Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Week7Lec02 Pumping Systems
Transféré par
Ramprasad YandapalliCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Week7Lec02 Pumping Systems
Transféré par
Ramprasad YandapalliDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
Pumping Systems
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
IIT Madras
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
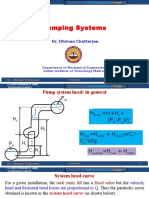
Pump system head: in general
Pdr
CP
Hstatic=Hi+Hd+
(Pdr-Psr)/
CP
Hd
HP
Psr
Hloss=Hsloss + Hdloss+(CP2Cs2)/2g
Hi
C S HS
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
Hsystem=Hloss + Hstatic
IIT Madars
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
System head curve
For a given installation, the total static lift has a fixed value but the velocity
head and frictional head losses are proportional to Q. Thus the parabolic curve
obtained is known as the system head curve (as shown below).
Hsystem
H loss KQ 2
Q
Hstatic
Q
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
IIT Madars
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
System head curve calculation: an example
Hf6
90 elbow
Hf6
Hf
Valve
Hf7
L2,DP
Pump
L1,DS
Hstatic
Hf4
90 elbow
Hf2 Hf3
90 elbow
H system H static H loss
H loss H f 1 H f 2 H f 3 H f 4 H f 5 H f 6 H f 7
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
Hf1
IIT Madars
Foot valve
4
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
Pump performance curve
Qd
Constant speed pump characteristics
Note: This is usually related with the a single-stage centrifugal
pump (volute type). Typical specific speed, Ns=20.
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
IIT Madars
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
Operating point
For steady-state flow of a liquid through a pipeline system the total head (H) developed by a
pump must be equal to the system head (Hsystem) at a given flow-rate. This point is known as
operating point of a pump.
Hsystem
H
Qoper
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
Attempt should be made to match
the pump with the system in such a
way that the point of operation is
at/near the design/best efficiency
point.
Q
IIT Madars
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
Pump performance curve
Constant speed pump characteristics
Q
Note: This is usually related with the an axial-flow pump. Typical specific
speed, Nq=213.
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
IIT Madars
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
Discussion on pump performance curves
Unstable characteristics curve: A head-capacity curve which has a peak is called an unstable
characteristic because the same head can be obtained at two different values of discharge. If
required to operate in the range in which the characteristic is unstable, the pump tends to
hunt between the two points on the H-Q curve for which H is the same.
Hsystem
A
S
H
Unstable
Stable
Q
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
Unstable characteristics can be avoided by:
i) decreasing blade outlet angle (2)
ii)
reducing number of vanes and decreasing
frictional losses,
extending the inlet edge of the blade towards
the eye of the impeller.
iii)
IIT Madars
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
Series operation of pumps
HB
Q
S
A
Pump-A
Pump-B
Q
HA+B
HA
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
Two similar pumps connected in series
Q
IIT Madars
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
Parallel operation of pumps
H
HA
HA+B
QA B
Pump-A
QA
HB
Pump-B
QB
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
IIT Madars
10
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
Summary
System curve for a pump has been explained and the intersection of the pump curve with
the system curve gives the operating point.
Series and parallel operations of pumps are also explained.
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
IIT Madars
11
FLUID DYNAMICS AND
TURBOMACHINES
PART-C Module-2 Pumps
THANK YOU
Dr. Dhiman Chatterjee
IIT Madras
12
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 2012 Al 6061 - Wettability ContrastDocument12 pages2012 Al 6061 - Wettability ContrastRamprasad YandapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer: Matic Može, Matevž Zupan Ci C, Iztok Golobi CDocument13 pagesInternational Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer: Matic Može, Matevž Zupan Ci C, Iztok Golobi CRamprasad YandapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermochimica Acta: Vishal V. Nirgude, Santosh K. SahuDocument11 pagesThermochimica Acta: Vishal V. Nirgude, Santosh K. SahuRamprasad YandapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Week7Lec02 Pumping SystemsDocument12 pagesWeek7Lec02 Pumping SystemsRamprasad YandapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Week7Lec06 TutorialsDocument11 pagesWeek7Lec06 TutorialsRamprasad YandapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Ansys Fluent 18 Tutorial Guide PDFDocument1 052 pagesAnsys Fluent 18 Tutorial Guide PDFaliafsin100% (1)
- 03 Nucleate BoilDocument22 pages03 Nucleate BoilWeb LogueandoPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - PolycrystallineDocument24 pages5 - PolycrystallineYogesh DanekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Qip Ice 16 Ignition SystemsDocument28 pagesQip Ice 16 Ignition SystemsRamprasad YandapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Qip Ice 16 Ignition SystemsDocument28 pagesQip Ice 16 Ignition SystemsRamprasad YandapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - Crystal Structure PDFDocument66 pages4 - Crystal Structure PDFManoj SelvamPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Transfer Modes in 40 CharactersDocument50 pagesHeat Transfer Modes in 40 CharactersJacob Onjwaya MbegoPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - Solid SolutionsDocument9 pages8 - Solid Solutionstaak41Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Transfer JournalDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer JournalRamprasad YandapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - Crystal Structure PDFDocument66 pages4 - Crystal Structure PDFManoj SelvamPas encore d'évaluation
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Journal On Heat TransferDocument2 pagesJournal On Heat TransferRamprasad YandapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- ME364 Combining FusionDocument7 pagesME364 Combining FusionRamprasad YandapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- GateDocument6 pagesGateParveen SwamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotary Swaging GBDocument16 pagesRotary Swaging GBMoustaffaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer For Optimization of Pin-Fin Heat SinksDocument339 pagesModeling of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer For Optimization of Pin-Fin Heat SinksAlif FirdausPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Design of Small Antennas Based On DNG MetamaterialsDocument4 pagesDesign of Small Antennas Based On DNG MetamaterialsSumaiya AbedinPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Casting Speed On Continuous Casting of Steel Slab: January 2014Document12 pagesEffect of Casting Speed On Continuous Casting of Steel Slab: January 2014Prakash SarangiPas encore d'évaluation
- Effective mass theory of a two-dimensional quantum dot in the presence of magnetic fieldDocument8 pagesEffective mass theory of a two-dimensional quantum dot in the presence of magnetic fieldJOHN ALEXANDER OSORIO HENAOPas encore d'évaluation
- All About Waves NotesDocument1 pageAll About Waves NotesRusherPas encore d'évaluation
- 2-1 Solving One-Step Equations - : Christmas Color Match ActivityDocument4 pages2-1 Solving One-Step Equations - : Christmas Color Match ActivityDulce CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Class XI ch.01Document7 pagesChem Class XI ch.01Navin KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 0625 November 2011 Paper 23 Mark SchemeDocument7 pages0625 November 2011 Paper 23 Mark SchemeDionisio UssacaPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Flow and Heat ExchangeDocument409 pagesEngineering Flow and Heat ExchangeDimitri MantauPas encore d'évaluation
- Irjet V5i5256 PDFDocument5 pagesIrjet V5i5256 PDFMuhsinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-Icing in Gas Turbines PDFDocument133 pagesAnti-Icing in Gas Turbines PDFAbelio TavaresPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mole Concept ExplainedDocument12 pagesThe Mole Concept ExplainedVictor OkosunPas encore d'évaluation
- IP 15 Calculations in Support of IP15 The Area Classification Code For Petroleum Installations November 2001Document63 pagesIP 15 Calculations in Support of IP15 The Area Classification Code For Petroleum Installations November 2001Yonatan Cristie100% (2)
- Equivalent Force Systems and Free Body Diagrams Solved ProblemsDocument14 pagesEquivalent Force Systems and Free Body Diagrams Solved ProblemsYun RamPas encore d'évaluation
- NumerovDocument5 pagesNumerovdiego-crPas encore d'évaluation
- Plastic HingesDocument10 pagesPlastic HingesBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Tablas de VaporDocument4 pagesTablas de VaporUlises Perez CandiaPas encore d'évaluation
- CFD Simulation of A Co-Current Spray Dryer: February 2010Document7 pagesCFD Simulation of A Co-Current Spray Dryer: February 2010muhammad farisPas encore d'évaluation
- Berryman. 2003. On Principles, Laws and Theory in Population Ecology. OikosDocument7 pagesBerryman. 2003. On Principles, Laws and Theory in Population Ecology. OikosValentina¬Pas encore d'évaluation
- FBD StaticDocument5 pagesFBD StaticBrianChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Sheet: Capacitor For Power ElectronicsDocument6 pagesData Sheet: Capacitor For Power Electronicsraza239Pas encore d'évaluation
- J. Electrochem. Soc.-2017-Monroe-E3547-51Document5 pagesJ. Electrochem. Soc.-2017-Monroe-E3547-51Geovanny JaenzPas encore d'évaluation
- Procedure Field Inspection & Testing Electrical EquipmentDocument21 pagesProcedure Field Inspection & Testing Electrical Equipmentarifadha446100% (5)
- Muammer Yildiz - Over-Unity Homopolar Electrical Generator - Patent, ArticlesDocument29 pagesMuammer Yildiz - Over-Unity Homopolar Electrical Generator - Patent, ArticlesMohd FakhriPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of flat glass plates with 4 edges simply supported and uniform loadingDocument1 pageDesign of flat glass plates with 4 edges simply supported and uniform loadingSHANIL051Pas encore d'évaluation
- F. Reif - Statistical Physics - Chapter 1 PDFDocument51 pagesF. Reif - Statistical Physics - Chapter 1 PDFIndrawati WilujengPas encore d'évaluation
- NSEJS/NSEC Physics, Chemistry, Biology QuizDocument31 pagesNSEJS/NSEC Physics, Chemistry, Biology Quizamit starboyPas encore d'évaluation
- 13c Candyium LabDocument2 pages13c Candyium Labapi-285693263Pas encore d'évaluation
- Generalized Amplitude Damping Channel: The Single Greatest Qubit Mystery in Quantum Shannon TheoryDocument80 pagesGeneralized Amplitude Damping Channel: The Single Greatest Qubit Mystery in Quantum Shannon TheoryMark M. Wilde100% (1)
- 4 Lab Sheet BDA27401 Sem 1 20182019 Edition1 2018Document73 pages4 Lab Sheet BDA27401 Sem 1 20182019 Edition1 2018Zarul IkramPas encore d'évaluation