Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
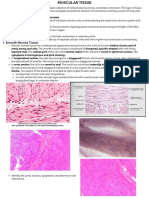
K02 Histology of Muscle Tissue
Transféré par
agnes0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
34 vues43 pagesSlide Kuliah
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentSlide Kuliah
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
34 vues43 pagesK02 Histology of Muscle Tissue
Transféré par
agnesSlide Kuliah
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 43
FUNCTION : Movement, heart beat,
vascular contraction, peristaltic,
gallbladder emptying, etc. (1,2)
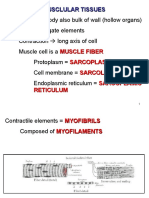
Muscle cell Muscle fiber coz its
elongated shape(2)
Develop from mesoderm (1)
Most abundant tissue in human
body (2)
Structure of skeletal muscle :
Formed by long cylindrical,
multinucleated cell/fiber
Cross-striations on muscle
fiber
Contraction : fast & voluntary
FASICLE/FASIKULUS : groups of
muscle fibers. Group of fasicle
muscle
Generally do not branch
except in face & tongue(2)
Surrounded by :
Epimysium
Perimysium
Endomysium
Epi/Peri/Endomysium
continous layer
with blood & lymph
vessel, nerves.
Sarcolemma
Sarcoplasm
Mutinucleated cell,
peripherally placed
nuclei, located
below the
sarcolemma/sub
sarcolemma
Sarcosom
Sarcoplamic reticulum :
Has sarcotubules
form a mesh around
each myofibril called
TERMINAL
CISTERNAE
2 T. cisternae & T-
tubule (originated
from sarcolemma)
form TRIAD of
skeletal muscle
Elongated, threadlike
structures in the
sarcoplasm, run the length
of muscle muscle fiber
Consist of :
1. Thin fillament :
Actin
Tropomyosin
Troponin
2. Thick fillament :
Myosin
Elastic filament (titin)
Thick & thin fillament
Banding in skeletal muscle :
A band (dark band) : thin &
thick filament overlapping
I band (light band) : thin
filament only
H band : thick filament only
M line : separate direction of
Myosin orientation
Z line : separate sarcomeres
Sarcomere : contraction unit
between 2 Z line in myofibril
The bracket spans a distance of 10 sarcomeres.
Branches of a motor nerve
end on the muscle fiber
Appear as slightly elevated
plaque on muscle fiber
accumulation of nuclei
Consist of :
Unmyelinated axon
Primary synaptic clefts
from axon, with synaptic
vesicle filled with
acetylcholine
Secondary synaptic clefts
from sarcolemma of musle
fiber
Neurotransmitter
Acetylcholine carries
the message across
the cleft!
NEUROMUSCULAR
SPINDLE/MUSCLE SPINDLE
: modified skeletal muscle
fiber associated with
sensory and motor nerves
Intrafusal fibers
2 types of intrafusal fibers :
1. Nuclear bag fiber :
larger
2. Nuclear chain fiber :
thinner, nuclei form
single row
FIG. 4. Normal-appearing muscle from a 4-year-old girl. The
center of the image contains a normal-appearing muscle spindle.
(H&E, 200x)
Ca 2+ released from
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Thin filament shift to myosin
move inward A band
Space between I band & H
band shortens
Z line move toward A band
sarcomere shortens
Contraction
Ca2+ return to sarcoplasmic
reticulum Relaxation
Adenosine triphosphate
(ATP) Mitochondria
ATP from aerobic or
anaerobic metabolism
Found only in heart (2)
Contraction : automatic,
spontaneous & involuntary(1,
2)
Structure of cardiac muscle :
(1, 2)
Striated but involuntary
Surrounded by conn tissue
as in skeletal muscle
more irregular due to
branching fibers
Elongated, cylindrical &
branching fiber
Each fiber contains only 1 or
2 nuclei, centrally placed
Cross striations similar to
skeletal muscle (A/I/H band
& M/Z line)
Sarcoplasm contain
numerous large
mitochondria
Longitudinal section of cardiac muscle.
The endomysium is shown by (a)
The arrowheads show intercalated discs.
The arrows indicate regions of branching
(b) shows lipochrome granules which appear in the cytoplasm near the nuclei of cardiac
muscle.
Special junctions at the end
of two cardiac fiber
Light microscope : dark
lines crossed the cardiac
fiber
3 junctions :
1. Fascia adherens
2. Macula adherens
(desmosome)
3. Gap junctions
Modification of
cardiac muscle
transfer impulse faster
than ordinary cardiac
muscle
Purkinje fiber : thicker,
larger diameter, more
cytoplasm & contain
less myofibril
Distribution : whole body
(blood vessel, GI tract,
respiratory tract, dermis,
reproductive system)(2)
No cross striations(1, 2)
Contraction : slow,
continue & involuntary(1,
2)
Vary in length in different
organs (20 m in small
blood vessel to 500-600
m in pregnant uterus)
Squamous cell,
expanded central region,
tapering ends
Squamous nuclei, single
& centrally placed
Sarcoplasm : no
striations
homogenous
Cardiac muscle : unable to regenerate scar
tissue
Skeletal muscle : able to regenerate perform
by satellite cell
Smooth muscle : limited ability to regenerate
perform by mitosis of muscle cell
1. Histologi Dasar, Edisi 8, L. Carlos Junquira MD,
Jose Carneiro MD, Robert O. Kelley PhD, EGC,
1995. Hal. 220-238
2. Essentials Of Human Histology, Second Edition,
William J. Krause PhD, Little Brown &
Company (Inc), 1996. Hal. 117-137
3. Color Textbook of Histologi, 2nd edition, Gartner LP,
Hiatt JL, WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia,
Pennsylvania, 2001.
1. Ny. Nana, 40 thn, datang ke Poliklinik dgn keluhan diare. Hal ini
dialami sejak tadi malam. Frekwensi 8 kali. Buang air besar
disertai lendir, darah dan rasa mulas. Dari hasil pemeriksaan
didapati rasa mulas berasal dari kontraksi berlebihan otot usus
Ny. Nana.
Pernyataan yg sesuai untuk otot usus Ny. Nana adalah.
A. Serat silindris dan bercabang
B. Terdapat intercalated disc
C. Bentuk serat squamous
D. Terdapat striation pada sarcoplasma
E. Nucleus terletak subsarcolemma
JAWAB : C
2. Pernyataan yang benar untuk inti sel pada soal diatas adalah
A. Inti sel 1 atau 2 buah
B. Nucleus multiple
C. Nucleus subsarcolemma
D. Nucleus terletak dibagian perifer
E. Nucleus terletak di bagian central sel
JAWAB : E
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Muscle Tissue - Wo AudioDocument33 pagesMuscle Tissue - Wo Audiozahra nabilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle TissueDocument33 pagesMuscle TissueFady FadyPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular Tissue and Nervous TissueDocument29 pagesMuscular Tissue and Nervous Tissuenikitachaudhary1220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4 Muscular TissueDocument44 pagesModule 4 Muscular Tissuelarry machonPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology of Nervous Tissue: - Neuroglia - Neurons - MyelinationDocument40 pagesHistology of Nervous Tissue: - Neuroglia - Neurons - MyelinationRed StonePas encore d'évaluation
- Histology of Cardiac Muscle by DR. RoomiDocument13 pagesHistology of Cardiac Muscle by DR. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (2)
- Тема 11 (author O.Mazuru) PDFDocument51 pagesТема 11 (author O.Mazuru) PDFCornelMaximciucPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 - Muscle Tissue DR - Vera 2021-2Document45 pages6 - Muscle Tissue DR - Vera 2021-2Wilmarilys Ramos MartellPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleDocument73 pagesHistology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleShehryar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleDocument73 pagesHistology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleShehryar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Tissues - PakaiDocument54 pagesMuscle Tissues - PakaiAisyah RaihanPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument24 pagesMuscle PhysiologyArmando AlehandroPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Muscle 2022Document39 pages04 Muscle 2022AlkadafePas encore d'évaluation
- A&p 1Document44 pagesA&p 1HARI KRISHNA G LPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Histology Lecture, Structure of Muscular TissueDocument37 pages10 - Histology Lecture, Structure of Muscular TissueAMIRA HELAYELPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular TissueDocument37 pagesMuscular Tissueمؤمل عدنان الشمخيPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular and Nervous Tissue Handout 1Document17 pagesMuscular and Nervous Tissue Handout 1Wheteng YormaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Tissue - HistologyDocument35 pagesMuscle Tissue - HistologyjabirPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 6Document4 pagesLecture 6A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaiePas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Tissue (1) 094116Document49 pagesMuscle Tissue (1) 094116OushahPas encore d'évaluation
- MUSCLE CELL PHYSIOLOGY MBCHB YEAR 1 2016-2Document289 pagesMUSCLE CELL PHYSIOLOGY MBCHB YEAR 1 2016-2AdminPas encore d'évaluation
- 2-Muscle StructureDocument33 pages2-Muscle Structureasaad AseeePas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Tissue 2012Document13 pagesMuscle Tissue 2012ST. Fatimah KadirPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology 6 MuscleDocument88 pagesHistology 6 MuscleAbdul RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- MascularDocument39 pagesMascularAive BelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- MUSCLE and NERVOUSHISTOLOGYDocument78 pagesMUSCLE and NERVOUSHISTOLOGYAerielle De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord and Nerve Plexii: by Dr. TDocument20 pagesSpinal Cord and Nerve Plexii: by Dr. TthwisemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle DentalDocument74 pagesMuscle Dentalapi-3710331Pas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle and Nerve HistoPHysioDocument91 pagesMuscle and Nerve HistoPHysioashley nicholePas encore d'évaluation
- CNS Lecture MaucoDocument42 pagesCNS Lecture Maucothatomosala849Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4.1 PhysDocument27 pages4.1 PhysshivaniPas encore d'évaluation
- The Spinal Cord,, and Blood Supply To The BrainDocument78 pagesThe Spinal Cord,, and Blood Supply To The BrainMartha MulusaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular SystemDocument12 pagesMuscular SystemChrisjohn Aster OsioPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle TissueDocument3 pagesMuscle Tissuekugmo89Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Are The Important Topics of The General AnatDocument1 pageWhat Are The Important Topics of The General AnatSanjeev VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3Document22 pagesLab 3202310446Pas encore d'évaluation
- 10th Week - Cardiac Muscle HistologyDocument15 pages10th Week - Cardiac Muscle Histologyნია გელაშვილიPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Tissue-Wl06.11Document54 pagesMuscle Tissue-Wl06.11api-19641337Pas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular TissueDocument6 pagesMuscular TissueChezkaMayC.OliverosPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of MusclesDocument8 pagesTypes of MusclesJoan Vito CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle TissueDocument31 pagesMuscle Tissueaimi BatrisyiaPas encore d'évaluation
- MuscularDocument61 pagesMuscularFranz DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle: Gerald Dale Giron MD Department of Human Structural BiologyDocument23 pagesMuscle: Gerald Dale Giron MD Department of Human Structural BiologyMarx AsuncionPas encore d'évaluation
- 15th Proper 1301 SeqDocument21 pages15th Proper 1301 SeqAfk SystemPas encore d'évaluation
- Veterinary Normal HistologyDocument10 pagesVeterinary Normal HistologyIshtar Katherine ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal Muscle StructureDocument38 pagesSkeletal Muscle Structuretoyy100% (1)
- Muscle Tissue VnaDocument55 pagesMuscle Tissue Vnavaryvira6677Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lec.8 DR - Thaer: Muscles PhysiologyDocument24 pagesLec.8 DR - Thaer: Muscles Physiologyroqaia roqaiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Pgy - 222Document48 pagesMuscle Pgy - 222SAVIOUR BANDAPas encore d'évaluation
- A - Muscle and Nervous TissueDocument53 pagesA - Muscle and Nervous TissueObsinan HeboPas encore d'évaluation
- Anfis Ke 4Document60 pagesAnfis Ke 4Adeputra WijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle TissueDocument30 pagesMuscle TissueAhwaar Chaudary100% (1)
- ANAPHY - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesANAPHY - Muscular SystemSoleil RiegoPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology Muscle & Nerve: Dr. JagadeeshDocument38 pagesHistology Muscle & Nerve: Dr. JagadeeshcheckmatePas encore d'évaluation
- 3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015Document34 pages3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015yigermalamanuel32Pas encore d'évaluation
- Spinalcord and It's Connections Neuro Anatomy - 2Document30 pagesSpinalcord and It's Connections Neuro Anatomy - 2Jamaru NishaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Tissue OutlineDocument4 pagesMuscle Tissue OutlinePeachy PiePas encore d'évaluation
- HistologyDocument28 pagesHistologyzoomies homiesPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal Muscle Histology by DR RoomiDocument16 pagesSkeletal Muscle Histology by DR RoomiGhadeer M HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesD'EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesPas encore d'évaluation
- K2 - Strongyloides StercoralisDocument16 pagesK2 - Strongyloides StercoralisagnesPas encore d'évaluation
- Bakul K13 Ectoparasite - RevisiDocument28 pagesBakul K13 Ectoparasite - RevisiagnesPas encore d'évaluation
- K1-Histo Kuliah Kulit, Februari 2014Document42 pagesK1-Histo Kuliah Kulit, Februari 2014Patrick TianPas encore d'évaluation
- K1 - BBS-Introduction To ParasitologyDocument54 pagesK1 - BBS-Introduction To ParasitologyagnesPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Microbiology: Department of Microbiology Medical Faculty USUDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology: Department of Microbiology Medical Faculty USUagnesPas encore d'évaluation
- DS-K9 Microbe Causing Skin DiseaseDocument42 pagesDS-K9 Microbe Causing Skin DiseaseSures Amoeba RajPas encore d'évaluation
- K18 Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi ObatDocument32 pagesK18 Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi ObatCatherine ElizabetPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution: Dept. Pharmacology & Therapeutic FK - UsuDocument16 pagesDistribution: Dept. Pharmacology & Therapeutic FK - UsuagnesPas encore d'évaluation
- K11-Urethral Stricture DiseaseDocument14 pagesK11-Urethral Stricture DiseaseagnesPas encore d'évaluation
- Genitourinary Cancer: Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera UtaraDocument31 pagesGenitourinary Cancer: Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera UtaraagnesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ashari Adi Abimantrana 22010112130062 LapKTI Bab7Document22 pagesAshari Adi Abimantrana 22010112130062 LapKTI Bab7agnesPas encore d'évaluation
- K-36 Urologic TraumaDocument48 pagesK-36 Urologic TraumaDesi Indah LaisPas encore d'évaluation
- K-36 Urologic TraumaDocument48 pagesK-36 Urologic TraumaDesi Indah LaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Scrotal SwellingDocument34 pagesScrotal SwellingViviViviPas encore d'évaluation
- K2 - IKK - Global Strategy For The Prevention STI (IKK)Document26 pagesK2 - IKK - Global Strategy For The Prevention STI (IKK)enriPas encore d'évaluation
- Lehninger - 7e - PPT - ch05 - Final (Autosaved)Document53 pagesLehninger - 7e - PPT - ch05 - Final (Autosaved)Chance SwansonPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Physiology Course NotesDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course NotesAdam Linoby100% (16)
- (ZOO301) Chapter 11 - MusclesDocument17 pages(ZOO301) Chapter 11 - MusclesRain Hong100% (1)
- Basic Clinical Massage TherapyDocument654 pagesBasic Clinical Massage Therapykkism100% (11)
- Bird Et Al (2005)Document11 pagesBird Et Al (2005)Ewan MurrayPas encore d'évaluation
- ANP 300 Exam 1 ReviewDocument8 pagesANP 300 Exam 1 ReviewNerdy Notes Inc.Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 2muscular System 1Document23 pages1 2muscular System 1api-343368893Pas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper 2022-FinalDocument13 pagesResearch Paper 2022-Finalapi-610696822Pas encore d'évaluation
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument210 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemDr. Serin KuriakosePas encore d'évaluation
- 11.2 MovementDocument24 pages11.2 MovementAndyChoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 - Musculoskeletal SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 8 - Musculoskeletal SystemIbby HooriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Meat (Beef and Pork)Document53 pagesMeat (Beef and Pork)Maria Athenna MallariPas encore d'évaluation
- PMUS1-11 Biology of Muscles IDocument68 pagesPMUS1-11 Biology of Muscles IVictor ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Six The Muscular SystemDocument30 pagesChapter Six The Muscular SystemabiyotPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle System kd13Document46 pagesMuscle System kd13Side PoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscles of Mastication FarhanDocument117 pagesMuscles of Mastication FarhanankitaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2) SKELETAL MUSCLES A) Basic Skeletal Muscle PhysiologyDocument17 pages2) SKELETAL MUSCLES A) Basic Skeletal Muscle Physiologyfebruary141979Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Critical Evaluation of The Biological ConstructDocument23 pagesA Critical Evaluation of The Biological ConstructRosaneLacerdaPas encore d'évaluation
- AQA A2 Biology 20 Sample Synoptic EssaysDocument41 pagesAQA A2 Biology 20 Sample Synoptic EssaysHuck Polenski100% (4)
- Natural Bodybuilding and Body Recomposition Slim With Muscles 2021Document173 pagesNatural Bodybuilding and Body Recomposition Slim With Muscles 2021tsuki.lightPas encore d'évaluation
- Tortora Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesTortora Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologybebePas encore d'évaluation
- ACT Personal Trainer Certification Textbook v1 2Document315 pagesACT Personal Trainer Certification Textbook v1 2AwyrMerddyn100% (7)
- Biomechanics of Skeletal MuscleDocument42 pagesBiomechanics of Skeletal MuscleDesta Amanda Awalia50% (2)
- 1 MusclesDocument29 pages1 MusclesGideon CavidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Physiology PDFDocument103 pagesMuscle Physiology PDFedabzan234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal Muscle PhysiologyDocument12 pagesSkeletal Muscle PhysiologyGuizzudo CraftPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers Chapter 10 and 11 ExamDocument7 pagesAnswers Chapter 10 and 11 ExamMara Romanoff75% (4)
- T1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoDocument6 pagesT1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoMartín Benítez del HoyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Pse U1 L2Document16 pagesBio Pse U1 L2AlalafsaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Muscular System Part 2Document34 pagesThe Muscular System Part 2ISTORYAPas encore d'évaluation