Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Local Area Networks
Transféré par
budiabuy0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
178 vues19 pagesLAN is a high-speed data network that covers a relatively small geographic area. It typically connects workstations, personal computers, printers, servers, and other devices. LAN Topologies define the manner in which network devices are organized.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentLAN is a high-speed data network that covers a relatively small geographic area. It typically connects workstations, personal computers, printers, servers, and other devices. LAN Topologies define the manner in which network devices are organized.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
178 vues19 pagesLocal Area Networks
Transféré par
budiabuyLAN is a high-speed data network that covers a relatively small geographic area. It typically connects workstations, personal computers, printers, servers, and other devices. LAN Topologies define the manner in which network devices are organized.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 19
Local Area Networks
LAN-Local Area Network
A LAN is a high-speed data network that covers a relatively
small geographic area. It typically connects workstations,
personal computers, printers, servers, and other devices.
LANs offer computer users many advantages, including shared
access to devices and applications, file exchange between
connected users, and communication between users via
electronic mail and other applications.
LAN standard specify cabling and signaling at physical and data
link layer
OSI Model
LAN Data Link Layer
LLC sublayer
Provide versatile service to network layer
Participate in encapsulating
MAC sublayer
Provide access method to physical media
Define MAC address
LAN Media-Access Methods
two main ways:
carrier sense multiple access collision detect (CSMA/CD)
token passing
CSMA/CD (Ethernet), when a device has data to send, it first
listens to see if any other device is currently using the network.
If not, it starts sending its data. After finishing its transmission, it
listens again to see if a collision occurred. A collision occurs
when two devices send data simultaneously. When a collision
happens, each device waits a random length of time before
resending its data.
LAN Media-Access Methods
token-passing ( Token Ring and FDDI), a special
network packet called a token is passed around the
network from device to device. When a device has data
to send, it must wait until it has the token and then sends
its data. When the data transmission is complete, the
token is released so that other devices may use the
network media
LAN Transmission Methods
LAN data transmissions fall into three classifications:
unicast, multicast, and broadcast.
In a unicast transmission, a single packet is sent from the
source to a destination on a network.
A multicast transmission consists of a single data packet
that is copied and sent to a specific subset of nodes on the
network.
A broadcast transmission consists of a single data packet
that is copied and sent to all nodes on the network.
LAN Topologies
LAN topologies define the manner in which network
devices are organized.
Four common LAN topologies exist:
bus
ring
Star
Mesh
These topologies are logical architectures, but the
actual devices need not be physically organized in
these configurations.
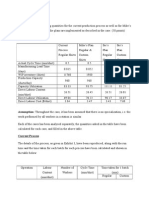
Pro’s and Con’s
Topologies Advantages Disadvantages
Bus Easy to connect a computer or Entire network shuts down if
peripheral to a linear bus. there is a break in the main
Requires less cable length than a cable.
star topology. Terminators are required at
both ends of the backbone cable.
Difficult to identify the problem
Star Easy to install and wire. More cable hub
No disruptions +/- devices. Concentrator fails, nodes
Easy to detect faults and to remove attached are disabled.
parts. Concentrator Expensive
Ring Easy to install and wire Concentrator expensive
Less cable if physical topology also Concentrator fails, nodes
ring attached are disabled
Considerations When
Choosing a Topology
Money. A linear bus network may be the least expensive way
to install a network; you do not have to purchase
concentrators.
Length of cable needed. The linear bus network uses shorter
lengths of cable.
Future growth. With a star topology, expanding a network is
easily done by adding another concentrator.
Cable type. The most common cable in schools is unshielded
twisted pair, which is most often used with star topologies.
LAN Devices
Devices commonly used in LANs include
Repeaters/hubs
Bridges and LAN switches
Routers
Layer 1 devices: repeater/hub
Hub amplify signal
Hub propagate signal
through the networks
Hub do not require filtering
Hub do not require path
determination or switching
Used as network
concentration point
Layer 2 devices: NIC and Switch
NIC is consider layer 2 devices because
carries unique MAC address
Bridge are more intelligent than hub, it can
forward or drop packet based on MAC
addressing information
Bridge keep local traffic locally
Bridge create more collision domain
Bridge maintain MAC address table
Switch: Multiport bridge
Layer 3 devices: Router and
Multilayer Switches
Router perform
addressing based on
IP address
Multilayer switch in
addition to switch
using MAC
addressing also use
Layer 3 (IP
addressing).
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Neal Peres Da CostaDocument507 pagesNeal Peres Da CostaNoMoPoMo576100% (1)
- L5CoachMentorReflectiveLog TemplateDocument9 pagesL5CoachMentorReflectiveLog TemplateHadusssPas encore d'évaluation
- Pertemuan 8Document29 pagesPertemuan 8budiabuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pertemuan 7Document17 pagesPertemuan 7budiabuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5: Applications of Discrete Probability DistributionsDocument19 pagesLecture 5: Applications of Discrete Probability DistributionsbudiabuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Binomial Distribution and Continuous DistributionsDocument13 pagesBinomial Distribution and Continuous DistributionsbudiabuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pertemuan 3Document21 pagesPertemuan 3budiabuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2: Graphical Techniques and Numerical MeasuresDocument40 pagesLecture 2: Graphical Techniques and Numerical MeasuresbudiabuyPas encore d'évaluation
- C57.12.29 Pad-Mounted Equipment-Enclosure Integrity For Coastal EnvironmentsDocument26 pagesC57.12.29 Pad-Mounted Equipment-Enclosure Integrity For Coastal EnvironmentsSureshKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 Principles of Cooperative ConversationDocument9 pagesLesson 2 Principles of Cooperative Conversationdelilah o balladPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 8 - A Closer Look 2Document3 pagesUnit 8 - A Closer Look 2Trần Linh TâmPas encore d'évaluation
- 33392-01 Finegayan Water Tank KORANDO PDFDocument3 pages33392-01 Finegayan Water Tank KORANDO PDFShady RainPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelley DavisDocument3 pagesKelley Davisapi-626701108Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mbeya University of Science and TecnologyDocument8 pagesMbeya University of Science and TecnologyVuluwa GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Lifestyle Mentor. Sally & SusieDocument2 pagesLifestyle Mentor. Sally & SusieLIYAN SHENPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Heat BoilerDocument7 pagesWaste Heat Boilerabdul karimPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide For H Nmr-60 MHZ Anasazi Analysis: Preparation of SampleDocument7 pagesGuide For H Nmr-60 MHZ Anasazi Analysis: Preparation of Sampleconker4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Restrictions AOP30 enDocument1 pageRestrictions AOP30 enRicardo RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Coding Prony 'S Method in MATLAB and Applying It To Biomedical Signal FilteringDocument14 pagesCoding Prony 'S Method in MATLAB and Applying It To Biomedical Signal FilteringBahar UğurdoğanPas encore d'évaluation
- A.O: Against Order: Desktop Hard Disk Laptop Hard Disk Scsi Hard Disk Adaptec Cards External Hard DiskDocument28 pagesA.O: Against Order: Desktop Hard Disk Laptop Hard Disk Scsi Hard Disk Adaptec Cards External Hard DiskArul brittoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM 111 Assignment 2024Document3 pagesCHEM 111 Assignment 2024Ben Noah EuroPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment #3 Venturi Meter: Home Unquantized ProjectsDocument7 pagesExperiment #3 Venturi Meter: Home Unquantized ProjectsEddy KimathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Review Is The Backbone of ResearchDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Is The Backbone of Researchafmzweybsyajeq100% (1)
- Transient Thermal Conduction ExampleDocument14 pagesTransient Thermal Conduction ExampleDevendra BangarPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Plate Count Agar and R2A Medium For Enumeration of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Natural Mineral WaterDocument4 pagesComparison of Plate Count Agar and R2A Medium For Enumeration of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Natural Mineral WaterSurendar KesavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Symptoms and DiseasesDocument8 pagesSymptoms and Diseaseschristy maePas encore d'évaluation
- Briefing Evaluation: Yes / No High / Low Yes / No High / Low Good / Inferior Yes / NoDocument4 pagesBriefing Evaluation: Yes / No High / Low Yes / No High / Low Good / Inferior Yes / NoAmmarah AzharPas encore d'évaluation
- Galaxy A8 User ManualDocument193 pagesGalaxy A8 User ManualHüseyin ACARPas encore d'évaluation
- Executive Shirt CompanyDocument6 pagesExecutive Shirt CompanyPramod kPas encore d'évaluation
- Prestressed Concrete ProblemDocument9 pagesPrestressed Concrete ProblemPrantik Adhar SamantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Curriculum For Secondary Schools: Mathematics Form 2Document139 pagesIntegrated Curriculum For Secondary Schools: Mathematics Form 2Izawaty IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- Storage Tank Design Calculation - Api 650: Close Floating RoofDocument32 pagesStorage Tank Design Calculation - Api 650: Close Floating RoofhgagPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Civil Engineering and Planning Civil Engineering Department Petra Christian UniversityDocument59 pagesFaculty of Civil Engineering and Planning Civil Engineering Department Petra Christian Universitykenny liePas encore d'évaluation
- Project Scheduling: Marinella A. LosaDocument12 pagesProject Scheduling: Marinella A. LosaMarinella LosaPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Gyramatic-Operator Manual V2-4-1Document30 pages01 Gyramatic-Operator Manual V2-4-1gytoman100% (2)
- (Dust of Snow) & 2 (Fire and Ice) - NotesDocument3 pages(Dust of Snow) & 2 (Fire and Ice) - NotesdakshPas encore d'évaluation