Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Search Tree in Which The Balance Factor of Every Node, Which Is Defined As The
Transféré par
Happy0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
9 vues22 pagesAn AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree that ensures the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one. It performs rotations to balance the tree after insertions or deletions. Single and double rotations are used to balance the tree when a node's balance factor becomes -2 or +2. AVL tree operations have O(log n) time complexity.
Description originale:
kkgjjbk
Titre original
17442_avl,2-3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentAn AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree that ensures the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one. It performs rotations to balance the tree after insertions or deletions. Single and double rotations are used to balance the tree when a node's balance factor becomes -2 or +2. AVL tree operations have O(log n) time complexity.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
9 vues22 pagesSearch Tree in Which The Balance Factor of Every Node, Which Is Defined As The
Transféré par
HappyAn AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree that ensures the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one. It performs rotations to balance the tree after insertions or deletions. Single and double rotations are used to balance the tree when a node's balance factor becomes -2 or +2. AVL tree operations have O(log n) time complexity.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 22
AVL
DEFINITION An AVL tree is a binary
search tree in which the balance factor
of every node, which is defined as the
difference between the heights of the nodes
left and right subtrees, is either 0 or +1 or
1. (The height of the empty tree is defined
as1. Of course, the balance factor can also
be computed as the difference between the
numbers of levels rather than the height
difference of the nodes left and right
subtrees.)
If an insertion of a new node makes an
AVL tree unbalanced, we transform the
tree by a rotation. A rotation in an AVL
tree is a local transformation of its
subtree rooted at a node whose balance
has become either +2 or 2. If there are
several such nodes, we rotate the tree
rooted at the unbalanced node that is
the closest to the newly inserted leaf.
single right rotation, or
R-rotation.
this rotation is performed after a new
key is inserted into the left subtree of
the left child of a tree whose root had
the balance of +1 before the
insertion.
L-rotation
The symmetric single left rotation,
or L-rotation, is the mirror image
of the single R-rotation. It is
performed after a new key is inserted
into the right subtree of the right
child of a tree whose root had the
balance of 1 before the insertion.
DOUBLE LR AND RL
ROTATION
It is performed after a new key is
inserted into the right subtree of the
left child of a tree whose root had the
balance of +1 before the insertion.
The double right-left rotation
(RL-rotation) is the mirror image
of the double LR-rotation and is left
for the exercises.
Double LR AND RL
ROTATION
5,6,8,3,2,4,7
Complexity
Theta (log n)
A 2-3 tree is a tree that can have
nodes of two kinds: 2-nodes and 3-
nodes.
A 2-node contains a single key K
and has two children: the left child
serves as the root of a subtree whose
keys are less than K, and the right
child serves as the root of a subtree
whose keys are greater than K.
A 3-node contains two ordered keys
K1 and K2 (K1<K2) and has three
children.
The leftmost child serves as the root of a
subtree with keys less than K1,
the middle child serves as the root of a
subtree with keys between K1 and K2,
and the rightmost child serves as the root
of a subtree with keys greater than K2
The last requirement of the 2-3 tree is that
all its leaves must be on the same level.
In other words, a 2-3 tree is always
perfectly height-balanced:
the length of a path from the root to a leaf
is the same for every leaf. It is this
property that we buy by allowing more
than one key in the same node of a search
tree.
9,5,8,3,2,4,7
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- PPT7 - AVL TreeDocument30 pagesPPT7 - AVL TreeRapik HardiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Avl 1Document6 pagesAvl 1dharna28gsPas encore d'évaluation
- 3d3f0ef1 1603358945498Document38 pages3d3f0ef1 1603358945498Hai SuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Algorithms Analysis and DesignDocument30 pagesAdvanced Algorithms Analysis and DesignMuhammad ArishPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3Document13 pagesUnit 32004pujadasPas encore d'évaluation
- AvlDocument5 pagesAvlSumeet PardeshiPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreeDocument3 pagesAVL Treealiahmadfareed chPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Tree - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesAVL Tree - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaapamparoPas encore d'évaluation
- A07Document35 pagesA07Er Ankur SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- AVLDocument5 pagesAVLepanicu2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hierarchical Data StructuresDocument21 pagesHierarchical Data StructuresGobara DhanPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are AVL TreesDocument7 pagesWhat Are AVL TreesGyu.tarwristPas encore d'évaluation
- AVLTreesDocument70 pagesAVLTreesAman Pushpinder BirdiPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreeDocument27 pagesAVL TreeTanmay BaranwalPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreesDocument25 pagesAVL TreesjoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreeDocument5 pagesAVL TreeChippyVijayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Avl PDFDocument60 pagesAvl PDFaliPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledAnand SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Trees AVL Trees: Unit 4: Height-Balanced TreesDocument32 pagesAVL Trees AVL Trees: Unit 4: Height-Balanced TreesNIDHIP TANEJAPas encore d'évaluation
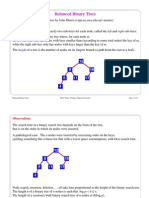
- Balanced Search TreesDocument63 pagesBalanced Search TreesAbdurezak ShifaPas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Adjusting TreeDocument80 pagesSelf-Adjusting Treeviere1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Tree: Made By: Pulkit Aggarwal 755/IT/12Document22 pagesAVL Tree: Made By: Pulkit Aggarwal 755/IT/12Pulkit AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
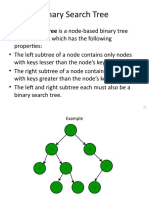
- Binary Search Tree Is A Node-Based Binary TreeDocument22 pagesBinary Search Tree Is A Node-Based Binary TreeJatin ValechaPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreesDocument34 pagesAVL TreesSaleha MasoodPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreesDocument31 pagesAVL Treespooja0letscrackitPas encore d'évaluation
- TreesDocument40 pagesTreesFurkan KÖROĞLUPas encore d'évaluation
- 54f7de3b 1648268910821Document33 pages54f7de3b 1648268910821Ramanpreet KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- TreeDocument50 pagesTreesoumaadak.23Pas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreeDocument12 pagesAVL TreeZoya AmaanPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL PresentationDocument11 pagesAVL Presentationyalnar erumPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Tree DatastructureDocument7 pagesAVL Tree DatastructureSaumya TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Tree Data StructureDocument7 pagesAVL Tree Data Structurewhisper hhmmPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4 - AVL TreesDocument26 pagesLecture 4 - AVL TreesArbaz AliPas encore d'évaluation
- AVLtreesDocument11 pagesAVLtreesFlor del CPas encore d'évaluation
- TreeDocument48 pagesTreeminichelPas encore d'évaluation
- Q1) Sort The Given List Using Heap Sort Technique:: AVL Tree OperationsDocument12 pagesQ1) Sort The Given List Using Heap Sort Technique:: AVL Tree Operationsnancy_01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit4 Binary TreeDocument34 pagesUnit4 Binary TreeJigar AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Traversal AlgorithmsDocument13 pagesTraversal Algorithmsn02019697mPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures and Algorithms - Avl Tree and Max HeapDocument39 pagesData Structures and Algorithms - Avl Tree and Max Heaperikalast.acadPas encore d'évaluation
- Trees Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Balanced Binary Search TreesDocument61 pagesTrees Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Balanced Binary Search TreesImaPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 AvlDocument15 pages16 AvlAzaroathPas encore d'évaluation
- TreesDocument49 pagesTreesRajan singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Template Library: The Probabilities For All The CharactersDocument8 pagesStandard Template Library: The Probabilities For All The CharactersrocksplitPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures Using C, 2e Reema Thareja: © Oxford University Press 2014. All Rights ReservedDocument19 pagesData Structures Using C, 2e Reema Thareja: © Oxford University Press 2014. All Rights ReservedRajan JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures: AVL TreesDocument13 pagesData Structures: AVL TreesMercyless K1NG-Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trees As Data StructuresDocument78 pagesTrees As Data Structuresbirenhirapara16Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ds III Unit NotesDocument36 pagesDs III Unit NotesAlagandula KalyaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Define Tree. List Its Features.: Lecture NotesDocument32 pagesDefine Tree. List Its Features.: Lecture NotesShailesh WagholePas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4.14.2Document39 pagesModule 4.14.2sujand2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- 03 DataStructures BinaryTreeDocument40 pages03 DataStructures BinaryTreeAhmad AlarabyPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structure and Algorithms - AVL TREESDocument6 pagesData Structure and Algorithms - AVL TREESGood VibesPas encore d'évaluation
- Avl Tree L36Document13 pagesAvl Tree L36Anacademy FreePas encore d'évaluation
- Note 1467607525Document27 pagesNote 1467607525Sai KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 27Document17 pagesSession 27kreshmithasruthiPas encore d'évaluation
- BURHANDocument4 pagesBURHANZaini Pehlwan GPas encore d'évaluation
- Tree: A Non Linear Data StructureDocument22 pagesTree: A Non Linear Data StructureMd. Zubaer HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreeDocument13 pagesAVL TreePhạmVănNgoanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tree Data StructureDocument7 pagesTree Data Structuresel&nitPas encore d'évaluation
- Irctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Document2 pagesIrctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)HappyPas encore d'évaluation
- Nptel Week2 Module7 QuicksortDocument36 pagesNptel Week2 Module7 QuicksortHappyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture18-19 13897 FlowcontrolDocument21 pagesLecture18-19 13897 FlowcontrolHappyPas encore d'évaluation
- OSAssignment K1508Document15 pagesOSAssignment K1508Happy0% (1)
- Single Source Shortest PathDocument12 pagesSingle Source Shortest PathHappyPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication SkillsDocument9 pagesCommunication SkillsHappyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ip Class 12 Sumita Arora Solved Questions Concept of InheritanceDocument3 pagesIp Class 12 Sumita Arora Solved Questions Concept of InheritanceHappy17% (6)
- SRS ForDocument14 pagesSRS Forbaddamraju67% (3)
- UNIT IVDocument23 pagesUNIT IVAjay GanesanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Question BankDocument3 pages2 Question BankghuklPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper On Tree Data StructureDocument5 pagesResearch Paper On Tree Data Structurej0b0lovegim3100% (1)
- Dsa Assignment (Bikash Ranjan Das)Document9 pagesDsa Assignment (Bikash Ranjan Das)Himangshu ChoudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structure Unit-3 QuizDocument6 pagesData Structure Unit-3 QuizJaganath SPas encore d'évaluation
- 2) Binary Search Tree PDFDocument21 pages2) Binary Search Tree PDFLol TelrPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ On Tree Data StructuresDocument17 pagesMCQ On Tree Data StructuresAditya KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Elementary AlgorithmsDocument618 pagesElementary AlgorithmsAditya Paliwal100% (1)
- Data Structure and Algorithms - AVL TREESDocument6 pagesData Structure and Algorithms - AVL TREESGood VibesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Order TraversalDocument17 pagesPre Order TraversalJunaid khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Binary Search TreeDocument177 pagesBinary Search TreeAyesha FidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Min Max HeapDocument9 pagesMin Max HeapShubhamMittalPas encore d'évaluation
- Balanced Binary Search Trees (BBSTS) : William FisetDocument95 pagesBalanced Binary Search Trees (BBSTS) : William FisetRupesh Kumar NidhiPas encore d'évaluation
- hw06 Solution PDFDocument7 pageshw06 Solution PDFsiddharth1kPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper On Avl TreeDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Avl Treewtdcxtbnd100% (1)
- I Nyoman Arijaya Putra - 13 NovDocument2 pagesI Nyoman Arijaya Putra - 13 NovArijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 3&4Document20 pagesLec 3&4Hariharan RavichandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Priority Queue Using HeapDocument4 pagesPriority Queue Using HeapLycelleRamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures and Algorithms Mid-Semester Test: BITS Pilani-K K Birla Goa CampusDocument2 pagesData Structures and Algorithms Mid-Semester Test: BITS Pilani-K K Birla Goa CampusAnnwesha PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Priority Queue (Data Structures) - JavatpointDocument11 pagesPriority Queue (Data Structures) - JavatpointGovinda DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures - GeeksforGeeksDocument22 pagesData Structures - GeeksforGeeksJohn PrestonPas encore d'évaluation
- Splay Tree OpeationsDocument2 pagesSplay Tree OpeationsdpacePas encore d'évaluation
- Cs 301Document1 pageCs 301foggybluuePas encore d'évaluation
- Balanced Binary Search Trees - Data Structures and Algorithms With PythonDocument20 pagesBalanced Binary Search Trees - Data Structures and Algorithms With PythonFrankie LiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tree Is A Tree That Is Not RootedDocument3 pagesTree Is A Tree That Is Not RootedVinoth GodiPas encore d'évaluation
- B Trees and Its VariantsDocument55 pagesB Trees and Its VariantszareePas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreeDocument24 pagesAVL TreerohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures in PythonDocument20 pagesData Structures in PythonBien MLPas encore d'évaluation
- Tree Material (3 Classes) PDFDocument23 pagesTree Material (3 Classes) PDFNaveen GowdruPas encore d'évaluation
- CSI 2110 Midterm 2014Document11 pagesCSI 2110 Midterm 2014Hussam ShahPas encore d'évaluation