Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Genetics 2nd Weeks, Monohybrid Crosses
Transféré par
Alam Nuanza0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
83 vues25 pagespersilangan monohibrid
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentpersilangan monohibrid
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
83 vues25 pagesGenetics 2nd Weeks, Monohybrid Crosses
Transféré par
Alam Nuanzapersilangan monohibrid
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 25
Monohybrid Crosses,
Co-dominance, and Intermediate
Weeks II
Wednesday, September 11
th
2013
It s time to quizz!!!!!
(b)
(d) (e)
(f)
(a)
(h)
(c)
(g)
Some important terms in Genetics
At each locus, a diploid organism possesses
two alleles located on different homologous
chromosomes
The seventh characteristics of Pisum sativum
in Mendels experiments
Mendels Experiment with Pisum sativum
Mendels
experiment
result
Albinism in human being is usually
inherited as a recessive trait
(Richard Dranitzke/SS/Photo Researchers)
The Law of Segregation
Mendel's first law of genetics
The two members of a gene pair segregate randomly
and equally into the gametes, which then combine at
random to form the next generation.
Segregation results
from the separation
of homologous
chromosomes in
meiosis
Phenotypic ratios for simple genetic crosses
(crosses for a single locus)
Genotypic ratios for simple genetic crosses
(crosses for a single locus)
Back cross and Test cross
A back cross: mating the F1 hybrid to one of the
parental types. There are two possible backcrosses in
the system.
Tt x TT. Back crossing to the dominant parent. The Tt
plant will produce 1/2 T gametes and 1/2 t gametes.
The TT plant will produce only T gametes. The offspring
will thus be 1/2 TT and 1/2 Tt. Both of these types are
tall, so the result of a backcross to the dominant parent
is all offspring with the dominant type.
Tt x tt. Back crossing to the recessive parent. The Tt
parent produces 1/2 T gametes and 1/2 t gametes, and
the tt parent produces only t gametes. The offspring
will be 1/2 Tt (tall) and 1/2 pp (dwarf). The offspring of a
test cross are in the same ratio as the gametes from the
organism being tested: 1/2 T (tall) and 1/2 t (dwarf).
Test cross:
one individual of
unknown genotype is
crossed with another
individual with
homozygous
recessive genotype
for the trait.
How about the back
cross?
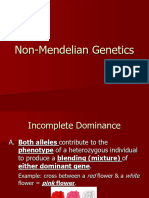
Incomplete Dominance
In incomplete dominance the heterozygote exhibits a
phenotype that is intermediate between the
corresponding homozygotes and different from either one
Example:
Flower color in the four oclock plant
Two alleles
C
R
= wild-type allele for red flower color
C
W
= allele for white flower color
Note how the nomenclature has changed from Cc to
superscripts ("C" is still the gene)
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display
1:2:1 phenotypic
ratio NOT the 3:1
ratio observed in
simple Mendelian
inheritance
In this case, 50% of
the C
R
protein is not
sufficient to produce
the red phenotype
P generation
x
Pink
Gametes
Red White
Gametes
Egg
Sperm
Self-fertilization
C
R
C
W
C
W
C
W
C
R
C
R
F
1
generation
F
2
generation
C
R
C
W
C
R
C
R
C
R
C
W
C
W
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
C
W
C
R
C
R
C
R
C
W
C
R
C
W
C
W
C
W
Fruit color in
eggplant is inherited
as an incompletely
dominant trait
In Codominance, heterozygotes express the
phenotypes of both parents
The ABO blood group provides an example
Phenotype (A, B, AB or O) is determined by the type of
antigen present on the surface of red blood cells
Antigens are substances that are recognized by
antibodies produced by the immune system
As shown in figure below, there are three different
alleles that determine which antigen(s) are present
on the surface of red blood cells
Allele I
A
, adds antigen A to H antigen
Allele I
B
, adds antigen B to H antigen
Allele i, doesn't add anything to H antigen
Codominance
Allele i is recessive to both I
A
and I
B
Alleles I
A
and I
B
are codominant
They are both expressed in a heterozygous individual
Blood type:
Genotype:
Surface antigen:
Serum antibodies:
O
RBC RBC RBC RBC
Antigen A
N-acetyl-
galactosamine
Antigen B Antigen B Antigen A
neither A or B
against A and B
A
I
A
I
A
or I
A
i ii
A
against B
B
I
B
I
B
or I
B
i
B
against A
AB
I
A
I
B
A and B
none
Galactose
(a) ABO blood type
H antigen
RBC
Glycosyl transferase
encoded by I
A
allele
N-acetyl-
galactosamine
Active
site
Glycosyl transferase
encoded by I
B
allele
Galactose
Active
site
RBC
RBC
Antigen A
RBC
Antigen B
(b) Formation of A and B antigen by glycosyl transferase
Monohybrid Exercises
1. Mendel found that in pea plants, red flower color
dominant is over white.
a). A heterozygous red flowered plant is crossed with a
white flowered one. Find:
a) genotypes of each parent
b) genotype and phenotype for F1 generation
b) A homozygous red flowered plant is crossed with a
white flowered one.
a) genotypes of each parent
b) genotype and phenotype for F1 generation
c) genotype and phenotype for F2 generation
2. Anto memiliki sifat yang sama dengan kakeknya, yaitu rambut lurus,
padahal kedua orang tua Anto berambut keriting. Secara genetika
sifat rambut lurus pada kakek Anto adalah
(A) dominan (B) resesif (C) intermedier (D) semi dominan
3. Persilangan bunga Mirabilis jalapa merah dengan Mirabilis jalapa
putih menghasilkan keturunan F1 berwarna merah muda semua.
Bagaimanakah perbandingan fenotip keturunan F2-nya jika terjadi
penyerbukan sendiri?
(A) 25% merah: 25% merah muda: 50% putih
(B) 25% merah: 50% merah muda: 25% putih
(C) 75% merah: 25% putih
(D) 50% merah: 50% putih.
4. Kakek Wahyu dapat menggulung lidahnya (sifat dominan). Kakek
Wahyu mempunyai dua orang anak yaitu Ayah Wahyu yang dapat
menggulung lidah dan Bibi Wahyu yang tidak dapat menggulung
lidah, sama dengan sifat ibu Wahyu. Berapa kemungkinan Wahyu
dapat menggulung lidahnya?
A.25 % (B) 50 % (C) 75 % (D) 100 %
5. Sejumlah marmut hitam dari genotip yang sama dikawinkan.
Dihasilkan 81 keturunan berwarna hitam dan 28 berwarna
putih. Apa genotip dari kedua induk?
6. Bentuk lobak bisa panjang (S
L
S
L
), bulat (S
R
S
R
) atau oval (S
L
S
R
).
Jika lobak panjang disilangkan dengan lobak oval, lalu
keturunan F1 dibiarkan kawin sesamanya secara acak, apa
rasio fenotipik yang diharapkan pada F2?
7. Jika ayam dengan dibulu berwarna semburat putih
dikawinkan dengan ayam berbulu hitam, keturunannya semua
bebulu biru batu tulis (biru andalusia). Jika ayam biru
andalusia saling disilangkan, dihasilkan keturunan semburat
putih, biru, dan hitam berturut-turut dengan rasio 1:2:1.
a) Bagaimana cara pewarisan sifat bulu tersebut?
b) Dengan menggunakan simbol-simbol yang sesuai, tuliskan
genotip bagi masing-masing fenotip.
8. A cross of F1-hybrid plants: A genetic cross between two F1-hybrid
pea plants for spherical seeds will yield what percent spherical-
seeded plants in the F2 generation? (Recall, spherical-shaped seeds
are dominant over dented seeds.)
(A) 100% (B) 75% (C) 50% (D) 25%
9. A woman with type A blood and a man with type B blood could
potentially have offspring with which of the following blood types?
(A) type A (B) type B (C) type AB (D) type 0
(E) all of the above
10. If the unknown is homozygous, all of the offspring of the test cross
have the __________ phenotype. If the unknown is heterozygous, half
of the offspring will have the __________ phenotype.
(A) dominant, incompletely dominant (B) recessive, dominant
(C) dominant, epistatic (D) codominant, complimentary
(E) dominant, recessive
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Unit8 - GeneticsProblems - Assignment KeyDocument5 pagesUnit8 - GeneticsProblems - Assignment KeyJasmine KingPas encore d'évaluation
- Mendelian Genetics: Dominant & Recessive Review: Genotype: PP Genotype: PP Genotype: PPDocument36 pagesMendelian Genetics: Dominant & Recessive Review: Genotype: PP Genotype: PP Genotype: PPangela0% (1)
- Brain TeasersDocument13 pagesBrain Teasersshan_batiPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFDocument10 pagesGenetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFejanlindsay50% (2)
- Genetics Nonmendelian 150722002319 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument81 pagesGenetics Nonmendelian 150722002319 Lva1 App6891 PDFLeby Fastidio100% (1)
- Population Genetics Practice Problems For StudenetsDocument10 pagesPopulation Genetics Practice Problems For Studenetskaram aliPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO - 10 - 41 - V2 - DM - Interaction of Allelic and Non-Allelic GenesDocument5 pagesBIO - 10 - 41 - V2 - DM - Interaction of Allelic and Non-Allelic GenesAlbina YulmukhametovaPas encore d'évaluation
- New Genetic ProblemsDocument8 pagesNew Genetic Problemsmzunl25476Pas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Problems 11Document10 pagesGenetics Problems 11Antonio López JiménezPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology - Genetics Review 2Document15 pagesBiology - Genetics Review 2lanichung100% (1)
- Homework For Unit 6Document5 pagesHomework For Unit 6yanhcharliePas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 - Unit 2 - Booklet - Genetics - 2 - SonDocument32 pagesGrade 10 - Unit 2 - Booklet - Genetics - 2 - SonBenanPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 Patterns of InheritanceDocument27 pagesModule 3 Patterns of InheritancePapi0% (1)
- Test Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Wessler Carroll Doebley 1464109486 9781464109485 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Wessler Carroll Doebley 1464109486 9781464109485 Full Chapter PDFjane.boyles334100% (15)
- 2.2 Non-Mendelian InheritanceDocument26 pages2.2 Non-Mendelian InheritanceJayas Maria De PeraltaPas encore d'évaluation
- Principle of Inheritance Variations: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument23 pagesPrinciple of Inheritance Variations: Multiple Choice QuestionsUrja Moon100% (1)
- Apgeneticsworksheet 1Document7 pagesApgeneticsworksheet 1Omar MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation - Revision WorksheetDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation - Revision Worksheetafsheenfatima2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Worksheet 1 - Genetics (Grade 12)Document19 pagesBiology Worksheet 1 - Genetics (Grade 12)ramPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics 2nd Weeks, Monohybrid CrossesDocument40 pagesGenetics 2nd Weeks, Monohybrid CrossesAna RosyidahPas encore d'évaluation
- Even More Genetics PracticeDocument4 pagesEven More Genetics PracticeMichael ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics ProblemDocument2 pagesGenetics ProblemnaomiPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Mendelian GeneticsDocument22 pagesNon Mendelian GeneticsJoraine Nichole Roquero VillajuanPas encore d'évaluation
- InheritanceDocument116 pagesInheritanceYasmeen EhfanPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Mendelian GeneticsDocument64 pagesNon Mendelian GeneticsDipanshi shahPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyto TalentoDocument6 pagesCyto TalentoJethro TalentoPas encore d'évaluation
- Deviation From Mendelian Genetic 1Document38 pagesDeviation From Mendelian Genetic 1Yuliandini Pangestika Wiyono100% (1)
- Genetics Problem SetDocument6 pagesGenetics Problem SetKunvarPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Medelian - Genetics TunayDocument41 pagesNon-Medelian - Genetics TunayCHARMAINE ORUGAPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 GeneticsDocument6 pagesChapter 5 GeneticsMohamed Ali AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- CHPT 15 Genetics Practice ProblemsDocument7 pagesCHPT 15 Genetics Practice ProblemsFatimah AliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Part A: Multiple Choice: Answer With The Best Choice. Make Sure That You Clearly Circle TheDocument8 pagesPart A: Multiple Choice: Answer With The Best Choice. Make Sure That You Clearly Circle TheQueng ElediaPas encore d'évaluation
- GENETICS EXERCISES 2nd TERM RETAKE 1Document3 pagesGENETICS EXERCISES 2nd TERM RETAKE 1adrianaespinosa2008Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4455 Genetics Questions and AnswersDocument13 pages4455 Genetics Questions and Answersmikejose704Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Solution 4&5Document9 pagesTutorial Solution 4&5Nguyen Minh HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Mendelian Genetics: Inheritance Patterns That Don't Follow The RulesDocument29 pagesNon-Mendelian Genetics: Inheritance Patterns That Don't Follow The RulesCza VerwinPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 1Document3 pagesProblem Set 1Serene SheikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Principles of Life 2nd Edition HillisDocument33 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Life 2nd Edition Hillispatrickgarciaewzrbtosai100% (19)
- Variation and GeneticsDocument11 pagesVariation and GeneticsTasawar Hussain DayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Mendelian GeneticsDocument25 pagesNon Mendelian GeneticsGeronimo Miano HitosisPas encore d'évaluation
- Dihybrid Cross Problems 2015Document1 pageDihybrid Cross Problems 2015api-233757247Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz - Simple Mendelian CrossDocument4 pagesQuiz - Simple Mendelian CrossShaden MasriPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller N°1 Genetica Mendeliana PDFDocument2 pagesTaller N°1 Genetica Mendeliana PDFmiguel angel figueroaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Segregation and Interaction: Jonah S. San Sebastian, MS Faculty, BSDDocument33 pagesGene Segregation and Interaction: Jonah S. San Sebastian, MS Faculty, BSDKate CamachoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study - Genetic XIIDocument5 pagesCase Study - Genetic XIISwethaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 QB 1Document8 pagesChapter 5 QB 1aprema570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Incomplete Dominance and CodominanceDocument25 pagesIncomplete Dominance and CodominanceJONJONPas encore d'évaluation
- BAB 14 - PerwarisanDocument12 pagesBAB 14 - PerwarisanKuok HuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Monohybrid Cross Problem SetDocument4 pagesMonohybrid Cross Problem SetivonnePas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic ProblemsDocument20 pagesGenetic Problemsatik0% (2)
- Dihybrid Cross Problems 2013Document1 pageDihybrid Cross Problems 2013kirancanada1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Inheritance & Variation-Neet Pyqs-6290457667-SampleDocument95 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance & Variation-Neet Pyqs-6290457667-Sampleseetharaman8341Pas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Genetics Canadian 2Nd Edition by Hartwell Goldberg Fischer Isbn 1259370887 9781259370885 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Genetics Canadian 2Nd Edition by Hartwell Goldberg Fischer Isbn 1259370887 9781259370885 Full Chapter PDFdavid.caple542100% (14)
- Genetics Problems 2Document8 pagesGenetics Problems 2Clara Moya GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017-SPRING-Genetics ProblemsDocument8 pages2017-SPRING-Genetics ProblemsSteven Wong100% (1)
- Incomplete Dominance and CodominanceDocument43 pagesIncomplete Dominance and Codominancecocosarang439Pas encore d'évaluation
- ACTIVITYGeneticspracticequestions 2Document6 pagesACTIVITYGeneticspracticequestions 2prem19999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Non MedelianDocument27 pagesNon MedelianmichellePas encore d'évaluation
- 400 Q For G11 1st TermDocument85 pages400 Q For G11 1st Termromaehab201912Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Class X Chapter 9 Heredity AssignmentDocument7 pagesBiology Class X Chapter 9 Heredity AssignmentAyush jhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Andrew, J.L., and Tim, C., 2005. Antimicrobial Activity of FlavonoidsDocument14 pagesAndrew, J.L., and Tim, C., 2005. Antimicrobial Activity of FlavonoidsTan Shuie MinPas encore d'évaluation
- 1017 2021 1 SMDocument6 pages1017 2021 1 SMArnes Marda SellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecules: ISSN 1420-3049Document25 pagesMolecules: ISSN 1420-3049Jesus LirioPas encore d'évaluation
- Schmelzer GH - PROTAProtabase Record Medicinal PlantsDocument7 pagesSchmelzer GH - PROTAProtabase Record Medicinal PlantsAlam NuanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis Protein Lengkap 311008Document46 pagesSintesis Protein Lengkap 311008Alam NuanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Uv-VisDocument8 pagesJurnal Uv-VisRaina96Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis Protein Lengkap 311008Document46 pagesSintesis Protein Lengkap 311008Alam NuanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Therapeutic Agents From Tissue Cultures of Medicinal Plants 2329 6836.1000118Document5 pagesTherapeutic Agents From Tissue Cultures of Medicinal Plants 2329 6836.1000118Alam NuanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth of BacteriaDocument47 pagesGrowth of BacteriaAlam NuanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 FungiDocument51 pages09 FungiAlam NuanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Practice Problems PDFDocument9 pagesGenetics Practice Problems PDFanaphade5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - Lesson Plan - Genotypes and PhenotypesDocument4 pagesUnit - Lesson Plan - Genotypes and PhenotypesShannuRRasheedPas encore d'évaluation
- BMS415 - Lesson Plan & Conduct of ClassDocument5 pagesBMS415 - Lesson Plan & Conduct of ClassOjisanPas encore d'évaluation
- Independent Honors 4 9 18 Mendelian Genetics Guided NotesDocument5 pagesIndependent Honors 4 9 18 Mendelian Genetics Guided Notesapi-428068416Pas encore d'évaluation
- ds93 Unit 8 Summative AssessmentDocument3 pagesds93 Unit 8 Summative Assessmentapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Purple Flowers Are Dominant To White Flowers. Brown Eyes Are Dominant To Blue EyesDocument4 pagesPurple Flowers Are Dominant To White Flowers. Brown Eyes Are Dominant To Blue EyesJaznMonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pedigree Charts WorksheetDocument3 pagesPedigree Charts Worksheetapi-518315180Pas encore d'évaluation
- ACTIVITYGeneticspracticequestions 2Document6 pagesACTIVITYGeneticspracticequestions 2prem19999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Variation & Selection 3 QPDocument13 pagesVariation & Selection 3 QPAinul SyazanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics 101 + ExercisesDocument36 pagesGenetics 101 + ExercisesSanaa Samko100% (1)
- DU MSC Zoology 2021 Entrance Paper PDFDocument15 pagesDU MSC Zoology 2021 Entrance Paper PDFSuchismita BanerjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Student Copy of GeneticsDocument122 pagesStudent Copy of GeneticsJofran TisuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Backg - Pre-Lab - Lab Assig - GeneticsDocument13 pagesBackg - Pre-Lab - Lab Assig - GeneticsmurphmikalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pendugaan Rasio Genotipe Dan Fenotipe, Polihibrid, Chi SquareDocument34 pagesPendugaan Rasio Genotipe Dan Fenotipe, Polihibrid, Chi Squarekartika shollaPas encore d'évaluation
- Inheritance Chap 17Document23 pagesInheritance Chap 17Rayan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sex Linkage: Characters Which Are Associate More With One GenderDocument28 pagesSex Linkage: Characters Which Are Associate More With One GenderFakhri NasharulPas encore d'évaluation
- Pedigree Worksheet: Name: Keellie JohnsonDocument3 pagesPedigree Worksheet: Name: Keellie JohnsonDaddyBraccPas encore d'évaluation
- LinkageDocument35 pagesLinkageRaj MalhotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Ed Sept 2021Document35 pagesGen Ed Sept 2021Tom FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1-3 (Mtap Notes)Document94 pagesLecture 1-3 (Mtap Notes)Ma. Mecy COMAHIGPas encore d'évaluation
- NMAT Review 2018 Module - BiologyDocument34 pagesNMAT Review 2018 Module - BiologyRaf Lin DrawsPas encore d'évaluation
- GeneticsDocument55 pagesGeneticsEl Cruz100% (1)
- Week 6 Experiment Answer Sheet ROOTDocument8 pagesWeek 6 Experiment Answer Sheet ROOTOksana Kristina Root0% (1)
- Mendelism: Basic Principles of InheritanceDocument42 pagesMendelism: Basic Principles of InheritanceNicole Ongbit ManogPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurofibromatosis 1Document10 pagesNeurofibromatosis 1Minelle Sanchez InsoPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGY 2 (Pedigree Analysis) A4Document7 pagesBIOLOGY 2 (Pedigree Analysis) A4Mark Lorence CuevasPas encore d'évaluation
- Julianne Mercolita - Activity 9 Gen 2021Document4 pagesJulianne Mercolita - Activity 9 Gen 2021Julianne MercolitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Heredity CDPDocument7 pagesHeredity CDPRituraj ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics TerminologyDocument7 pagesGenetics TerminologyBHADRAPas encore d'évaluation