Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cleveland Clinic Skugor Oral Antidiabetic Medications
Transféré par
tmdgus0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
21 vues76 pagesCleveland Clinic Skugor Oral Antidiabetic
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentCleveland Clinic Skugor Oral Antidiabetic
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
21 vues76 pagesCleveland Clinic Skugor Oral Antidiabetic Medications
Transféré par
tmdgusCleveland Clinic Skugor Oral Antidiabetic
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 76
Oral Anti-diabetic Medications
Mario Skugor, MD FACE
Endocrine and Metabolic Institute
Cleveland Clinic
Insulin
secretaguages
Insulin
sensitizers
Incretin
based
therapies
Alpha-
glucosidase
inhibitors
CNS acting
Long acting
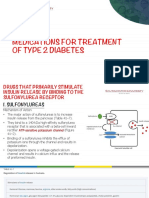
Sulphonylureas
Liver
Metformin
PPD-4
inhibitors
Acarbose Bromocriptine
Short acting
Meglitinides
Muscle and Fat
Thiazolidinediones
Miglitol
Other
Bile acid sequestrants
Orlistat
CLASSES OF ORAL ANTIDIABETIC MEDICATIONS
In development
Dual PPAR gamma agonists
SGLT-2 antagonists
Insulin
secretaguages
Insulin
sensitizers
Incretin
based
therapies
Alpha-
glucosidase
inhibitors
CNS acting
Long acting
Sulphonylureas
Liver
Metformin
PPD-4
inhibitors
Acarbose Bromocriptine
Short acting
Meglitinides
Muscle and Fat
Thiazolidinediones
Miglitol
Other
Bile acid sequestrants
Orlistat
CLASSES OF ORAL ANTIDIABETIC MEDICATIONS
In development
Dual PPAR gamma agonists
SGLT-2 antagonists
Canagliflozin just approved.
METFORMIN
French lilac used in folk
medicine for centuries.
Synthesized in 1920s
In 1950 Metformin was used to
treat influenca and noted to
lower blood glucose to
physiologic levels.
METFORMIN
In 1957 first clinical trial of diabetes treatment was
published in France
Approved in 1958 in UK, 1972 in Canada and in
1995 in US.
METFORMIN
Suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis through
activation AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK).
Improves glucose uptake in muscle and fat.
Causes weight loss in some individuals.
Improves menstrual cycle and fertility in PCOS
May improve NASH.
May reduce risk of range of different carcinomas
METFORMIN
Comes in 500, 850 and 1000 mg pills.
Extended release pills are available (but more
expensive)
Usual dose is 1000 mg twice a day.
Main side effects is abdominal cramping and diarrhea
Metformin extended release is better tolerated by
some patients
Even mild renal failure (Cr>1.4 in males and >1.5 in
females) is contraindication for use
Metformin Bottom line
Clearly the first line.
Cheap
Improves physiology
Has other benefits.
Unfortunately, significant proportion of patients has
contraindications or cannot tolerate it.
SULPHONYLUREAS
Marcel Janbon and co-workers discovered
hypoglycemic effect of sulfonylurea in 1942.
They were studying sulfonamide antibiotics and
discovered that the compound sulfonylurea
induced hypoglycemia in animals
Sulphonylureas
First sulfonylurea for treatment of DM introduced in 1955.
General structure:
Sulphonylurea
First generation Binds to the proteins in the blood.
Tolbutamide
Chlorpropamide
Tolazamide
Acetohexamide
Carbutamide
Sulphonylurea
Second generation Not bound to serum proteins.
Glipizide
Glyburide (glibenclamide)
Gliclazide
Glibornuride
Gliquidone
Glisoxepide
Glyclopyramide
Sulphonylurea
Third generation
Glimepiride
SUFONYLUREAS
Sulfonylurea
Advantages
Fast acting
Once a day dosing
Gliclazide may be particularly beneficial
Disadvantages
Risk of hypoglycemia
Weight gain
Possible problems with ischemic preconditioning
Glicilizide
Inhibits platelet aggregation
Associated with lower mortality from malignant
neoplasms.
Improves repair of DNA damage caused by oxidative
stress in tissue cultures.
Sulfonylureas Bottom line
Fast acting
Older ones are cheap
Do not improve physiology
Hypoglycemia is significant risk
Require strict regime of diet
Meglitinides
Nategelinde
Repaglinide
Act on same potassium channel as sulfonylurea but
bind to different part of the molecule.
Short acting taken 0-30 min before meal.
Risk of hypoglycemia is small
Meglitinides Bottom line
Useful in small number of patients for relatively short
period of time.
Allow for some flexibility in timing of the meals.
TZD-s actually Pioglitazone
The proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-)
and to a lesser extent PPAR- agonist in the muscle,
adipose tissue, and the liver.
Pioglitazone reduces insulin resistance in the liver and
peripheral tissues.
Pioglitazone decreases the level of triglycerides and
increases HDL without changing LDL and total
cholesterol.
Pioglitazone - 15 - 30 - 45 mg pills
Peripheral edema is main side effect.
More hospitalizations for CHF in studies with all
TZD-s
Effect is maintained when combined with metformin
and incretin based therapies.
Pioglitazone
Thiazolidinediones and bladder cancer.
Colmers IN, et al. CMAJ 2012I:10.1503
TZD-s and fracture risk
Toulis KA, et al. CMAJ, 2009, 180 (8) 841-842
TZD-s and fractures
TZD-s are associated with fractures in females over 50
years of age.
In men risk is increased if TZD-s are used with loop
diuretic
Bilik D, et al. JCEM. 2010 (10) 1210.
Bottom line on Pioglitazone
Benefits are still higher than risks.
There is some evidence that lower dose is not
associated with risk of bladder cancer.
However at this time Metformin and PPD-4 inhibitors
are clearly ahead of Pioglitazone as choices for
treatment.
Incretins
Gut-derived hormones, secreted in response to nutrient ingestion,
that potentiate insulin secretion from islet cells in a glucose-
dependent fashion, and lower glucagon secretion from islet cells
Two predominant incretins:
Glucagon-like peptide1 (GLP-1)
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP)
(also known as gastric inhibitory peptide)
Incretin effect is impaired in type 2 diabetes
Known as GLP-1 deficiency
Incretin system and DPP-4 physiologic action
Native GLP-1 is rapidly degraded by DPP-IV
Human ileum,
GLP-1 producing
L-cells
Capillaries,
DPP-IV (Di-Peptidyl
Peptidase-IV)
Adapted from: Hansen et al. Endocrinology 1999;140:53565363.
Double immunohistochemical staining for DPP-IV (red)
and GLP-1 (green) in the human ileum
Slide Source:
Lipids Online Slide Library
www.lipidsonline.org
Glucagon-Like Peptide1 Normalizes
Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Patients
with Type 2 Diabetes
Nauck MA et al. Acta Diabetol. 1998;35:117-129.
Time (h)
P
l
a
s
m
a
g
l
u
c
o
s
e
(
m
g
/
d
l
)
0
300
100
50
150
200
250
2 3 4 1 0 1
Infusion
GLP-1 [7-36 amide]
1.2 pmol/kg/min
Placebo
Liquid meal
0
300
100
50
150
200
250
2 3 4 1 0 1
Infusion
GLP-1 [7-36 amide]
1.2 pmol/kg/min
Placebo
Liquid meal
P
l
a
s
m
a
g
l
u
c
o
s
e
(
m
g
/
d
l
)
Healthy subjects T2DM patients
Time (h)
Slide Source:
Lipids Online Slide Library
www.lipidsonline.org
Continuous Glucagon-Like Peptide1
Infusion Reduces Appetite over 6 Weeks
All data for patients treated with glucagon-like peptide1 (n = 10).
No changes in these parameters were observed in the saline group.
0
100
200
300
400
500
Mean (SE)
AUC for
Visual
Analogue
Score (mm)
vs Time (h)
Time (wk)
6 1 0
Zander M et al. Lancet. 2002;359:824830.
Time (wk)
*Prospective food intake
*Hunger
*Satiety
*Fullness
*p<.05
Slide Source:
Lipids Online Slide Library
www.lipidsonline.org
Glycemic Control with GLP-1 Receptor
Agonists in Head-to-Head Clinical Trials
*Significant difference
vs comparator GLP-1
receptor agonist
1
Buse JB et al. Lancet. 2009;374:39-47 |
2
Drucker DJ et al. Lancet. 2008;372:1240-1250 |
3
Blevins T, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:1301-1310 |
4
Buse JB et al. Presented at
47th EASD Annual Meeting, Lisbon, Portugal, 14 September 2011.
Trial:
Size (N):
Study length (weeks):
LEAD-6
1
464
26
DURATION-1
2
303
30
DURATION-5
3
254
24
DURATION-6
4
912
26
-0.8
-1.5
-0.9
-1.3
-1.1
-1.9
-1.6
-1.5
-2.0
-1.5
-1.0
-0.5
0.0
A
1
C
C
h
a
n
g
e
(
%
)
*
*
*
EXN BID
LIRA
EXN QW
Slide Source:
Lipids Online Slide Library
www.lipidsonline.org
Comparison of Incretin Modulators
GLP-1 Analogues DPP-4 Inhibitors
Administration route Injection Oral
GLP-1 Sustained Meal-related
Effect on A1C
Effects on body weight
Side effects
Nausea,
Rare: pancreatitis
(Well tolerated)
Nasopharyngitis, skin rashes,
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
-cell function
GLP-1=glucagon-like peptide1; DDP-4=dipeptidyl peptidase4
DPP 4 inhibitors
Sitagliptin
Saxagliptin
Linagliptoin
Alogliptin
Vildagliptin marketed in EU
More in development
Gemigliptin
DPP4 inhibitors
All taken once a day
Sitaglipitin 100 mg daily
50 mg if Cr 1.7-3.0 for men and 1.5-2.5 for women
25 mg in ESRD
Saxagliptin 5 mg per day
2.5 mg in renal impairment
2.5 if taken with cytochrome P450 inhibitors
(ketoconazole)
Linagliptin 5 mg daily
Sitagliptin - example
DPP-4 inhibitors
Side effects are minimal
Acute pancreatitis is seen
Linagliptin 15.2/10.000 patients
Placebo 3.7/10,000 patients
Saxaglipin No data but some postmarketing cases
are reported
Sitagliptin There is 88 cases in 2.5 years in
postmarketing reporting.
DDP-4 inhibitors Bottom Line
Very well tolerated
Improve physiology
Expensive
So far, no serious adverse effects with long term use.
No increased risk of pancreatic caner.
Alpha-Glucosidase inhibitors
Acarbose - 25, 50 or 100 mg tablets
Miglitol - 25, 50 and 100 mg tablets
They block intestinal enzyme breaking sugars to
monosaccharides.
This slows down and blocks some of carbohydrate
absorption.
Postprandial peak is diminshed and Hba1c
improves.
Alpha-Glucosidase inhibitors
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
Taken with each meal.
Side effects are flatulence and diarrhea
This can be diminished with low carb, high fiber diet
and slow titration of the dose form 25 mg to 100 mg
per day.
Very low risk of hypoglycemia
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors Bottom line
Very useful if tolerated
Relatively cheap.
Bromocriptine
Bromocriptine mesylate given within 2 hours of waking
up in the morning improves glycemic control by
unknown mechanism.
It is given in escalating dose starting with 0.8 mg and
increasing by 0.8 mg every week to maximal tolerated
dose.
Therapeutic dose is between 1.6 to 4.8 mg per day.
Very low risk of hypoglycemia.
About 25% of patients experience some nausea.
Bromocriptine
Bromocriptine
Bromocriptine Bottom line
Useful if tolerated.
Still expensive
Many patients are discuoraged by need to use 2-6 pills
at once (In US only 0.8 mg pill is available).
Bile acid sequestrants
Colesevelam
Cholestyramine
Colestid
Mechanism is unknown
In db/db mice these drugs increase metabolic
utilization of glucose in peripheral tissues which
corelates with decrease in muscle long chain
acylcarnitine content
Meissner M, et al. PLOS 2011 (6)11 e24564.
Coleselavam
Cholestyramine
Colesevalam
Colesevalam
Orlistat
Effect on weight
Effects on Hba1c
Chao EC, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2010;9:551-559.
Targeting the Kidney
Chao, EC & Henry RR. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2010;9:551-559.
Renal Glucose Transport
Rationale for SGLT2 Inhibitors
SGLT2 is a low-affinity, high capacity glucose transporter
located in the proximal tubule and is responsible for 90% of
glucose reabsorption
Mutation in SGLT2 transporter linked to hereditary renal
glycosuria, a relatively benign condition in humans
Selective SGLT2 inhibitors have a novel & unique mechanism of
action reducing blood glucose levels by increasing renal
excretion of glucose
Decreased glycemia will decrease glucose toxicity leading to
further improvements in glucose control
Selective SGLT2 inhibition, would also cause urine loss of the
calories from glucose, potentially leading to weight loss
Brooks AM, Thacker SM. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;42(7):1286-1293.
Canagliflozin
*P.001 vs. placebo calculated using LS means Rosenstock J, et al. Abstract 77-OR. ADA 2010.
Metformin + Canagliflozin Dose-Ranging Study
Mean Baseline
A1C (%)
7.71 8.01 7.81 7.57 7.70 7.71 7.62
*
*
*
*
*
*
Changes from Baseline in Body Weight
in Phase 3 Dapagliflozin Studies
Placebo Dapa 2.5mg Dapa 5mg Dapa 10mg
Wilding JPH, et al. Abstract 78-OR. ADA 2010; Strojek K, et al. Abstract 870. EASD 2010;
Ferrannini E, et al. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(10):2217-2224; Bailey CJ, et al. Lancet. 2010;375(9733):2223-2233.
Canagliflozin Trials
Symptomatic genital infections in 3-8%
canagliflozin arms
2% placebo
2% SITA
Urinary tract infections in 3-9% canagliflozin arms
6% placebo
2% SITA
Hypoglycemia in 0-6% canagliflozin arms
2% placebo
5% SITA
Rosenstock J, et al. Abstract 77-OR. ADA 2010.
Treatment and cancer risk
metformin
sulphonylurea
metformin + sulpha
insulin
No treatment
Treatment and colorectal cancer risk
metformin
sulphonylurea
metformin + sulpha
insulin
Treatment and pancreatic cancer risk
metformin
sulphonylurea
metformin + sulpha
insulin
ADOPT and RECORD Trials
ADOPT and RECORD Trials
METFORMIN
METFORMIN
Are all sulphonylureas the same?
Retrospective cohort study
Glibenclamide treated N-378
Gliclizide treated N-190
5 year follow up
Cancer mortality higher for
glibenclamide after
adjustments for age and sex,
BMI, metformin and insulin
treatment- HR 3.56 (1.1-11.9)
Are all sulphonylureas the same?
Matched case-control study
195 diabetic patients with incident malignancy
195 matched diabetic patients with no malignancy
Matched for sex, age, BMI, duration of diabetes, Hba1c,
smoking and alcohol abuse
Exposure to antidiabetic drugs over last 10 years was
analyzed.
Are all sulphonylureas the same?
Possible mechanism
New Classes Presently in Development
Long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonists
Ranolazine
11 Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase (HSD)- 1 inhibitors
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase inhibitors
Glucokinase activators
G protein-coupled Receptor (GPR)- 40 & -119 agonists
Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase (PTB)- 1b inhibitors
Camitine- Palmitoyltransferase (CPT)- 1 inhibitors
Acetyl COA Carboxylase (ACC)- 1 & -2 inhibitors
Glucagon receptor antagonists
Salicylate derivatives
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Treatments For Diabetes MellitusDocument21 pagesTreatments For Diabetes MellitusValeria OboroceanuPas encore d'évaluation
- JanubDocument65 pagesJanubRoel PalmairaPas encore d'évaluation
- Effi Cacy and Safety of Sitagliptin in The Treatment of Type 2 DiabetesDocument10 pagesEffi Cacy and Safety of Sitagliptin in The Treatment of Type 2 DiabetesAnjeli KhairunnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin and Antidiabetic Drugs: BSC Nursing Online and Offline Lecture SeriesDocument27 pagesInsulin and Antidiabetic Drugs: BSC Nursing Online and Offline Lecture SeriesSayan ChatterjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Novel Targets in DMDocument60 pagesNovel Targets in DMP meruguPas encore d'évaluation
- DMDocument29 pagesDMFhatsa ObiPas encore d'évaluation
- IKAFI DPP4 InhibitorDocument25 pagesIKAFI DPP4 InhibitorYuliarni HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: Their Role in The Management of Type 2 DiabetesDocument3 pagesDipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: Their Role in The Management of Type 2 DiabetesRidha Surya NugrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- IKAFI - DPP4 InhibitorDocument25 pagesIKAFI - DPP4 InhibitorYuliarni Hasan100% (1)
- Endocrinology DM TherapeuticsDocument23 pagesEndocrinology DM Therapeuticsfire_n_icePas encore d'évaluation
- PM2020 I+EndocrinologyDocument676 pagesPM2020 I+Endocrinologychongyu888xiongPas encore d'évaluation
- Epperly - Whats New in Diabetes2007 5Document20 pagesEpperly - Whats New in Diabetes2007 5Andy F MonroePas encore d'évaluation
- SEMAGLUTIDEDocument27 pagesSEMAGLUTIDEcalliburn03Pas encore d'évaluation
- Terapi DMDocument65 pagesTerapi DMditaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus: Salient Features of Type 1 Am D Type 2 DMDocument20 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Salient Features of Type 1 Am D Type 2 DMPriyanka Karnik100% (1)
- Pancreatic Hormones Antidiabetic Drugs Part 2Document24 pagesPancreatic Hormones Antidiabetic Drugs Part 2jenet soleilPas encore d'évaluation
- Linagliptin - Farmacology, Efficacy and SafetyDocument7 pagesLinagliptin - Farmacology, Efficacy and SafetyMisaelDominguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument61 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionAmir HamzahPas encore d'évaluation
- 08&09 Oral Hypoglycemics-Level 11Document48 pages08&09 Oral Hypoglycemics-Level 11Usman Ali AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 Diabetes Mellitus 2021Document39 pagesLecture 7 Diabetes Mellitus 2021Ahmed ShakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution of Gliptins Over The Last 5 Years: Apurba Kumar MukherjeeDocument6 pagesEvolution of Gliptins Over The Last 5 Years: Apurba Kumar MukherjeeHoàng Hải PhạmPas encore d'évaluation
- Zmeili 2014 IMDocument40 pagesZmeili 2014 IMscribdPas encore d'évaluation
- Endo Pharma ElhDocument14 pagesEndo Pharma Elhodiodi57Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 - Update Article New Oral Antidiabetic AgentsDocument7 pages02 - Update Article New Oral Antidiabetic AgentsMuhammad Lutfi Al AyubiPas encore d'évaluation
- British Journal of Diabetes & Vascular Disease-2013-Day-2-6Document6 pagesBritish Journal of Diabetes & Vascular Disease-2013-Day-2-6JrYounoezMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs in Type 2 DMDocument18 pagesDrugs in Type 2 DMhussain AltaherPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Antidiabetic Drugs Pharmacy-IIDocument69 pagesUnit 1 Antidiabetic Drugs Pharmacy-IIAsad MirajPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of Diabetes MellitusDocument31 pagesTreatment of Diabetes MellitusIrfan IdealistPas encore d'évaluation
- DR - Mohammed Qasim 2017-2018 4 GradeDocument60 pagesDR - Mohammed Qasim 2017-2018 4 GradeFarah Bashar Al-RawachyPas encore d'évaluation
- Aronson, JK. Sulonylurea. Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs (Sixteenth Edition)Document19 pagesAronson, JK. Sulonylurea. Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs (Sixteenth Edition)SupriPas encore d'évaluation
- Thiazolidinediones (NCBI) : Go ToDocument5 pagesThiazolidinediones (NCBI) : Go ToPatrick CommettantPas encore d'évaluation
- DiabetesAlgorithm Stanford2018Document7 pagesDiabetesAlgorithm Stanford2018Rogelio MoscosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes LinagliptinaDocument7 pagesDiabetes LinagliptinaFatimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus in The US:: PrevalenceDocument48 pagesDiabetes Mellitus in The US:: PrevalenceokibreazyPas encore d'évaluation
- Incretin PharmDocument3 pagesIncretin PharmSlim SaaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of Diabetes MellitusDocument25 pagesTreatment of Diabetes MellitusPurnima ChoudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Therapy in Diabetes: Dr. Joe George MD, DNB, DM (Endocrinology) Department of Endocrinology, KEM Hospital, MumbaiDocument44 pagesDrug Therapy in Diabetes: Dr. Joe George MD, DNB, DM (Endocrinology) Department of Endocrinology, KEM Hospital, Mumbaijoe georgePas encore d'évaluation
- AntacidsDocument2 pagesAntacidsMa Corazon MelecioPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Management of Diabetes MellitusDocument36 pagesDrug Management of Diabetes MellitusHassan.shehri100% (15)
- 4 Oral Hypoglycaemic DrugsDocument10 pages4 Oral Hypoglycaemic DrugsNashat SaadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Management of Diabetes Type IIDocument34 pagesOral Management of Diabetes Type IIYasser Gebril100% (1)
- Available Online Through: Glucagon Like Peptide - 1: A New Era in Treatment of Type-2 Diabetes MellitusDocument8 pagesAvailable Online Through: Glucagon Like Peptide - 1: A New Era in Treatment of Type-2 Diabetes MellitusRidha Surya NugrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors For The Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument12 pagesDipeptidyl Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors For The Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes MellitusAdi PrayogaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacokinetics and Clinical Implications of Semaglutide: A New Glucagon-Like Peptide (GLP) - 1 Receptor AgonistDocument10 pagesPharmacokinetics and Clinical Implications of Semaglutide: A New Glucagon-Like Peptide (GLP) - 1 Receptor AgonistNguyễn PhúcPas encore d'évaluation
- DM IshipDocument42 pagesDM IshipAriani Putri Devanti PuputPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs That Affect The Endocrine SystemDocument75 pagesDrugs That Affect The Endocrine SystemTadela MengashaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: DM Section: 4 Group NamesDocument8 pagesTopic: DM Section: 4 Group NamesTurkish DizilerPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 Diabetes - Type 2 DiabetesDocument34 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Type 1 Diabetes - Type 2 DiabetesDrsarfaraz SiddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- ANTI-DIABETIC AGENTS (OHAs)Document42 pagesANTI-DIABETIC AGENTS (OHAs)Prajwal Rao KPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology of Metabolic Drugs: Nurlaili SusantiDocument58 pagesPharmacology of Metabolic Drugs: Nurlaili Susantimillennia zulfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology of Metabolic Drugs: Nurlaili SusantiDocument58 pagesPharmacology of Metabolic Drugs: Nurlaili Susantimillennia zulfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus.Document42 pagesDiabetes Mellitus.betablockers100% (1)
- Optimizing The Care of Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Using Incretin-Based Therapy: Focus On GLP-1 Receptor AgonistsDocument12 pagesOptimizing The Care of Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Using Incretin-Based Therapy: Focus On GLP-1 Receptor AgonistsRidha Surya NugrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Incretin Mimetics and EnhancersDocument3 pagesIncretin Mimetics and EnhancersRoger CPas encore d'évaluation
- BPJS DMDocument28 pagesBPJS DMAdhi TjahyadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nsaid & DislipidemiaDocument17 pagesNsaid & DislipidemiayoloswegxxxPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety and Efficacy of Linagliptin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients With Common Renal and Cardiovascular Risk FactorsDocument11 pagesSafety and Efficacy of Linagliptin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients With Common Renal and Cardiovascular Risk FactorsmichaelwillsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes Mellitus: Dr. Ave Olivia Rahman, Msc. Bagian Farmakologi Fkik UnjaDocument42 pagesPharmacotherapy of Diabetes Mellitus: Dr. Ave Olivia Rahman, Msc. Bagian Farmakologi Fkik UnjaEya Prepti SerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Update On Diabetes Treatment - 2018Document33 pagesUpdate On Diabetes Treatment - 2018Nanda SalmasPas encore d'évaluation
- KAPS Ques - July 2022Document2 pagesKAPS Ques - July 2022majid tariq100% (1)
- Pemba Has AnDocument15 pagesPemba Has AnYuyun PujiartiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anesthesiology Quick Reference (Adult) : Intubating MaintenanceDocument2 pagesAnesthesiology Quick Reference (Adult) : Intubating Maintenanceanestesi unpadPas encore d'évaluation
- Pricelist Februari 2023abDocument13 pagesPricelist Februari 2023abIka WahyuningsihPas encore d'évaluation
- Kapect CompoundDocument1 pageKapect Compoundmahgad100% (1)
- Ats, TT, Tig: Anti Tetanus Serum, Tetanus Toxoid, Tetanus Immuno-GlobulinDocument15 pagesAts, TT, Tig: Anti Tetanus Serum, Tetanus Toxoid, Tetanus Immuno-Globulinjisoo100% (2)
- (Dala M Rupi AH) Loka Si: Sem Ua: Sam Pai Tang Gal 25 Mei 2022Document20 pages(Dala M Rupi AH) Loka Si: Sem Ua: Sam Pai Tang Gal 25 Mei 2022Henry BudiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelompok 1Document14 pagesKelompok 1Aurent WidjanarkoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharma QuestionerDocument38 pagesPharma Questionerjohn100% (2)
- Chemotherapy of Protozoal InfectionsDocument34 pagesChemotherapy of Protozoal InfectionsSri RamPas encore d'évaluation
- TIVA Clinical Application FRCADocument4 pagesTIVA Clinical Application FRCAAmay SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- TamsulosinDocument27 pagesTamsulosinAnna WidiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug SheetDocument3 pagesDrug Sheetavause2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Meglitinide Analogues Are Classified As Insulin Secretagogues and Have Actions andDocument6 pagesMeglitinide Analogues Are Classified As Insulin Secretagogues and Have Actions andRifqoh Aulia AlthofunnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ashton Manual English PDFDocument58 pagesAshton Manual English PDFMalissa Bowen100% (2)
- NNF 2ndDocument235 pagesNNF 2ndRuDy RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Coumadin ConsultationDocument5 pagesCoumadin ConsultationLara KlaitPas encore d'évaluation
- Nebulizer TherapyDocument10 pagesNebulizer TherapyjerinthomasrajanPas encore d'évaluation
- SertralineDocument3 pagesSertralineFrenzy TaherPas encore d'évaluation
- DepressantsDocument6 pagesDepressantsArvinjohn GacutanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study FormatDocument13 pagesDrug Study FormatMa'rose Briones100% (1)
- TUGAS ANALISA ABC-icaDocument93 pagesTUGAS ANALISA ABC-icaMuhammad SultoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl Lourenz DeysolongPas encore d'évaluation
- DIURETICSDocument40 pagesDIURETICSNiña Jean Tormis AldabaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Different Types of COVIDDocument5 pagesThe Different Types of COVIDBach Hua HuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Government of Canada Report On Pricing of Crestor (Rosuvastatin)Document2 pagesGovernment of Canada Report On Pricing of Crestor (Rosuvastatin)jennabushPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Drugs Questions Part IDocument110 pagesCardiac Drugs Questions Part ISanaz Niksefat100% (2)
- Pharma - M1L1 - Rational Drug PrescribingDocument6 pagesPharma - M1L1 - Rational Drug PrescribingEric Meynard SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Brief Review On Clinical TrialsDocument23 pagesBrief Review On Clinical TrialssallurajPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)