Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
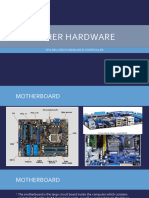
What is a Motherboard? USB 2.0 vs 3.0 Speed and Ports
Transféré par
Ahmed QaziTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
What is a Motherboard? USB 2.0 vs 3.0 Speed and Ports
Transféré par
Ahmed QaziDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
What is a
Motherboard? Definition and How
Motherboards Work
What are the Different
Motherboard Form Factors?
The Difference Between USB 2.0
and 3.0
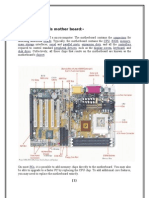
What is Mother Board
Function of MotherBoard
Function of Motherboard
BIOS OF MOTHERBOARD
Other than being the connection headquarters, a motherboard is
also home to the BIOS (Basic Input/output System), making it the
control center of your computer as well.
The motherboard BIOS performs hardware checks whenever your
computer powers on and allows you to access system settings
such as:
view hardware information and status
change your computer's boot-up device (e.g. hard drive, disc drive,
flash drive etc.)
manage power settings and savings
overclock or under clock the CPU and RAM
What are the Different
Motherboard Form Factors?
Motherboard Form Factor Comparison
MicroATX
ATX
Chart Mini-ITX
In addition to the
Maximum Size
17 x 17 cm
6.7 x 6.7 in
24.4 x 24.4 cm
9.6 x 9.6 in
30.5 x 24.4 cm
12 x 9.6 in
RAM Slots
2 to 4
2 to 8
RAM Type
DIMM, SODIMM
DIMM
DIMM
Expansion Slots
2 to 4
4 to 7
Graphics Cards
0 to 1
1 to 3
1 to 4
SATA ports
2 to 6
4 to 8
4 to 12
above difference, you
will often find that the
cheapest
motherboards are in
MicroATX form. This
makes sense since
Mini-ITX boards require
more refined
manufacturing while
ATX boards have more
components.
That being said, highend motherboards
come in all three form
factors including
MicroATX ones.
What do These Motherboards
Have in Common?
1. They can support the same CPU
As long as they are of the same generation, all three form
factors will have the same CPU socket. This is a big deal, since it
means that a Mini-ITX motherboard is able to pack as much as
computing punch as its full-sized ATX cousin (provided you're
not overclocking or going for top end CPUs like Intel-E).
They run the same graphics
IF the motherboard has a PCI-Express x 16 slot AND the
cards
graphics card is able to fit into the computer case.
However, high-end graphics cards tend to be massive so
most Mini-ITX cases (and some MicroATX ones) won't
have enough space to accommodate these behemoths.
For those of you relying on integrated graphics, the good
news is that motherboard size no longer affects graphics
performance ever since Intel and AMD fused their
graphics processing unit with the CPU (instead of leaving
it on the motherboard).
3. Their back panel ports are
The space taken up by back panel ports and
similar
connectors (see image below) on a motherboard is
about the same regardless of its size. Rather, the
number and type of back panel ports on a
motherboard are influenced by its price (expensive
board = more and better ports).
USB 2.0 and 3.0
Since its release in 2000, USB 2.0 has made its way
in almost every device imaginable... computers,
laptops, tablets, phones, cameras, storage devices,
televisions and even bitcoin miners. While it has
enjoyed tremendous popularity for over a decade, its
successor USB 3.0 has been gaining rapid adoption
among newer devices.
USB 2.0 vs 3.0: Speed
Difference
On paper, USB 2.0 is capable of transfer speeds
of up to 480 Mbps while USB 3.0 caps out at
5,000 Mbps. This would suggest that USB 3.0 is
at least 10 times than USB 2.0, but we all know
these figures are meaningless unless it's backed
Real World Test
To verify this, we performed our own USB 3.0 vs 2.0 speed test.
We connected a Toshiba Canvio USB 3.0 external hard drive to an
idle desktop computer and measured its transfer speed with
CrystalDiskMark. We first connected it to an USB 2.0 port and
recorded its speed, then repeated the process with a USB 3.0
port. Here are our speed test results:
USB 2.0
USB 3.0
Speed
Difference
Read
Speed
34.82 MB/s
75.19 MB/s + 218%
Write
Speed
30.68 MB/s
74.48 MB/s + 243%
Our results indicate that USB 3.0 is about 2.5 times faster,
which tallies with findings of the other real world tests.
USB 2.0 vs 3.0: Charging and
A USB 2.0 port is able to deliver 0.5 A of power while USB 3.0 is
Power
able to output 0.9 A. This means two things: USB 3.0 devices are
able to charge faster and USB 3.0 ports can support more powerhungry devices.
Samsung's Galaxy Note 3 is the first phone in the world with a USB
3.0 port, making it ideal for comparing USB 2.0 and USB 3.0
charging speeds.
USB 3.0
Wall Charger
USB 2.0
7 h 48 min
5 h 8 min
2 h 15 min
USB 2.0 vs 3.0: Ports and
Cables
Color is the key to telling the difference between USB 2.0
and 3.0 ports. In almost all cases, USB 3.0 ports are blue
while USB 2.0 ports are black or white in color
Is USB 2.0 and 3.0 Compatible
with Each Other?
USB 3.0 is backwards compatible, so the short answer is
yes. To make things clear and simple:
USB 2.0 port + USB 2.0 device = USB 2.0 performance
USB 2.0 port + USB 3.0 device = USB 2.0 performance
USB 3.0 port + USB 2.0 device = USB 2.0 performance
USB 3.0 port + USB 3.0 device = USB 3.0 performance
Any combination will work... but to take advantage USB
3.0's improved speed and charging, you'll need 3
ingredients: USB 3.0 port, USB 3.0 device and USB 3.0
cable.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3D'EverandMega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of the Computer and Their Uses ExplainedDocument7 pagesParts of the Computer and Their Uses ExplainedEmmelow EstoresPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.10 Inside A Computer Cabinet: 2.10.1 MotherboardDocument3 pages2.10 Inside A Computer Cabinet: 2.10.1 MotherboardAashish KandelPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3. Hardware (I) Internal ComponentsDocument20 pagesUnit 3. Hardware (I) Internal ComponentschinesePas encore d'évaluation
- Ahmed PDFDocument11 pagesAhmed PDFfaris daboolPas encore d'évaluation
- Otherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3Document54 pagesOtherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3somerandomhedgehog100% (1)
- Hardware BibleDocument123 pagesHardware BibleMitko JosifoskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit1 ComputersDocument32 pagesUnit1 ComputersElena CrufePas encore d'évaluation
- Comfiguração Da BIOS-SETUPDocument44 pagesComfiguração Da BIOS-SETUPEliasPas encore d'évaluation
- MotherboardDocument9 pagesMotherboardAhmed AbuNasserPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer MotherboardDocument15 pagesComputer MotherboardElsabet KindePas encore d'évaluation
- Core Hardware NotesDocument27 pagesCore Hardware NotesVishal100% (1)
- Computer SystemsDocument29 pagesComputer SystemsMohammed SiddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bus Bus Bus CPU Bus Bus: Basic Input-Output Services and The System BusDocument10 pagesBus Bus Bus CPU Bus Bus: Basic Input-Output Services and The System Busbharath_mv7-1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computer ComponentsDocument53 pagesComputer ComponentsAlbert Magno CaoilePas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of A Computer: MotherboardDocument6 pagesParts of A Computer: MotherboardJoshua PorcionculaPas encore d'évaluation
- Micro Project Report On MotherboardDocument15 pagesMicro Project Report On Motherboardabu100% (14)
- The Main Circuit Board of A MicrocomputerDocument16 pagesThe Main Circuit Board of A Microcomputeramandeep123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Resumen ComputersDocument4 pagesResumen Computerssantiago duquePas encore d'évaluation
- Laptop QuestionsDocument40 pagesLaptop QuestionsMujahid IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A ComputerDocument5 pagesWhat Is A ComputerAnshu Kumar023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of ComputerDocument33 pagesAnatomy of ComputerPrateek GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 03 The MotherboardDocument17 pagesUnit 03 The MotherboardSneaky petePas encore d'évaluation
- Computers in Plain English: The System Box or CaseDocument9 pagesComputers in Plain English: The System Box or Casethesingh_0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Course Hardware TrouDocument12 pagesCourse Hardware TrouSomasekhar Chowdary KakaralaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prashanti Institute of Technology & ScienceDocument18 pagesPrashanti Institute of Technology & Sciencezalanipulkit0% (1)
- Sitti Analyn P. Omar Dcmt-1 Batch-2Document15 pagesSitti Analyn P. Omar Dcmt-1 Batch-2Maher ArakamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Motherboard SGDocument23 pagesMotherboard SGasi555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Components of A MotherboardDocument14 pagesComponents of A MotherboardvcinfotechPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture On WebsiteDocument5 pagesLecture On WebsitePythiusPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 4 HardwareDocument40 pagesWeek 4 HardwareKylene VicenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Motherboard Review: Understanding the Key ComponentsDocument6 pagesMotherboard Review: Understanding the Key ComponentsAshutosh JadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- MotherboardDocument27 pagesMotherboardமகான் சிறோன்Pas encore d'évaluation
- REPORT ON MOTHERBOARD PRESENTATIONDocument10 pagesREPORT ON MOTHERBOARD PRESENTATIONmanjeetsinghnavab100% (1)
- Module 5 Motherboard: Understanding the Heart of Your PCDocument37 pagesModule 5 Motherboard: Understanding the Heart of Your PCyuva_sriPas encore d'évaluation
- The Physical Parts of a Computer System and Their FunctionsDocument33 pagesThe Physical Parts of a Computer System and Their FunctionsMia Dess Angawa Ananayo100% (1)
- A002 The CS9000 Microcomputer SandfelterDocument4 pagesA002 The CS9000 Microcomputer SandfelterkgrhoadsPas encore d'évaluation
- Motherboard Architecture GuideDocument7 pagesMotherboard Architecture GuideKiruba KaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Familiarize yourself with computer hardwareDocument32 pagesFamiliarize yourself with computer hardwareSantpreet Singh Kalra83% (6)
- SD InterfacingDocument16 pagesSD InterfacingBinit KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 1 Computer HardwareDocument57 pages1.1 1 Computer HardwareJhon Coen DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To The PCDocument61 pagesIntroduction To The PCLucia ErhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Motherboard ComponentsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Motherboard ComponentsallamPas encore d'évaluation
- CP and I AssigenmentDocument59 pagesCP and I Assigenmentfagixa3491Pas encore d'évaluation
- Motherboard (The Mother To All The Other Components)Document5 pagesMotherboard (The Mother To All The Other Components)Mandakini SasmalPas encore d'évaluation
- How PCs WorkDocument9 pagesHow PCs WorkfabiobonadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are The Parts of A MotherboardDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Parts of A MotherboardPRincess ScarLetPas encore d'évaluation
- A+ Certification Exam Guide ExtractsDocument111 pagesA+ Certification Exam Guide ExtractsAbdulganiyu TeslimPas encore d'évaluation
- Maxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsDocument16 pagesMaxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsOlúwaṣẹ́gunPas encore d'évaluation
- Motherboards Routers and SwitchesDocument3 pagesMotherboards Routers and SwitchesELISABETH KNOLPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of MotherboardDocument6 pagesTypes of MotherboardmariannePas encore d'évaluation
- A+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationDocument40 pagesA+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationLindasharon AwourPas encore d'évaluation
- Motherboard Explained: Parts, Form Factors & How It WorksDocument14 pagesMotherboard Explained: Parts, Form Factors & How It Workskurdo salahPas encore d'évaluation
- For The Free Video Please SeeDocument18 pagesFor The Free Video Please Seevenkatasubbu rathinamPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Cable Types and DescriptionsDocument16 pagesComputer Cable Types and DescriptionsAsif Ali ArainPas encore d'évaluation
- Motherboard SGDocument23 pagesMotherboard SGapi-310243177Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Kelompok 6Document8 pagesTugas Kelompok 6Rika ElsiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nintendo DS Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #14D'EverandNintendo DS Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Online Cloud Based Compilers System: February 2016Document5 pagesOnline Cloud Based Compilers System: February 2016Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating System: Lesson 8 (Deadlocks)Document45 pagesOperating System: Lesson 8 (Deadlocks)Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document50 pagesChapter 2douglasnegro14Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6016 4Document19 pages6016 4Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture11 SystemStabilityDocument23 pagesLecture11 SystemStabilityAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- 6016 2Document15 pages6016 2Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- MIPS Assembly Language Programmer's GuideDocument244 pagesMIPS Assembly Language Programmer's Guidekusasi@Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2012091412514219832407003072949Document19 pages2012091412514219832407003072949Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture3 ModellingMechanicalSystemsIDocument19 pagesLecture3 ModellingMechanicalSystemsIAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- 28 October 2016 PGE312 SlıdesDocument27 pages28 October 2016 PGE312 SlıdesAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- 6016 6Document23 pages6016 6Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document46 pagesChapter 1Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Control of Siso SystemsDocument64 pagesControl of Siso SystemsAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- 6016 1Document26 pages6016 1Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Wye DeltaTransformationDocument5 pagesWye DeltaTransformationAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuits I Lect11Document17 pagesCircuits I Lect11Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuits1 Lect13Document19 pagesCircuits1 Lect13Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Half Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesHalf Wave RectifierAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuits I Lect10Document17 pagesCircuits I Lect10Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuits I Lect10Document17 pagesCircuits I Lect10Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- PythonDocument540 pagesPythonronnny11100% (3)
- Circuit Analysis I Lecture Mesh and Nodal AnalysisDocument16 pagesCircuit Analysis I Lecture Mesh and Nodal AnalysisAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 23 Finishing StacksDocument5 pagesClass 23 Finishing StacksAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- CIRCUIT ANALYSIS I KEY CONCEPTSDocument18 pagesCIRCUIT ANALYSIS I KEY CONCEPTSAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessor Architecture and Assembly LanguageDocument52 pagesMicroprocessor Architecture and Assembly LanguageAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit Analysis I: Chapter 4 Circuit TheoremsDocument14 pagesCircuit Analysis I: Chapter 4 Circuit TheoremsAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Pylists 2Document23 pagesPylists 2Ahmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - InterruptsxDocument26 pagesChapter 5 - InterruptsxAhmed QaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Lenovo IdeaPad 320-15iap Compal DG424 - DG524 NM-B301 Rev1.0 Schematic DiagramDocument58 pagesLenovo IdeaPad 320-15iap Compal DG424 - DG524 NM-B301 Rev1.0 Schematic DiagramLeonardo DiegoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rajalakshmi Engineering College, Thandalam. Department of Ece Laboratory PlanDocument1 pageRajalakshmi Engineering College, Thandalam. Department of Ece Laboratory PlanBalaji DuraiyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Intel DP43TF E41955001usDocument86 pagesIntel DP43TF E41955001useb_geekPas encore d'évaluation
- Travelmate 630: Service GuideDocument134 pagesTravelmate 630: Service GuidescribdermaniacPas encore d'évaluation
- Damaged Micro Usb (Soldered) On WD Elements SE 1TB External. How-To Geek ForumsDocument6 pagesDamaged Micro Usb (Soldered) On WD Elements SE 1TB External. How-To Geek ForumsNilesh YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- A41g V1 7Document46 pagesA41g V1 7Nair De Lima AbregoPas encore d'évaluation
- DS D2990-A1Document3 pagesDS D2990-A1Mr LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- 7367v1 0 (G52-73671X1) PDFDocument95 pages7367v1 0 (G52-73671X1) PDFErnesto GodoyPas encore d'évaluation
- HP Pavilion 15Document4 pagesHP Pavilion 15MARUFPas encore d'évaluation
- J14im2x DDR3 2dimm PDFDocument30 pagesJ14im2x DDR3 2dimm PDFMario Rodriguez Jurado0% (2)
- Service Manual & Troubleshooting Guide ForDocument175 pagesService Manual & Troubleshooting Guide Forharis ansoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Micro-Star Int'L Co.,Ltd Micro-Star Int'L Co.,Ltd Micro-Star Int'L Co.,LtdDocument33 pagesMicro-Star Int'L Co.,Ltd Micro-Star Int'L Co.,Ltd Micro-Star Int'L Co.,LtdLeoned Cova OrozcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Teknologi Maklumat Dalam Pendidikan: Data StorageDocument91 pagesTeknologi Maklumat Dalam Pendidikan: Data StorageFattihi EkhmalPas encore d'évaluation
- GIGABYTE 8VM800M Schematics: Sheet Title Sheet TitleDocument32 pagesGIGABYTE 8VM800M Schematics: Sheet Title Sheet TitleSjf NetPas encore d'évaluation
- 7592v2.0 (G52 75921X2) (G41TM E33 - G41TM E43 - G41TM E35) (100x150)Document153 pages7592v2.0 (G52 75921X2) (G41TM E33 - G41TM E43 - G41TM E35) (100x150)Pchome SabaoaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 6-Laboratoriya Ishi Parallеl Tеbranish Konturining Tadqiq Etish Ishning maqsadi - parallеl tеbranish konturining chastotaviy tavsiflarini,Document45 pages6-Laboratoriya Ishi Parallеl Tеbranish Konturining Tadqiq Etish Ishning maqsadi - parallеl tеbranish konturining chastotaviy tavsiflarini,A FargoniyPas encore d'évaluation
- MS-7309 uATX Motherboard Block DiagramDocument35 pagesMS-7309 uATX Motherboard Block DiagramDmitriy BabinichPas encore d'évaluation
- Broadwell ULV Processor with DDR3L Schematics DocumentDocument63 pagesBroadwell ULV Processor with DDR3L Schematics DocumentkasimkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lista de Precios !!!!Document40 pagesLista de Precios !!!!Edu FerreiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Debug 1214Document3 pagesDebug 1214Gramada Silvia-StefaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Devices DemoDocument26 pagesComputer Devices DemoSonia Manalon AgustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Easy USB to Serial Adapter Setup for Windows VistaDocument3 pagesEasy USB to Serial Adapter Setup for Windows VistaGilmar SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- USB and PCI Device EnumerationDocument3 pagesUSB and PCI Device Enumerationsuli89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Antec 550w Psu BP550 Plus en ManualDocument6 pagesAntec 550w Psu BP550 Plus en Manualsdfsdf dddPas encore d'évaluation
- Acer Aspire 1300 - Quanta ET2S PDFDocument26 pagesAcer Aspire 1300 - Quanta ET2S PDFMustafa AkanPas encore d'évaluation
- Beckhoff Products 2011Document80 pagesBeckhoff Products 2011safindit100% (1)
- EFM32 Product Overview PDFDocument125 pagesEFM32 Product Overview PDFkeviPas encore d'évaluation
- Proliant m110 g6Document3 pagesProliant m110 g6Marcos Alexis PF0% (1)
- PDL MK - Iii Gardt: ® ARINC 615/615A Portable Data LoaderDocument2 pagesPDL MK - Iii Gardt: ® ARINC 615/615A Portable Data LoaderAbhishek RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Acer Aspire 4130 4130G 5530 5530G JALB0 (Compal LA-4171P) PDFDocument50 pagesAcer Aspire 4130 4130G 5530 5530G JALB0 (Compal LA-4171P) PDFMustafa AkanPas encore d'évaluation