Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ORA000002 CDMA Communication Flow (NSS) ISSUE1.3
Transféré par
Matthew Johnson0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues58 pagesUpon completion of this course, you will be able to: Understand the basic flows of CDMA Understand the information name Understand the meaning of important parameters Improve the capabilities of problem analysis and fault location according to the flows.
Description originale:
Titre original
ORA000002 CDMA Communication Flow(NSS)ISSUE1.3.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentUpon completion of this course, you will be able to: Understand the basic flows of CDMA Understand the information name Understand the meaning of important parameters Improve the capabilities of problem analysis and fault location according to the flows.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues58 pagesORA000002 CDMA Communication Flow (NSS) ISSUE1.3
Transféré par
Matthew JohnsonUpon completion of this course, you will be able to: Understand the basic flows of CDMA Understand the information name Understand the meaning of important parameters Improve the capabilities of problem analysis and fault location according to the flows.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 58
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
All rights reserved
www.huawei.com
Internal
ORA000002 CDMA
Communication
flows( NSS)
ISSUE 1.3
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 2
Upon completion of this course, you will be able to:
Understand the basic flows of CDMA
Understand the information name
Understand the meaning of important parameters
Improve the capabilities of problem analysis and fault
location according to the flows
Memorize the abbreviation of messages .
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 3
Chapter 1 Brief introduction of CDMA Flows
Chapter 2 Communication flows of CDMA
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 4
Brief introduction of CDMA flows
Registration flows
Authentication flows
Calling flows
Handoff flows
Supplementary service flows
Short message flows
Basic CDMA flows
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 5
Brief introduction of CDMA flows
Mobile phone power on/off: location updating flows and authentication flows
Mobile phone calling: calling flows and authentication flows
Migration in the conversation: handoff flows and authentication flows
Mobile phone hooks up : calling flows
Short message: short message flows and authentication flows
Supplementary service: supplementary service flows and authentication
flows
The flows that the main services may involved in are as follows:
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 6
Chapter 1 Brief introduction of CDMA Flows
Chapter 2 Communication flows of CDMA
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 7
Chapter 2 Communication flows of CDMA
2.1 Location registration flows
2.2 Authentication flows
2.3 Calling flows
2.4 Handoff flows
2.5 Supplementary service flows
2.6 Short message flows
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 8
Location Registration flow( involve VLR and HLR)
LOCATION UPDATE REQ: Location Update Request
REGNOT : Register Notification
LOCATION UPDATE ACCEPT: Location update Accept
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 9
Location Registration flow ( Cross VLR)
LOCATION UPDATE REQ: Location Update Request
REGNOT : Register Notification
REGCANC: Register Cancellation
LOC ACP: Location update Accept
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 10
Location Registration flow for Switch off
LOCATION UPDATE REQ: Location Update Request
MSINACT: MS inactive
LOCATION UPDATE ACCETP: location update accept
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 11
Questions
Why not all the location registrations are sent to
HLR?
What is the meaning of MSCID in the location
registration message, and what is the function ?
Why does the switch off message need to be
registered ?
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 12
Answers
Question 1: Not all the requests of location registrations are sent to HLR.
If the subscribers data has already existed in VLR and the subscriber is
activated, the registration is processed by VLR. Otherwise the
registration requests are sent to HLR, and processed by HLR.
Question 2: MSCID is the identification of MSC mainly including
SID( System Identification) and SWNO( Switch No.). It uniquely
identifies one switch entity, and is used to determine whether the MS is
roaming.
Question 3: Switch off registration are mainly used to inform HLR that
the subscriber has already powered off. If other subscribers call it,
system can send the access refuse directly to the calling party according
to the subscribers status in HLR.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 13
Chapter 2 Communication flows of CDMA
2.1 Location registration flows
2.2 Authentication flows
2.3 Calling flows
2.4 Handoff flows
2.5 Supplementary service flows
2.6 Short message flows
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 14
The Parameters in Authentication
Parameters involved in authentication: RAND, RANDC, ESN, MIN,
SSD
Parameters involved in SSD updating: A_KEY, RANDSSD, ESN,
RANDBS, RANDU
Random number involved in authentication: RAND, RANDC,
RANDSSD, RANDBS, RANDU
Authentication results in authentication: AUTHR, AUTHBS,
AUTHU
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 15
Generation of Authentication Parameters
Authentication Parameters generated by HLRRANDSSD
RANDU (When SSD is not shared )
Authentication Parameters generated by MSC/VLRRAND
RANDU (When SSD is shared )
Authentication Parameters generated by BSCRAND
Authentication Parameters generated by MSRANDBSRANDC
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 16
The Parameters in Authentication
SSD Algorism:
RNADSSD
56bits
ESN
32bits
SSD Algorism
SSD_A SSD_B
64 bits 64 bits
A_Key
64bits
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 17
The Parameters in Authentication
CAVE (Cellular Authentication and Voice Encryption)
RNAD_CHALLENGE
32 bits
ESN
32 bits
CAVE
AUTHR/AUTHU/AUTHBS
18 bits
AUTH_DATA
24 bits
SSD
64 bits
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 18
Authentication flow when SSD is not shared
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 19
Authentication flow when SSD is shared
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 20
SSD Update when SSD is not shared
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 21
SSD Update when SSD is shared
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 22
Questions
What is the meaning of SSD_sharing?
How does the SSD_sharing influence the authentication flows?
Why is the SSD update flow introduced?
Describe the SSD update flow when SSD is not shared.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 23
Answers
Question 1: SSD_sharing means that the SSD is stored in VLR.
Question 2 : whether the SSD is shared determines where the
authentication is done. If SSD is shared, authentication is able to be
done at the VLR, else this work is done at the AC.
Question 3: The introduction of SSD update flows is mainly for the
protection of invalid authentication when SSD is stolen.
Question 4: Please refers to slide introduced before.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 24
Chapter 2 Communication flows of CDMA
2.1 Location registration flows
2.2 Authentication flows
2.3 Calling flows
2.4 Handoff flows
2.5 Supplementary service flows
2.6 Short message flows
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 25
MS calls MS ( in local MSC)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 26
MS calls MS ( cross MSC)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 27
MS calls PSTN
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 28
PSTN calls MS
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 29
Questions
What is the difference between the local call and
inter-office call?
Please describe the flows triggered when the MS
registered in Beijing makes a call in Shenzheng.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 30
Answers
Question 1: There are two essential differences between
Intra-office mobile calling and Inter-office mobile calling: one is
that whether the location request message carry the TLDN or
not, local office assigns the TLDN in intra-office calling flows,
the called office assigns the TLDN in inter-office calling flows;
the other is that whether the signals route outgoing according
as the TLDN.
Question 2: Location Register flow, Authentication flow,
Calling flow
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 31
Chapter 2 Communication flows of CDMA
2.1 Location registration flows
2.2 Authentication flows
2.3 Calling flows
2.4 Handoff flows
2.5 Supplementary service flows
2.6 Short message flows
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 32
HandOff flow on A interface in one BSC
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 33
HandOff flow on A interface between BSCs
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 34
Forward HandOff
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 35
Backward HandOff
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 36
HandOff to Third Party
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 37
Questions
What is the difference between Forward HandOff
and Backward HandOff?
When does the third parties handoff happen?
What is the main function of FACDIR
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 38
Answers
Question 1: the Forward Handoff is that MS handoff from the serving
MSC to a new target MSC; and the Backward HandOff is that MS
handoff from the serving MSC to the primary controlling MSC.
Question 2: Whether HandOff to Third Party happens depends on the
startup standard value of Third Party HandOff and handoff depth
together, when the current handoff times, viz. the handoff depth equal to
the startup standard value of Third Party Handoff, the MS will handoff to
the third party.
Question 3: FACDIR is used to set up inter_office handoff circuits,
which is MAP circuit.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 39
Chapter 2 Communication flows of CDMA
2.1 Location registration flows
2.2 Authentication flows
2.3 Calling flows
2.4 Handoff flows
2.5 Supplementary service flows
2.6 Short message flows
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 40
FEATURE SERVICE
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 41
Call Forwarding Unconditional( CFU)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 42
Call Forwarding Busy( CFB)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 43
Call Forwarding No Answer ( CFNA)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 44
Call Forwarding Default( CFD)
Note:
In the following cases, the call does not be connected to the serving MSC when the CFD
is subscribed.
1. Do-not-Disturb Service has been activated
2. MS has not registered
3. MS has been deactivated
4. Dont activate calling transfer
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 45
Conference Call(CC)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 46
Message Waiting Notification(MWN)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 47
Questions
What is the priority of 4 types of call forwarding?
What is the difference between CFNA and CFB ?
In Conference Call flow, if a user exits, will the
conference call terminated?
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 48
Answers
Question 1: CFU>CFB>CFNA>CFD
Question 2: There are two differences between CFNA and CFB :
CFNA has gotten a TLDN and set up a call to the
called office, while CFB dose not get any TLDN from
the HLR to which the called MS belongs;
Forwarded-to number of CFNA is retrieved by the
calling MSC from the HLR to which the called MS
belongs, while in CFB, it is sent by the HLR to which
the called MS belongs directly.
Question 3: In CC, if the main controlling user exits, the
conference call terminates; but if a common user exits, other
users continue the conference call.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 49
Chapter 2 Communication flows of CDMA
2.1 Location registration flows
2.2 Authentication flows
2.3 Calling flows
2.4 Handoff flows
2.5 Supplementary service flows
2.6 Short message flows
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 50
MS Sends Short Message in Access Channel
BSS MSC MC
ADDS Transfer
SMSDPP
smsdpp(ack)
ADDS Page
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 51
MS Sends Short Message in Service Channel
BSS MSC MC
ADDSDeliver
SMSDPP
smsdpp(ack)
ADDSDeliver Ack
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 52
MS Receives Short Message in Paging Channel
BSS HLR MC MSC
SMSREQ
smsreq
SMSDPP
ADDSPage
ADDSPageAck
smsdpp
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 53
MS Receives Short Message in Service Channel
BSS
HLR
MC
MSC
SMSREQ
smsreq
SMSDPP
ADDS Deliver
ADDS Deliver Ack
smsdpp
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 54
Questions
1. If the subscriber receives an extremely short
message during conversation, which channel is
used to deliver the Short message?
2. What is the influence of the length of the short
message when a MS originates a short message?
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 55
Answers
Question 1: ADDS Deliver Message.
Question 2: The length of the short message may
affect the A_interface message . If the length of the
short message is less than a certain threshold, it is
sent from the access channel using the ADDS
transfer message; if the length is more than a
certain threshold, it is sent from the service channel,
using the ADDS deliver message.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 56
Review
This section mainly describes common flows of
CDMA including: location registration,
authentication, calling, handoff, supplementary
services and short message.
Describing the important messages and
parameters in each flow.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Page 57
References
IOS40 Interface A Specifications
ANSI41D Interface C/D
Specifications
ANSI-664 Supplementary Service
www.huawei.com
Thank You
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- 2013 CAPP Lifting PracticesDocument64 pages2013 CAPP Lifting PracticesAhmed KhaledPas encore d'évaluation
- MSS SP-92-2012Document25 pagesMSS SP-92-2012Hadi VeysePas encore d'évaluation
- Frick CompressorDocument66 pagesFrick Compressoronkarrathee67% (3)
- PLANT Commissioning PDFDocument35 pagesPLANT Commissioning PDFhenybamPas encore d'évaluation
- FDocument42 pagesFSteawardPas encore d'évaluation
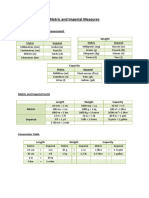
- Metric and Imperial Measures: Most Common Units of Measurement Length WeightDocument2 pagesMetric and Imperial Measures: Most Common Units of Measurement Length WeightDeepakPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1 Identifying Network Architectures and EquipmentsDocument17 pagesLab 1 Identifying Network Architectures and EquipmentsFarisHaikalPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Tutorial Cisco Packet TracerDocument3 pagesManual Tutorial Cisco Packet TracerHamami InkaZo0% (1)
- KEPServer Enterprise v5.30 and v4.50 Release NotesDocument8 pagesKEPServer Enterprise v5.30 and v4.50 Release NotesZaaCk AranoPas encore d'évaluation
- DB2DevCLIVol2 Db2l2e953Document533 pagesDB2DevCLIVol2 Db2l2e953Charles MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative - Steam Exhaust Fan R1Document6 pagesComparative - Steam Exhaust Fan R1Dhirender KapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- BS0-1 (1981) PDFDocument12 pagesBS0-1 (1981) PDFKobe ZhuPas encore d'évaluation
- 3400-CP-009-PB02 01082015 1.5 MbpsDocument18 pages3400-CP-009-PB02 01082015 1.5 MbpsHarry Rony Alvarez HuancaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grason-Stadler GSI Tympstar Manual V1 Rev CDocument285 pagesGrason-Stadler GSI Tympstar Manual V1 Rev CHabiB-BoyGuysPas encore d'évaluation
- 443 840 840C 850 880 Computer Link Descr of Message FramesDocument140 pages443 840 840C 850 880 Computer Link Descr of Message FramesООО ЛантисPas encore d'évaluation
- RCI510 Setup PDFDocument10 pagesRCI510 Setup PDFDaniel Castillo PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota 4runner BrochureDocument18 pagesToyota 4runner BrochureMeor Amri100% (1)
- ISO 9001 - HutchinsonDocument2 pagesISO 9001 - HutchinsonUğurPas encore d'évaluation
- TrendNXT Wintel L1 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTrendNXT Wintel L1 QuestionsboxofyuviPas encore d'évaluation
- Prall TesterDocument3 pagesPrall TesterCooper TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Kathy SUMP BUDDY - Performance For Smaller System Cooling TowersDocument12 pagesKathy SUMP BUDDY - Performance For Smaller System Cooling TowersaavianiacPas encore d'évaluation
- Upfs11 p4 Uefi Gop AmdDocument30 pagesUpfs11 p4 Uefi Gop Amd張佑民Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wm4096deng270510 PDFDocument32 pagesWm4096deng270510 PDFFabián MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Manual (CDJ 350 W CDJ 350) Eng EspDocument80 pagesOperating Manual (CDJ 350 W CDJ 350) Eng EspcaimanaterPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelly CompDocument529 pagesKelly Compzerophick1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Cce Mpv-d5h8Document52 pagesManual Cce Mpv-d5h8marcelobolPas encore d'évaluation
- Description Description Description: 600-1G161-BASE-100Document42 pagesDescription Description Description: 600-1G161-BASE-100alejandro martin cerdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rman TutorialDocument19 pagesRman Tutorialsymphonic82Pas encore d'évaluation
- TCP Cong ControlDocument34 pagesTCP Cong ControlrockerptitPas encore d'évaluation
- Blackmagic 3G-SDI Arduino Shield PDFDocument262 pagesBlackmagic 3G-SDI Arduino Shield PDFTariq AngelPas encore d'évaluation