Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Crystal Katherine I. Parungao 6 - St. Perpetua: The Earth and Its Dynamic Processes
Transféré par
Crystal Parungao0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
24 vues10 pagesThis presentation includes brief and short descriptions related to earth.
Titre original
The Earth
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis presentation includes brief and short descriptions related to earth.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
24 vues10 pagesCrystal Katherine I. Parungao 6 - St. Perpetua: The Earth and Its Dynamic Processes
Transféré par
Crystal ParungaoThis presentation includes brief and short descriptions related to earth.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 10
The Earth and Its Dynamic Processes
The Earth
Crystal Katherine I. Parungao
6 St. Perpetua
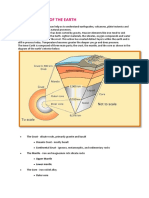
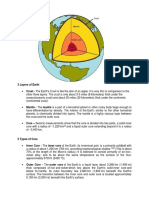
The earth is composed of three layers: the crust,
the mantle, and the core. Scientists study the
earths interior through seismic waves.
The crust is the thinnest layer. It is divided into
continental crust and oceanic crust. The crust is
thinnest in the ocean than in the continents.
The mantle is the thickest layer. It is made up of
molten rock. The mantle is divided into upper
mantle and lower mantle.
The core is the center of the earth. It is divided
into liquid outer core and solid inner core.
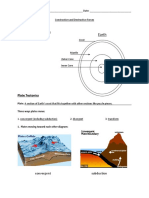
The lithosphere is divided into many plates that
move in relation to each other due to tectonic
forces.
The plates are structures that support the crust.
They are located above the asthenosphere. These
plates move in three different ways. They move
away from each other, they collide or move
against each other, or they slide past each other.
Plate boundaries are areas where two plates meet.
Plates collide at a convergent plate boundary;
they move apart in the divergent boundary and
slide past over another in a transform fault
boundary.
Geology is the science that deals with the study of
the earth, its history and the various processes
that shape it.
An earthquake is a sudden movement or vibration
in the earths crust. This sudden motion causes
seismic waves to radiate from their point of origin
called the focus and travel directly above the focus
called the epicenter. Earthquakes are strongest
near their epicenter. The closer an earthquake is
to its epicenter, the stronger it is.
Strong and devastating earthquakes are related
to the sudden movement of tectonic plates. This
earthquake is called tectonic earthquake.
Earthquakes are triggered by volcanic activities.
This earthquake is called a volcanic earthquake.
The Pacific Ring of Fire is an area circling the
Pacific Ocean where earthquakes and volcanic
activities occur in this area. The Philippines is
part of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
A seismograph measures the magnitude and intensity
of an earthquake. Magnitude is the energy released by
an earthquake. Magnitude is measured using a
Richter Scale. Intensity is a measure of how much
damage an earthquake causes on the surface.
Intensity is measured on the Mercalli Intensity Scale.
A volcano is an opening at the earths crust where
gases, pyroclasts, and lava are ejected on to the
surface. Volcanoes are classified using different bases.
According to the shape and composition of the
cone, volcanoes are classified as having a
composite cone, cinder cone, and shield cone.
According to an activity, volcanoes are classified
as active, dormant, and extinct. Volcanic
eruption may be violent or quiet, depending on
the composition of the molten material.
Volcanic eruptions can cause serious human,
economic, and environmental impacts, but
volcanoes can also be rich sources of materials
and provide benefits to man and all sectors of
society.
Volcanic eruption preparedness includes
knowing what to do before, during, and after an
earthquake to minimize damage.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksD'EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Peeling The Earth Like An Onion : Earth Composition - Geology Books for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksD'EverandPeeling The Earth Like An Onion : Earth Composition - Geology Books for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - 3 Engineering SeismologyDocument55 pagesUnit - 3 Engineering Seismologyci_balaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Test Study Sheet: General Facts About Earth'sDocument5 pagesScience Test Study Sheet: General Facts About Earth'sapi-281100019Pas encore d'évaluation
- VolcanoesDocument6 pagesVolcanoesJessa Samantha ParanePas encore d'évaluation
- ch03 Sec1 RevisedDocument35 pagesch03 Sec1 Revisedapi-239353579Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - EarthquakeDocument39 pages1 - EarthquakeJustine Marie BalderasPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of The EarthDocument47 pagesStructure of The Earthapi-270383743100% (1)
- Science 10 First Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience 10 First Quarter ReviewerPlayer 456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Global Plate TectonicsDocument11 pagesTheory of Global Plate TectonicsHannylet OcatePas encore d'évaluation
- PlatesDocument33 pagesPlatesJhana MontefalcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Shaping Earths SurfaceDocument14 pagesShaping Earths Surfacenadamohey99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geology LO1 G12Document2 pagesGeology LO1 G12يوسف وليدPas encore d'évaluation
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsgildeddivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements of Earthquake EngineeringDocument41 pagesElements of Earthquake EngineeringAnjaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Volcanoes Earthquakes and Mountain RangesDocument17 pagesVolcanoes Earthquakes and Mountain RangesChrist VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 Distribution of Active Volcanoes, EarthquakeDocument31 pagesLesson 1 Distribution of Active Volcanoes, EarthquakeVergil S.YbañezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemically, The Layers of Earth Are As Follow: Crust, Upper Mantle, LowerDocument8 pagesChemically, The Layers of Earth Are As Follow: Crust, Upper Mantle, LowerMarg EraesPas encore d'évaluation
- Science ReviewerDocument14 pagesScience ReviewerIrish EloisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tektonik Lempen - 1Document17 pagesTektonik Lempen - 1riskiafdalsaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- 21 Structural Geology and Plate Tectonics - OdpDocument34 pages21 Structural Geology and Plate Tectonics - OdpTremaine JamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Plates Volcanoes EarthquakesDocument45 pagesPlates Volcanoes EarthquakesAbigail HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Plate Tectonics: Earth's Plates and Continental DriftDocument31 pagesPlate Tectonics: Earth's Plates and Continental DriftTeena SeiclamPas encore d'évaluation
- Continental and Oceanic CrustDocument38 pagesContinental and Oceanic CrustEvelyn MayorPas encore d'évaluation
- 11mss Earth Chapter09Document86 pages11mss Earth Chapter09igyanchandaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Plate Tectonics-1Document22 pagesPlate Tectonics-1Navya PuttaguntaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument33 pages2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKen Verona Ferrera100% (2)
- Earth's Internal ForcesDocument22 pagesEarth's Internal ForcesAmreka HoseinPas encore d'évaluation
- Plate TectonicsDocument41 pagesPlate TectonicsJohn100% (1)
- Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument8 pagesPlate Tectonics TheoryWendelyn Sumpo100% (1)
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesJohn BenedictPas encore d'évaluation
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesvinod pPas encore d'évaluation
- Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument43 pagesPlate Tectonics TheoryKirfan 123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Interior of Earth Formation of Earth Crust Geomorphic Process Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics 751653236350454 PDFDocument11 pagesInterior of Earth Formation of Earth Crust Geomorphic Process Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics 751653236350454 PDFGaurav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Interior of Earth Formation of Earth Crust Geomorphic Process Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Updated English 11Document10 pagesInterior of Earth Formation of Earth Crust Geomorphic Process Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Updated English 11Team RaagPas encore d'évaluation
- GeomorphologyDocument37 pagesGeomorphologykalluri ganeshPas encore d'évaluation
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsnoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Geo GeoDocument83 pagesGeo GeoKiran BPas encore d'évaluation
- Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocument18 pagesEarthquake Resistant StructuresMinsha SalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Plate TectonicsDocument30 pagesGrade 10 Plate TectonicsJhen Bon82% (17)
- Plate TectonicsDocument38 pagesPlate TectonicsKhanett DagohoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Structure Plate TectonicsDocument47 pagesEarth Structure Plate TectonicsAl Jawad100% (3)
- Plates Tectonics 2Document57 pagesPlates Tectonics 2Mark LourencePas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic WavesDocument16 pagesSeismic WavesKKMMPas encore d'évaluation
- Science PPTDocument28 pagesScience PPTquencia beth radinPas encore d'évaluation
- EndogenicDocument38 pagesEndogenicAngelica SeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 10 - Notes Local Local LocalDocument7 pagesChapter - 10 - Notes Local Local LocalBryan YasgilPas encore d'évaluation
- Interior EarthDocument43 pagesInterior EarthSergioPas encore d'évaluation
- SciencemidtermDocument9 pagesSciencemidtermapi-281100019Pas encore d'évaluation
- DSTMDocument18 pagesDSTMDesh Deepak kantPas encore d'évaluation
- Sea Floor Spreading and Plate TectonicsDocument26 pagesSea Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonicsbking bbPas encore d'évaluation
- 6th Grade Science-Plate Tectonics and Earths InteriorDocument41 pages6th Grade Science-Plate Tectonics and Earths Interiorleojohn2100% (1)
- Geo RevisionDocument4 pagesGeo RevisionFarfi UddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Geology Final Exam NotesDocument14 pagesGeology Final Exam NotesKuhoo UPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 3 Plate TectonicsDocument74 pagesWeek 3 Plate TectonicsmuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Notes - 10Document6 pagesEarth Notes - 10angelea9mariPas encore d'évaluation
- NAT ReviewerDocument4 pagesNAT ReviewerAllen Aquino PradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Discussion NotesDocument4 pagesScience Discussion NotesIvan TroyPas encore d'évaluation
- Seafloor Spreading TheoryDocument16 pagesSeafloor Spreading TheoryMark Anthony Evangelista Cabrieto100% (1)
- PlatesDocument43 pagesPlatesMerrie Anne BagsicPas encore d'évaluation
- Inqskwela - For March 14-18, 2022Document2 pagesInqskwela - For March 14-18, 2022Rholen LumanlanPas encore d'évaluation
- PhHistory Week 1 11Document48 pagesPhHistory Week 1 11AljohnPas encore d'évaluation
- GW2 Dragon Lore 1-1aDocument55 pagesGW2 Dragon Lore 1-1aRas ButtonPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Document 2Document56 pagesPDF Document 2RiannPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Challenge 2Document130 pagesReading Challenge 2Night NataPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 Disaster Awareness Preparedness and ManagementDocument58 pagesModule 3 Disaster Awareness Preparedness and Managementlouie jay aguadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Test of Standard English (Tose) PreparationDocument28 pagesTest of Standard English (Tose) PreparationAlwan Zahran MajidPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 456 g10Document52 pagesModule 456 g10jean de los santosPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Rescue and Relief OperationsDocument52 pagesBasic Rescue and Relief OperationsArchie French100% (1)
- Catastrophe Eruption at Pinatubo ScriptDocument68 pagesCatastrophe Eruption at Pinatubo ScriptMary Rose PateñoPas encore d'évaluation
- William Angelo - Week-7.AssessmentDocument2 pagesWilliam Angelo - Week-7.Assessmentsup shawtyPas encore d'évaluation
- PHED 213 MODULE PRELIM-okDocument19 pagesPHED 213 MODULE PRELIM-okSarah DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Presentation 1M - Ring of FireDocument9 pagesScience Presentation 1M - Ring of FireKhor Theng ThengPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 1 BarreraDocument40 pagesActivity 1 BarreraCess RiveroPas encore d'évaluation
- Science: Quarter 1 Module 1: Volcanoes, Earthquakes, and Mountain RangesDocument38 pagesScience: Quarter 1 Module 1: Volcanoes, Earthquakes, and Mountain RangesMaria LayupanPas encore d'évaluation
- Red Elk SiteDocument234 pagesRed Elk Sitemadproducer75% (4)
- Exercise 2 - The Ring of FireDocument2 pagesExercise 2 - The Ring of FireAmazing VideosPas encore d'évaluation
- Kisi KisiDocument9 pagesKisi KisiShin OzzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mapping The Ring of FireDocument4 pagesMapping The Ring of Fireapi-251355123Pas encore d'évaluation
- RIPHDocument93 pagesRIPHAngelica MaunahanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Vocabulary Packet (1) 23Document4 pagesUnit 2 Vocabulary Packet (1) 23georgia :DPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesAndrie Vonn Perocho NerpiolPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Layers of EarthDocument18 pages3 Layers of EarthDaddyDiddy Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- THM 101 - Philippine Culture and Tourism Geography - M1L1Document47 pagesTHM 101 - Philippine Culture and Tourism Geography - M1L1Laura AndreaPas encore d'évaluation
- July 15 Science 10 Q1 M1 VolcanoesEarthquakesandMountainRanges Ver6 FINAL PDFDocument40 pagesJuly 15 Science 10 Q1 M1 VolcanoesEarthquakesandMountainRanges Ver6 FINAL PDFEya Guerrero Calvarido80% (5)
- Natural DisastersDocument19 pagesNatural Disasterskuldeep_chand10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ch15 l2 WorksheetDocument7 pagesCh15 l2 WorksheetLegend btdPas encore d'évaluation
- 22-23 Constructive Destructive Study GuideDocument5 pages22-23 Constructive Destructive Study Guideapi-234287636Pas encore d'évaluation
- PLN HSG9 Anh 03Document10 pagesPLN HSG9 Anh 03ekaterinenhatlinh28Pas encore d'évaluation