AtchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Actinomycetes: by Jagrity SinghDocument32 pagesActinomycetes: by Jagrity SinghIsworo RukmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure Function2Document28 pagesCell Structure Function2Ritesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Absorbtion in PlantsDocument15 pagesAbsorbtion in PlantsHema KamatPas encore d'évaluation
- WHO Research Agenda for RF FieldsDocument10 pagesWHO Research Agenda for RF FieldsAbhinav AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Which Came First, The Feather or The BirdDocument10 pagesWhich Came First, The Feather or The BirdPabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Function of RBCDocument9 pagesFunction of RBCAthea MelosantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Lesson 3Document5 pagesBiology Lesson 3Sean Mevrick VegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemical Tests Dietary IntakeDocument10 pagesBiochemical Tests Dietary IntakeDawlat SalamaPas encore d'évaluation
- KVL Wefvrb: Wøzxq Aa VQDocument21 pagesKVL Wefvrb: Wøzxq Aa VQHasin IsraqPas encore d'évaluation
- Pingol, Jessica - LAS Q4 W1 LIFE PROCESSESDocument5 pagesPingol, Jessica - LAS Q4 W1 LIFE PROCESSESjhzcartPas encore d'évaluation
- NIH Public Access: Olfaction in Parkinson's Disease and Related DisordersDocument63 pagesNIH Public Access: Olfaction in Parkinson's Disease and Related DisordersCarmen CiursaşPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: Tle-Cookery Assessment - Grade 10 Quarter 1 Week 1Document2 pagesDepartment of Education: Tle-Cookery Assessment - Grade 10 Quarter 1 Week 1IvyRoseBarcilloAlivioPas encore d'évaluation
- Cladogram CH 19 Part ADocument3 pagesCladogram CH 19 Part AJasmine lee100% (1)
- MED12 mutations common in breast phyllodes tumours and fibroadenomasDocument6 pagesMED12 mutations common in breast phyllodes tumours and fibroadenomasLuis GuzmánPas encore d'évaluation
- DP1 BIO - Test - Topic 1 Paper 1 PDFDocument6 pagesDP1 BIO - Test - Topic 1 Paper 1 PDFSaima SyedaPas encore d'évaluation
- WBCS MAINS 2022 Handout 1 Biotechnology FactsDocument29 pagesWBCS MAINS 2022 Handout 1 Biotechnology Factsrahul royPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOENG - FA1-2 (Combined)Document21 pagesBIOENG - FA1-2 (Combined)Aceriel VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2. Keanekaragaman Makhluk Hidup (Fungi)Document42 pages3.2. Keanekaragaman Makhluk Hidup (Fungi)Bagus Dwi PermanaPas encore d'évaluation
- HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY KEY FUNCTIONSDocument17 pagesHUMAN PHYSIOLOGY KEY FUNCTIONSplsssssPas encore d'évaluation