Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Power Electronics: Dr. Abdul Majid
Transféré par
Adnankhan BangashDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Power Electronics: Dr. Abdul Majid
Transféré par
Adnankhan BangashDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Power Electronics
Dr. Abdul Majid
M.Sc Electronics: University of Peshawar
MS System on Chip Linkoping University Sweden
PhD Mid Sweden University Sweden
Professional titles
Chartered Engineer (CEng) Engineering Council UK
Professional Engineer (P.E) Pakistan Engineering Council
What is power electronics?
Definition
Power Electronics: is the electronics applied to conversion and control of
electric power.
Power Electronics is used to change the characteristics (voltage and current
magnitude and/or frequency) of electrical power to suit a particular
application.
A more exact explanation:
The primary task of power electronics is to process and control the flow
of electric energy by supplying voltages and currents in a form that is
optimally suited for user loads.
Range of power scale :
milliwatts(mW)
Megawatts(MW)
Gigawatts(GW)
Power electronics versus Linear Electronics
Linear Electronics
Power semiconductor
devices are operated in linear
region
Line frequency transformers
are used
Each linear regulator has an
average energy efficiency of
3550%
Power Electronics
Power semiconductor devices
are operated in active or cut-off
region
High frequency transformers
are used
Power loss is minimum hence
higher energy efficiency can be
Linear versus Switch Mode Power
Supply (SMPS)
Role of Power Electronics
Process and control the flow of electric energy
Source
Power output
Power input
Vi
ii
Electric utility
battery
other electric energy source
power converter
Power
Converter
io
Vo
Load
Electric Motor
light
Measurements
heating
Controller
other electric equipment
Reference power converter
Power Unit
Power semiconductor devices
Magnetics, capacitors
Control Unit
Linear Ics, Digital signal Processors
Load
Linear Ics, Digital signal Processors
Desirable features of Power
Conversion Process
Reduced Power loss
High energy efficiency
Lowers the operating cost
of converter
Reduced heat sink
requirement
Reduction of size, weight
and cost
Low Electromagnetic
emissions
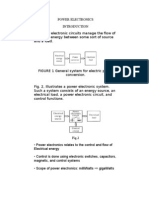
Generic structure of a power electronic
system
Control is invariably required. Power converter along with its
controller including the corresponding measurement and interface
circuits, is also called power electronic system.
Power
input
Feedforward
( measurements
of input signals )
Power
Converter
Control input
Controller
Reference
Power
output
Feedback
(measurements
of output signals )
A typical power electronic system
Source
Power output
Power input
Vi
ii
Electric utility
battery
other electric energy source
power converter
Power
Converter
io
Measurements
Controller
Reference
Vo
Load
Electric Motor
light
heating
other electric equipment
power converter
Modern SMPS requirements
Compact and light weight
High energy density and energy
efficiency
Low Electromagnetic Interference
Fig. 1
Challenges
Power Transformer
Line Filter
Selection of suitable converter topology
Influence of parasitic elements and PCB layout
Proportional relationship between switching
frequency and switching loss in semiconductor
devices
Fig. 2
9
Interdisciplinary nature of Power Electronics
Circuit Ct
theory
Electric
machines
Power
systems
Systems&
Control theory
Signal
processing
Control
theory Power
electronics
electr
oni
cs
Electromagnetics
electr
Simulation &
computing
electronics
Solid state
physics
History of power semiconductor
devices
Power diodes (or rectifiers)
Bipolar transistor 1948
Power BJT (bipolar junction transistor) - 1960
Thyristor or SCR (Silicon controlled rectifier) 1957
Power MOSFETs (Metal oxide semiconductor
field effect transistor) - 1970
IR 400V 25A power MOSFET 1978
IGBT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) 1990
a hybrid between a MOSFET and a BJT
Applications of Power Electronics
Transportation
Electric/ Hybrid Electric
Vehicles
Electric Locomotives
Electric Trucks, Buses,
Construction
Aircraft power systems
Ship power systems
Applications of Power Electronics
Industrial/ Commercial
Motor drive systems
Electric machinery and
tools
Pumps/ compressors
Process control
Factory automation
Applications of Power Electronics
Consumer Products
Air conditioners/ Heat
pumps
Computers
Lighting
Telecommunications
Uninterruptible power
supplies
Battery chargers
Applications of Power Electronics
Utilities
Generating systems
Grid interface for alternative
energy resources (solar, wind,
fuel cells, etc.)
HVDC
Solid state transformer
Solid state fault current limiter
Solid state circuit breaker
Project Design Flow Chart
Theoretical &
feasibility
study(Conceptualization)
Simulation
Model
Circuit
Implementatio
n
Optimization
Unsatisfactory
results
Optimization
Unsatisfactory
results
Final prototype
16
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lec-1 Scope of Power ConvertersDocument26 pagesLec-1 Scope of Power Convertersjameelahmad100% (1)
- Industrial ElectronicsDocument108 pagesIndustrial ElectronicsChristian Dave TamparongPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics and Input RelayDocument7 pagesPower Electronics and Input RelayDaus EmersansPas encore d'évaluation
- Power ElectronicsDocument28 pagesPower Electronicspavan96100% (5)
- Circuits Devices and ApplicationsDocument30 pagesCircuits Devices and ApplicationsTe NgPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument6 pagesIntroductionJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document31 pagesUnit 1bilal alkhPas encore d'évaluation
- Power ElectronicsDocument30 pagesPower ElectronicsRohit SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson #2 Introduction To Power Electronics-2Document17 pagesLesson #2 Introduction To Power Electronics-2Nyoka DunnPas encore d'évaluation
- Relation With Multiple Disciplines: Oni CsDocument5 pagesRelation With Multiple Disciplines: Oni CsHossein DavijaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Power ElectronicsDocument32 pagesPower ElectronicsmnamkyPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics: Semester 7 Electronics Engineering: What Is Power Electronics and Explain Its Block Diagram?Document6 pagesPower Electronics: Semester 7 Electronics Engineering: What Is Power Electronics and Explain Its Block Diagram?Asha DurafePas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronic System PDFDocument10 pagesPower Electronic System PDFMohd HakimPas encore d'évaluation
- ECEg 7411 Lecture 1 Introduction Advanced Power ElectronicsDocument14 pagesECEg 7411 Lecture 1 Introduction Advanced Power Electronicsbisrat yeshidagnaPas encore d'évaluation
- EEE 338 Power ElectronicsDocument28 pagesEEE 338 Power ElectronicsdaudPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1Document12 pagesLecture 1Mouath AlsebaiePas encore d'évaluation
- Power ElectronicsDocument29 pagesPower Electronicsgrbavithra100% (1)
- Lecture1 Syllabus IntroDocument21 pagesLecture1 Syllabus Introperumburesuresh3762Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1-Transducers & PLC: SyllabusDocument29 pagesModule 1-Transducers & PLC: SyllabusRaja G VPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronicsanon_514500460Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics PPT 1st Module (Autosaved)Document61 pagesPower Electronics PPT 1st Module (Autosaved)chetan100% (1)
- 6305ele S1L1Document33 pages6305ele S1L1M Moiz IlyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof. Dr. Tahir Izhar: Lecture-1Document15 pagesProf. Dr. Tahir Izhar: Lecture-1Engr MohsinPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronic:: Dr. F. Danang Wijaya, ST, MT Lab. TTLDocument18 pagesPower Electronic:: Dr. F. Danang Wijaya, ST, MT Lab. TTLVeby Enandes StalonyPas encore d'évaluation
- l1 Introduction To Power Electronics 130627131834 Phpapp02 PDFDocument15 pagesl1 Introduction To Power Electronics 130627131834 Phpapp02 PDFGanesh Dharmireddy100% (1)
- 1.2 Applications of Power ElectronicsDocument7 pages1.2 Applications of Power ElectronicsSwamy100% (1)
- Power Converter and Its TopologiesDocument13 pagesPower Converter and Its TopologiesAkshit SamadhiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Purdue ECE 433 - Lecture 1Document25 pagesPurdue ECE 433 - Lecture 1John DoePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Power SuppliesDocument7 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To Power SuppliesBricksoe NgwenyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsSiddarameshwara HNPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 1Document27 pagesPart 1Mustafa AlhumayrePas encore d'évaluation
- Notes 01 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument138 pagesNotes 01 Introduction To Power ElectronicsPARTHIBAN.BPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Notes 2Document36 pagesModule 1 Notes 2canusha820Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Power Electronics, History & Applications (1), Semiconductor Devices EtcDocument73 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronics, History & Applications (1), Semiconductor Devices Etckomal phulpotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics IntroductionDocument38 pagesPower Electronics IntroductionOmar Bin ShehabPas encore d'évaluation
- On Power ElectronicsDocument30 pagesOn Power ElectronicsMuhammed Ahmed93% (41)
- (524567096) l1 Introduction To Power Electronics 130627131834 Phpapp02Document15 pages(524567096) l1 Introduction To Power Electronics 130627131834 Phpapp02Gaby FilipescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To PE L1Document29 pagesIntroduction To PE L1Subhash MurkutePas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Department of Electronics & Electrical Engineering Electronics & Electrical EngineeringDocument27 pagesDepartment of Department of Electronics & Electrical Engineering Electronics & Electrical EngineeringSunil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument38 pagesLec 1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsAfiqah Zainuddin100% (1)
- EE 303 Introduction 2013Document49 pagesEE 303 Introduction 2013vepnisxaPas encore d'évaluation
- Over and Under Voltage Protection RelayDocument44 pagesOver and Under Voltage Protection RelaySeven Hills100% (3)
- Pe IntroductionDocument31 pagesPe IntroductionJunaxic MuxicPas encore d'évaluation
- PowerElec-Course Outline Intro Assign1Document15 pagesPowerElec-Course Outline Intro Assign1Ndunya WestleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics FinalDocument470 pagesPower Electronics FinalAyushmaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1Document69 pagesLecture 1kaybeall7584Pas encore d'évaluation
- EEE4040 Power Electronics - 2022Document71 pagesEEE4040 Power Electronics - 2022kj bull j rayPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter1 PDFDocument18 pagesChapter1 PDFANKIT KUMAR SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronic Module - Chapter 1Document27 pagesPower Electronic Module - Chapter 1jayxcell100% (1)
- Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument6 pagesPower Semiconductor DevicesNassor Nassor APas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsRajaiah JagariPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution of Power Electronics Engineering PDFDocument7 pagesEvolution of Power Electronics Engineering PDFMahesh VadhavaniyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems, Fundamentals and Hard-switching ConvertersD'EverandPower Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems, Fundamentals and Hard-switching ConvertersPas encore d'évaluation
- Soft Switching Boost Converter With MPPT For Solar (1) 2233Document29 pagesSoft Switching Boost Converter With MPPT For Solar (1) 2233satheesh_240Pas encore d'évaluation
- 01 - Introduction To Multilevel InvertersDocument53 pages01 - Introduction To Multilevel InvertersAnnas QureshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1-18EE53-NotesDocument20 pagesModule 1-18EE53-NotesAshwiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageAdvanced Power ElectronicshoangductuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Power 1Document6 pagesPower 1john enockPas encore d'évaluation
- 30 WattDocument81 pages30 WattMadham KondaiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce2202 - Mechanics of FluidsDocument3 pagesCe2202 - Mechanics of FluidsPrashant GaradPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Circular ShaftDocument7 pagesDesign of Circular Shaftจอม อรรฐาเมศร์Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math Formula SheetDocument8 pagesMath Formula SheetHidayah TeacherPas encore d'évaluation
- Honda IDSI SM - 5 PDFDocument14 pagesHonda IDSI SM - 5 PDFauto projectPas encore d'évaluation
- Spelling RulesDocument5 pagesSpelling RulesvijthorPas encore d'évaluation
- ELEMAGDocument1 pageELEMAGJasper BantulaPas encore d'évaluation
- LCS21 - 35 - Polar PlotsDocument14 pagesLCS21 - 35 - Polar Plotsgosek16375Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ap Unit 1 NotesDocument42 pagesAp Unit 1 NotesDhruv GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Histograms - 2Document6 pagesHistograms - 2Sonia HalepotaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hot and Cold ApplicDocument33 pagesHot and Cold Appliccamille_12_15100% (1)
- Mackie USB Driver InstructionsDocument4 pagesMackie USB Driver InstructionsSamuel CotoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Perform Industry CalculationsDocument90 pages3 Perform Industry CalculationsRobinson ConcordiaPas encore d'évaluation
- AtomDocument15 pagesAtomdewi murtasimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ace Om 230Document3 pagesAce Om 230michaelliu123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 - EarthingDocument26 pagesUnit 6 - Earthinggautam100% (1)
- Programming For Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesProgramming For Problem SolvingAPOLLO Sem 4 I.T.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rekonfigurasi Jaringan Distribusi Radial Untuk Mengurangi Rugi Daya Pada Penyulang Jatirejo Rayon Mojoagung Menggunakan Metode BinaryDocument4 pagesRekonfigurasi Jaringan Distribusi Radial Untuk Mengurangi Rugi Daya Pada Penyulang Jatirejo Rayon Mojoagung Menggunakan Metode BinaryNurindra CahyantaPas encore d'évaluation
- IIM Nagpur Test 1 Version 1 2016Document6 pagesIIM Nagpur Test 1 Version 1 2016Saksham GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- 15Document20 pages15Allen Rey YeclaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle Goldengate: Oracle Installation and Setup Guide 11 Release 2 (11.2.1.0.0)Document188 pagesOracle Goldengate: Oracle Installation and Setup Guide 11 Release 2 (11.2.1.0.0)kashifmeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Apl 220014Document2 pagesApl 220014Elprince MidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ims PrecalDocument10 pagesIms PrecalRhea GlipoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrocarbon RecoveryDocument29 pagesHydrocarbon RecoveryAlekhya BandaruPas encore d'évaluation
- DLP Mathematics 6 q1 w6Document5 pagesDLP Mathematics 6 q1 w6Kathlyn PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ugc Model Curriculum Statistics: Submitted To The University Grants Commission in April 2001Document101 pagesUgc Model Curriculum Statistics: Submitted To The University Grants Commission in April 2001Alok ThakkarPas encore d'évaluation
- C V RamanDocument8 pagesC V RamanJayesh KomalwarPas encore d'évaluation
- S406 Specifications For The Supply of Stone PDFDocument6 pagesS406 Specifications For The Supply of Stone PDFMfanelo MbanjwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Refining Corrosion Technologist NACE-RCT-001: NACE Cathodic Protection Technician (CP 2) Written ExamDocument16 pagesRefining Corrosion Technologist NACE-RCT-001: NACE Cathodic Protection Technician (CP 2) Written Examshoaib1985100% (1)
- Introduction To PIC and Embedded SystemsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To PIC and Embedded Systemsheno ahPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Principles of Rigid and Flexible PavementsDocument66 pagesDesign Principles of Rigid and Flexible PavementsWycliffe otienoPas encore d'évaluation