Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Distribution Channel
Transféré par
Ashish VermaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Distribution Channel
Transféré par
Ashish VermaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DISTRIBUTION
CHANNEL
8/19/15
DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
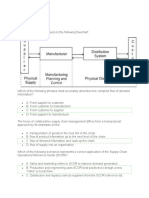
Nature and importance of channels
Most businesses use third parties or intermediaries to bring
their products to market.
They try to forge a "distribution channel" which can be defined
as All the organizations through which a product must
pass between its point of production and consumption
Why does a business give the job of selling its products to
intermediaries?
The answer lies in efficiency of distribution costs. Intermediaries
are specialists in selling. They have the contacts, experience and
scale of operation which means that greater sales can be
achieved than if the producing business tried to run a sales
operation itself.
8/19/15
DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
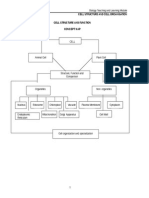
Channel design decisions
Analyzing customer needs
(a) Lot size (b) Waiting and delivery time (c) Spatial convenience
(d) Product variety (e) Service backup
Establishing channel objectives
Channel objectives should be stated in terms of targeted service
output levels. Channel design must take into account the strengths
and weaknesses of different types of intermediaries.
Identifying major channel alternatives
A channel alternative is described by three elements : (a)the types of
available business intermediaries, (b) the number of intermediaries
needed, (c) and the terms and responsibilities of each channel
member.
8/19/15
CHANNEL
Evaluating
major channelDISTRIBUTION
alternatives
Analyzing customer needs
(a)Lot size :
() In buying cars for its fleet, Hertz prefers a channel from
which it can buy a large lot size.
()A Household wants a channel that permits buying a lot
size of one.
8/19/15
DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
(b) Waiting and delivery time
The average time customers of that channel wait for receipt
of the goods. Customers increasingly prefer faster and faster
delivery channels.
8/19/15
DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
(c) Spatial convenience :
The degree to which the marketing channel makes it easy for
customers to purchase the product.
Example : Chevrolet offers greater spatial convenience than
Cadillac, because there are more Chevrolet dealers.
Chevrolets greater market decentralization helps customers save
on transportation and search costs in buying and repairing an
automobile.
8/19/15
DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
(d) Product variety :
The assortment breadth provided by the marketing
channel.
Normally, customers prefer a greater assortment
because more choices increase the chance of finding what
they
need.
United Spirits Limited (USL) is the largest spirits
company in the world by volume, selling 114 million
cases for the fiscal ending March 21, 2011.
8/19/15
DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
(e) Service backup :
The add-on services are the credit, delivery,
installation, repairs and others provided by the channel.
The greater the service backup, the greater the work
provided by the channel.
8/19/15
DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
ablishing channel objectives
Channel objectives are a part of and result from the companys
marketing
objectives that need to be stated in terms of targeted service
output levels.
Profit considerations and asset utilization must be reflected in
channel objectives and the resultant design.
It should be the Endeavour of the channel members to minimize
the total channel costs and still provide with the desired level
ofservice outputs.
For example,
Perishable products require more direct marketing because of
the dangers associated with delays and repeated handling.
Products requiring installation and/or maintenance services are
usually sold and maintained
by the company or exclusively 9
8/19/15
DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
branches dealers.
DISTRIBUTION PROCESS:
8/19/15
DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
10
8/19/15
DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
11
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Distribution Channel Design DecisionsDocument11 pagesDistribution Channel Design DecisionsAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution Channels: Prof. AbhishekDocument18 pagesDistribution Channels: Prof. Abhishekabhi7219Pas encore d'évaluation
- Group1 120923135422 Phpapp02Document16 pagesGroup1 120923135422 Phpapp02vikul bhandariPas encore d'évaluation
- Nature and Importance of Channels Channel Behavior & Organization Channel Design Decisions Channel Management DecisionsDocument16 pagesNature and Importance of Channels Channel Behavior & Organization Channel Design Decisions Channel Management DecisionsSaad BukhariPas encore d'évaluation
- Question One: Choose The Correct AnswerDocument5 pagesQuestion One: Choose The Correct Answerahmedwael79Pas encore d'évaluation
- 18.marketing ChannelsDocument9 pages18.marketing Channelssasithar jaisankaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing the Optimal Channel StructureDocument22 pagesDesigning the Optimal Channel Structureinflibnet inflibnetPas encore d'évaluation
- Channel design decisions and their impactDocument22 pagesChannel design decisions and their impactVINITHA100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - MarketingDocument35 pagesChapter 8 - MarketingKidan AmarePas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing MGT - Module 3 - Delivering ValueDocument23 pagesMarketing MGT - Module 3 - Delivering Valuenoushad kPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 4-Marketing ChannelDocument18 pagesGroup 4-Marketing ChannelBaiju DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- MP 10Document8 pagesMP 10Pei Xin YauPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IV Logistics Management PromotionDocument23 pagesUnit IV Logistics Management PromotionDaniel AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution Value NetworksDocument22 pagesDistribution Value NetworksHarshit Raj KarnaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesMarketing Exam Multiple Choice Questionskarim100% (1)
- Channel Design Decision ParadigmDocument17 pagesChannel Design Decision ParadigmHanchalu LikesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Channels, Supply Chain MgtDocument11 pagesMarketing Channels, Supply Chain MgtSyed Ali XaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- DC QuizDocument6 pagesDC QuizMohammed QatariPas encore d'évaluation
- Channel Selection and Design DesignDocument16 pagesChannel Selection and Design DesignsagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Channel For DistributionDocument17 pagesMarketing Channel For DistributionMahendra PratapPas encore d'évaluation
- Channel Decisions 2Document27 pagesChannel Decisions 2JANICE DMELLOPas encore d'évaluation
- Loyalty Cards Through HPCL Outlets in Bangalore CityDocument83 pagesLoyalty Cards Through HPCL Outlets in Bangalore Cityjitendra jaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Distribution Policy and PlansDocument47 pagesPhysical Distribution Policy and PlansMelese WaktolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution ChannelsDocument21 pagesDistribution ChannelsSavya JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing and Managing Integrated Marketing ChannelsDocument43 pagesDesigning and Managing Integrated Marketing ChannelsIqra KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 5 Sales and DistributionDocument13 pagesUNIT 5 Sales and DistributionJake SullyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 DistributionDocument30 pagesUnit 3 DistributionhaokipPas encore d'évaluation
- MCB-Thao Luan Chu de 7Document4 pagesMCB-Thao Luan Chu de 7NGUYÊN ĐINH NGỌC ÁNHPas encore d'évaluation
- Armstrong Mai08 Im 10Document25 pagesArmstrong Mai08 Im 10AleciafyPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 11 Fall 2014 STMKTG PDFDocument44 pagesWeek 11 Fall 2014 STMKTG PDFfaisal3096Pas encore d'évaluation
- BME Midterm ExaminationDocument5 pagesBME Midterm ExaminationJD BogartPas encore d'évaluation
- E Channels TEST BANK 2Document86 pagesE Channels TEST BANK 2Noor Al JburiPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution ChannelDocument7 pagesDistribution ChanneljuangoogelPas encore d'évaluation
- Channel Design and IMPLEMENTATIONDocument18 pagesChannel Design and IMPLEMENTATIONprateekPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing Marketing ChannelsDocument20 pagesDesigning Marketing ChannelsPamela ZamoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Hofers DPMDocument39 pagesHofers DPMramansharmachdPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 8Document16 pagesCH 8KEDIR USMAELPas encore d'évaluation
- Channels of Distribution: Functions & Types in 40 CharactersDocument7 pagesChannels of Distribution: Functions & Types in 40 Charactersfelize padllaPas encore d'évaluation
- DapAnQuizz 4 MKTDocument93 pagesDapAnQuizz 4 MKTNguyen Duong Tu Quynh (K17 HCM)Pas encore d'évaluation
- 21MB201 LM9Document29 pages21MB201 LM9GOKUL KPas encore d'évaluation
- Channels of DistributionDocument27 pagesChannels of DistributionVinesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12Document21 pagesChapter 12RosyLeePas encore d'évaluation
- UPES MBA CCE TEST - Marketing ManagementdocxDocument32 pagesUPES MBA CCE TEST - Marketing ManagementdocxManjunath Venkatesh100% (2)
- Marketing Channel CocDocument12 pagesMarketing Channel Cocwakjiraworku9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Channel of DistributionDocument22 pagesChannel of DistributionLakkhanRobidasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-10: Marketing Channels Marketing ChannelsDocument4 pagesChapter-10: Marketing Channels Marketing ChannelsMohammad Ashraful AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- L10 - Marketing ChannelsDocument45 pagesL10 - Marketing Channelsjack hoPas encore d'évaluation
- Channel Distribution and Management 1-2 UnitDocument71 pagesChannel Distribution and Management 1-2 UnitRashmi SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Channel Choice - PpsDocument14 pagesFactors Affecting Channel Choice - PpsSmriti KhannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Multi-Channel Distribution QuizDocument3 pagesMulti-Channel Distribution Quizsherryl caoPas encore d'évaluation
- Câu Hỏi Trắc No Đi Thi ScraceDocument70 pagesCâu Hỏi Trắc No Đi Thi ScraceHoàng VũPas encore d'évaluation
- DistributionDocument10 pagesDistributionAnna BrasoveanPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsSatyender Kumar JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Value Chain StrategyDocument21 pagesValue Chain StrategyDonald PicaulyPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Channels FinalDocument18 pagesMarketing Channels FinalGerald Belandres PascuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Channel Function and Flows, Channel Levels, Module 7Document6 pagesChannel Function and Flows, Channel Levels, Module 7shravya kotianPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Three: Channels of Distribution ManagementDocument20 pagesChapter Three: Channels of Distribution ManagementmuhdfirdausPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution Channels: ABHINAV (18157) MEHAK (18185)Document41 pagesDistribution Channels: ABHINAV (18157) MEHAK (18185)Abhinav AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Channels of Distribution: The Marketing Executive's Complete GuideD'EverandManaging Channels of Distribution: The Marketing Executive's Complete GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Unlock Multi-Channel Profits: Proven Strategies for Business GrowthD'EverandUnlock Multi-Channel Profits: Proven Strategies for Business GrowthPas encore d'évaluation
- UnemploymentDocument22 pagesUnemploymentAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alibaba's giant $25 billion IPODocument6 pagesAlibaba's giant $25 billion IPOAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Green LogisticsDocument19 pagesGreen LogisticsAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Service ProcessesDocument4 pagesService ProcessesAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- BPSM PPT ReviewDocument9 pagesBPSM PPT ReviewAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- MedisysDocument6 pagesMedisysAshish Verma100% (1)
- AIC NetbooksDocument7 pagesAIC NetbooksAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Federal ExpressDocument21 pagesFederal ExpressAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Foldrite Furniture Co.: Planning To Meet A Surge in DemandDocument7 pagesFoldrite Furniture Co.: Planning To Meet A Surge in DemandAshish Verma0% (1)
- GalanzDocument9 pagesGalanzAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Icici Securities LTDDocument21 pagesIcici Securities LTDAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- CSR Jindal SteelDocument16 pagesCSR Jindal SteelAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- AIC NetbooksDocument7 pagesAIC NetbooksAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Regulation of Food Industry in IndiaDocument6 pagesRegulation of Food Industry in IndiaAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fed ExDocument14 pagesFed ExAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete - Kit Updated 2014-16Document28 pagesComplete - Kit Updated 2014-16Ashish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microsoftcorporation BcommDocument15 pagesMicrosoftcorporation BcommAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- CSR Jindal SteelDocument16 pagesCSR Jindal SteelAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Report e LearningDocument75 pagesReport e LearningAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alibaba's giant $25 billion IPODocument6 pagesAlibaba's giant $25 billion IPOAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Woman SafetyDocument6 pagesWoman SafetyAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amul CSD PresentationDocument14 pagesAmul CSD PresentationAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- AlibabaDocument17 pagesAlibabaAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microsoftcorporation BcommDocument15 pagesMicrosoftcorporation BcommAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Budget On FMCG SectorDocument8 pagesImpact of Budget On FMCG SectorAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Loft Securities: Why Doesn't This HR Department Get Any Respect?Document9 pagesLoft Securities: Why Doesn't This HR Department Get Any Respect?Ashish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- FedEx Worldwide Logistics and Delivery ServicesDocument18 pagesFedEx Worldwide Logistics and Delivery ServicesAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyber CrimeDocument15 pagesCyber CrimeAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Budget On FMCG SectorDocument8 pagesImpact of Budget On FMCG SectorAshish VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bildiri Sunum - 02Document12 pagesBildiri Sunum - 02Orhan Veli KazancıPas encore d'évaluation
- Exhibit 1 18 116 PDFDocument27 pagesExhibit 1 18 116 PDFSimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Teamcenter 10.1 Business Modeler IDE Guide PLM00071 J PDFDocument1 062 pagesTeamcenter 10.1 Business Modeler IDE Guide PLM00071 J PDFcad cad100% (1)
- Architecture Vernacular TermsDocument3 pagesArchitecture Vernacular TermsJustine Marie RoperoPas encore d'évaluation
- Art of Editing PDFDocument8 pagesArt of Editing PDFpremPas encore d'évaluation
- 3RT10241AB00 Datasheet enDocument7 pages3RT10241AB00 Datasheet enanon_92005543Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manual For Master Researchpproposal - ThesisDocument54 pagesManual For Master Researchpproposal - ThesisTewfic Seid100% (3)
- H. P. Lovecraft - The Music of Erich ZannDocument14 pagesH. P. Lovecraft - The Music of Erich ZannMarco BologniniPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 5420 5 General Food Defense PlanDocument11 pagesForm 5420 5 General Food Defense PlanBenjamin AlecPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 (Teacher)Document19 pagesChapter 2 (Teacher)ajakazPas encore d'évaluation
- A 231 - A 231M - 15 PDFDocument4 pagesA 231 - A 231M - 15 PDFأسامة وحيد الدين رمضانPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive Relay PDFDocument3 pagesAutomotive Relay PDFSimon MclennanPas encore d'évaluation
- 28/08/2016 1 Advanced Research Methodology... RU, Bangalore-64Document38 pages28/08/2016 1 Advanced Research Methodology... RU, Bangalore-64Ananthesh RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo Bombas PedrolloDocument80 pagesCatalogo Bombas PedrolloChesster EscobarPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Cisco - DPC3925Document106 pagesManual Cisco - DPC3925HábnerTeixeiraCostaPas encore d'évaluation
- MF Formula Sheet - FullDocument10 pagesMF Formula Sheet - FullublehkogeniusPas encore d'évaluation
- Consular Assistance For Indians Living Abroad Through "MADAD"Document12 pagesConsular Assistance For Indians Living Abroad Through "MADAD"NewsBharatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gabi InfoDocument21 pagesGabi Infoangel antoinette dagoyPas encore d'évaluation
- TBEM CII Exim Bank Award ComparisonDocument38 pagesTBEM CII Exim Bank Award ComparisonSamPas encore d'évaluation
- Rate of Change: Example 1 Determine All The Points Where The Following Function Is Not ChangingDocument5 pagesRate of Change: Example 1 Determine All The Points Where The Following Function Is Not ChangingKishamarie C. TabadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Global POVEQ NGADocument2 pagesGlobal POVEQ NGABonifacePas encore d'évaluation
- 7.1 (149 Marks) : MarkschemeDocument51 pages7.1 (149 Marks) : MarkschemeSemwezi Enock100% (1)
- Project Close OutDocument12 pagesProject Close OutWeel HiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 150 C++ BitsDocument55 pages150 C++ BitsRavi Varma D V SPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Nighttime Image Enhancement Using A NewDocument7 pages5 Nighttime Image Enhancement Using A NewNithish CenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Relief Scenarios: Contingency DataDocument3 pagesSummary of Relief Scenarios: Contingency Dataimtinan mohsinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 ResearchDocument14 pagesChapter 2 ResearchabibualPas encore d'évaluation
- MCT-MST Formative Report Form 2bashaer AwadDocument9 pagesMCT-MST Formative Report Form 2bashaer Awadapi-315648941Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine MaintenanceDocument146 pagesGas Turbine MaintenanceMamoun1969100% (8)
- Sales TAX FORMATDocument6 pagesSales TAX FORMATMuhammad HamzaPas encore d'évaluation