Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Mintz Berg Ten School of Thought For Strategy Formation
Transféré par
NawafZaferTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Mintz Berg Ten School of Thought For Strategy Formation
Transféré par
NawafZaferDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
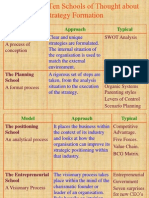
Mintzbergs Ten Schools of Thought about Strategy
Formation
Model
The Design
School
A process of
conception
Approach
Clear and unique strategies
are
formulated. The internal
situation of
the organisation is used to
match
Basis
Architectur
e
as a
metaphor.
the external environment.
Contributions
Order.
Reduced ambiguity.
Useful in relatively stable
environment
Limitations
Simplification may distort reality.
Typical
SWOT Analysis
Strategy has many variables and is
inherently
complex.
Ashridge Mission
Model
Support strong and visionary
Bypassing learning, inflexible in fastchanging
leadership.
environment.
High risk of resistance
The Planning
School
A formal process
A rigorous set of steps are
taken,
from the analysis situation to
the
execution of the strategy
Urban
Gives clear direction.
Can become too static
Theory of Mechanistic
planning,
Enables resource allocation.
Risk of groupthink
and Organic Systems
system
Control
Predicting is difficult
Parenting styles
Top Management must create strategy
from an
ivory tower
SAME AS PLANNING SCHOOL.
Levers of Control
Scenario Planning
theory,
cybernetics
The Positioning
School
An analytical
process
It places the business within
the
context of its industry and
looks at
how the organisation can
improve its
strategic positioning within
that
industry
Industrial
organisatio
n
and military
strategy
Strategic Management is a
science.
Provides content in a systematic
way to
the existing way of looking at
strategy
Focus on hard facts.
Particularly useful in early stage
of
strategy development, when
date is
Neglects
power, politics, culture, social
perspective
elements.
Is biased towards large firms.
Number-oriented.
Competitive
Advantage.
Five Forces.
Value Chain
BCG Matrix.
Game Theory.
The Art of War (Sun
Tzu)
analysed.
The
Entrepreneurial
School
The visionary process takes
place
within the mind of the
charismatic
A visionary rudykameereddy@gmail
founder or leader of an
process
.com organisation.
Rely heavily on intuition,
judgement,
wisdom, experience and
Economics
A sound vision and a visionary
CEO can
help organisation to sail
cohesively
Sailing a predefined course can blind
someone
for potential developments or
unexpected
through muddy waters especially dangers.
in
early or very difficult years for
the
organisation.
Entrepreneurial
Government
Seven
surprises for
Page
new1
How to find the right leader?
CEOs
Entrepreneurial, visionary leaders have a Leadership styles
Mintzbergs Ten Schools of Thought about Strategy
Formation
Mod
el
The Cognitive
School
A mental
process
Approa
ch people perceive
Analyses how
patterns and process
information. Concentrates on
what is happening in the
mind of the strategist and
how it processes the
information
Bas
is
Psycholo
gy
The Learning
School
An emergent
process
Management pays close
attention over time to
what does work and what
does not work. They
incorporate lessons
learned into their overall
plan of action.
The world is too complex
to allow strategies to be
developed all at once.
As clear plans or visions.
Strategies must emerge
in small
steps
The
strategy
is as
developed as
organisation
or
a process of adapts
negotiation
learns. power holders
between
within the company, and/or
between the company and its
external stakeholders.
Educatio
n.
Learning
Theory
The Power
School A
process of
negotiation
Tries to involve various
groups and departments
within the company.
Strategy formation is
viewed as a fundamentally
collective and cooperative
process.
The strategy that is
developed is a reflection of
rudykameereddy@gmail
the corporate culture of
The Cultural
School
A collective
process
.com
Politic
al
Scienc
e
Anthropolo
gy
Contributi
onsas a cognitive
Sees strategy
process in the mind of the
strategist.
Strategies emerge as
concepts, maps, schemas
and frames of reality.
Stresses the creative side of
the strategy process. Strong
at the level of an individual
strategist.
Offers
a solution to deal
Very
to explain
with useful
complexity
and why
our minds are imperfect.
unpredictability
in strategy
formation.
More people can learn than
just the leader.
No need for omnipotent
leader.
Can be combined with
emergent views. Strong in
complex conditions with
continuous change.
Can
help
to let the strongest
Strong
professional
organisations.
people
survive in the
corporate jungle.
Can help to ensure that all
sides of an issue is fully
debated.
Can help to break through
obstacles to necessary
change.
Democratic.
Can help to decrease
resistance after a decision is
made.
Emphasises
the crucial role
Realistic.
that
social processes,
Particularly
useful to beliefs
and
values are
playing in
understand
Strategic
decision-making
and in and
Alliances, Joint-Ventures
strategy
formation.Analysis.
to do Stakeholder
Explains resistance to strategic
change and helps to deal with
mergers and acquisitions.
Limitati
onsbeyond the
Not very practical
conceptual stage. Not very practical
to conceive great ideas or strategies.
Currently not useful to guide
collective strategy processes.
Typic
al
Whole Brain
Model Johari
Window
Groupthink
Cognitive Bias
Myers-Briggs
Type Indicator
Could lead to having no strategy or
just doing some tactical
manoeuvring.
Not useful at all during crises.
Not very useful in stable conditions.
Taking many sensible steps does not
add up to a sound overall strategy.
There are costs associated with
learning.
Organisational
Learning Forget
Borrow Learn
Framework
Knowledge
Management SECI
Model
Politics can be divisive, uses a lot
of energy, causes wastage and
distortion and is costly. Can lead
to aberrations.
Can lead to having no strategy or
just
doing
some
tactical
manoeuvring.
Overstates the role of power in
strategy formation.
Bases of Social
Power Power
Distance
Stakeholder
Value
Perspective
Core Group
Theory Force
Field Analysis
Stakeholder
Mapping
Vague, can feed resistance to change
and can be misused to justify statusquo.
Give few clues on how things should
become.
Appreciative
Inquiry Cultural
Dimensions
Cultural
Intelligence
Ashridge Mission
Model
Page
2
Mintzbergs Ten Schools of Thought about Strategy
Formation
the organisation.
Model
The
Environmental
School
A reactive process
The
Configuration
School
A process of
transformati
on
Approach
The strategy is a response to
the
challenges imposed by the
external environment.
Where the other schools
sees the environment as a
factor, the Environmental
School sees it as an actor.
Strategy formation is a
process of
transforming the
organisation from one type
of decision-making
structure to another.
Source:
12manage.com
rudykameereddy@gmail
.com
Basis
Biology
Contributions
Give a central role to the
environment
in strategy formation
Limitations
The dimension of the environment is
often vague
and aggregated. This renders it less
useful for strategy formation.
Denies real strategic choice for
organisations. Unrealistic
Typical
Contingency Theory
Situational
Leadership
Context
Strategy and organisational
shape
(Organisational
development) are closely
integrated and should be
reconciled.
An organisation can be
described in terms of some
stable configuration of its
characteristics, which it adopts
for a period of time in a
particular type of context. This
causes it to behave in
particular ways, that give rise
to a particular set of
strategies.
The period of stability are
interrupted occasionally by
some process of
transformation.
Key to strategic management is
most of the time: to sustain
stability, or at least adaptable
strategic change, but
periodically there is a need for
transformation and to be able
to manage that disruptive
process without destroying he
organisation.
The way of strategy
formation must adapt to its
own time and context, while
it takes one or more of the
10 mentioned forms. Hence
strategy formation itself has
configurations.
In reality there are many shades of grey,
not just
a limited number of valid configurations.
The pattern is in the eye of the beholder,
if you
describe reality by using configurations,
then you are distorting reality to be
able to explain it.
Organisational
Configurations
Chaos Theory
Catastrophe
Theory Disruptive
Innovations
Page
3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Business Process Outsourcing Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionD'EverandBusiness Process Outsourcing Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- Stakeholder Analysis A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionD'EverandStakeholder Analysis A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- Mintzberg's Ten Schools of Thought About Strategy FormationDocument7 pagesMintzberg's Ten Schools of Thought About Strategy Formationbtec1005mPas encore d'évaluation
- Schools of StrategyDocument25 pagesSchools of StrategyismailPas encore d'évaluation
- Ansoff Revisited: How Ansoff Interfaces With Both The Planning and Learning Schools of Thought in StrategyDocument24 pagesAnsoff Revisited: How Ansoff Interfaces With Both The Planning and Learning Schools of Thought in Strategyaappaarr100% (1)
- Business Models Origin Development and Future Research PerspectivesDocument19 pagesBusiness Models Origin Development and Future Research PerspectivesHarris DianPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6 - Moving The NeedleDocument9 pagesModule 6 - Moving The Needleapi-413069794Pas encore d'évaluation
- Johari WindowsDocument9 pagesJohari WindowssubratabanerjeePas encore d'évaluation
- 11 - Chapter - 2Document47 pages11 - Chapter - 2SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic ManagementDocument34 pagesStrategic ManagementDewi PuspitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mapping Strategic DiversityDocument26 pagesMapping Strategic Diversitybozzaitabob4493100% (1)
- Least Preferred Coworker ScaleDocument2 pagesLeast Preferred Coworker ScaleOmar Oudeh100% (1)
- Management School of ThoughtDocument36 pagesManagement School of ThoughtAckah OwusuPas encore d'évaluation
- CHP 7 Strategy and StructureDocument21 pagesCHP 7 Strategy and StructureBBHR20-A1 Wang Jing TingPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovation and Firm Performance Research ReportDocument67 pagesInnovation and Firm Performance Research ReportSaad Salih HusseinPas encore d'évaluation
- MBA Operational Management Dissertation Writing ServicesDocument2 pagesMBA Operational Management Dissertation Writing ServicesvasiacpPas encore d'évaluation
- Competitive StrategiesDocument44 pagesCompetitive StrategiesAmit GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pfeffer (2005) Producing Sustainable PDFDocument15 pagesPfeffer (2005) Producing Sustainable PDFdoncupidPas encore d'évaluation
- AnsoffDocument4 pagesAnsoffrodrigoaltair100% (1)
- Analyzing the Internal EnvironmentDocument56 pagesAnalyzing the Internal EnvironmentAbel RonaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Revolution of Thought - A Iain McGilchrist LectureDocument14 pagesA Revolution of Thought - A Iain McGilchrist LectureMarioPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Marketİng - The Core ConceptsDocument10 pagesWhat Is The Marketİng - The Core Conceptskhare43Pas encore d'évaluation
- ORGANIZATIONAL RESTRUCTURING AND ITS CONSEQUENCES: Rhetorical and StructuralDocument19 pagesORGANIZATIONAL RESTRUCTURING AND ITS CONSEQUENCES: Rhetorical and StructuralSilvio CandidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategy LensesDocument1 pageStrategy Lensesnawalbakou100% (2)
- 1993EvaluatingBusiness RumeltDocument11 pages1993EvaluatingBusiness RumeltAhsan MujeebPas encore d'évaluation
- How Organizational Capability Leads To Competitive Advantage Through Core CompetenceDocument29 pagesHow Organizational Capability Leads To Competitive Advantage Through Core CompetenceAnthony Cappucci100% (8)
- MintzbergDocument4 pagesMintzbergdan2donPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing the Challenges of Matrix OrganizationsDocument6 pagesManaging the Challenges of Matrix Organizationsomgan1042Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organizational Theory, Design, and Change: Decision Making, Learning, Knowledge Management, and Information TechnologyDocument19 pagesOrganizational Theory, Design, and Change: Decision Making, Learning, Knowledge Management, and Information TechnologymidoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic HR Management Key for SME Success in SerbiaDocument14 pagesStrategic HR Management Key for SME Success in SerbiaDavid Susilo NugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaining Competive Advantage Through Human ResourcesDocument7 pagesGaining Competive Advantage Through Human ResourcesThanChan ShimrayPas encore d'évaluation
- Determinants of Organizational Effectiveness inDocument11 pagesDeterminants of Organizational Effectiveness indecker4449Pas encore d'évaluation
- Criticisms of MaslowDocument3 pagesCriticisms of MaslowNathalie Presillas100% (1)
- Chapter Three: Competitor AnalysisDocument22 pagesChapter Three: Competitor AnalysisANDELYNPas encore d'évaluation
- Meeting A Preferred Future - A Case Study of Tennis Canada - Richard NormanDocument65 pagesMeeting A Preferred Future - A Case Study of Tennis Canada - Richard NormanRichard Norman100% (2)
- The Strategy Clock, Value Chain and Porter's Five Forces ExplainedDocument6 pagesThe Strategy Clock, Value Chain and Porter's Five Forces ExplainedChristophe Dormenval100% (1)
- The Future of WorkDocument24 pagesThe Future of WorkMoinak Sarkar100% (1)
- A Study On Value Innovation Strategies of China's Economy Hotel IndustryDocument5 pagesA Study On Value Innovation Strategies of China's Economy Hotel IndustryjessicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Organizational Strategy Structure and ProcessDocument18 pagesOrganizational Strategy Structure and ProcessmncoutinhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Brand Positioning GuideDocument30 pagesBrand Positioning GuidePruthviraj RathorePas encore d'évaluation
- Organizational Theory Design DevelopmentDocument4 pagesOrganizational Theory Design DevelopmentXeenPas encore d'évaluation
- A General Summary of Organizational BehaviorDocument41 pagesA General Summary of Organizational BehaviorDr. Kerem KoseogluPas encore d'évaluation
- STR348 - Week 2 - Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument31 pagesSTR348 - Week 2 - Introduction To Operations ManagementMeglena Velevska50% (2)
- Matching People With Organizational CultureDocument7 pagesMatching People With Organizational Culturezara_Pas encore d'évaluation
- Functional StrategyDocument35 pagesFunctional StrategyvishakhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Organisational Behaviour - BBA SEM1Document116 pagesOrganisational Behaviour - BBA SEM1winallPas encore d'évaluation
- Creative Forces of Self Organization CompactDocument28 pagesCreative Forces of Self Organization CompactWombatenPas encore d'évaluation
- OCEAN Personality ScaleDocument3 pagesOCEAN Personality ScaleBushra ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic CapabilityDocument34 pagesStrategic CapabilityMetta PadmaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diversification Strategy AssignmentDocument6 pagesDiversification Strategy Assignmentisra robinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Choices 7: Corporate Strategy and DiversificationDocument15 pagesStrategic Choices 7: Corporate Strategy and DiversificationKhin Sandar Tun0% (1)
- The Strategy ProcessDocument34 pagesThe Strategy ProcessOliver SalacanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vision Subject Strategic ManagementDocument6 pagesVision Subject Strategic ManagementabrarPas encore d'évaluation
- Blue Ocean Simulation: StrategyDocument38 pagesBlue Ocean Simulation: StrategyArif Kamal BasyariahPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Organisational PsychologyDocument31 pagesIndustrial Organisational PsychologyDeepak Sah100% (1)
- Business Acumen Accelerates Strategy ExecutionDocument2 pagesBusiness Acumen Accelerates Strategy ExecutionAshchrisPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Competitive Intelligence and Its Subtypes On Achieving Market PerformanceDocument16 pagesThe Role of Competitive Intelligence and Its Subtypes On Achieving Market PerformanceBruna StippPas encore d'évaluation
- The Power of Networking for Entrepreneurs and Founding TeamsDocument28 pagesThe Power of Networking for Entrepreneurs and Founding TeamsAngela FigueroaPas encore d'évaluation
- Competitive AdvantageDocument60 pagesCompetitive AdvantageFibin Haneefa100% (1)
- Emerging Themes and Contemporary Issues in Management PracticesDocument11 pagesEmerging Themes and Contemporary Issues in Management PracticesEmma AllisonPas encore d'évaluation
- UAB "Digiteka": Invoice DGTP 00170423Document1 pageUAB "Digiteka": Invoice DGTP 00170423NawafZaferPas encore d'évaluation
- Cry To Cry: HFJHSQFKQSJFKJQSMJFKJSQDocument1 pageCry To Cry: HFJHSQFKQSJFKJQSMJFKJSQNawafZaferPas encore d'évaluation
- Cry To Cry: HFJHSQFKQSJFKJQSMJFKJSQDocument1 pageCry To Cry: HFJHSQFKQSJFKJQSMJFKJSQNawafZaferPas encore d'évaluation
- Getting JudgeDocument1 pageGetting JudgeNawafZaferPas encore d'évaluation
- M0945019-Justice-This Land Is My LandDocument2 pagesM0945019-Justice-This Land Is My LandThái Hoàng NguyênPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance of Marriage in Islam by Zaki BaqriDocument21 pagesImportance of Marriage in Islam by Zaki BaqriMUHAMMAD MANSHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Thinking Objects Tim Parsons 2009 PDFDocument210 pagesThinking Objects Tim Parsons 2009 PDFGăgeanu RalucaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hans Urs Von Balthasar and The Tarot A Review of Meditations On The Tarot by Anonymous Valentin TombeDocument6 pagesHans Urs Von Balthasar and The Tarot A Review of Meditations On The Tarot by Anonymous Valentin TombeStrannik RuskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gender in International Relations Feminist PerspectiveDocument109 pagesGender in International Relations Feminist PerspectiveEshrat RifatPas encore d'évaluation
- Thself ModuleDocument103 pagesThself ModuleAshera MonasterioPas encore d'évaluation
- Session-3 Motivation and Involvement, Attitudes and PersonalityDocument23 pagesSession-3 Motivation and Involvement, Attitudes and PersonalityVipul VyasPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Circular Cumulative Causation A La Myrdal & KappDocument10 pages01 Circular Cumulative Causation A La Myrdal & Kappapi-292047125Pas encore d'évaluation
- John Deely Basics of Semiotics Advances in Semiotics 1990Document125 pagesJohn Deely Basics of Semiotics Advances in Semiotics 1990zhanainaPas encore d'évaluation
- Regan & Sachs: Ain't MisbehavingDocument22 pagesRegan & Sachs: Ain't MisbehavingNew England Law ReviewPas encore d'évaluation
- Benedict Anderson Imagined Communities - Reflections On The Origins & Spread of NationalismDocument4 pagesBenedict Anderson Imagined Communities - Reflections On The Origins & Spread of NationalismEmma-Andreea ZaharcuPas encore d'évaluation
- Christian Approach to Philosophy of TimeDocument19 pagesChristian Approach to Philosophy of TimeFrJohn SomersPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Freedom and the Power of ChoiceDocument5 pagesHuman Freedom and the Power of ChoiceJerico LapurgaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Value of SPSR 2001Document18 pagesThe Value of SPSR 2001chrispalmer21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Thinking 4Document12 pagesCritical Thinking 4syofwanPas encore d'évaluation
- PSY 406 Handouts 1-45 (Final)Document86 pagesPSY 406 Handouts 1-45 (Final)Aman AlviPas encore d'évaluation
- Five Years of Theosophy by VariousDocument270 pagesFive Years of Theosophy by VariousGutenberg.orgPas encore d'évaluation
- AbstractDocument4 pagesAbstractAR RafiPas encore d'évaluation
- Theosophy On SuicideDocument18 pagesTheosophy On SuicideMark R. JaquaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rowe's Decision Style InventoryDocument3 pagesRowe's Decision Style InventorySubhan AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Stoic 30 Day Daily PlanDocument9 pagesStoic 30 Day Daily PlanbanuiliutaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sto Tomas National High SchoolDocument3 pagesSto Tomas National High SchoolAngelica GementizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nam Myoho Renge Kyo Lotus SutraDocument2 pagesNam Myoho Renge Kyo Lotus SutraMagda Preda100% (2)
- Module 1 Buss. ReserachDocument3 pagesModule 1 Buss. ReserachMÿćcä CañetePas encore d'évaluation
- Cosmos, Man and Society - 1989 PDFDocument139 pagesCosmos, Man and Society - 1989 PDFmadekPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument4 pagesInstructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatArgie Corbo BrigolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhetorical Appeals and Techniques Graphic OrganizerDocument3 pagesRhetorical Appeals and Techniques Graphic OrganizermaleahrfornaPas encore d'évaluation
- Daft - Chapter 10 - Organizational Culture and Ethical ValuesDocument20 pagesDaft - Chapter 10 - Organizational Culture and Ethical Valuesvero100% (1)
- Writing The Argumentative/Persuasi Ve EssayDocument29 pagesWriting The Argumentative/Persuasi Ve EssayJames BondPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2: UTILITARIANISM LessonsDocument11 pagesChapter 2: UTILITARIANISM LessonsBenBhadzAidaniOmboyPas encore d'évaluation