Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Abnormal ECG
Transféré par
devilbataCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Abnormal ECG
Transféré par
devilbataDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
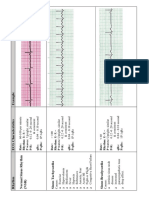
BASIC ABNORMAL ECG
BY TANYA TULLAO
INTERVALS/DURATION
P WAVE
When studying the P
wave, always look at I, II,
avF and V1
Normal:
How tall? 0.5-2.5 mm
How wide? 0.10 sec
P wave is upright in all
leads except sometimes it
is biphasic in V1
P WAVE
Look at leads I, II,
avF
Are there any P
waves too tall
(>2.5 mm)?
YES: Right Atrial
Enlargement (RAE)
P WAVE
Look at leads I, II,
avF
Are there any P
waves too wide
(>0.10 sec)? Any
bifid P waves?
YES: Left Atrial
Enlargement (LAE)
PR INTERVAL
Normal:
0.12-0.20 secs.
PR INTERVAL
Look at your
measurements
Is the PR interval
short (<0.12 sec)?
YES: Bypass of the
AV node
PR INTERVAL
Look at your
measurements
Is the PR interval
long (>0.20 sec)?
YES: First degree AV
Block
Q WAVE
Q wave is present when
the first QRS deflection is
downward
Observed in each lead
Are there any
pathological Q waves?
If:
> 2 small squares deep
> 25% of the height of the
following R wave
> 1 small square wide
YES: Infarction
Q WAVE
If:
Pathological Q wave
No ST segment
depression
Normal T wave
YES: Old Infarction/
Fibrosis/ Previous
documented MI
Where is the location?
Identify the leads.
Leads Location
I, avL High Lateral
II, III, avF Inferior
(right coronary artery)
V1, V2 Septal
V3, V4 Anterior
(left main artery)
V5, V6 Lateral
Q WAVE
If:
Pathological Q wave
ST segment depression
T wave inversion
YES: New Infarction
(MED EMERGENCY!)
Where is the location?
Identify the leads.
Leads Location
I, avL High Lateral
II, III, avF Inferior
(right coronary artery)
V1, V2 Septal
V3, V4 Anterior
(left main artery)
V5, V6 Lateral
R AND S WAVES
Are any R or S waves too
big?
YES: Left ventricular
hypertrophy
Check using:
Sokolow-Lyon index:
SV1 + (RV5 or RV6) >3.5 mV
Cornell voltage criteria:
SV3 + RavL 2.8 mV (men)
SV3 + RavL 2.0 mV (women)
R AND S WAVES
Look at leads V1 to V6
Normal:
R wave increases in height from V1 to V6
S wave decreases in depth from V1 to V6
R AND S WAVES
Look at leads V1 to V6
Are the R waves persistent in sizes (<5 mm)?
YES: Poor R wave progression
R AND S WAVES
Look at leads V1 to V6
Are the S waves persistent in sizes?
YES: Persistent posterobasal forces
QRS COMPLEX
Normally varies in
different ECG leads
Normal:
< 0.12 sec
< 3 small squares
QRS is upright in all leads
except in avR
QRS COMPLEX
Is there any bizarre
looking QRS with deep S
wave?
Premature, wide,
aberrant, notched QRS, >
0.12s in duration?
YES: Premature
ventricular complex
(PVC)
QRS COMPLEX
Are any QRS complexes
too wide (> 0.12 secs)?
YES: Bundle Branch
Block
QRS COMPLEX
Look at V1, V2 and V5,
V6
If:
Wide QRS complex
M sign or rSR in V1
YES: Right Bundle Branch
Block (RBBB)
Wide QRS complex
Deep S in V6
YES: Complete BBB
QRS COMPLEX
Look at V1, V2 and V5,
V6
If:
Wide QRS complex
srS in V1
M sign in the peak of R
YES: Left Bundle Branch
Block (LBBB)
Wide QRS complex
Deep S in V6
YES: Complete BBB
QRS COMPLEX
Look at V1, V2 and V5,
V6
If:
Normal QRS complex
BBB morphology
YES: Incomplete BBB
ST SEGMENT
Isoelectric ( Lies at the
same level as the
baseline)
Normal:
Deviate between -0.5 and
+1 mm from the baseline
ST SEGMENT
Are the ST segments
elevated (raised above
level of baseline)?
YES: Acute MI to normal
variant
ST SEGMENT
ST SEGMENT
Are the ST segments
depressed ( > 2 small
squares below level of
baseline)?
YES: Myocardial
ischemia
ST SEGMENT
ST SEGMENT
Does the J point ensue early at repolarization?
YES: Early Repolarization Pattern
ST SEGMENT
Is there flattening of T waves?
YES: Non-specific ST wave changes (NSSTWC)
T WAVE
Normal:
Not clearly defined
Guide:
Should not be > size of
the preceding QRS complex
T wave is usually not above
10 mm in any precordial
leads
T WAVE
Look at V2, V3, V4
Are the T waves too tall (>10 mm)?
YES: Peak T waves (Hyperkalemia or AMI)
T WAVE
Is the T wave inverted (>
1 mm)?
YES: Myocardial
Ischemia
U WAVE
Prominent in V3
Normal:
Not >1 mm amplitude
U WAVE
Do the U waves appear
too prominent?
YES: Prominent U
waves (Hypokalemia,
Hypercalcemia,
Hyperthyroidism)
RHYTHM
SINUS RHYTHM
Presence of P wave
Followed by QRS complex
Regular rate
Normal:
60-100 bpm
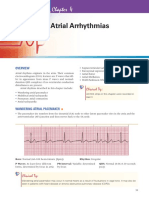
SINUS ARRHYTHMIA
Presence of P wave
Followed by QRS complex
Irregular sinus rhythm at rate <100 bpm
Cycle vary by 10% or more
PREMATURE ATRIAL COMPLEX
(PAC)
Premature P wave which results from a premature
ectopic, supraventricular impulse that originates
somewhere in the atria outside of the SA node
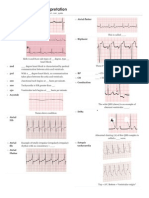
CARDIAC RATE
BRADYCARDIA
RR <60 bpm
Regular
P wave
Sinus
Bradycardia
No P wave
Narrow
QRS
Junctional
Wide QRS
Idio-
ventricular
No P-QRS
relation
3
rd
degree
AV Block
Irregular
No P wave
Slow AF
P wave but
abn PR
Group
beating
2
nd
degree
AV Block
BRADYCARDIA
Sinus Bradycardia
BRADYCARDIA
3
rd
degree AV Block
BRADYCARDIA
2
nd
degree AV Block
Type 1
Type 2
TACHYCARDIA
RR > 100 bpm
Narrow QRS
Regular
P wave; 100-
140 bpm
Sinus
tachycardia
No P wave;
150 bpm
SVT
Irregular
No P wave
AF
Flutter waves;
saw tooth;
>300 bpm
Atrial flutter
Wide QRS
V tach
BRADYCARDIA
Sinus Tachycardia
BRADYCARDIA
SVT
BRADYCARDIA
AF
BRADYCARDIA
Atrial flutter
BRADYCARDIA
V-tach
AXIS
LEFT ANTERIOR FASCICULAR
BLOCK (LAFB)
Mean QRS axis of -45 to -90 degrees
> -30 degrees is the hallmark
rS pattern in II, III and avF
qR pattern in I and avL
Normal QRS duration (<0.12 sec)
LEFT ANTERIOR FASCICULAR
BLOCK (LAFB)
LEFT POSTERIOR FASCICULAR
BLOCK (LPFB)
Mean QRS axis of 120 degrees
rS pattern in I and avL
qR pattern in II, III, avR
Normal QRS duration ( <0.12 sec)
LEFT ANTERIOR FASCICULAR
BLOCK (LAFB)
RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPY
(RVH)
Mean QRS axis of >90 degrees
qR in V1 or R wave in V1 7 mm or R/S ratio of 1 or
rSR in RBBB
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ecg Cheat Sheet 35Document2 pagesEcg Cheat Sheet 35jessjaylee80% (5)
- ECG Rhythms Guide: Normal, Abnormal & Example TracingsDocument9 pagesECG Rhythms Guide: Normal, Abnormal & Example Tracingsdiani arisandhi100% (1)
- EKG Interpretation GuideDocument2 pagesEKG Interpretation GuideFabian Ramirez HincapiéPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG InterpretationDocument52 pagesECG InterpretationMarcus, RN98% (44)
- ECG Mastery Improving Your ECG Interpretation SkillsDocument23 pagesECG Mastery Improving Your ECG Interpretation SkillsHitesh Deora100% (2)
- EKG Flash CardsDocument5 pagesEKG Flash CardsRyann Sampino FreitasPas encore d'évaluation
- EcgDocument57 pagesEcgenii_ta100% (9)
- Dysrhythmias ChartDocument6 pagesDysrhythmias Chartjkrix100% (1)
- ECG InterpretationDocument1 pageECG InterpretationCecil-An DalanonPas encore d'évaluation
- ACLS EKG Rhythms and InterpretationDocument10 pagesACLS EKG Rhythms and Interpretationdonheyzz_02Pas encore d'évaluation
- Easy ECG GuideDocument17 pagesEasy ECG GuideDr.Chinmay Kulkarni83% (12)
- ElectrocardiogramDocument11 pagesElectrocardiogramAbby BhevPas encore d'évaluation
- Blue Bio V DoH and HFMADocument21 pagesBlue Bio V DoH and HFMAShane StarlingPas encore d'évaluation
- HeparinDocument2 pagesHeparinNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (4)
- Krishnan - EKG Basics Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesKrishnan - EKG Basics Lecture NotesanishdPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg CookbookDocument2 pagesEcg CookbookCalin Popa100% (1)
- Basic ECG ReadingDocument41 pagesBasic ECG ReadingBenj100% (3)
- EKG InterpretationDocument65 pagesEKG Interpretationpaskariatne probo dewi100% (1)
- Ecg Made EasyDocument45 pagesEcg Made Easyfisiopop100% (4)
- ECG InterpretationDocument95 pagesECG InterpretationShiela Mae Lopez100% (10)
- Ekg Guidelines PDFDocument7 pagesEkg Guidelines PDFd.ramadhan100% (1)
- ECG LectureDocument214 pagesECG Lecturensyuzon100% (1)
- ECG Made Easy For Allied Health ProfessionalsDocument47 pagesECG Made Easy For Allied Health ProfessionalsDr GowrishankarPotturi PT100% (3)
- Ecg Reading Made EasyDocument59 pagesEcg Reading Made EasyAngealyn GaviolaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Interpretation: DR S J Bhosale DM, FPCC (Canada) Associate Professor Tata Memorial CentreDocument90 pagesECG Interpretation: DR S J Bhosale DM, FPCC (Canada) Associate Professor Tata Memorial Centrevaishali TayadePas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Guide: Anatomy, Physiology, Interpretation and AbnormalitiesDocument102 pagesECG Guide: Anatomy, Physiology, Interpretation and AbnormalitiesMustafa A. DawoodPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Master Class-1Document132 pagesECG Master Class-1Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- ECG InterpretationDocument5 pagesECG InterpretationRichelle Dianne Ramos-Giang100% (3)
- Read ECGDocument128 pagesRead ECGrehmatakuPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG tutorial covers basics, axis, waves, intervals, hypertrophy and moreDocument56 pagesECG tutorial covers basics, axis, waves, intervals, hypertrophy and morefeby_valPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFDocument16 pages11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFBìnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ECG Interpretation 20-Question Practice TestDocument7 pagesBasic ECG Interpretation 20-Question Practice Testemmaaziz100% (1)
- Basic ECG LectureDocument148 pagesBasic ECG LectureAradhanaRamchandaniPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG: A Noob's Guide to Understanding ElectrocardiographyDocument103 pagesECG: A Noob's Guide to Understanding ElectrocardiographyGhaidaa Sadeq100% (1)
- ECG Fast and EasyDocument37 pagesECG Fast and EasyKofi Ziggy100% (1)
- Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideDocument7 pagesCardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideAya KamajayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument9 pagesCardiac DysrhythmiasMandy JameroPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Anas Yasin - MDDocument58 pagesDr. Anas Yasin - MDMahfouzPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument9 pagesCardiac ArrhythmiasRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg Made EasyDocument130 pagesEcg Made EasyJOHN ARBIE TATTAO, RN96% (49)
- Ecg Reading NotesDocument17 pagesEcg Reading NotesMarian FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG InterpretationDocument11 pagesECG InterpretationAndrea AndradaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Made Easy by Mallareddy SripujaDocument46 pagesECG Made Easy by Mallareddy Sripujagrreddy836100% (3)
- Ecg ReadingsDocument11 pagesEcg ReadingsAnton Laurenciana100% (5)
- Cardiac MedsDocument7 pagesCardiac MedsMary Fair DelcidPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormal ECG Fadhly SharimanDocument55 pagesAbnormal ECG Fadhly SharimanFadhly SharimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Joseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPDocument70 pagesJoseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPcarmsPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrocardiogramDocument169 pagesElectrocardiogramjitendra magarPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Abnormal ECG FadhlyDocument55 pagesBasic Abnormal ECG FadhlyFadhly SharimanPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG at A GlanceDocument53 pagesECG at A Glancenurliah armandPas encore d'évaluation
- Suatu Alat LaboratorisDocument78 pagesSuatu Alat LaboratorisHematology 2016Pas encore d'évaluation
- Suatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisDocument78 pagesSuatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisAnonymous 3LwVkUsdPas encore d'évaluation
- Significance of The Various Waveforms + Chamber EnlargementDocument45 pagesSignificance of The Various Waveforms + Chamber EnlargementKai Zi (凯)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kursus Ekg DR Ismi-1Document78 pagesKursus Ekg DR Ismi-1Sekar Ayu WulandariPas encore d'évaluation
- Suatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisDocument78 pagesSuatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisMohammad AlmuhaiminPas encore d'évaluation
- 5Hypertrophy and MIDocument116 pages5Hypertrophy and MIsamooanatenaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG For InternsDocument31 pagesECG For InternsAgus SyaifudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg Presentation 2013Document40 pagesEcg Presentation 2013Samuel FpPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy, Physiology & Conduction System of The HeartDocument122 pagesAnatomy, Physiology & Conduction System of The HeartShelly Lavenia Sambodo100% (1)
- EKG Interpretation: UNS Cardiovascular Dept Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument85 pagesEKG Interpretation: UNS Cardiovascular Dept Medical Student Lecture Seriesandina rosmalianti100% (1)
- ECG InterpretationDocument83 pagesECG InterpretationJuana Maria Garcia Espinoza100% (2)
- ECG at A GlanceDocument53 pagesECG at A GlancePetrus TjiangPas encore d'évaluation
- B CellDocument10 pagesB CellSonia Elizabeth SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Foliar FertilizerDocument7 pagesFoliar FertilizerDjugian GebhardPas encore d'évaluation
- Pass MRCP Part 2 (Sample)Document26 pagesPass MRCP Part 2 (Sample)Ahmad Shokry100% (1)
- Posture and AlignmentDocument1 pagePosture and AlignmentNell KeenePas encore d'évaluation
- Meridians and Points PDFDocument35 pagesMeridians and Points PDFHamdon Hamad100% (9)
- How Can We Use Neurotransmitters in Emotion and Reward System To Study DepressionDocument22 pagesHow Can We Use Neurotransmitters in Emotion and Reward System To Study DepressionGlobal Research and Development ServicesPas encore d'évaluation
- Doppler US Validates Portal Vein Flow in CirrhosisDocument5 pagesDoppler US Validates Portal Vein Flow in CirrhosisL0v3B00k5Pas encore d'évaluation
- ReadingsDocument246 pagesReadingsFul WgPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul Anatomi Blok 7Document27 pagesModul Anatomi Blok 7Dewandaru I A BPas encore d'évaluation
- SP FinalDocument18 pagesSP Finalapi-344954734Pas encore d'évaluation
- FORENSIC SEROLOGY AND BLOOD ANALYSISDocument16 pagesFORENSIC SEROLOGY AND BLOOD ANALYSISBARCELON, CHRISTOPHER JAMESPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER SUMMARY-opiod AnalgesicDocument9 pagesCHAPTER SUMMARY-opiod AnalgesicNuttiya WerawattanachaiPas encore d'évaluation
- C5 - Metabolism and Enzyme Part 1Document20 pagesC5 - Metabolism and Enzyme Part 1Daniel LohPas encore d'évaluation
- The Third International Consensus Definitions For Sepsis and Septic Shock Sepsis-3 - JAMA 2016Document10 pagesThe Third International Consensus Definitions For Sepsis and Septic Shock Sepsis-3 - JAMA 2016Miguel Angel Quiroz CristobalPas encore d'évaluation
- PharmD 1st Year SyllabusDocument21 pagesPharmD 1st Year SyllabusAshwat APas encore d'évaluation
- Branches of ZoologyDocument3 pagesBranches of ZoologyVivek Morya100% (1)
- Battle of BrainDocument7 pagesBattle of BrainKhalida Zia SiregarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Anterior Cranial FossaDocument4 pagesThe Anterior Cranial FossaArshad hussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal SurgeryDocument166 pagesAbdominal SurgeryIndera VyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Refeeding SyndromeDocument4 pagesRefeeding SyndromeallyPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Bio Perlis 2009 Serta SkemaDocument96 pagesSPM Bio Perlis 2009 Serta Skemahilmi72100% (1)
- 10th BIOLOGY PPT CH. NO. 8Document13 pages10th BIOLOGY PPT CH. NO. 8Aastha BorhadePas encore d'évaluation
- ANAESTHESIOLOGYDocument38 pagesANAESTHESIOLOGYcollinsmagPas encore d'évaluation
- Poster 10 NLS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFDocument1 pagePoster 10 NLS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFAndy XiaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document10 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1RUTH PIANGPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDeity Ann ReuterezPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition in Plants and AnimalsDocument3 pagesNutrition in Plants and AnimalsHaris Ur RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document7 pagesChapter 4R LashPas encore d'évaluation