Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
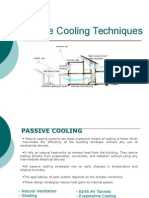
Passive Cooling Techniques
Transféré par
taapsiii0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
187 vues21 pagespassive cooling
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentpassive cooling
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
187 vues21 pagesPassive Cooling Techniques
Transféré par
taapsiiipassive cooling
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 21
Passive cooling techniques.
Passive cooling techniques can be used to
reduce or eliminate mechanical air
conditioning requirements in areas where
cooling is a dominant problem.
By Convective method.
Natural ventilation: By providing
appropriate openings in suitable locations.
The oldest straight forward method admits
cool night air to drive out the warm air.
2.Buoyancy ventilation: It is more
commonly referred to as temperature
induced or stack ventilation. Cool air is
heavier than warm air at the same
humidity. Thus air flow is generated by
dropping of the heavier air, forcing the
lighter air to exhaust.
Proper position of openings.
Another convective cooling strategy is the
drawing of outdoor air through tubes buried
in the ground and dumped into the house.
Made of material that allows easy thermal
transfer, these tubes are buried several feet
deep to avoid the warmer daytime surface
temperatures.
Warm outdoor air entering the tube gives up
its heat to the cooler earth, and cools
substantially before entering the house.
Thermal saturation of the surrounding earth
must be addressed, by means of surface
landscaping and watering, thereby removing
the gained thermal energy from the
tube/earth transfers.
Though condensation is rarely a problem
in dry climates, such tubes should be
sloped slightly and have adequate
drainage to insure that water build-up
doesn't block the passage of air. The
intake end should be screened and
placed in a shady spot away from foot
traffic. When properly built and sized,
these underground tubes can supply cool
air during the peak load daytime even in
the hottest climates.
By using under ground buried air
tubes.
Shady devices:
A horizontal over
hang or an awning
above a south
window is an
inexpensive effective
solution.
Wing Walls.
Wing walls are vertical solid panels placed
alongside of windows perpendicular to the
wall on the windward side of the house.
Figure 4
Top View of Wing Walls Airflow Pattern
Wing walls will accelerate the natural wind
speed due to pressure differences created by
the wing wall.
Top View of Wing Walls Airflow Pattern;
Thermal Chimney:
A thermal chimney employs convective
currents to draw air out of a building. By
creating a warm or hot zone with an exterior
exhaust outlet, air can be drawn into the
house ventilating the structure.
Sunrooms can be designed to perform this
function. The excessive heat generated in a
south facing sunroom during the summer can
be vented at the top. With the connecting
lower vents to the living space open along
with windows on the north side, air is drawn
through the living space to be exhausted
through the sunroom upper vents. (The
upper vents from the sunroom to the living
space and any side operable windows must
be closed and the thermal mass wall in the
sunroom must be shaded.)
A trellis with deciduous
vines can be used.
Another good
strategy is the use of
deciduous trees that
shade the south face
and roof during the
summer. All these
shading methods
work equally well
with Trombe walls,
water walls,
greenhouses, and
other south-wall
passive solar
collector strategies.
EVAPORATIVE COOLING METHODS
When water evaporates it absorbs a
large amount of heat from its surroundings.
Evaporative methods can be used to
enhance the cooling rates in convective
cooling systems.
Using earth tubes and by using cooling
towers.
A cool tower requires no blower fans to
move the cool air. The only power required
is for a small 12 volt DC pump to circulate
water over the cooler pads.
Basic cool tower design: Cool
towers use gravity to move
cool air without any fans.
Generally cool towers are
6x6 to 10x10, 20 to 30 tall
for a building with one or 2
storey. These cool towers will
cool 1000 to 2500 sq.ft. Air
flow for these cool towers will
range from 2500 to 8000
CFM.
Basic cool tower design:
Common cool tower design:
Advanced cool tower design:
Common cool tower design.
Consists of wet pads in tower. Water must flow
down pads air must pass through them in order to
have evaporation needed to cool the air.
As wind blows through the wet pads, water absorbs
heat from air, and evaporates. Thus making the air
cool. Vents must have a larger openinh than those
used with a forced air system because there is no
pressurized fan blower in this system.This tower is
6x6x30in dimensions.
Advanced cool tower design.
To create a large air flow down the cool
tower, there will be one large swivel scoop
above the pads in the tower.The scoops
should have a venturi system to keep the
scoop oriented into the wind.Instead of one
large opening ,install smaller openings in the
roof with down wind swivel scoops to remove
the heat. With this system the wind can blow
from any direction and cool tower will
continue to function.This is a more efficient
design than using a solar chimney.
The intake air scoop should be made o/o
aluminium or designed with an aluminium frame
with canvas stretched over it.The canvas scoop
is recommended because it is lighter and
generates no noise.
In this design the pads are just below the scoop
inside the tower with ducting to direct the air
flow into and through the pads.This reduces the
size area of the cooler pads, thus reducing the
cost.The design requires about 20 sqft of 4 thk
pads.Cooler pads that are inside the tower and
below the scoop are protected from the direct
sunlight.The tower size is 6 square 30 high.
The air scoop occupies the top 4. Two pads of
3 square 4 thk located just below the air
scoop.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Build Your Own Solar Water HeaterDocument115 pagesBuild Your Own Solar Water HeaterMoreMoseySpeed100% (4)
- Cooling tower evaporative technologyDocument22 pagesCooling tower evaporative technologyFatin AnisahPas encore d'évaluation
- DomesDocument30 pagesDomesKhiZra ShahZad100% (1)
- Earth Moving Equipment GuideDocument19 pagesEarth Moving Equipment Guidetaapsiii100% (1)
- The Dome Builders Handbook PDFDocument113 pagesThe Dome Builders Handbook PDFsersol83% (12)
- Glass Bottle WallsDocument27 pagesGlass Bottle WallsHiwi Negash100% (1)
- Passive Solar DesignDocument44 pagesPassive Solar DesignnandantharejaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Principles of Passive Cooling DesignDocument14 pages6 Principles of Passive Cooling Designamrit6003Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geography Grade 12 Term1 Week 1 To 3Document50 pagesGeography Grade 12 Term1 Week 1 To 3Nkhensani Hlungwani100% (1)
- Passive Low Energy Architecture in Hot and Dry ClimateDocument10 pagesPassive Low Energy Architecture in Hot and Dry ClimatePavithra SuparamanianPas encore d'évaluation
- YOURHOME PassiveDesign PassiveCooling PDFDocument14 pagesYOURHOME PassiveDesign PassiveCooling PDFKeyur PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative Test 3rd Quarter 9scienceDocument3 pagesSummative Test 3rd Quarter 9scienceSharonPas encore d'évaluation
- A Step-by-Step Guide To Building An Underground Year-Round GreenhouseDocument33 pagesA Step-by-Step Guide To Building An Underground Year-Round GreenhousemajaproductionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument809 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningVenkata Harish YadavalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Solar Heat Gains and Casual Heat SourcesDocument31 pagesBuilding Solar Heat Gains and Casual Heat Sourcesguzman_10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mitsubishi Electric MUZ-FH VE Service Manual EngDocument54 pagesMitsubishi Electric MUZ-FH VE Service Manual Engcronnin20044967Pas encore d'évaluation
- Climatic Data For Building Design Standards: - Public Review DraftDocument186 pagesClimatic Data For Building Design Standards: - Public Review DraftSwan Htet AungPas encore d'évaluation
- Six Rules for Low Cost Passive HeatingDocument63 pagesSix Rules for Low Cost Passive HeatingAman KashyapPas encore d'évaluation
- DomeDocument16 pagesDomeJan RubiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stack EffectDocument19 pagesStack EffectSourav Kanti Nath100% (1)
- Super Adobe ConstructionDocument3 pagesSuper Adobe ConstructionGilles GautierPas encore d'évaluation
- Stack VentilationDocument36 pagesStack VentilationTulika Galani100% (1)
- Space Frames and Geodesic DomesDocument36 pagesSpace Frames and Geodesic DomesartPas encore d'évaluation
- California Create Your Own Rain Garden - Sacramento County Rain Garden GuidelinesDocument11 pagesCalifornia Create Your Own Rain Garden - Sacramento County Rain Garden GuidelinesFree Rain Garden ManualsPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Ventilation Strategies in Tropical ClimateDocument50 pagesNatural Ventilation Strategies in Tropical ClimateFirrdhaus Sahabuddin100% (3)
- Straw Bale PrimerDocument8 pagesStraw Bale PrimerVmeupPas encore d'évaluation
- A Solar Cooling System For Greenhouse Food Production in Hot Climates PDFDocument8 pagesA Solar Cooling System For Greenhouse Food Production in Hot Climates PDFAvikGhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- TROP3Document33 pagesTROP3louisePas encore d'évaluation
- Seresco Natatorium Design Guide 2013Document36 pagesSeresco Natatorium Design Guide 2013Luis Giagante100% (1)
- Expansion Tank SizingDocument36 pagesExpansion Tank SizingEngFaisal AlraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Guideline For Sel of Cool Roof Surface (Roof Treatment)Document23 pagesGuideline For Sel of Cool Roof Surface (Roof Treatment)Jawad AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Solar Design: Dr. William J. MakofskeDocument60 pagesPassive Solar Design: Dr. William J. Makofskesubhajit29inPas encore d'évaluation
- UEBA3523 Asian Architecture: PART B: The Malaysian HouseDocument16 pagesUEBA3523 Asian Architecture: PART B: The Malaysian HouseNg Tzeway100% (1)
- High Quality Rammed Earth StructuresDocument9 pagesHigh Quality Rammed Earth Structuresalicekubrickk100% (1)
- Hydronic Radiant-Floor HeatingDocument8 pagesHydronic Radiant-Floor Heatingkasandra01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Cooling TechniquesDocument16 pagesPassive Cooling TechniquesPrakhar JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Architectural reference books guideDocument1 pageArchitectural reference books guidetaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- KKT KrausDocument24 pagesKKT KrausDaniel TibreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive CoolingDocument8 pagesPassive CoolingMohamed AbdelbakyPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Solar Design Guide for Homes and BuildingsDocument90 pagesPassive Solar Design Guide for Homes and BuildingsKrystal LambPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Cooling of BuildingDocument57 pagesPassive Cooling of BuildingexperthvachomePas encore d'évaluation
- Window Mounted Solar Hot Air FurnaceDocument14 pagesWindow Mounted Solar Hot Air FurnaceEduardo J Villalobos GPas encore d'évaluation
- Umbrella HouseDocument6 pagesUmbrella HouseGonzalo Agulló FernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Tips For The Hot Humid ClimateDocument3 pagesDesign Tips For The Hot Humid ClimateakshayjanuPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Thermal MassDocument5 pages13 Thermal MassaomareltayebPas encore d'évaluation
- Cordwood Construction PDFDocument8 pagesCordwood Construction PDFamondaca100% (1)
- A Design For High-Torque, Low-Speed Vertical Axis Wind TurbineDocument11 pagesA Design For High-Torque, Low-Speed Vertical Axis Wind TurbineMostafa RashedPas encore d'évaluation
- Bamboo Shelter Solution for RefugeesDocument8 pagesBamboo Shelter Solution for RefugeesDinesh Poudel100% (1)
- LandscapeDocument13 pagesLandscapetaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Midea Service GuideDocument121 pagesMidea Service GuideChairul Fatah100% (2)
- Energy Efficient Architecture DesignDocument31 pagesEnergy Efficient Architecture DesigntaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Berming and Air TunnelsDocument27 pagesEarth Berming and Air TunnelsAbishaTeslin100% (1)
- Design and Fabrication of Solar Powered Ice BoxDocument5 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Solar Powered Ice BoxesatjournalsPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Solar Architecture For Mediterranean AreaDocument176 pagesPassive Solar Architecture For Mediterranean Areaal_herna2100% (4)
- Unit-2 Case Study Embedded System For Automatic Washing MachineDocument11 pagesUnit-2 Case Study Embedded System For Automatic Washing Machinesujith84% (19)
- Cooling by Underground Earth Tubes PDFDocument4 pagesCooling by Underground Earth Tubes PDFtrola666910Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 XX Passive CoolingDocument114 pagesUnit 3 XX Passive CoolingtinabhuvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Consious Architecture Passive Solar HeatingDocument26 pagesEnergy Consious Architecture Passive Solar HeatingAr Ambuj SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Solar Energy My EditDocument199 pagesPassive Solar Energy My Editmarkovit0% (1)
- Passive Solar Building Design SasDocument26 pagesPassive Solar Building Design Sassanu222Pas encore d'évaluation
- Building A Better Trombe WallDocument2 pagesBuilding A Better Trombe WallAbdulrahman SalemPas encore d'évaluation
- Indigenous Architecture and Natural CoolingDocument8 pagesIndigenous Architecture and Natural CoolingShruti JalodiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Passive CoolingDocument20 pages11 Passive CoolingParth Shah100% (1)
- Building Envelope: Envelopes For Climate TypesDocument9 pagesBuilding Envelope: Envelopes For Climate Typesdhanya1995Pas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Solar Design Principles for Building Science LectureDocument40 pagesPassive Solar Design Principles for Building Science LectureLawrence Babatunde OgunsanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hot-Dry Shelter DesignDocument37 pagesHot-Dry Shelter Designwhatever530Pas encore d'évaluation
- (U598.Book) Download PDF Manual of Section by Paul Lewis, Marc Tsurumaki, David J. LewisDocument5 pages(U598.Book) Download PDF Manual of Section by Paul Lewis, Marc Tsurumaki, David J. LewisYelena170% (3)
- IX. TRUSS and ROOF SYSTEMSDocument38 pagesIX. TRUSS and ROOF SYSTEMSkriengsak ruangdechPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual of Section Paul Lewis Marc TsurumakiDocument1 pageManual of Section Paul Lewis Marc TsurumakiDipankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Solar Building Design for Energy IndependenceDocument9 pagesPassive Solar Building Design for Energy IndependenceRakesh VdPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive DesignDocument68 pagesPassive DesignGeremy GalleneroPas encore d'évaluation
- Module-4: Sunderdeep College of ArchitectureDocument7 pagesModule-4: Sunderdeep College of ArchitectureAbhish Ek KurilPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and passive air conditioning systems for tropical regionsDocument6 pagesActive and passive air conditioning systems for tropical regionsGanaka Kodithuwakku50% (2)
- Stay Cool in The Hot DesertDocument6 pagesStay Cool in The Hot DesertCoevicPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - Passive CoolingDocument47 pagesModule 1 - Passive CoolingDHEESHNA DILEEP 200545Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7343696Document9 pages7343696taapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 - Plumbing and DrainageDocument12 pages15 - Plumbing and DrainagetaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation 1Document1 pagePresentation 1taapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Used in Bijapur SiteDocument5 pagesMaterial Used in Bijapur SitetaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Plan Plan: Administration BlockDocument1 pagePlan Plan: Administration BlocktaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation 1Document1 pagePresentation 1taapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Trees in Bijapur SiteDocument2 pagesTrees in Bijapur SitetaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Proposed Artisan'S Village at Dharwad: Case Study: Janapada Loka, RamanagaraDocument2 pagesProposed Artisan'S Village at Dharwad: Case Study: Janapada Loka, RamanagarataapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Produced by An Autodesk Educational ProductDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Educational ProducttaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Crafts of KarnatakaDocument6 pagesCrafts of KarnatakataapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Constructionequipment 130411074220 Phpapp01Document88 pagesConstructionequipment 130411074220 Phpapp01phankhoa83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scale of Fees of An ArchitectDocument2 pagesScale of Fees of An ArchitecttaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Elevation: WorkshopDocument1 pageElevation: WorkshoptaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Proposed Artisan'S Village at Dharwad: Case Study: Janapada Loka, RamanagaraDocument2 pagesProposed Artisan'S Village at Dharwad: Case Study: Janapada Loka, RamanagarataapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Agricultural Farms: 9m Wide RoadDocument1 pageAgricultural Farms: 9m Wide RoadtaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Crafts of KarnatakaDocument6 pagesCrafts of KarnatakataapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Falling of The Holy Spirit On GroupsDocument10 pagesThe Falling of The Holy Spirit On GroupstaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Log BookDocument3 pagesLog BooktaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- RCC TbeamDocument29 pagesRCC TbeamrohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Green BuildingDocument26 pagesGreen BuildingtaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 15Document7 pagesLecture 15gendadeyu552625Pas encore d'évaluation
- FillerDocument7 pagesFillertaapsiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dixell Operating Instructions: Temperature and Humidity Controller For Freezing - Proving CabinetsDocument5 pagesDixell Operating Instructions: Temperature and Humidity Controller For Freezing - Proving CabinetsJennifer Eszter SárközyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fog PresentationDocument12 pagesFog PresentationYvainePas encore d'évaluation
- DDC System Commissioning Acceptance Procedure: Example Project/Building DescriptionDocument3 pagesDDC System Commissioning Acceptance Procedure: Example Project/Building DescriptionGraezelPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Pump Swimming Pool HeatersDocument4 pagesHeat Pump Swimming Pool HeatersMohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Fronts and Frontal DepressionsDocument3 pagesFronts and Frontal Depressionscptmehmetkaptan100% (1)
- Sanyo HVAC CatalogDocument28 pagesSanyo HVAC Cataloge-ComfortUSAPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Water Cooling IWSeptember2014Document4 pagesProcess Water Cooling IWSeptember2014FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- RAC Domestic Refrigerator Test RigDocument11 pagesRAC Domestic Refrigerator Test RigShashi Bhushan Patel67% (3)
- Refrigeration and Heat PumpDocument21 pagesRefrigeration and Heat PumpAnantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Form 4 MRSM Kuala KlawangDocument26 pagesPhysics Form 4 MRSM Kuala KlawangAhmed SabryPas encore d'évaluation
- Layers of The AtmosphereDocument20 pagesLayers of The AtmosphereMiles RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan in Tve (Electricity I)Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Tve (Electricity I)Mhar BulanadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Urban Heat Island Acrostic 1Document2 pagesUrban Heat Island Acrostic 1aslPas encore d'évaluation
- TASK 01:: Name: Syed Tanzeel Ur Rehman ROLL NO: 2020-BSCS-037 Sec: ADocument8 pagesTASK 01:: Name: Syed Tanzeel Ur Rehman ROLL NO: 2020-BSCS-037 Sec: ASahil JagdeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Plume BehaviourDocument19 pagesPlume Behaviourutkarsh tiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Weather Word MapDocument3 pagesWeather Word Mapapi-224842598Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clear Air TurbulanceDocument2 pagesClear Air TurbulanceAchmad Arifudin HidayatullohPas encore d'évaluation
- Vapor Compression Test RigDocument3 pagesVapor Compression Test RigTARUN DHUNNA0% (1)
- Test Report For Air-Conditioner Models (Air-Enthalpy Method)Document2 pagesTest Report For Air-Conditioner Models (Air-Enthalpy Method)erpinPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermistor 50KDocument2 pagesThermistor 50Kfredjbps@gmail.comPas encore d'évaluation