Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Jeopardy Game NPB 101L
Transféré par
kkk13whyDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Jeopardy Game NPB 101L
Transféré par
kkk13whyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NPB101L Jeopardy
Lab2
Lab3
Lab4
Lab5
Lab6
Lab7
Lab8
$100
$100
$100
$100
$100
$100
$100
$200
$200
$200
$200
$200
$200
$200
$300
$300
$300
$300
$300
$300
$300
$400
$400
$400
$400
$400
$400
$400
$500
$500
$500
$500
$500
$500
$500
$600
$600
$600
$600
$600
$600
$600
$700
$700
$700
$700
$700
$700
$700
Final
Lab 2 - $100
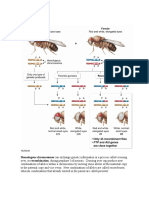
This structure consists of a motor neuron
and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
Motor Unit
Lab 2 - $200
This describes the rule in which motor
units are activated from smallest to largest
Henneman Size Principle
Lab 2 - $300
These invaginations of the muscle cell
membrane allow action potentials to
spread inward to the sarcoplasmic
reticulum
Transverse or T-tubules
Lab 2 - $400
Excitation contraction coupling for
neuronal stimulation relies on this critical
ion in both ECF and intracellular sources.
Calcium (Ca2+)
Lab 2 - $500
The paralytic effects of Tubocurare can be
circumvented by this method of
stimulation.
Direct
Lab 2 - $600
When high levels of stimulation are
achieved, this special type of summation is
observed
Tetany
Lab 2 - $700
These receptors transmit the electrical AP
into a mechanical opening of the SR,
forming a key component of excitationcontraction coupling.
Ryanodine (RyR) and Dihydropyridine
(DHPR) Receptors
Lab 3 - $100
Receptor, Integretor, and Effector are all
components of this.
Reflex Arc
Lab 3 - $200
This refers to APs traveling in their
normal (forward) direction.
Orthodromic.
Lab 3 - $300
These reflexes can integrate multiple
sources of information before initiating an
effector response.
Polysynaptic reflexes.
Lab 3 - $400
This causes inhibition of the H Reflex
under certain conditions
Renshaw Cells
Lab 3 - $500
This result of the vestibular-ocular reflex is
an attempt to coordinate visual field with
perception of acceleration.
Nystagmus
Lab 3 - $600
When angular acceleration is detected,
hair cells transmit motion into an electrical
signal via this mechanism
Bending of stereocilia/kinocilia to open
channels and de/hyper- polarize the hair
cells.
Lab 3 - $700
While most peoples H wave appears at a
lower stimulus than the M, this reason
would cause the M wave to appear first
instead.
An alpha motor neuron that is larger (and
thus less resistant) than the 1A afferent
neuron.
Lab 4 - $100
This is defined as the volume of blood
pumped by the ventricles per minute.
Cardiac Output
Lab 4 - $200
These mechanically sensitive proteins
detect stretch to measure a cardiovascular
parameter in the aortic arch and carotid
sinus
Baroreceptors
Lab 4 - $300
This is the name for the sounds heard
when performing sphygmomanometry by
auscultation
Korotkov sounds
Lab 4 - $400
The skeletal muscle pump, the venous
valves, venoconstriction are all methods
for improving this.
Venous Return
Lab 4 - $500
Metabolite buildup and oxygen demand
due to riding a bicycle will cause this reflex
of the cardiovascular system
Active Hyperemia
Lab 4 - $600
Capillaries lack most vessel tissue layers
except this one due to their specific
diffusion functions.
Endothelial cells
Lab 4 - $700
These highly distensible vessels are thin
walled and have a layer of smooth muscle
that actively changes the diameter.
Veins/venules
Lab 5 - $100
These pacemaker cells in the frog are
equivalent to the SA node
Sinus Venosus
Lab 5 - $200
This law states that the contraction after a
compensatory pause should be bigger.
Frank-Starling Law
Lab 5 - $300
This phase of the cardiac cycle includes
isovolumetric contraction and ventricular
ejection.
Systole
Lab 5 - $400
Instead of T-tubules mechanically
connected to the SR, a cardiac cell relies
on this mechanism.
Calcium-induced Calcium Release (CICR)
Lab 5 - $500
This is when second fastest pacemaker
cells restore heart rhythm when the SA
Node fails.
Vagal Escape
Lab 5 - $600
The effective refractory period of the heart
prevents this from happening.
Tetany
Lab 5 - $700
Increased permeability to K+ at the SA
node is caused by this type of neuronal
stimulation.
Parasympathetic
Lab 6 - $100
This is the tool used to measure lung
volumes.
Spirometer
Lab 6 - $200
This lung volume is composed of
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) + Tidal
Volume (TV) + Inspiratory Reserve Volume
(IRV)
Vital Capacity (VC)
Lab 6 - $300
These chemoreceptors primarily sense
arterial PO2
Peripheral Chemoreceptors
Lab 6 - $400
This control center modulates both
inspiratory and expiratory efforts
Ventral Respiratory Group
Lab 6 - $500
This is another name for the stretchactivated inspiratory-off-switch.
Hering-Breuer Reflex
Lab 6 - $600
These are the three ways that CO2 is
carried in the blood
1. Dissolved in plasma, 2.
Carbaminohemoglobin (HbCO2), 3.
Bicarbonate buffer (CO2+H2O H++HCO3-)
Lab 6 - $700
This increase in breathing does not cause
a corresponding decrease in PCO2.
Exercise Hyperpnea
Lab 7 - $100
These are the four basic renal processes
Filtration, Reabsorption, Secretion,
Excretion
Lab 7 - $200
This is defined as the volume of plasma
that a substance has been removed from
per unit time, and ranges from 0->GFR.
Clearance
Lab 7 - $300
When a beverage contains MORE solute
than the plasma, this is what it would be
called, and the effect it would have on GFR
Hypertonic, decrease
Lab 7 - $400
When a person regularly uses a lot of
bicarbonate-based antacid chews, this
would happen to their urine.
pH would be increased above normal
Lab 7 - $500
Of the two clearances you measured, this
one was predicted to DECREASE for the
HYPOTONIC subject.
Sodium clearance.
Lab 7 - $600
This special bundle of cells on the distal
tubule come alongside the granular cells
of the corpuscle and sense changes in
NaCl
Macula Densa
Lab 7 - $700
This hormone is the end-product of a
signaling cascade beginning with Renin,
and causes sodium reabsorption to
increase
Aldosterone
Lab 8 - $100
This layer of the GI tract contains 2 layers
of smooth muscle cells involved in gut
motility
Muscularis Externa
Lab 8 - $200
These cells create the basal electrical
rhythm that excite smooth muscle cells
Interstitial cells of cajal
Lab 8 - $300
Unlike its effects in other muscle types,
this neurotransmitter will decrease
excitability in smooth muscle.
Epinephrine (or adrenaline)
Lab 8 - $400
This essential difference between skeletal
& smooth muscle is how smooth muscle
gets its name
Lack of sarcomeres / regular arrangement
Lab 8 - $500
These two ion currents are essential for
slow wave production
Calcium and potassium
Lab 8 - $600
These are the possible regulatory proteins
that Ca-CaM can bind to and initiate
contraction
Route 1: Caldesmon or Calponin. Route 2:
MLCK (myosin light chain kinase)
Lab 8 - $700
This mechanism is why ADP can have
opposite results despite using similar
second messengers to Acetylcholine.
Calcium sparks
Final Jeopardy
An alpha motor neuron, parasympathetic
innervation of the heart, and excitatory
neurons of the enteric nervous system all
have this in common.
Acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Physiology of A Frog Heart With The Effects of Temperature, Neurotransmitters, and Electrical IsolationDocument17 pagesThe Physiology of A Frog Heart With The Effects of Temperature, Neurotransmitters, and Electrical IsolationAbir Hasan ShuvoPas encore d'évaluation
- StanniusDocument5 pagesStanniusDeilePhila OanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kanamycin Summary Report 2 Committee Veterinary Medicinal Products - enDocument9 pagesKanamycin Summary Report 2 Committee Veterinary Medicinal Products - enilhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Water and SolutionsDocument16 pagesWater and SolutionsSofia RuanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 The Electrochemical Basis of Nerve FunctionDocument33 pages3 The Electrochemical Basis of Nerve FunctionEvets JarusPas encore d'évaluation
- IP-Worksheet-3-Endocrine System The Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis (Estomagulang)Document2 pagesIP-Worksheet-3-Endocrine System The Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis (Estomagulang)Filmae Estomagulang0% (1)
- CalculationsDocument9 pagesCalculationsSherneceKalicharanPas encore d'évaluation
- IP-Worksheet-4-Endocrine System Response To Stress (Estomagulang)Document2 pagesIP-Worksheet-4-Endocrine System Response To Stress (Estomagulang)Filmae EstomagulangPas encore d'évaluation
- Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System: Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Secretes ReninDocument18 pagesRenin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System: Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Secretes Reninnur khomariahPas encore d'évaluation
- Bekker S 1991Document5 pagesBekker S 1991dupuytrenPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 9 NotesDocument5 pagesUNIT 9 NotesMariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mel Drum 1973Document6 pagesMel Drum 1973Putri Wulan SukmawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- BioDocument10 pagesBioYashodya WimalagunasekaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Notes 1Document180 pagesBio Notes 1JyNadarilPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous CommunicationDocument13 pagesNervous CommunicationWang PengfeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Experiments Manual: AdinstrumentsDocument10 pagesPharmacology Experiments Manual: AdinstrumentsbobguvPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 BiomedicalDocument93 pagesModule 1 Biomedicalp75072722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System Lab ReportDocument3 pagesNervous System Lab Reportapi-296589906Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ureter Do RatoDocument6 pagesUreter Do Ratonilberto2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology of Elasmobranch Fishes: Internal ProcessesD'EverandPhysiology of Elasmobranch Fishes: Internal ProcessesPas encore d'évaluation
- David Attwell - Pericytes in Neurovascular Coupling in Health and DiseaseDocument39 pagesDavid Attwell - Pericytes in Neurovascular Coupling in Health and DiseaseFondation Singer-PolignacPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 11 & Frog Heart LabDocument5 pagesLab 11 & Frog Heart LabCourtneyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sodium Theory Revisited: Or 45 Years of a Full Time Cnrs NeurophysiologistD'EverandThe Sodium Theory Revisited: Or 45 Years of a Full Time Cnrs NeurophysiologistPas encore d'évaluation
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemAnuvabPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrophysiology Measurements for Studying Neural InterfacesD'EverandElectrophysiology Measurements for Studying Neural InterfacesPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology and Pharmacology of The Renal Pelvis andDocument88 pagesPhysiology and Pharmacology of The Renal Pelvis andmauricio parachePas encore d'évaluation
- Neurophysiology, Neurotransmitters and The Nervous SystemDocument69 pagesNeurophysiology, Neurotransmitters and The Nervous SystemKUNNAMPALLIL GEJO JOHN100% (1)
- A04 PDFDocument16 pagesA04 PDFQueen JazPas encore d'évaluation
- Benefits of Use of Power Lab in Practica PDFDocument4 pagesBenefits of Use of Power Lab in Practica PDFRoy HarperPas encore d'évaluation
- Acetyl CholineDocument8 pagesAcetyl Cholinepranjal10295Pas encore d'évaluation
- Essay On Physiology (Excitable)Document33 pagesEssay On Physiology (Excitable)Emmanuel IshiomaPas encore d'évaluation
- OF THE York Academy: Study Activity SingleDocument18 pagesOF THE York Academy: Study Activity Singleedycs10Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH 3b Synaptic TransmissionDocument31 pagesCH 3b Synaptic TransmissionWOw WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Generated Flows Through Clips Placed On The Earlobes Output Current Adjustable From 80 To 600 Microamperes Circuit DiagramDocument6 pagesCurrent Generated Flows Through Clips Placed On The Earlobes Output Current Adjustable From 80 To 600 Microamperes Circuit DiagramemiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Biophysical Basis of Physiology and Calcium Signaling Mechanism in Cardiac and Smooth MuscleD'EverandBiophysical Basis of Physiology and Calcium Signaling Mechanism in Cardiac and Smooth MusclePas encore d'évaluation
- Lab08 Frog HeartDocument4 pagesLab08 Frog HeartAbie CaponponPas encore d'évaluation
- The Energetic HeartDocument26 pagesThe Energetic HeartAnca Baciu100% (2)
- Mice Nerve Lab ReportDocument3 pagesMice Nerve Lab ReportRania AlkhozaePas encore d'évaluation
- The Physics of Hearing: Fluid Mechanics and The Active Process of The Inner EarDocument46 pagesThe Physics of Hearing: Fluid Mechanics and The Active Process of The Inner EarGirish SubashPas encore d'évaluation
- Scalar Energy PendantDocument12 pagesScalar Energy PendantNicole WeatherleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Vestibular System PrimerDocument17 pagesVestibular System PrimerfadhillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Structures and Processes of The Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesStructures and Processes of The Nervous SystemAna G. VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluorescence Flow Cytometry: Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument2 pagesFluorescence Flow Cytometry: Frequently Asked Questionsuber6791Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ion ChannelsDocument35 pagesIon ChannelsnancyPas encore d'évaluation
- Action PotenialDocument21 pagesAction PotenialSanjay MaharjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomedical InstrumentationDocument16 pagesBiomedical InstrumentationGhanshyam DhruwPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced 2physiology Assighnment On Automaticity & Rhythmici2ty (Autorecovered) (Autorecovered)Document28 pagesAdvanced 2physiology Assighnment On Automaticity & Rhythmici2ty (Autorecovered) (Autorecovered)Muhammad Mudassar ChudaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of Labyrinth by DR Inam Ur RehmanDocument29 pagesAnatomy of Labyrinth by DR Inam Ur RehmanasssadulllahPas encore d'évaluation
- Key of SEQs Heart, Nerve and Muscle Revision TestDocument11 pagesKey of SEQs Heart, Nerve and Muscle Revision TestMudassar Roomi100% (2)
- UNIT I Electro-Physiology and BiopotentiDocument45 pagesUNIT I Electro-Physiology and BiopotentiAshok KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- NEUROBIOLOGY NW Lab ManualDocument61 pagesNEUROBIOLOGY NW Lab ManualReetikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Steotonin and Dopamine Relation With TestoDocument7 pagesSteotonin and Dopamine Relation With Testoupgratesleet704Pas encore d'évaluation
- T.G.J. Allen and G. Burnstock - Intracellular Studies of The Electrophysiological Properties of Cultured Intracardiac Neurones of The Guinea-PigDocument18 pagesT.G.J. Allen and G. Burnstock - Intracellular Studies of The Electrophysiological Properties of Cultured Intracardiac Neurones of The Guinea-PigLuammmPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise For Fitness 1 Semester Week 2 Module 2: Lesson 2: The Energy SystemsDocument4 pagesExercise For Fitness 1 Semester Week 2 Module 2: Lesson 2: The Energy SystemsKristine Renellie Calibuso BatagPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurobiology of Motor Control: Fundamental Concepts and New DirectionsD'EverandNeurobiology of Motor Control: Fundamental Concepts and New DirectionsScott L. HooperPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysioEx 6Document5 pagesPhysioEx 6skyhigh299100% (2)
- A P Muscular Chap 7Document41 pagesA P Muscular Chap 7api-285078865Pas encore d'évaluation
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXD'EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Cliches and Mini ProfilesDocument20 pagesCliches and Mini Profileskkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab+2-+Properties+of+Skeletal+Muscle+ NOTESDocument28 pagesLab+2-+Properties+of+Skeletal+Muscle+ NOTESkkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- BestBeatonEarth 1Document5 pagesBestBeatonEarth 1kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- BIS 102 Final Exam Example With AnswersDocument6 pagesBIS 102 Final Exam Example With Answerskkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- How+to+read+a+philosophy+paper 116Document2 pagesHow+to+read+a+philosophy+paper 116kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab+2+Skeletal+Muscle+Prelab+ 1Document19 pagesLab+2+Skeletal+Muscle+Prelab+ 1kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 6 Respiratory PrelabDocument23 pagesLab 6 Respiratory Prelabkkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- How+to+read+a+philosophy+paper 116Document2 pagesHow+to+read+a+philosophy+paper 116kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers PGR Week8Document3 pagesAnswers PGR Week8kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers PGR Week9 2016Document11 pagesAnswers PGR Week9 2016kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers PGR Week10Document3 pagesAnswers PGR Week10kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers PGR Week7Document8 pagesAnswers PGR Week7kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers PGR Week6Document8 pagesAnswers PGR Week6kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Enroll in A Course SESSION in EnCCoMPass UniversityDocument3 pagesHow To Enroll in A Course SESSION in EnCCoMPass Universitykkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Week9 MonMay23 Regulationgeneexpressioneukaryotes 2016Document73 pagesWeek9 MonMay23 Regulationgeneexpressioneukaryotes 2016kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 7 Discussion QsDocument1 pageLab 7 Discussion Qskkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- OCHEM118C Spr11 FinalDocument11 pagesOCHEM118C Spr11 Finalkkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultimate Internet OutlawDocument54 pagesUltimate Internet Outlawkkk13why100% (1)
- 118 C Fall 15 Final FullDocument12 pages118 C Fall 15 Final Fullkkk13why100% (1)
- Exam 2 S2013Document9 pagesExam 2 S2013kkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Moss RacusinDocument1 pageMoss Racusinkkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- 17C Test 2 Old ExamDocument1 page17C Test 2 Old Examkkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- American Boys Book of Camp Lore and WoodcraftDocument292 pagesAmerican Boys Book of Camp Lore and Woodcraftkkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- Middle Ages HygieneDocument6 pagesMiddle Ages Hygienekkk13whyPas encore d'évaluation
- FINAL Na DLP ZOOLOGYDocument18 pagesFINAL Na DLP ZOOLOGYDarlyn Joy TolentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- TrypanosomiasisDocument6 pagesTrypanosomiasisANTHONY KHAOYAPas encore d'évaluation
- MMRDocument84 pagesMMRKelly YeowPas encore d'évaluation
- MasterMind 2 Unit 1 WordlistDocument3 pagesMasterMind 2 Unit 1 WordlistRolando Guzman MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lethal Dose 50Document18 pagesLethal Dose 50h3cn1r3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Matching Words To Pictures WorksheetsDocument26 pagesMatching Words To Pictures WorksheetsUdpk FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Alchemist Extracts: Level 1 Extracts Level 3 ExtractsDocument17 pagesAlchemist Extracts: Level 1 Extracts Level 3 ExtractsRodrigo Lemão SouzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic Traditional MedicineDocument225 pagesDiagnostic Traditional MedicineJRA100% (17)
- Tan, Jolwin Laugo 2361052561Document6 pagesTan, Jolwin Laugo 2361052561JolwinTanPas encore d'évaluation
- 4ES0 02 Que 20110617Document8 pages4ES0 02 Que 20110617Syed AhadPas encore d'évaluation
- Wildlife Rehabilitator License ApplicationDocument1 pageWildlife Rehabilitator License ApplicationDavePas encore d'évaluation
- Triangles of The NeckDocument65 pagesTriangles of The NeckPaulo Duata100% (3)
- 18XX OutlawDocument4 pages18XX OutlawConnor BrassfieldPas encore d'évaluation
- Mollusks & EchinodermDocument18 pagesMollusks & EchinodermRoselle GuevaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CrocodilesDocument3 pagesCrocodilesPeculiarMemoriesPas encore d'évaluation
- SpecialtiesDocument5 pagesSpecialtiesRaMinah86% (7)
- Factors Associated With Menstrual Cycle Irregularity and MenopauseDocument11 pagesFactors Associated With Menstrual Cycle Irregularity and MenopauseRyan IlhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Small Pox Is DeadDocument46 pagesSmall Pox Is Deadtummalapalli venkateswara raoPas encore d'évaluation
- Food and Man 1Document25 pagesFood and Man 1Rejoice Gumboc MabilogPas encore d'évaluation
- TESTDocument5 pagesTESTnoralizaaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Animals SimilesDocument1 pageAnimals SimilesacademiaedelPas encore d'évaluation
- Shed No Tears For The Defeated by William Hunt-VincentDocument30 pagesShed No Tears For The Defeated by William Hunt-VincentAustin Macauley Publishers Ltd.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class 1 CBSE English Worksheets Term 2-DBXDocument10 pagesClass 1 CBSE English Worksheets Term 2-DBXBS100% (1)
- Adrienne EnglishDocument13 pagesAdrienne EnglishMiguel Sulis100% (1)
- Wildlife Fact File - Birds - 31-40Document20 pagesWildlife Fact File - Birds - 31-40ClearMind84100% (2)
- Chicken Wing DissectionDocument13 pagesChicken Wing DissectionJaga_Sahsiny_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Knife of Never Letting Go by Patrick Ness - First ChapterDocument15 pagesThe Knife of Never Letting Go by Patrick Ness - First ChapterWalker Books22% (9)
- HAYDUKE, George - ''Make'Em Pay - Ultimate Revenge Techniques From The Master Trickster''Document125 pagesHAYDUKE, George - ''Make'Em Pay - Ultimate Revenge Techniques From The Master Trickster''Mitko Krumov100% (3)
- Question Report 2478Document11 pagesQuestion Report 2478Raghav gupta100% (1)
- Test Dos InglesDocument4 pagesTest Dos Inglesgbøniillaa75% (4)