Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
O & M of Sub-Station Equipment: Narender Kumar Me Mba Mie
Transféré par
waleedalzaidiTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
O & M of Sub-Station Equipment: Narender Kumar Me Mba Mie
Transféré par
waleedalzaidiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
O & M OF SUB-STATION
EQUIPMENT
NARENDER KUMAR
ME MBA MIE
SUB STATION
LOCATION WHERE A GROUP OF ELECTRICAL
EQUIPMENT IS CONCENTRATED FOR
TRANSFORMATION OF ELECTRICAL POWER
FROM ONE VOLTAGE LEVEL TO OTHER OR
FROM ONE FORM TO ANOTHER LIKE AC TO
DC ETC.
CLASSIFICATION OF SUB STATIONS
LT DISTRIBUTION SUB-STATION p & p
Caters to the consumers of 440V and 230V rating,
by means of 3 phase, 4 wire system.
HT / PRIMARY DISTRIBUTION SUB-STATION
CATERS TO 11 KV, 33 KV & 132 KV LOADS
TRANSMISSION SUB STATION
400/220,22/132,132/33 KV PRIMARY
TRANSMISSION SUB STATION
GENERATION SUB STATIONS.
INDOOR/OUTDOOR SUB STATIONS.
OUTDOOR SUB-STATION Vs INDOOR SUB-STATIONS
Minimal constructional works.
Less quantity of building materials.
Installation cost of switchgear is low.
Reduced possibility of faults due to enhanced space between
equipments.
Minimum erection time.
Fault location easier due to enhanced visibility.
Provision for extension can be provided.
While these are positive points in favor of outdoor sub-stations, there are
a few negative points.
Require large area
Accumulation of dust and dirt and pollutants over insulators and
contacts.
Operational difficulties during rains.
Selection criteria
A Number of factors are to be considered while
designing a sub-station, the most important of
which are :
Capacity (based on load studies)
Type whether outdoor or indoor
Method of control
Number of outgoing/incoming feeders
Reliability
Safety
Flexibility
Simplicity
Space availability
Cost
VARIOUS EQUIPMENT IN THE
SUB-STATION
1.BUS BAYS
2.LAS
3.AB SWITCHES/ISOLATORS
4.CIRCUIT BREAKERS
5.INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS
6.POWER TRANSFORMERS
7.AUXILIARY SUPPLIES
8.EARTHING
9.STRUCTURE
10.CONTROL PANELS, AC/DC PANELS
11.ANNUNCIATION SYSTEM AND PANELS
12.BATTERY BANK
13.BATTERY CHARGERS
14.STATION TRANSFORMERS
15.RELAYS
16.CAPACITOR BANKS
17.CONTROL ROOM
18.MARSHALLING PANEL
19.SCADA PANELS
20.LIGHTING/YARD LIGHTING
21.COMMUNICATION EQUIPMENT
22.FENCING
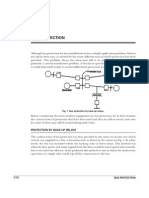
BUS BAY
The location of entry and exit points of the 3 phases of a circuit into/from
a Bus is called a Bus Bay.
The connection from the Bus to the Equipment is made of aluminum
stranded conductor or some cases, panther by means of a clamp, made of
Aluminum alloy, designed to hold the jumper according to its size.
The term Bus is used for three conductors that acts as a junction for
entry and exit of various circuits.
The conductors of the Bus are generally made of standard aluminum
conductors of size Panther/Dog, or of Copper/Aluminum pipe
40mm/80mm diameter.
Each 33 KV and 11 KV Bay is of dimension 4.7 meters and the length of
the Bus depends on the number of circuits to be accommodated.
LIGHTING ARRESTOR
A Protective equipment that is erected at the entry point of a line, this equipment
prevents a surge Voltage entering a sub-station and damaging the associated
equipments. Surge Voltages are created either due to lightning or switching
operations
LINE ISOLATOR/BUS ISOLATOR
Theses are the isolating switches that can be operated electrically or manually.
Mostly manual operation is the norm that is followed here. The isolators can be of
single break type or double break type and are designed based on the rated
current to be carried.
A Bus Isolator connects the bus to the equipment by means of jumpers
and clamps.
A line isolator connects the line to the equipment by similar means.
A line isolator has and extra fitting in the form an earth switch, that
connects the line to the earth.
CIRCUIT BREAKER
A Circuit Breaker interrupts the flow of current in a Circuit.
Interruptions are caused either in intentionally, in order to
isolate a system or the interruption is caused automatically
due to a fault.
Quenching of an arc that is generated at the time of a Circuit
opening is the primary function of a Circuit breaker.
Circuit Breakers can be divided on the basis of the quenching
medium that is used.
The mediums that are used are
High pressure air
SF6 gas
Transformer oil
Vacuum
In most of the 33KV Sub-stations, the vacuum type of
breakers are used, while SF6 gas breakers are used in EHT
System.
The air break circuit breakers and oil circuit breakers are
being phased out gradually owing to increasing repair and
maintenance costs.
The circuit breakers can also be divided based on the mechanism it
adopts.
The operating mechanism is an absolute necessity and an
integral part of a breaker, in view of the speed that is required to
open or close the contacts in a breaker.
The breakers can be divided again based on the operating
mechanism
Pneumatic type where compressed air under high pressure is used to
operate the contacts. The pressures used vary from design to design and
will be between 13 to 15 atmospheres.
Hydraulic breakers in which a hydraulic liquid by trade name Aero Shell is
used. This liquid is maintained at a pressure of 300 psi in order to operate
the contacts.
A spring charge mechanism in which the stored energy of a spring is used
to activate the moving contacts.
While all the three types of mechanisms are used in EHT sub-
stations, only spring charge mechanism is used in 33/11 KV sub-
stations.
CURRENT TRANSFORMERS
Current Transformers are equipments designed to transform the
current from a high value (Primary Current) to low value
(Secondary current).
The standards of low value that are in use are 1 Amp and
5 Amps called the secondary current.
The need for secondary current is to help in measurement of
primary current which is made possible by the linear
relationship between the primary and secondary circuits.
One other function of a CT is to help protecting the system and
equipments from high fault currents by isolating the faulty
section.
CTs are rated for different current ratings and are
manufactured as per specifications.
A Single CT can be used for connecting to any one of
3 different rated Currents and is called Available Ratio.
The single rated current to which it is connected is called
Connected Ratio or Adopted Ratio.
The purpose of this available ratio is to help alter the primary
connection from one rated current to another one, without
the need for changing the CT or disconnecting the Cables,
there by reducing the time to undertake the change.
A CT has one primary coil and a number of secondary coils
designed as per specifications and purpose.
The CTs are always connected in series
POTENTIAL TRANSFORMER : (P.T.)
A PTs role is same as that of a C.T.
It measures Voltage in a system
In addition to measurement, the P.T. secondary Voltage is also made use of
, for distance protection in EHT Systems.
P.T. supply is also utilized for measuring energy consumed or sent, that
facilities billing and energy audit,
The secondary Voltage in a potential transformer in Vogue is 110V, phase to
phase, irrespective of the primary voltage, like 400 KV, 220KV, 132KV, 33KV
& 11KV.
The P.T.s are generally connected in parallel.
For industrial consumers P.Ts and CTs are combined together to form a single
unit. This helps in sealing of the unit in order to avoid tampering
POWER TRANSFORMER
Power transformers are equipments that transform the power
at a given voltage to another
Power transformers consist of two windings primary and
secondary and are designed on the basis of specific
requirements and purpose.
The windings are placed in an insulating medium, i.e., the
transformer oil filled in a tank for the purpose.
The purpose of oil is to insulate and cool the windings, since
the windings of undergo a temperature rise while in service.
The transformers are provided with OLTCs (on load tap
changes) which are operated to raise of lower the voltages as
per requirement.
The capacity of a transformer is measured in terms of
KVA/MVA, and every transformer can only take load
commensurate with its capacity.
When load grows beyond the capacity of a single transformer,
additional transformer of similar capacity is provided, the
characteristics of the additional transformer should be similar to
that of the existing transformer to facilitate parallel operation.
The transformer is a costliest equipment in a sub-station and
hence a number of protective devices such as Temp, Alarm,
Bucholtz, and differential protection in addition to the overload
and earth fault relays.
These relays are set to isolate the transformer in the event of
an abnormal fault condition, which may harm the equipment if
not isolated.
The transformers upto 8.0 MVA capacity are provided with a group
control breaker on HV side and individual breakers on LV side. In a
few cases, group control breakers on HV side is dispensed with and
instead, a HG fuse is used on the HV side.
The life of a transformer depends on its conditions of operation,
over loaded transformers, transformers operating under high
temperatures tend to loose their life span.
Frequent faults on lines exerts additional pressures on the winding
of the transformers. Both electrical and mechanical forces come
into play.
The quality of the oil in a transformer also contributes to the life of
a transformer.
Transformer oil is hence tested once in 6 months for its Break
Down Voltage (BDV), which is a measure of the insulation value of
the oil.
Transformer oil is subjected to filtration in case of low BDV values
or once in a year.
In addition to these test the transformer oil is also subjected to
various other tests such as tan delta test, DGA test and acidity test
AUXILLIARY SUPPLY
A Sub-station requires supplies such as 440V & 230V AC supply
and 230V, 48V or 24V DC supply depending upon the DC
Voltage rating of auxiliaries to meet other types of loads which
operates under these voltages.
A.C. SUPPLY
AC Supply in a sub-station is used for spring charge motors,
OLTC motors, lighting circuits, charger supply etc.,.
AC auxiliary supply is availed from a distribution transformer
of 11 KV/440 V rating of adequate capacity.
The AC supply is distributed to various loads by means of a
AC Distribution board which is provided with a number of
outlets with independent fuse controls.
D.C.SUPPLY
DC Supply is required basically to isolate the faulty feeders from the
healthy system. This process is carried out by tripping the breaker
of a faulty circuit. The tripping is carried out by means of a DC
Supply, which is fed to the tripping coil in a breaker.
DC supply is generally obtained from a charger unit, which converts
AC supply to DC supply.
In addition to the charger unit, a back up source of DC supply is a
set of batteries which feed the DC loads as end when AC supply
fails for some reason or the other.
Maintenance of the uninterrupted DC supply is crucial for a sub-
station since a fault can occur at any movement and loss of DC
supply would be a LUXURY
1.structure
2.insulators
3.control panels
4.battery and batter charger
5.ac/dc panels
6.annunciation panels
7.station transformers
8.capacitor banks
9.relays.
OPERATION
Operation in a sub-station involves :
Supervision of equipments and their critical operating recommendations.
Measurement of electrical parameters.
Inspection and reporting.
Circuit isolation activities.
Reclosing functions for breakers after fault clearance.
Load transfer coordination.
Communication with feeding sub-station.
Load control
Voltage control
Batteryl voltage and specific gravity measurements and general check-up.
Issue of line clears.
MAINTENANCE :
A sub-station performance lies in its effective maintenance activities.
Effective maintenance in turn results in minimum interruption to the
consumers, and a low down time always results in increased revenue for the
utility.
One should aim at Maintaining the utility system equipment as close to brand
new condition as possible.
Complete all preventive and predictive maintenance work regularly on
scheduled basis without exceeding the point of the diminishing returns on
investment for the labor, tools & materials.
Maintenance activities are of two types
Preventive maintenance (PM)
Preventive maintenance is the scheduled inspection or servicing of equipment
at specific times frames as advised by the manufacturer, in order to retain the
functional capabilities of the unit that is serviced.
CORRECTIVE MAINTENANCE :
CM or Break down maintenance as is popularly called, is the
unscheduled repair of a failed equipment to restore its
functional capabilities. CM is generally found to be time
consuming and uneconomical in terms of operating cost. CM
is generally resorted to only when the equipment fails either
totally or partially.
The goal hence, shall be to develop a maintenance plan that
will offer reliability in function and at the same time fulfills the
budgetary goals.
CORRECTIVE OR BREAK DOWN MAINTENANCE
Consists of the actions taken to restore a failed system to
operational status.
The cost of corrective maintenance is substantially higher and
may result in short term/long term interruptions.
The C.M. needs to be performed at unpredicted intervals
since there is no advance intimation of a system component
failure.
The Three steps in which it is carried out are : -
Diagnosis of the problem
Repair & replacement of faulty component.
Rectification for a successful repair by checking its operation
GENERAL OBJECTIVES OF UTILITY MAINTENANCE :
Reduce utility and energy costs.
Control inventory and assets
Extend life of the equipment.
Increase productivity.
Improve maintenance responsiveness.
Improve facility appearance.
Reduce facility and personal liability risks.
Anticipate scheduled maintenance.
ELEMENTS OF A UTILITY MAINTENANCE PLAN :
The Plan Should, at the minimum, target the following goals :
Assess and minimise risks.
Ensure operational reliability.
Identify equipment included in the programme.
Ensure testing, inspection and maintenance of critical components.
Provide utility system plans and layouts to personnel operating the
system.
Investigate utility failures and identify necessary corrective actions.
Provide training and education to all personnel responsible for operation
and maintenance of the system.
Develop performance standards for personnel, equipment operation,
maintenance and repair.
Develop emergency procedures detailing the initial response to utility
failures.
There are quite a few modern technologies available to
develop maintenance program to meet individual
requirements such as :
Infra red thermography
Ultra sonic and vibration detection
Breaker Diagnostic maintenance
THANK YOU
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Electric CalDocument20 pagesElectric CalRisky RiyanshPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Substation Equipment and ProtectionDocument32 pagesStudy of Substation Equipment and ProtectionDeepak DhanpalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter6 PDFDocument38 pagesChapter6 PDFJaved LakanwalPas encore d'évaluation
- CEA GuidelineDocument25 pagesCEA GuidelinepussykhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 220 KV Sub-StationDocument17 pages220 KV Sub-StationJaat Pankaj BurraPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of KV Switch YardDocument35 pagesStudy of KV Switch YardRamana ParavastuPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Safety and Protection of Ehv Substation Including The Effects of Power System TransientsDocument62 pagesElectrical Safety and Protection of Ehv Substation Including The Effects of Power System TransientsMuhammad Asif IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- 400kv Sub - Station Final PPT by RAVIDocument14 pages400kv Sub - Station Final PPT by RAVIbanwala33% (3)
- Intoduction To 400Kv Switchyard: Single Line Diagram of 400kV SubstationDocument3 pagesIntoduction To 400Kv Switchyard: Single Line Diagram of 400kV SubstationPratik LahanePas encore d'évaluation
- Nuisance TrippingDocument6 pagesNuisance TrippingSeindahNyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Components: Citation NeededDocument2 pagesComponents: Citation Neededarundas16Pas encore d'évaluation
- EHV Substation DesignDocument10 pagesEHV Substation DesignVamsi ManojPas encore d'évaluation
- EDOC-Practical Considerations in Surge ProtectionDocument15 pagesEDOC-Practical Considerations in Surge ProtectionEl Comedor BenedictPas encore d'évaluation
- 132 GssDocument40 pages132 GssSonu Lovesforu100% (1)
- Power System Protection: Shoaib Ahmed Shaikh Lecturer (EE) Sukkur IBA UniversityDocument67 pagesPower System Protection: Shoaib Ahmed Shaikh Lecturer (EE) Sukkur IBA Universityfaizan100% (1)
- Minimum Clearance in SubstationDocument6 pagesMinimum Clearance in SubstationAjay YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Lighting Arrester - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument14 pagesLighting Arrester - Electrical Notes & Articlesbramhanand vermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Xpert UX - Presentation PDFDocument47 pagesPower Xpert UX - Presentation PDFpayolin77Pas encore d'évaluation
- KP PPTDocument22 pagesKP PPTSaurabh AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 220 KV 4400pF CVTDocument13 pages12 220 KV 4400pF CVTAshwin SevariaPas encore d'évaluation
- INDIAN ELECTRICITY RULES AND INDUSTRIAL SAFETY One Point E & C PDFDocument5 pagesINDIAN ELECTRICITY RULES AND INDUSTRIAL SAFETY One Point E & C PDFHarshal VaidyaPas encore d'évaluation
- MobileDocument31 pagesMobileTELECOM INJINIYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Ssasaaaxaaa11111......... Desingconstructionof33kv11kvlines 150329033645 Conversion Gate01Document167 pagesSsasaaaxaaa11111......... Desingconstructionof33kv11kvlines 150329033645 Conversion Gate01Sunil Singh100% (1)
- Relay Coordination Chapter3Document13 pagesRelay Coordination Chapter3Chân Gà NướngPas encore d'évaluation
- Midway Report: Project Semester: Study of 220KV Substation and SLDCDocument15 pagesMidway Report: Project Semester: Study of 220KV Substation and SLDCdamanpreet singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction of Electric Power Transmission and DistributionDocument100 pagesIntroduction of Electric Power Transmission and DistributionUmair BeygPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 FailureDocument80 pages1 FailureSunil SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- SwitchgearDocument23 pagesSwitchgearAnonymous Yq9ibs100% (1)
- What Is Insulation CoordinationDocument9 pagesWhat Is Insulation Coordinationnarik100% (1)
- CERC Guidelines On Capital Cost For Transmission SystemDocument34 pagesCERC Guidelines On Capital Cost For Transmission Systemrahulmangalca9997Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bus Coupler Specs PDFDocument11 pagesBus Coupler Specs PDFRaj ChavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Losses in Power Distribution and Transmission Lines 1Document7 pagesTotal Losses in Power Distribution and Transmission Lines 1mohannad87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Maintenance Procedure For Switchyard Equipment Volume-II (EHV CBS, CTs Etc)Document68 pagesMaintenance Procedure For Switchyard Equipment Volume-II (EHV CBS, CTs Etc)Anonymous axyNzhPas encore d'évaluation
- CEA ElecDocument31 pagesCEA Elecajith143420Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On SubstationDocument21 pagesNotes On SubstationamriscribdPas encore d'évaluation
- Busbar Differential ProtectionDocument19 pagesBusbar Differential ProtectionVijay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Substations - Volume V - CircuitDocument44 pagesSubstations - Volume V - CircuitAbdul Wadood GharsheenPas encore d'évaluation
- 132 33kv SubstationDocument44 pages132 33kv SubstationRatnesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison Between Vacuum and SF6 Circuit BreakerDocument9 pagesComparison Between Vacuum and SF6 Circuit BreakerMohammed MadiPas encore d'évaluation
- 420KV SF6 Circuit Breaker Operation and TestingDocument18 pages420KV SF6 Circuit Breaker Operation and TestingArlone ManaladPas encore d'évaluation
- Approved - 400kV LADocument22 pagesApproved - 400kV LAGuru MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Substation EquipmentsDocument4 pagesSubstation EquipmentsBilal JavedPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line ProtectionDocument111 pagesTransmission Line ProtectionPankaj100% (1)
- Lightning ArresterDocument25 pagesLightning ArresterMidhun Varghese100% (1)
- Radial Feeder Protection: by N.Sarveshwar G.Ravikumar Panimalar Institute of TechnologyDocument35 pagesRadial Feeder Protection: by N.Sarveshwar G.Ravikumar Panimalar Institute of TechnologySarveshwar Nethaji100% (1)
- 220 KV Switchyard EquipmentsDocument3 pages220 KV Switchyard EquipmentsRaj Kumar Prajapati100% (1)
- Transmission Line PrincipleDocument9 pagesTransmission Line PrincipletamsidePas encore d'évaluation
- Lightning Arrester: Working Principle, Types and DifferencesDocument7 pagesLightning Arrester: Working Principle, Types and DifferencesNasifPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Analysis: Merger TestDocument8 pagesPower System Analysis: Merger TestAnonymous mNQq7ojPas encore d'évaluation
- TR - Line ProtectionDocument55 pagesTR - Line Protectionavg100% (2)
- Design & Selection of Lightning ArresterDocument5 pagesDesign & Selection of Lightning ArresterAnkur_soni0% (1)
- Notes On Substation PDFDocument21 pagesNotes On Substation PDFKushal PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Substation Maintenance Inspection ListDocument327 pagesSubstation Maintenance Inspection Listjohndavsg8022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Substation 220kv 132kvDocument40 pagesProject On Substation 220kv 132kvindianapsterPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityD'EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityPas encore d'évaluation
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsD'EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsPas encore d'évaluation
- Power-system protection A Complete GuideD'EverandPower-system protection A Complete GuideÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- Submitted To, Name-Mr. Ankush Tandon Sir (Assistant Professor)Document15 pagesSubmitted To, Name-Mr. Ankush Tandon Sir (Assistant Professor)Himanshu Soni100% (1)
- Case Study: Srikalahasti 132 KV SubstationDocument34 pagesCase Study: Srikalahasti 132 KV SubstationwaleedalzaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Emerging Trends in Thermal Power Stations: K Sreerama MurthyDocument22 pagesEmerging Trends in Thermal Power Stations: K Sreerama MurthywaleedalzaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Earthing System - MaintenanceDocument53 pages2 Earthing System - MaintenancewaleedalzaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- الاستمارة الالكترونيةDocument1 pageالاستمارة الالكترونيةwaleedalzaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Procedure FireDocument28 pagesProcedure FireRichard D DuPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Puerto Rico at PonceDocument16 pagesUniversity of Puerto Rico at Ponceapi-583167359Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ds0h Ufaa68 ProposalDocument11 pagesDs0h Ufaa68 Proposaledward baskaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Congenital Flexural Deformity in CalfDocument6 pagesCongenital Flexural Deformity in CalfBibek SutradharPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhert - EoDocument2 pagesBhert - EoRose Mae LambanecioPas encore d'évaluation
- BMJ 40 13Document8 pagesBMJ 40 13Alvin JiwonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug-Nutrient Interaction in Prescriptions ForDocument7 pagesDrug-Nutrient Interaction in Prescriptions ForRafika DitaPas encore d'évaluation
- PMI Framework Processes PresentationDocument17 pagesPMI Framework Processes PresentationAakash BhatiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plica PDFDocument7 pagesPlica PDFIVAN VERGARAPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual PDFDocument68 pagesLab Manual PDFSantino AwetPas encore d'évaluation
- 6Document2 pages6Min Hsuan HsianPas encore d'évaluation
- "Next Friend" and "Guardian Ad Litem" - Difference BetweenDocument1 page"Next Friend" and "Guardian Ad Litem" - Difference BetweenTeh Hong Xhe100% (2)
- Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and EstersDocument11 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and EstersNATURE COMPUTERPas encore d'évaluation
- Organogram - Qa / QC: Srinivasan SrinivasanDocument4 pagesOrganogram - Qa / QC: Srinivasan SrinivasanGowtham VenkatPas encore d'évaluation
- GrowNote Faba South 3 Pre PlantingDocument22 pagesGrowNote Faba South 3 Pre PlantingDawitPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electrical Engineering NotesDocument25 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering NotesAnas AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Solo ParentsDocument1 pageSolo ParentsOZ CincoPas encore d'évaluation
- Latest Low NOx Combustion TechnologyDocument7 pagesLatest Low NOx Combustion Technology95113309Pas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Health Management: Mokhlis Al Adham Pharmacist, MPHDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Health Management: Mokhlis Al Adham Pharmacist, MPHYantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Management A Technicians Guide Staples TOCDocument5 pagesProject Management A Technicians Guide Staples TOCAnonymous NwnJNO0% (3)
- Sample SWMSDocument4 pagesSample SWMSJuma KavesuPas encore d'évaluation
- Royal British College IncDocument5 pagesRoyal British College IncLester MojadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Blueprint Huynh My Ky Duyen 2022 McDonald'sDocument2 pagesBlueprint Huynh My Ky Duyen 2022 McDonald'sHuỳnh Mỹ Kỳ DuyênPas encore d'évaluation
- DT 2107Document1 pageDT 2107Richard PeriyanayagamPas encore d'évaluation
- S ELITE Nina Authors Certain Ivey This Reproduce Western Material Management Gupta Names Do OntarioDocument15 pagesS ELITE Nina Authors Certain Ivey This Reproduce Western Material Management Gupta Names Do Ontariocarlos menaPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Cold ChainDocument22 pagesLaboratory Cold ChainEmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Refinería Kirkuk PDFDocument11 pagesRefinería Kirkuk PDFcesarinarragaPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily Staff Food Consumption Reports Sep-2019Document4 pagesDaily Staff Food Consumption Reports Sep-2019Manjit RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Keys: Science, Biology ReviewerDocument3 pagesAnswer Keys: Science, Biology ReviewerEnc TnddPas encore d'évaluation
- Employment Offer: 1. Employer InformationDocument2 pagesEmployment Offer: 1. Employer InformationnavidPas encore d'évaluation