Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 - Configuring A Network Operating System
Transféré par
000den0000 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
419 vues59 pagescbfc
Titre original
Chapter 2 - Configuring a Network Operating System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentcbfc
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
419 vues59 pagesChapter 2 - Configuring A Network Operating System
Transféré par
000den000cbfc
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 59
2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Confidential Presentation_ID 1
Chapter 2:
Configuring a Network
Operating System
Introduction to Networks
Presentation_ID 2 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Chapter 2
2.1 IOS Bootcamp
2.2 Getting Basic
2.3 Address Schemes
2.4 Summary
Presentation_ID 3 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
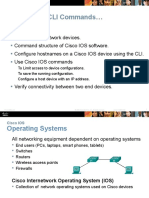
Chapter 2 - Objectives
Explain the purpose of Cisco IOS.
Explain how to access and navigate Cisco IOS to configure network
devices.
Describe the command structure of Cisco IOS software.
Configure hostnames on a Cisco IOS device using the CLI.
Use Cisco IOS commands to limit access to device configurations.
Use Cisco IOS commands to save the running configuration.
Explain how devices communicate across network media.
Configure a host device with an IP address.
Verify connectivity between two end devices.
2.0.1.1
Presentation_ID 4 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
2.0.1.2 Class Activity - It Is Just an Operating System
2.0.1.2
Presentation_ID 5 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Cisco IOS
Operating Systems
2.1.1.1
Presentation_ID 6 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Cisco IOS
Operating Systems
All networking equipment dependent on operating systems
End users (PCs, laptops, smart phones, tablets)
Switches
Routers
Wireless access points
Firewalls
Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS)
Collection of network operating systems used on Cisco devices
2.1.1.1
Presentation_ID 7 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Cisco IOS
Purpose of OS
PC operating systems (Windows 8 & OS X) perform technical
functions that enable
Use of a mouse
View output
Enter text
Switch or router IOS provides options to
Configure interfaces
Enable routing and switching functions
All networking devices come with a default IOS
Possible to upgrade the IOS version or feature set
2.1.1.2
Presentation_ID 8 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Cisco IOS
Location of the Cisco IOS
IOS stored in Flash
Non-volatile storage not lost when power is lost
Can be changed or overwritten as needed
Can be used to store multiple versions of IOS
IOS copied from flash to volatile RAM
Quantity of flash and RAM memory determines IOS that can be used
IOS stored on Flash
Configuration on Non
Volatile (NV) RAM
2.1.1.3
Presentation_ID 9 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Cisco IOS
IOS Functions
Major functions performed or enabled by Cisco routers and
switches include:
2.1.1.4
Know Bullets on
2.1.1.4
Presentation_ID 10 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Cisco IOS
Getting the IOS
2.1.1.5
Watch video
As you wish
Presentation_ID 11 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Accessing a Cisco IOS Device
Console Access Method
Most common methods to access the Command Line Interface
Console
Telnet or SSH
AUX port
2.1.2.1
Presentation_ID 12 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Accessing a Cisco IOS Device
Console Access Method
Console port
Device is accessible even if no networking services have been
configured (out-of-band)
Need a special console cable
Allows configuration commands to be entered
Should be configured with passwords to prevent unauthorized access
Device should be located in a secure room so console port can not
be easily accessed
2.1.2.1
Presentation_ID 13 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Accessing a Cisco IOS Device
Telnet, SSH, and AUX Access Methods
Telnet
Method for remotely accessing the CLI over a network
Require active networking services and one active interface that is
configured
Secure Shell (SSH)
Remote login similar to Telnet but utilizes more security
Stronger password authentication
Uses encryption when transporting data
Aux Port
Out-of-band connection
Uses telephone line
Can be used like console port
2.1.2.2
Presentation_ID 14 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Accessing a Cisco IOS Device
Terminal Emulation Programs
Software available for
connecting to a networking
device
PuTTY
Tera Term
SecureCRT
HyperTerminal
OS X Terminal
2.1.2.3
We use
HyperTerminal
Presentation_ID 15 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Accessing a Cisco IOS Device
2.1.2.4 Activity Accessing Devices
2.1.2.3
Do in class:2.1.2.4
Activity Accessing
Devices
Presentation_ID 16 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Navigating the IOS
Cisco IOS Modes of Operation
2.1.3.1
Talk about how the
command prompt
changes
Presentation_ID 17 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Navigating the IOS
Primary Modes
2.1.3.2
> - User mode
# - Privileged mode
Presentation_ID 18 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Navigating the IOS
Global Configuration Mode and Submodes
2.1.3.3
Class activity
Packet tracer with
2911 router
Presentation_ID 19 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Navigating the IOS
Navigating between IOS Modes
2.1.3.4
Presentation_ID 20 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Navigating the IOS
Navigating between IOS Modes (cont.)
2.1.3.5
Do buttons on 2.1.3.5
Presentation_ID 21 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Navigating the IOS
Video Demonstration - Navigating the IOS
2.1.3.6
Watch
Video
2.1.3.6
Class activity
Packet tracer with
2911 router
Presentation_ID 22 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
The Command Structure
IOS Command Structure
2.1.4.1
Do buttons on 2.1.4.1
Presentation_ID 23 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
The Command Structure
Cisco IOS Command Reference
To navigate to Ciscos Command Reference to find a particular
command:
1. Go to www.cisco.com
2. Click Support.
3. Click Networking Software (IOS & NX-OS).
4. Click 15.2M&T (for example).
5. Click Reference Guides.
6. Click Command References.
7. Click the particular technology that encompasses the command you are
referencing.
8. Click the link on the left that alphabetically matches the command you are
referencing.
9. Click the link for the command.
2.1.4.2
Presentation_ID 24 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
The Command Structure
Context Sensitive Help
2.1.4.3
You can question
mark your way
through a command!
Demo with Packet
tracer
Presentation_ID 25 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
The Command Structure
Command Syntax Check
Do the buttons
on 2.1.4.4
2.1.4.4
Presentation_ID 26 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
The Command Structure
Hot Keys and Shortcuts
Tab - Completes the remainder of a partially typed command or
keyword
Ctrl-R - Redisplays a line
Ctrl-A Moves cursor to the beginning of the line
Ctrl-Z - Exits configuration mode and returns to user EXEC
Down Arrow - Allows the user to scroll forward through former
commands
Up Arrow - Allows the user to scroll backward through former
commands
Ctrl-Shift-6 - Allows the user to interrupt an IOS process such
as ping or traceroute.
Ctrl-C - Aborts the current command and exits the configuration
mode
Work smarter
not harder
Learn the short
cut commands
2.1.4.5
Needed to
abort a
command in
progress.
Presentation_ID 27 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
The Command Structure
IOS Examination Commands
2.1.4.6
Presentation_ID 28 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
The Command Structure
The show version Command
Do the buttons
on 2.1.4.7
2.1.4.7
Know what
show version
shows you.
Presentation_ID 29 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
The Command Structure
2.1.4.8 Packet Tracer - Navigating the IOS
Do packet
Tracer 2.1.4.8
For a Grade
2.1.4.8
Presentation_ID 30 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
The Command Structure
2.1.4.9 Lab - Establishing a Console Session
Hands on lab
2.1.4.9
For a Grade
2.1.4.9
Presentation_ID 31 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Hostnames
Why the Switch
Lets focus on
Creating a two PC network connected via a switch
Setting a name for the switch
Limiting access to the device configuration
Configuring banner messages
Saving the configuration
2.2.1.1
Presentation_ID 32 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Hostnames
Device Names
Some guidelines for naming conventions are that names should:
Start with a letter
Contain no spaces
End with a letter or digit
Use only letters, digits, and dashes
Be less than 64 characters in length
Without names, network
devices are difficult to
identify for configuration
purposes.
2.2.1.2
Presentation_ID 33 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Hostnames
Hostnames
Hostnames allow
devices to be
identified by
network
administrators
over a network or
the Internet.
2.2.1.3
Presentation_ID 34 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Hostnames
Configuring Hostnames
2.2.1.4
Do CLI
practice on
2.2.1.4
Presentation_ID 35 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Limiting Access to Device Configurations
Securing Device Access
The passwords introduced here are:
Enable password - Limits access to the
privileged EXEC mode
Enable secret - Encrypted, limits access to
the privileged EXEC mode
Console password - Limits device access
using the console connection
VTY password - Limits device access over
Telnet
Note: In most of the labs in this course, we will be
using simple passwords such as cisco or class.
2.2.2.1
Know each
password type
Presentation_ID 36 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Limiting Access to Device Configurations
Securing Privileged EXEC Access
use the enable secret command, not the
older enable password command
enable secret provides greater security because
the password is encrypted
2.2.2.2
Presentation_ID 37 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Limiting Access to Device Configurations
Securing User EXEC Access
Console port must be secured
reduces the chance of unauthorized personnel physically
plugging a cable into the device and gaining device access
vty lines allow access to a Cisco device via Telnet
number of vty lines supported varies with the type of
device and the IOS version
2.2.2.3
Presentation_ID 38 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Limiting Access to Device Configurations
Encrypting Password Display
service password-
encryption
prevents
passwords from
showing up as
plain text when
viewing the
configuration
purpose of this
command is to
keep unauthorized
individuals from
viewing passwords
in the configuration
file
once applied,
removing the
encryption service
does not reverse
the encryption
2.2.2.4
Do CLI
exercise on
2.2.2.4
in class
Presentation_ID 39 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Limiting Access to Device Configurations
Banner Messages
important part of
the legal process
in the event that
someone is
prosecuted for
breaking into a
device
wording that
implies that a login
is "welcome" or
"invited" is not
appropriate
often used for
legal notification
because it is
displayed to all
connected
terminals
2.2.2.5
Presentation_ID 40 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Saving Configurations
Configuration Files
Switch# reload
System configuration has
been modified. Save?
[yes/no]: n
Proceed with reload?
[confirm]
Startup configuration is
removed by using
the erase startup-config
Switch# erase startup-config
On a switch you must
also issue the delete
vlan.dat
Switch# delete vlan.dat
Delete filename [vlan.dat]?
Delete flash:vlan.dat?
[confirm]
2.2.3.1
Copy running-config startup-config
Presentation_ID 41 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Saving Configurations
Capturing Text
2.2.3.2
Do buttons on
2.2.3.2
Presentation_ID 42 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Saving Configurations
2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
2.2.3.3
Do packet
Tracer on
2.2.3.3
For a lab
grade
Presentation_ID 43 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
2.3 Address Schemes
2.3.1.1
Presentation_ID 44 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Ports and Addresses
IP Addressing in the Large
Each end device on a
network must be
configured with an IP
address
Structure of an IPv4
address is called dotted
decimal
IP address displayed in
decimal notation, with
four decimal numbers
between 0 and 255
With the IP address, a
subnet mask is also
necessary
IP addresses can be
assigned to both
physical ports and virtual
interfaces
2.3.1.1
Presentation_ID 45 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Ports and Addresses
Interfaces and Ports
Network communications depend on end user device interfaces,
networking device interfaces, and the cables that connect them
Types of network media include twisted-pair copper cables, fiber-
optic cables, coaxial cables, or wireless
Different types of network media have different features and benefits
Ethernet is the most common local area network (LAN) technology
Ethernet ports are found on end user devices, switch devices, and
other networking devices
Cisco IOS switches have physical ports for devices to connect to, but
also have one or more switch virtual interfaces (SVIs - no physical
hardware on the device associated with it; created in software)
SVI provides a means to remotely manage a switch over a network
2.3.1.2
Presentation_ID 46 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Addressing Devices
Configuring a Switch Virtual Interface
IP address - together with subnet mask, uniquely identifies end device on
internetwork
Subnet mask - determines which part of a larger network is used by an IP
address
interface VLAN 1 - interface configuration mode
ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0 - configures the IP address and
subnet mask for the switch
no shutdown - administratively enables the interface
Switch still needs to have physical ports configured and VTY lines to enable
remote management
2.3.2.1
Do CLI exercise on 2.3.2.1
in class
Presentation_ID 47 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Addressing Devices
Manual IP Address Configuration for End Devices
2.3.2.2
What is this computers IP address?
What is a default Gateway?
What is DNS server?
Why 2 DNS servers?
Presentation_ID 48 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Addressing Devices
Automatic IP Address Configuration for End Devices
2.3.2.3
Understand what DHCP is!!!
Presentation_ID 49 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Addressing Devices
IP Address Conflicts
2.3.2.4
This is why we use DHCP instead of
manually setting IP addresses.
Presentation_ID 50 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Addressing Devices
2.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Implementing Basic
Connectivity
2.3.2.5
Do packet
Tracer 2.3.2.5
for a lab grade
Presentation_ID 51 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Verifying Connectivity
Test the Loopback Address on an End Device
2.3.3.1
Do buttons on
2.3.3.1
Do CLI activity
on button 2
Presentation_ID 52 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Verifying Connectivity
Testing the Interface Assignment
2.3.3.2
Do CLI activity
on 2.3.3.2
Presentation_ID 53 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Verifying Connectivity
Testing End-to-End Connectivity
2.3.3.3
Do CLI activity
on 2.3.3.3
Presentation_ID 54 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Verifying Connectivity
Lab 2.3.3.4 Building a Simple Network
Lab 2.3.3.5 Lab Configuring a Switch Management Address
2.3.3.4
Do Lab 2.3.3.4
as a lab grade
in class
Do Lab 2.3.3.5
as a lab grade
in class
Presentation_ID 55 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Configuring a Network Operating System
2.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge
2.4.1.2
Do Lab 2.4.1.2
for extra credit
on lab
Presentation_ID 56 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Configuring a Network Operating System
Chapter 2 Summary
Services provided by the Cisco IOS accessed using a command-line
interface (CLI)
accessed by either the console port, the AUX port, or through telnet
or SSH
can make configuration changes to Cisco IOS devices
a network technician must navigate through various hierarchical
modes of the IOS
Cisco IOS routers and switches support a similar operating system
Introduced the initial settings of a Cisco IOS switch device
setting a name
limiting access to the device configuration
configuring banner messages
saving the configuration
2.4.1.3
Presentation_ID 57 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Configuring a Network Operating System
Chapter 2 Summary
2.4.1.3
Presentation_ID 58 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Configuring a Network Operating System
Chapter 2 Summary
2.4.1.3
Presentation_ID 59 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- NB instructorPPT Chapter2 FinalDocument49 pagesNB instructorPPT Chapter2 FinalSergio MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring A Network Operating System: Introduction To NetworksDocument52 pagesConfiguring A Network Operating System: Introduction To NetworksEmaPermanaSariPas encore d'évaluation
- It Is Just An Operating System: Network BasicsDocument48 pagesIt Is Just An Operating System: Network BasicsEddy Chinchay LujanPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring A Network Operating System: Chapter 2 - ObjectivesDocument17 pagesConfiguring A Network Operating System: Chapter 2 - ObjectivesHamron Soo FunnPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring A Network Operating System: Introduction To NetworksDocument51 pagesConfiguring A Network Operating System: Introduction To NetworksDuy TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Itn PPT Chap2Document51 pagesItn PPT Chap2LENIN VLADIMIR MONTENEGRO DIAZPas encore d'évaluation
- NB InstructorPPT Chapter2Document48 pagesNB InstructorPPT Chapter2QuocDat NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- IOS Switch Router Configuration - Chapter 2Document43 pagesIOS Switch Router Configuration - Chapter 2munaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To CLI: Network BasicsDocument27 pagesIntroduction To CLI: Network BasicsgurkansengulPas encore d'évaluation
- RSE6 Instructor Materials Chapter5Document42 pagesRSE6 Instructor Materials Chapter5andi.savePas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 4 Hardening HardwareDocument74 pagesChap 4 Hardening HardwareMesincahaya Masa KagebunshinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5: Switch Configuration: Routing and Switching Essentials v6.0Document39 pagesChapter 5: Switch Configuration: Routing and Switching Essentials v6.0AbeyMulugetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Securing Network Devices: CCNA-SecurityDocument74 pagesSecuring Network Devices: CCNA-SecurityJules LoukouPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Cisco Ios Software: Ethernet LansDocument19 pagesOperating Cisco Ios Software: Ethernet LansKeepmoving NevergiveupPas encore d'évaluation
- ITN6 Instructor Materials Chapter2Document23 pagesITN6 Instructor Materials Chapter2abdirazakiman97Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Scaling NetworksDocument33 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Scaling NetworksNah MárquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Netacad Chapter 2Document60 pagesCisco Netacad Chapter 2Qww Ekha NoviyantyPas encore d'évaluation
- ITN6 Instructor Materials Chapter2Document20 pagesITN6 Instructor Materials Chapter2Jacky LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Instructor Materials Chapter 2: Configure A Network Operating SystemDocument20 pagesInstructor Materials Chapter 2: Configure A Network Operating SystemHoney ShinePas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Cisco Ios Software: Ethernet LansDocument19 pagesOperating Cisco Ios Software: Ethernet Lansธนวรรณ โภคาอนนต์Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introducing The Review Lab: Small Network ImplementationDocument8 pagesIntroducing The Review Lab: Small Network ImplementationHải BùiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - Routing and SwitchingDocument21 pagesChapter 2 - Routing and SwitchingDivesha RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring and Testing Your NetworkDocument56 pagesConfiguring and Testing Your NetworkCahaya PenyayangPas encore d'évaluation
- RS InstructorPPT Chapter2Document55 pagesRS InstructorPPT Chapter2Christine Jan Dela VegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter2 Port SecurityDocument41 pagesChapter2 Port SecurityNewly CarePas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 2 - Configure A Network Operating System 2.0.1 Welcome 2.0.1.1 Chapter 2: Configure A Network Operating SystemDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Configure A Network Operating System 2.0.1 Welcome 2.0.1.1 Chapter 2: Configure A Network Operating Systemcamys18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 - Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationDocument32 pagesModule 2 - Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationMark SandovalPas encore d'évaluation
- ITN - Module - 2 - 1Document16 pagesITN - Module - 2 - 1Tharra ZPas encore d'évaluation
- ITN Module 2Document48 pagesITN Module 2John LagmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 2Document57 pagesWeek 2Javeed AhamedPas encore d'évaluation
- © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument18 pages© 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedVo Ngoc HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 Operating SystemDocument42 pagesLesson 3 Operating SystemserialsoraPas encore d'évaluation
- ITN Module 2Document62 pagesITN Module 2Eian Jose V Quintanilla (GCC INSTRUCTOR)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 2 - Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationDocument60 pagesTopic 2 - Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationIqi IcePas encore d'évaluation
- Let2 WDocument46 pagesLet2 WGetnete degemuPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2: Basic Switch and End Device Configuration: Instructor MaterialsDocument62 pagesModule 2: Basic Switch and End Device Configuration: Instructor MaterialsFernandoAsin0% (1)
- Module 2: Basic Switch and End Device Configuration: Instructor MaterialsDocument62 pagesModule 2: Basic Switch and End Device Configuration: Instructor MaterialsZulham Akbar AlfarobiPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocument52 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPcsalinasviPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 2 - 3th Ed Web Chapter 02Document31 pagesCCNA 2 - 3th Ed Web Chapter 02clu5t3rPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Network Device ConfigurationDocument50 pagesBasic Network Device Configurationsolomon khaluhiPas encore d'évaluation
- NET102 Chapter2ConfigureaNetworkOperatingSystemDocument52 pagesNET102 Chapter2ConfigureaNetworkOperatingSystemsteven EstevanPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring A Network Operating SystemDocument34 pagesConfiguring A Network Operating SystemAmanuel GebrePas encore d'évaluation
- 02 - Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationDocument45 pages02 - Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationMichael Angelo BerjaPas encore d'évaluation
- ITN Module 2Document42 pagesITN Module 2ChinPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 - Introduction To IOS CLIDocument42 pages11 - Introduction To IOS CLIAungMonPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2: Basic Switch and End Device Configuration: Introductions To Networks v7.0 (ITN)Document59 pagesModule 2: Basic Switch and End Device Configuration: Introductions To Networks v7.0 (ITN)Mohsan MinhasPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul 04-Network Operating System PDFDocument16 pagesModul 04-Network Operating System PDFMartyn OlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Configure A Network Operating System: Introduction To Networks v5.1Document55 pagesConfigure A Network Operating System: Introduction To Networks v5.1EkaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Scaling NetworksDocument35 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Scaling NetworksphilPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 NotesDocument18 pagesUnit 2 NotesRajkumar DharmarajPas encore d'évaluation
- W2 Configure A Network Operating SystemFileDocument10 pagesW2 Configure A Network Operating SystemFileNaih イ ۦۦPas encore d'évaluation
- ITN Module 2Document44 pagesITN Module 2Paulo Alexandre Buinhas FerreiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationDocument41 pagesBasic Switch and End Device Configurationyoussef hossamPas encore d'évaluation
- RS InstructorPPT Chapter4 FinalDocument56 pagesRS InstructorPPT Chapter4 Finalajikmadnoh_92Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Exploration Switching Chapter 2Document29 pagesCCNA Exploration Switching Chapter 2GµårÐïåñPas encore d'évaluation
- CN - 2020 - 02 - Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationDocument52 pagesCN - 2020 - 02 - Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationBarbie Bea BacalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2: Basic Switch and End Device Configuration: Introductions To Networks v7.0 (ITN)Document46 pagesModule 2: Basic Switch and End Device Configuration: Introductions To Networks v7.0 (ITN)Hesham OmarPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA1-CH2-Basic ConfigurationDocument58 pagesCCNA1-CH2-Basic Configurationkaramn3matPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical-1 Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationDocument19 pagesPractical-1 Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationSam JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3D'EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle Banking Virtual Account Management Installation GuideDocument13 pagesOracle Banking Virtual Account Management Installation Guidebr0k3n.s0ul44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Phoenix Liveview BetaDocument299 pagesProgramming Phoenix Liveview BetarodrigoPas encore d'évaluation
- AWS Foundation Course - Exercises: Instructions To Strictly FollowDocument4 pagesAWS Foundation Course - Exercises: Instructions To Strictly FollowPrabhakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nokia Con Cable Driver Installation enDocument8 pagesNokia Con Cable Driver Installation enAshwinkumar PatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Embedded Lab 3 ReportDocument11 pagesEmbedded Lab 3 ReportMohd Amer100% (1)
- Eal Estate Project With Source CodeDocument2 pagesEal Estate Project With Source CodeRDGAC CSDepartmentPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacity Plan TemplateDocument12 pagesCapacity Plan TemplatevanessaPas encore d'évaluation
- Commerce UpDocument11 pagesCommerce UpKaraPas encore d'évaluation
- LCR 600 Manual SetupDocument68 pagesLCR 600 Manual SetupAgista FifthoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Scripting Languages Indx-MergedDocument33 pagesScripting Languages Indx-Mergedyasaswi sonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Client Server ModelDocument15 pagesClient Server ModelChachu-420Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compiler Lab ReportDocument30 pagesCompiler Lab Reportnishanmainali56Pas encore d'évaluation
- TCL 1 2015.00 LGDocument37 pagesTCL 1 2015.00 LGSandeepPas encore d'évaluation
- Nginx Security Hardening GuideDocument12 pagesNginx Security Hardening Guidescrib_nokPas encore d'évaluation
- Elmer TutorialsDocument96 pagesElmer TutorialsMartin CaicedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Thayyil Pepper Nursery in Kattappana, Idukki - Thayyil Pepper Nursery, Kattappana Phone Numbers & AddressDocument3 pagesThayyil Pepper Nursery in Kattappana, Idukki - Thayyil Pepper Nursery, Kattappana Phone Numbers & AddressAnonymous kewC5C30cPas encore d'évaluation
- Aashish Malik 057 Information Technology Management LabDocument52 pagesAashish Malik 057 Information Technology Management LabRajeev TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Distinguish Between Systems Programs and Application ProgramsDocument9 pagesDistinguish Between Systems Programs and Application Programsapi-2478715820% (1)
- Corel Keygen Kako Sa KodovimaDocument1 pageCorel Keygen Kako Sa KodovimaRadislav MilankovPas encore d'évaluation
- Laravel 5.4 CollectiveDocument12 pagesLaravel 5.4 CollectiveszchmausserPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Break EventsDocument46 pagesControl Break EventsriteshPas encore d'évaluation
- Modicon Quantum Processors - Unity Operating Systems Compatibility Rules 0Document6 pagesModicon Quantum Processors - Unity Operating Systems Compatibility Rules 0VladPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume Mohammedrafiqraja Senior Software Engineer 7yearsDocument5 pagesResume Mohammedrafiqraja Senior Software Engineer 7yearsmohammedrafiqraja1600% (1)
- Teneth ManualDocument43 pagesTeneth ManualFaizul Azman80% (5)
- Data Migration For S4HANA-v1.2Document54 pagesData Migration For S4HANA-v1.2abhi100% (1)
- SEM-5-CSE - Operating Systems Lab (PCC-CS592) VimDocument8 pagesSEM-5-CSE - Operating Systems Lab (PCC-CS592) VimArkapratim GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Latex/Source Code Listings: 1 Using The Listings PackageDocument6 pagesLatex/Source Code Listings: 1 Using The Listings PackageGetnet Demil Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 300 Microprocessor Project Using The Texas Instruments MSP 430F449PZ ControllerDocument40 pagesECE 300 Microprocessor Project Using The Texas Instruments MSP 430F449PZ ControllerSadik PimpalkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Agriculture Monitoring System With Automated Irrigation and Water Tank SystemDocument32 pagesAgriculture Monitoring System With Automated Irrigation and Water Tank SystemRekha RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- PPSC Competitive Exam For The Post of Programmer: Question Paper Along With Answer KeyDocument22 pagesPPSC Competitive Exam For The Post of Programmer: Question Paper Along With Answer Keysharath100% (1)