Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
2.8 Understanding Gravity
Transféré par
Eric Mitchell0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
77 vues17 pagesThe document discusses key concepts relating to gravity including:
- Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration experienced by objects due to Earth's gravitational pull.
- Gravitational field is a region where objects experience gravitational force. Gravitational field strength is the gravitational force per unit mass.
- Weight is the gravitational force on an object and is calculated by multiplying mass by gravitational acceleration.
- Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and remains constant, while weight varies depending on location's gravitational field strength.
Description originale:
PPT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe document discusses key concepts relating to gravity including:
- Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration experienced by objects due to Earth's gravitational pull.
- Gravitational field is a region where objects experience gravitational force. Gravitational field strength is the gravitational force per unit mass.
- Weight is the gravitational force on an object and is calculated by multiplying mass by gravitational acceleration.
- Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and remains constant, while weight varies depending on location's gravitational field strength.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
77 vues17 pages2.8 Understanding Gravity
Transféré par
Eric MitchellThe document discusses key concepts relating to gravity including:
- Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration experienced by objects due to Earth's gravitational pull.
- Gravitational field is a region where objects experience gravitational force. Gravitational field strength is the gravitational force per unit mass.
- Weight is the gravitational force on an object and is calculated by multiplying mass by gravitational acceleration.
- Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and remains constant, while weight varies depending on location's gravitational field strength.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 17
Learning outcomes :
A students is able to:
Explain acceleration due to gravity
State what a gravitational field is
Define gravitational strength
Determine the value of acceleration due to
gravity
Define weight as the product of mass and
acceleration due to gravity
Solve problems involving acceleration due to
gravity
Gravity
A Universal Force
a) Until 17
th
century, - a heavy object would fall faster
than a light object as Aristotle once taught.
b) After research by Galileo Galilei - if air resistance
can be ignored, all bodies fall with an equal
acceleration.
The difference between a fall in air and a free fall in
a vacuum of a coin and a feather
5
Force of attraction between bodies that have
mass
Free falling
An object falling under the force of
gravity only
6
Acceleration due to gravity
t
1
< t
2
< t
3
FREE FALLING OBJECT
Is an object falling under
the force of gravity only
Does not encounter other
force (example : air
resistance or friction that
would oppose its motion
8
Gravitational field
A gravitational field is a region in which an object
experiences a force due to gravitational attraction.
g = F
m
Unit: N/kg
Gravitational field strength
The gravitational force acting on a 1kg mass
9
Gravitational acceleration
The acceleration of an object due to the pull
of the gravitational force.
The unit of gravitational acceleration is
m s
-2
Symbol: g
Gravitational field strength vs.
gravitational acceleration
Both the gravitational strength and
gravitational acceleration have the symbol g
and the same value on the surface of the
earth.
When considering a body falling freely, the g
is the gravitational acceleration.
When considering object at rest, g is the
earths gravitational field strength acting on it.
11
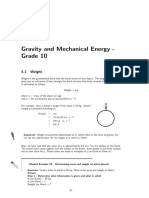
Weight (W)
The gravitational force acting on
the object
weight = mg
SI unit = newton (N)
vector quantity
question : what is the weight of
your friend your right?
Mass , m
Differences
Weight , w
The amount of matter
in the object.
definition
The force of gravity
on the object.
The mass of an object
is constant
everywhere.
Changing of value
Varies with the
magnitude of
gravitational field
strength, g of the
location.
Scalar quantity
Physical quantity
Vector quantity
Base quantity
Type of quantity
Derived quantity
Kilogram, kg
SI unit
Newton, N
QUIZ
QUESTION 1
An aeroplane is moving above
the earth at a particular point.
The mass of the aeroplane is
25000 kg and experiences a
gravitational force of 235000 N.
Find the gravitational field
strength at that point.
QUESTION 2
An apple fall vertically from the
tree over a distance of 8 m to the
ground. Calculate :
a) the time the apple takes to
reach the ground
b) the speed of the apple as it
strikes the ground.
(using g= 9.8 m s)
QUESTION 3
A stone is released from rest and
falls into a well. After 1.2 s, it hits
the bottom of the well.
(a) What is the velocity of the stone
when it hits the bottom?
(b) Calculate the depth of the well?
QUESTION 4
An object has a mass of 8 kg. find
its weight on
(a) The earth
(b) The moon
(The acceleration due to gravity on the Earth is
9.8 m s. the acceleration due to gravity on
the moon is 1.6 m s)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 2.8 Understanding Gravity: Chapter 2 Forces and MotionDocument43 pages2.8 Understanding Gravity: Chapter 2 Forces and MotionPauling ChiaPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction to Mass and Weight 3rd Grade : Physics for Kids | Children's Physics BooksD'EverandAn Introduction to Mass and Weight 3rd Grade : Physics for Kids | Children's Physics BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 11 Physics Best Notes For English Medium Session (2023-2024) Chapter - 8 GravitationDocument65 pagesClass 11 Physics Best Notes For English Medium Session (2023-2024) Chapter - 8 GravitationRohit GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- ESD User Handbook Rev2Document12 pagesESD User Handbook Rev2Amit B Kolekar100% (1)
- SCR Unit Chapter 3Document48 pagesSCR Unit Chapter 3stashkinvalriy100% (2)
- Kaiser - Electromagnetic Compatibility Handbook - ToCDocument18 pagesKaiser - Electromagnetic Compatibility Handbook - ToCbodymorph20% (5)
- GravitationDocument7 pagesGravitationUtpal BhatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Selection Calculations For Motors PDFDocument17 pagesSelection Calculations For Motors PDFbibhansuPas encore d'évaluation
- Sun DiagramDocument2 pagesSun DiagramEric Mitchell100% (1)
- Experiment No: 1 19bee069 Date: 20/01/2022 Aim: To Determine Magnetization Characteristics of A Given Current TransformerDocument11 pagesExperiment No: 1 19bee069 Date: 20/01/2022 Aim: To Determine Magnetization Characteristics of A Given Current TransformerR.D Sutariya100% (1)
- SVP 917 ManualDocument8 pagesSVP 917 ManualGalvao.endPas encore d'évaluation
- GravityDocument30 pagesGravityAien Zarin100% (1)
- Forces and Motion: 2.8:: Understanding GravityDocument20 pagesForces and Motion: 2.8:: Understanding GravitySiti Nur DalilaPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Tat Beng Physics Form 4 2.7 GravityDocument30 pagesSMK Tat Beng Physics Form 4 2.7 GravityTee Ting QIPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.8 GravityDocument16 pages2.8 Gravitykhodijahamin100% (1)
- CH 9 GravitationDocument5 pagesCH 9 GravitationBhovwtik ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass, Weight and ForceDocument36 pagesMass, Weight and ForcefruqaiyahamzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravity and Mechanical EnergyDocument19 pagesGravity and Mechanical EnergyMundu MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.8 Gravitational Force - Doc Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 ForceDocument12 pages2.8 Gravitational Force - Doc Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 ForceEzra Loganathan MuniandiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitation: Very Short Answer Type Questions-Pg-100Document53 pagesGravitation: Very Short Answer Type Questions-Pg-100DX GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitation: Very Short Answer TypeDocument12 pagesGravitation: Very Short Answer TypeKushagra GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Questions GravitationDocument2 pagesImportant Questions GravitationKushagra GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- As2021-22 g9 Physics GravitationDocument19 pagesAs2021-22 g9 Physics GravitationmiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.8 GravityDocument26 pages2.8 GravityShidevPas encore d'évaluation
- 05a MASS ACCELERATION AND WEIGHTDocument2 pages05a MASS ACCELERATION AND WEIGHTMohamed ShazlyPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 20gravitaionDocument41 pages10 20gravitaionnivikathed.1510Pas encore d'évaluation
- IX GravitationDocument4 pagesIX Gravitationsmi_santhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitation Short Q.A Class 9Document7 pagesGravitation Short Q.A Class 9Abhinav Chawla 4186Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation.Document15 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation.Navneet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- GRAVITATIONDocument3 pagesGRAVITATIONvaniak01028Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Topic 1 - SpaceDocument12 pagesPhysics Topic 1 - SpaceD RayPas encore d'évaluation
- There Are Four Known Fundamental Forces in Nature.: Gravity Weak Nuclear Electromagnetic Strong NuclearDocument54 pagesThere Are Four Known Fundamental Forces in Nature.: Gravity Weak Nuclear Electromagnetic Strong Nuclearapi-19790880Pas encore d'évaluation
- GravitationDocument4 pagesGravitationsuhaninanekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitational Acceleration and Free FallDocument46 pagesGravitational Acceleration and Free FallMayurie Phutharat SurinPas encore d'évaluation
- GravitationDocument9 pagesGravitationssPas encore d'évaluation
- Kaedah Pengajaran Fizik (Understanding Gravity)Document64 pagesKaedah Pengajaran Fizik (Understanding Gravity)dirza82Pas encore d'évaluation
- Spectrum Reading - Grade 6 EbookDocument22 pagesSpectrum Reading - Grade 6 Ebookmony.mohamed.89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitation Lecture NotesDocument20 pagesGravitation Lecture NotesAS HUMBLE PIANOPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitational ForceDocument4 pagesGravitational ForceHusna AdilaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3786 FdocDocument3 pages3786 FdocThandanani MdakanePas encore d'évaluation
- Gravity MeDocument15 pagesGravity MeNAJMILPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitation (MODULE-2)Document14 pagesGravitation (MODULE-2)umaPas encore d'évaluation
- Free FallDocument22 pagesFree FallOne ShotPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 9th Science ch-10 Gravitation NotesDocument4 pagesClass 9th Science ch-10 Gravitation NotesPlay like pro.Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2.8 Weight 2023Document13 pages2.8 Weight 2023Xinpei ShimPas encore d'évaluation
- Brilliant Education Centre: Science - PhysicsDocument2 pagesBrilliant Education Centre: Science - Physicsasamad54Pas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Gravity - PHYSICS FORM 4Document23 pagesUnderstanding Gravity - PHYSICS FORM 4Noor100% (3)
- Grade 9 Mass and Weight 2021-2022Document15 pagesGrade 9 Mass and Weight 2021-2022Shalini KulshresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitation Notes: According To Universal Law of GravitationDocument14 pagesGravitation Notes: According To Universal Law of GravitationKushagra GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 3Document13 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 3DarshilPas encore d'évaluation
- GravitationDocument31 pagesGravitationjesvinjesvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul Gerak Dan Gaya Fis 7 - MRDocument7 pagesModul Gerak Dan Gaya Fis 7 - MRMasdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Space: Physics Core Topic 9.2Document14 pagesSpace: Physics Core Topic 9.2pussyslayer2770Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 6 GravitationDocument10 pagesCh. 6 GravitationJoanne Aga EslavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument43 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionJhulia IlogonPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces NotesDocument13 pagesForces NotesAthena HuynhPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass and WeightDocument2 pagesMass and WeightDarrell NEwtonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 - GravitationDocument13 pagesChapter 10 - Gravitationnitika chawlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Terminal Velocity and ProjectilesDocument2 pagesTerminal Velocity and ProjectilesKariye Knowmore KalungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Ix (Science) : SESSION: 2021-2022 Handout On Gravitation (Physics) CHAPTER-11 (PART-1)Document4 pagesClass Ix (Science) : SESSION: 2021-2022 Handout On Gravitation (Physics) CHAPTER-11 (PART-1)Manan SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: ForcesDocument19 pagesTopic: ForcestuvvacPas encore d'évaluation
- 10th Science 1Document8 pages10th Science 1Daulatrao ShindePas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitation NotesDocument3 pagesGravitation NotesrajeshdranePas encore d'évaluation
- Confusion of Mass and WeightDocument3 pagesConfusion of Mass and WeightKarizamae MijaresPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2Document16 pagesCH 2IratechaosPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4work Energy & PowerDocument32 pagesChapter 4work Energy & PowerEric MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.3 Classification of PlantDocument3 pages3.3 Classification of PlantEric Mitchell100% (1)
- Forces in Equilibrium: QuestionsDocument10 pagesForces in Equilibrium: QuestionsEric MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 2: The World Through Our SensesDocument13 pagesScience Form 2: The World Through Our SensesEric MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Work, Energy, Power & EfficiencyDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Work, Energy, Power & EfficiencyEric MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces in EquilibriumDocument11 pagesForces in EquilibriumEric MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning OutcomesDocument80 pagesLearning OutcomesZarith Hidayah IsmilePas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics UsesDocument14 pagesTopic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics UsesNorhisham Mohamed SobriPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Linear MotionDocument4 pagesExercise Linear MotionEric MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Trial 2010 Physics Qa JohorDocument88 pagesSPM Trial 2010 Physics Qa JohorEric MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 3 Form 4Document17 pagesPaper 3 Form 4Eric MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Properties of Petroleum Flui 2017 Petroleum Production EngineeriDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Properties of Petroleum Flui 2017 Petroleum Production EngineeriZehron ChemicalsPas encore d'évaluation
- YASKAWA AC Drive V1000: Quick Start GuideDocument46 pagesYASKAWA AC Drive V1000: Quick Start GuideMaria TzagarakiPas encore d'évaluation
- WIZ SeriesDocument4 pagesWIZ SeriesJon HamonPas encore d'évaluation
- VSB ManualDocument166 pagesVSB Manualmukul9040Pas encore d'évaluation
- EE22-2 Homework 2Document2 pagesEE22-2 Homework 2Ryan De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Compass SystemsDocument14 pagesCompass SystemsAboody AL-ghamdyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Importance of The Third Law ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesThe Importance of The Third Law ThermodynamicsTrisa Fadhillah0% (1)
- Frequency Response: Reading: Sedra & Smith: Chapter 1.6, Chapter 3.6 and Chapter 9 (MOS Portions)Document40 pagesFrequency Response: Reading: Sedra & Smith: Chapter 1.6, Chapter 3.6 and Chapter 9 (MOS Portions)pravin patilPas encore d'évaluation
- Low Voltage CTS GB 2009 PDFDocument66 pagesLow Voltage CTS GB 2009 PDFAkram Del RioPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumbling Toast, Murphy's Law and The Fundamental Constants: European Journal of Physics July 1995Document6 pagesTumbling Toast, Murphy's Law and The Fundamental Constants: European Journal of Physics July 1995miguelPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Newtonian FluidsDocument31 pagesNon Newtonian Fluidsikechukwujoel8Pas encore d'évaluation
- S5 16003PS0 NS0Document2 pagesS5 16003PS0 NS0Antonio Solís MurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- DB - Pefy P VMHS eDocument26 pagesDB - Pefy P VMHS eAndi IrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemistryDocument47 pagesChemistryAnubhav ShrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 2Document7 pagesExercise 2satrio weka0% (1)
- Switch - Disconnector Base Mounting: 2P - 3P - 3P+NDocument9 pagesSwitch - Disconnector Base Mounting: 2P - 3P - 3P+NVildanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ece III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesDocument111 pagesEce III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesGautam Sharma80% (10)
- Chapter 2 Exercises Part2Document2 pagesChapter 2 Exercises Part2Cedric MunlawinPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulators 101 Panel Final ADocument84 pagesInsulators 101 Panel Final ABlakePas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Balance in Fusion WeldingDocument4 pagesHeat Balance in Fusion WeldingjohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Physics Sixth Edition: Halliday Resnick WalkerDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Physics Sixth Edition: Halliday Resnick WalkerAhmar KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- CATALOGO EVOLIS 24kvDocument80 pagesCATALOGO EVOLIS 24kvOgaihtsantosPas encore d'évaluation
- 5STP 06D2800: Phase Control ThyristorDocument5 pages5STP 06D2800: Phase Control ThyristorFernando_Paez_Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment On 'Refrigeration Cycle'Document3 pagesAssignment On 'Refrigeration Cycle'Anonymous GGtvR65MRPas encore d'évaluation