Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Organs of The Respiratory System For Today
Transféré par
Septian Putra0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
58 vues12 pagesThe document summarizes the key organs that make up the human respiratory system. It describes the nose, trachea, bronchi, lungs, pharynx, epiglottis, alveoli, and diaphragm. It provides details on the structure and function of each organ, including that air enters through the nose and passes through various structures before reaching the alveoli in the lungs where gas exchange occurs before exiting.
Description originale:
Titre original
Organs of the Respiratory System for today.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe document summarizes the key organs that make up the human respiratory system. It describes the nose, trachea, bronchi, lungs, pharynx, epiglottis, alveoli, and diaphragm. It provides details on the structure and function of each organ, including that air enters through the nose and passes through various structures before reaching the alveoli in the lungs where gas exchange occurs before exiting.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
58 vues12 pagesOrgans of The Respiratory System For Today
Transféré par
Septian PutraThe document summarizes the key organs that make up the human respiratory system. It describes the nose, trachea, bronchi, lungs, pharynx, epiglottis, alveoli, and diaphragm. It provides details on the structure and function of each organ, including that air enters through the nose and passes through various structures before reaching the alveoli in the lungs where gas exchange occurs before exiting.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 12
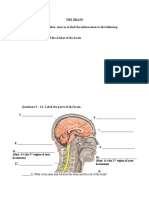
Organs of the Respiratory System
Nose
It is the organ through which air is inhaled and
exhaled. Nostrils (also known as external nares)
facilitate the process of inhalation and exhalation.
Vestibule is a part inside the nostrils lined by
coarse hair. Cavity of the nose is divided into two
parts by the nasal septum.
Nose
The superior and lateral walls of nasal cavity are
formed of the nasal, maxillary, ethmoid, frontal
and sphenoid bones. Floor of the nasal cavity is
composed of hard and soft palates. Cartilage is
external part of nose, which forms the tip and
bridge. Bony shelves which project from lateral
walls of the nose are known as inferior, middle and
superior nasal conchae.
Trachea
The trachea lies to the anterior side of the
esophagus. It is a tubular structure with 1 inch
diameter and a length of 4.25 inches. The length of
trachea spans between 6th cervical and 5th
thoracic vertebrae. Trachea is composed of around
15 - 20 'C' - shaped pieces of hyaline cartilage.
These pieces are held together by tracheal
muscles.
Bronchi
The tracheal tube when divided into two at the
caudal end, gives rise to left and right bronchi.
Bronchus is a passage that allows air flow into
lungs. Left bronchus, which is shorter than the
right one, further divides into 2 lobar bronchi;
right bronchus on the other hand is divided into 3
lobar bronchi
Lungs
The lungs are a pair of conical organs present in pleural
cavities; both the lungs together form an important part
of the human respiratory system. Left lung is divided
into 2 lobes (superior and inferior) while the right one in
3 (superior, inferior and middle). Each lung has a
median slit and hilus.
Pharynx
The pharynx is a body part common to both
respiratory and digestive systems. It is located
behind the nasal and oral cavities. The different
parts of pharynx are nasopharynx, oropharynx and
laryngopharynx. Pharynx is connected to skull
cavity by means of connective tissues and muscles.
Epiglottis
Composed of cartilaginous tissue, the epiglottis is
located at the opening of larynx i.e. at the back of
our tongue; it is covered by mucous. Since
epiglottis can get abraded easily, (as it lies in the
digestive tract) its surface is covered with
protective, non-keratinized and stratified
squamous epithelial cells.
Alveoli
The alveoli are sac-shaped bodies present inside
the lungs. These grape-like bodies are found only
in lungs of mammals and present at the end of
alveolar ducts. The alveoli functions as an interface
for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
between the lungs and capillaries that connect
with rest of the body.
Diaphragm
The diaphragm is a part of respiratory system
which plays an important role in breathing.
Contraction of muscles of diaphragm results into
expansion of thoracic cavity; this contraction of
diaphragm is important from the point of
expansion of lungs during inhalation.
of human respiratory
system
Air enters the nostrils
passes through the nasopharynx,
the oral pharynx
through the glottis
into the trachea
into the right and left bronchi, which branches and
rebranches into
bronchioles, each of which terminates in a cluster of
Alveoli
Picture of respiratory process
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Axial Skeleton SkullDocument36 pagesAxial Skeleton SkulltiiandiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System: Javaria ZahraDocument70 pagesNervous System: Javaria ZahraMuneeb JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord Injury Study GuideDocument8 pagesSpinal Cord Injury Study GuideAlice Gifford100% (3)
- Activity On The Respiratory and The Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesActivity On The Respiratory and The Circulatory SystemFheby ValeriePas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory System WorksheetDocument2 pagesRespiratory System WorksheetelizabethPas encore d'évaluation
- Male Reproductive System FinalDocument5 pagesMale Reproductive System FinalJohn Dale Lulu CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- The Integumentary System - The Dermis: T. RickDocument17 pagesThe Integumentary System - The Dermis: T. Rickapi-464344582Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exploring Anatomy Circulatory System WorksheetDocument4 pagesExploring Anatomy Circulatory System WorksheetBrian MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Alphabet Pronunciation NotesDocument4 pagesAlphabet Pronunciation NotesJameel KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Penile US and Doppler USDocument2 pagesPenile US and Doppler UShardrocker_2007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Pediatric Surgery PDFDocument463 pagesHandbook of Pediatric Surgery PDFDito DesdwiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory Systemapi-307592530Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition (Digestive System)Document57 pagesNutrition (Digestive System)anglie fePas encore d'évaluation
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument50 pagesMale Reproductive SystemFiona Claire LeePas encore d'évaluation
- NAFLD - NASH and Present & Future Management OptionsDocument78 pagesNAFLD - NASH and Present & Future Management OptionsSantosh AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument3 pagesNervous System WorksheetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument23 pagesCirculatory SystemAlexandra LigpitPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Digestive SystemDocument39 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSha KhinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of AnimalDocument12 pagesClassification of AnimalMustika Ayuni100% (1)
- AngerDocument27 pagesAngerikram ullah khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Edwards Critical Care Quick Guide To Cardiopulmonary Care PDFDocument188 pagesEdwards Critical Care Quick Guide To Cardiopulmonary Care PDFanonPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Exercise 1 FillableDocument16 pagesLaboratory Exercise 1 FillablePatricia Andrea Alexei FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Male & Female Reproductive System: Dr. Zainab Neamat Al-TaeeDocument46 pagesMale & Female Reproductive System: Dr. Zainab Neamat Al-TaeeIn UsPas encore d'évaluation
- C3 Anatomy and Physiology of Animals 1Document38 pagesC3 Anatomy and Physiology of Animals 1Jay Buelis100% (2)
- Rabbit RespirationDocument5 pagesRabbit RespirationshajehanPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive SystemDocument89 pagesReproductive SystemIbrahim Mahmoud Ali100% (1)
- Digestive System HandoutsDocument7 pagesDigestive System HandoutsClexandrea Dela Luz Corpuz100% (1)
- Reproductive SystemDocument29 pagesReproductive SystemGrace Marfa OreñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioPas encore d'évaluation
- 7th Class Respiratory SystemDocument14 pages7th Class Respiratory SystemCas Tan100% (1)
- Zoology PPT Skeletal SystemDocument28 pagesZoology PPT Skeletal SystemDian O. Velasquez100% (2)
- Excretory SystemDocument21 pagesExcretory SystemAnonymous 0C4OZmR100% (2)
- What Is FertilizationDocument8 pagesWhat Is Fertilizationapi-303065931Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive System of FrogDocument28 pagesDigestive System of FrogPaolo Naguit100% (1)
- RespiratoryDocument22 pagesRespiratorySaramanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Tissues 1Document45 pagesAnimal Tissues 1sirajPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP HypothermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HypothermiaJohn Paolo Ocampo100% (3)
- TMEGC Verkhoshansky Block System Training in Endurance RunningDocument3 pagesTMEGC Verkhoshansky Block System Training in Endurance Runningsdjuknic100% (1)
- Lab 7 - The Axial and Appendicular SkeletonDocument5 pagesLab 7 - The Axial and Appendicular Skeletonsidro123100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology,: Lecture OutlineDocument46 pagesAnatomy and Physiology,: Lecture OutlineRhona AngelaPas encore d'évaluation
- BMEN - Digestive System 2020Document76 pagesBMEN - Digestive System 2020OliviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anchorage Control in Bioprogressive Vs Straight-Wire Treatment PDFDocument6 pagesAnchorage Control in Bioprogressive Vs Straight-Wire Treatment PDFsolodont1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6th Class Digestive SystemDocument20 pages6th Class Digestive SystemJuvy MarquinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory SystemDocument16 pagesRespiratory SystemCristel Marie Matan Rojas100% (3)
- Laboratory Activity No. 9: The Frog Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 9: The Frog Respiratory SystemMaricris GuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument27 pagesThe Musculoskeletal SystemEduardoAlejoZamoraJr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure and Its EnvironmentDocument50 pagesCell Structure and Its EnvironmentCarol FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cilia and Flagella: Structure and Function in EukaryotesDocument10 pagesCilia and Flagella: Structure and Function in EukaryotesEr Purushottam PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Anatomy ModuleDocument48 pagesHuman Anatomy ModuleCielo CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Handouts in Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesHandouts in Skeletal SystemShiela Mae EslumPas encore d'évaluation
- Valence Electron and Ion PPT 2017Document15 pagesValence Electron and Ion PPT 2017api-283677111100% (2)
- Central Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesCentral Nervous SystemJames Lacuesta Tabiolo100% (1)
- Histology of Glands: Dr. Zana TahseenDocument28 pagesHistology of Glands: Dr. Zana TahseenAhmed JawdetPas encore d'évaluation
- File 1 AnaphyDocument3 pagesFile 1 Anaphyserainie maiPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory SystemHenry BuñagPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Activity 1 - Directional TermDocument4 pagesLab Activity 1 - Directional TermRio Geline EdralinPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 14 The Special SensesDocument8 pagesUnit 14 The Special SensesJess LPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Anatomical TermsDocument13 pagesBasic Anatomical TermsZehra JamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 9 Lesson 5Document21 pagesModule 9 Lesson 5Faatoots FatsPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4 - Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 4 - Circulatory Systemapi-307592530Pas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemtadashiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Spine Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSpine Lesson Planapi-37914933950% (2)
- 7es Respiratory System Lesson PlanDocument5 pages7es Respiratory System Lesson PlanJuliet Marabise-OpanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Puberty PDFDocument6 pagesPuberty PDFjoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Organs and Systems Worksheet 1Document1 pageHuman Organs and Systems Worksheet 1Ala AsAd100% (1)
- Endocrine & Reproductive SystemsDocument12 pagesEndocrine & Reproductive SystemsEfanPutra100% (1)
- DJ (Microtubules, Microfilaments and Intermediate Filaments) - DJGFDocument43 pagesDJ (Microtubules, Microfilaments and Intermediate Filaments) - DJGFNick_989893Pas encore d'évaluation
- EpitheliumDocument48 pagesEpitheliumdrpankaj28100% (1)
- The Structure and Function of Animal Cell Components: An Introductory TextD'EverandThe Structure and Function of Animal Cell Components: An Introductory TextPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemEmmeth ArdientePas encore d'évaluation
- And Classification. AO Foundation PublishingDocument1 pageAnd Classification. AO Foundation PublishingSeptian PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Obesitas Dan DMDocument4 pagesObesitas Dan DMSeptian PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pres. Histo. Sist. Imun - SNW '13Document34 pagesPres. Histo. Sist. Imun - SNW '13Septian PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- DM Tipe 2Document5 pagesDM Tipe 2Septian PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- DM in IranDocument5 pagesDM in IranSeptian PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkana, Alkena, AlkunaDocument32 pagesAlkana, Alkena, AlkunaSeptian PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM - Notes RepairedDocument19 pagesHUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM - Notes RepairedLoren EscotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 25 Biochemistry Chapter ObjectivesDocument10 pagesChapter 25 Biochemistry Chapter ObjectivesLyza KatePas encore d'évaluation
- A Seminar Report ON Blue BrainDocument20 pagesA Seminar Report ON Blue BrainAngela KaifPas encore d'évaluation
- RBCs Abnormal Morphology FinalDocument33 pagesRBCs Abnormal Morphology FinalInahkoni Alpheus Sky OiragasPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Behavior & Stimulus EnergyDocument17 pagesAnimal Behavior & Stimulus Energylevonbachdasarian100% (1)
- AbscessDocument26 pagesAbscessThusith WijayawardenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Organelles FunctionsDocument1 pageCell Organelles FunctionsFedomessi10 Is a geniusPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 1.5cell DivisionDocument2 pagesActivity 1.5cell Divisionfroilan obligadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Proliferasi in Vitro Dan Aklimatisasi Pisang Kepok Unti Sayang (ABB) Dengan Penambahan Bahan OrganikDocument10 pagesProliferasi in Vitro Dan Aklimatisasi Pisang Kepok Unti Sayang (ABB) Dengan Penambahan Bahan Organiksarah khoerun nisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nematology: Plant NotesDocument304 pagesNematology: Plant NotesLokesh AhirwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Juvenile HormoneDocument17 pagesJuvenile HormonejugesmangangPas encore d'évaluation
- Fas 161 PDFDocument2 pagesFas 161 PDFTonyPas encore d'évaluation
- OB Definition of TermsDocument9 pagesOB Definition of TermsWarrenSandovalPas encore d'évaluation
- Vestibular DisorderDocument22 pagesVestibular DisorderSumbal SalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Music Perception and Cognition: Development, Neural Basis, and Rehabilitative Use of MusicDocument11 pagesMusic Perception and Cognition: Development, Neural Basis, and Rehabilitative Use of MusicAutes AG100% (1)
- Active Principle: Lecture 10 Pharm Sci/Chem 177, University of California, IrvineDocument52 pagesActive Principle: Lecture 10 Pharm Sci/Chem 177, University of California, IrvineVivian PhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Sleep Disorders in ChildrenDocument10 pagesCommon Sleep Disorders in ChildrenHajrin PajriPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaRakanita Tiara PuspitasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnose of Submandibular Abscess PDFDocument13 pagesDiagnose of Submandibular Abscess PDFElvitrianaPas encore d'évaluation
- 23 Anatomy Physiology TermsDocument30 pages23 Anatomy Physiology TermsAlyssa Gwyneth GalubaPas encore d'évaluation