Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Biology 113 Quiz 2
Transféré par
Abhishek Isaac Mathew0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues17 pagesBiology 113 Quiz 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentBiology 113 Quiz 2
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues17 pagesBiology 113 Quiz 2
Transféré par
Abhishek Isaac MathewBiology 113 Quiz 2
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 17
Quiz 2
Biology 113
Prokaryotes to Fungi
1. One of the authors of The Genesis Flood in 1961:
(a) George Price
(b) Francis Collins
(c) John Walton
(d) Henry Morris
2. Which of the following is/are NOT correct in terms of Darwins
theory of natural selection:
(a) Members of a population vary in their inherited traits only
when the population is undergoing natural selection
(b) Only certain organisms can produce more offspring than
their environment can support
(c) Individuals in a population with favourable inherited traits
tend to leave more offspring
(d) a and b
(e) a, b and c
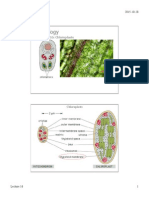
3. The figure on the right
demonstrates that:
(a) soapberry bugs may
feed efficiently on a variety of
fruits regardless of beak length
(b) soapberry bugs prefer
native plants but will feed on
invasive plants during a drought
(c) soapberry bugs are capable of rapid evolution in terms
of beak length
(d) b and c
(e) none of the above
4. How is an endemic species best defined?
(a) a native species
(b) an invasive species
(c) a species found nowhere else
(d) a dwarf version of a native species
5. Which pelvic bone is retained in the apparent evolution of
modern cetaceans?
(a) foot
(b) tibia
(c) pelvis
(d) femur (e) none
6. The concept of homology assumes organs are similar
because of:
(a) common function (b) common ancestry (c) a and b
7. Is the case of the
sugar glider and the
flying squirrel wing
structure
(a) homology or
(b) analogy?
8. Which is the most current classification:
(a) Archaeabacteria as a type of bacteria
(b) Archaea have their own domain
(c) Both bacteria and Archaea in same domain
(d) Archaea are Eukaryotes
9. Halophiles are archaeans that live in areas:
(a) with high concentrations of salt
(b) with high temperatures
(c) with high acidities
(d) with high amounts of methane
10. Average size of prokaryotes:
(a) 1-5 m (b) 10-100 m (c) 0.25-0.75 mm (d) 30-50 m
11. Are some cyanobacteria toxic?
(a) yes
(b) no
12. To which group does E. coli belong?
(a) Cyanobacteria (b) Archaea
(c) Intestinal Bacteria
(d) a and c
(e) none of the above
13. The bacteria pictured on the right are
being used to:
(a) consume harmful oil particles
(b) create ethanol
(c) produce PHA to make plastics
14. Which of the following is the cause of beaver fever?
(a) Trypanosoma (b) Volvox
(c) Spirulina
(d) Balantidium
(e) Giardia
15. To which supergroup does green algae (Chlorophyta)
belong?
(a) Unikonta (b) Archaeplastida
(c) Excavata
16. What is function of the
diatom raphe?
(a) reproduction (b) respiration
(c) movement
(d) salt removal
17. Why do some mushrooms form a fairy ring?
(a) because the hyphae only grow clockwise
(b) nutrients are depleted within the ring
(c) competition outside the ring is more intense
(d) the fairies need somewhere to sit
18. To which supergroup do fungi belong?
(a) Unikonta (b) Archaeplastida (c) Excavata
19. What is theorized to have given rise to chloroplasts via
primary endosymbiosis?
(a) green algae
(b) cyanobacteria (c) red algae
20. Which of the following contain(s) DNA?
(a) mitochondria
(b) chloroplasts
(c) nucleii
(d) b and c
(e) a, b and c
1. One of the authors of The Genesis Flood in 1961:
(a) George Price
(b) Francis Collins
(c) John Walton
(d) Henry Morris
2. Which of the following is/are NOT correct in terms of Darwins
theory of natural selection:
(a) Members of a population vary in their inherited traits only
when the population is undergoing natural selection
(b) Only certain organisms can produce more offspring than
their environment can support
(c) Individuals in a population with favourable inherited traits
tend to leave more offspring
(d) a and b
(e) a, b and c
3. The figure on the right
demonstrates that:
(a) soapberry bugs may
feed efficiently on a variety of
fruits regardless of beak length
(b) soapberry bugs prefer
native plants but will feed on
invasive plants during a drought
(c) soapberry bugs are capable of rapid evolution in terms
of beak length
(d) b and c
(e) none of the above
4. How is an endemic species best defined?
(a) a native species
(b) an invasive species
(c) a species found nowhere else
(d) a dwarf version of a native species
5. Which pelvic bone is retained in the apparent evolution of
modern cetaceans?
(a) foot
(b) tibia
(c) pelvis
(d) femur (e) none
6. The concept of homology assumes organs are similar
because of:
(a) common function (b) common ancestry (c) a and b
7. Is the case of the
sugar glider and the
flying squirrel wing
structure
(a) homology or
(b) analogy?
8. Which is the most current classification:
(a) Archaeabacteria as a type of bacteria
(b) Archaea have their own domain
(c) Both bacteria and Archaea in same domain
(d) Archaea are Eukaryotes
9. Halophiles are archaeans that live in areas:
(a) with high concentrations of salt
(b) with high temperatures
(c) with high acidities
(d) with high amounts of methane
10. Average size of prokaryotes:
(a) 1-5 m (b) 10-100 m (c) 0.25-0.75 mm (d) 30-50 m
11. Are some cyanobacteria toxic?
(a) yes
(b) no
12. To which group does E. coli belong?
(a) Cyanobacteria (b) Archaea
(c) Intestinal Bacteria
(d) a and c (e) none of the above
13. The bacteria pictured on the right are
being used to:
(a) consume harmful oil particles
(b) create ethanol
(c) produce PHA to make plastics
14. Which of the following is the cause of beaver fever?
(a) Trypanosoma
(d) Balantidium
(b) Volvox
(e) Giardia
(c) Spirulina
15. To which supergroup does green algae (Chlorophyta)
belong?
(a) Unikonta (b) Archaeplastida
(c) Excavata
16. What is function of the
diatom raphe?
(a) reproduction (b) respiration
(c) movement
(d) salt removal
17. Why do some mushrooms form a fairy ring?
(a) because the hyphae only grow clockwise
(b) nutrients are depleted within the ring
(c) competition outside the ring is more intense
(d) the fairies need somewhere to sit
18. To which supergroup do fungi belong?
(a) Unikonta (b) Archaeplastida (c) Excavata
19. What is theorized to have given rise to chloroplasts via
primary endosymbiosis?
(a) green algae
(b) cyanobacteria (c) red algae
20. Which of the following contain(s) DNA?
(a) mitochondria
(b) chloroplasts
(c) nucleii
(d) b and c
(e) a, b and c
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- In-Vivo Microbiologic Evaluation of Polytetrafluoroethylene and Cotton As Endodontic Spacer MaterialsDocument7 pagesIn-Vivo Microbiologic Evaluation of Polytetrafluoroethylene and Cotton As Endodontic Spacer MaterialsAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex Vivo Microbial Leakage Analysis of Polytetrafluoroethylene Tape and Cotton Pellet As Endodontic Access Cavity SpacersDocument7 pagesEx Vivo Microbial Leakage Analysis of Polytetrafluoroethylene Tape and Cotton Pellet As Endodontic Access Cavity SpacersAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiological Evaluation of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Tape, Cellulose Sponge and Cotton As Spacer Materials Combined With Intracanal Medicament-An in Vitro StudyDocument5 pagesMicrobiological Evaluation of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Tape, Cellulose Sponge and Cotton As Spacer Materials Combined With Intracanal Medicament-An in Vitro StudyAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- !!! Root Canal Morphology and It's Relationship To Endodontic Procedures - Frank J. Vertucci !!!Document27 pages!!! Root Canal Morphology and It's Relationship To Endodontic Procedures - Frank J. Vertucci !!!Puscas Madalina100% (1)
- Microbiologic Evaluation of Cotton and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Tape As Endodontic Spacer Materials in Primary Molars An in Vivo StudyDocument7 pagesMicrobiologic Evaluation of Cotton and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Tape As Endodontic Spacer Materials in Primary Molars An in Vivo StudyAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- In Vitro Microbiologic Evaluation of PTFE and Cotton As Spacer MaterialsDocument6 pagesIn Vitro Microbiologic Evaluation of PTFE and Cotton As Spacer MaterialsAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Ortho13 14Document64 pagesOrtho13 14priyasargunan100% (4)
- Chlorhexidine Gluconate, Its Properties and Applications in Endodontics 2008Document15 pagesChlorhexidine Gluconate, Its Properties and Applications in Endodontics 2008Abhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- An Interview With Benedict Wilmes: Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics December 2016Document9 pagesAn Interview With Benedict Wilmes: Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics December 2016Abhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Jerd 12572Document6 pagesJerd 12572Abhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- AAE Position Statement On Vital Pulp Therapy 2021Document10 pagesAAE Position Statement On Vital Pulp Therapy 2021Abhishek Isaac Mathew100% (1)
- 2.0 - Why Do We Have GovernmentDocument1 page2.0 - Why Do We Have GovernmentAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Caton Et Al-2018-Journal of Clinical PeriodontologyDocument8 pagesCaton Et Al-2018-Journal of Clinical PeriodontologyWirajulay Pratiwi SanusiPas encore d'évaluation
- What Material Do I UseDocument3 pagesWhat Material Do I UseAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOL2131Asgn5 SWDocument5 pagesBIOL2131Asgn5 SWAbhishek Isaac Mathew0% (1)
- Armfield Et Al-2013-Australian Dental JournalDocument18 pagesArmfield Et Al-2013-Australian Dental JournalAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- 1609cei Ellenbogen WebDocument8 pages1609cei Ellenbogen WebAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- DixonDocument13 pagesDixonAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- 12k Beginner Training GuideDocument20 pages12k Beginner Training GuideAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages and Dısadvantages of E-MAX and Zırconıa Crowns: Tamar Dolidze, Professor Ilona Bitarova, MADocument4 pagesAdvantages and Dısadvantages of E-MAX and Zırconıa Crowns: Tamar Dolidze, Professor Ilona Bitarova, MAAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Dental Arch Morphology in Normal OcclusionsDocument4 pagesDental Arch Morphology in Normal Occlusionsdianpn27Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAT WordlistDocument5 pagesSAT WordlistAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmeAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- 1610cei Shuman WebDocument10 pages1610cei Shuman WebAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Biol2131asgn4 SWDocument5 pagesBiol2131asgn4 SWAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- 223.16 Chloroplasts2015Document9 pages223.16 Chloroplasts2015Abhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Tourism Indicators 2010 The Year in ReviewDocument7 pagesTourism Indicators 2010 The Year in ReviewAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- 223.19 Endocytosis Exocytosis2015Document12 pages223.19 Endocytosis Exocytosis2015Abhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Biology: Lecture 223.17: Intracellular Compartments and Protein SortingDocument14 pagesCell Biology: Lecture 223.17: Intracellular Compartments and Protein SortingAbhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- 223.18 Vesicular Transport2015Document10 pages223.18 Vesicular Transport2015Abhishek Isaac MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- W0L0XCF0866101640 (2006 Opel Corsa) PDFDocument7 pagesW0L0XCF0866101640 (2006 Opel Corsa) PDFgianyPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper-Czechowski-Slow-strain-rate Stress Corrosion Testing of Welded Joints of Al-Mg AlloysDocument4 pagesPaper-Czechowski-Slow-strain-rate Stress Corrosion Testing of Welded Joints of Al-Mg Alloysjavo0128Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Part 2Document14 pagesReading Part 2drama channelPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis of TrypanosomiasisDocument82 pagesDiagnosis of TrypanosomiasisDrVijayata Choudhary100% (1)
- Coffee Quality Manual by Abra Rand Nig Use IDocument25 pagesCoffee Quality Manual by Abra Rand Nig Use IIpungPas encore d'évaluation
- Child DevelopmentDocument15 pagesChild Development4AndreeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blue Modern Company Profile PresentationDocument15 pagesBlue Modern Company Profile PresentationjanePas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On Traditional Medicinal Herbs Used by The Ethnic People of Goalpara District of Assam, North East IndiaDocument6 pagesA Study On Traditional Medicinal Herbs Used by The Ethnic People of Goalpara District of Assam, North East IndiaDr. Krishna N. SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- ff2023 Web 0 0Document2 pagesff2023 Web 0 0khaing khantPas encore d'évaluation
- Asco Series 238 ASCO Pilot Operated Solenoid Valves (Floating Diaphragm)Document2 pagesAsco Series 238 ASCO Pilot Operated Solenoid Valves (Floating Diaphragm)Khyle Laurenz DuroPas encore d'évaluation
- Wildlife Emergency and Critical CareDocument14 pagesWildlife Emergency and Critical CareRayssa PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintenance Páginas-509-580Document72 pagesMaintenance Páginas-509-580Alexandra Gabriela Pacheco PrietoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tabla de Avances de AcesoriosDocument3 pagesTabla de Avances de AcesoriosPedro Diaz UzcateguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecological Quality RatioDocument24 pagesEcological Quality RatiofoocheehungPas encore d'évaluation
- Beastlikebalsam - Muscle BuildingDocument10 pagesBeastlikebalsam - Muscle BuildingBalsam LaaroussiPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowerDocument6 pages9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowersivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- YoungMan EN131 GUIDEDocument16 pagesYoungMan EN131 GUIDErcpawar100% (1)
- Regression Analysis Random Motors ProjectDocument22 pagesRegression Analysis Random Motors ProjectPrateek AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinder DLL Week 8Document15 pagesKinder DLL Week 8Jainab Pula SaiyadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Haldex-Barnes 2-Stage Pump For Log SplittersDocument2 pagesHaldex-Barnes 2-Stage Pump For Log SplittersPer Akkamaan AgessonPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume: Satyam KumarDocument3 pagesResume: Satyam KumarEr Satyam Kumar KrantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wcdma Idle Mode (Ericsson)Document29 pagesWcdma Idle Mode (Ericsson)Hosein ShahbaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Tokyo Guidelines 2018Document115 pagesTokyo Guidelines 2018Alik Razi100% (1)
- SR No Service CodeDocument30 pagesSR No Service CodeShiva KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- BIF-V Medium With Preload: DN Value 130000Document2 pagesBIF-V Medium With Preload: DN Value 130000Robi FirdausPas encore d'évaluation
- Adaptive Reuse Architecture Documentation and Analysis 2168 9717 1000172Document9 pagesAdaptive Reuse Architecture Documentation and Analysis 2168 9717 1000172Komal HundiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kami Export - Subject Complements-1 PDFDocument3 pagesKami Export - Subject Complements-1 PDFkcv kfdsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adriano Costa Sampaio: Electrical EngineerDocument3 pagesAdriano Costa Sampaio: Electrical EngineeradrianorexPas encore d'évaluation
- 23001864Document15 pages23001864vinodsrawat33.asiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Practical Reference Guide ForDocument4 pagesThe Practical Reference Guide Forelias667Pas encore d'évaluation