Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
1.tech Features of RD Imp Projects - DR - Justo CM
Transféré par
ashoknr0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
2 vues37 pagesRoad
Titre original
1.Tech Features of Rd Imp Projects - Dr.justo Cm
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentRoad
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
2 vues37 pages1.tech Features of RD Imp Projects - DR - Justo CM
Transféré par
ashoknrRoad
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 37
Technical Features of Road
Improvement Projects
Dr. C.E.G. Justo
Honorary Professor, Bangalore University
Director, KRDCL
and Technical Advisor, IR Rasta
1. Introduction
1.1 National level Development
projects
NHDP (N-S and E-W Corridors, Golden
Quadrilateral by NHAI)
Other upgradation of NH stretches and
new bypasses by MORTH
Expressways and other BOT projects
1.2 State level Highway projects
State Highways improvement projects
(with World Bank loan assistance)
Road improvement projects through
State Road Development Corporations
and Road Boards
1.3 Rural Road Development projects
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana
(PMGSY)
Projects with assistance from other
agencies like NABARD
1.4 Urban Road Improvement
projects
Urban Infrastructure Development
projects with ADB loan assistance
Special schemes by Municipal
Corporations
1.5 General scope of these projects
Improvement of existing / Strengthening
roads
Rehabilitation / Reconstruction of Stretches of
Stretches
Upgradation of Geometrics
Upgradation by widening (Single / dual
carriageway)
Construction of new road stretches /
bypasses
2 Minor Road Improvement
works
2.1 Maintenance of drainage system
Longitudinal drains (desilting,
missing links / new drains)
Cross drainage system
Camber
Drainage on shoulders (see figures 1,
2(a) , 2(b) & 3)
Sub surface drainage
Figure 1
Figure 2 (a)
Figure 2 (b)
Figure 3
2.2 Treatment of Existing Pavement
- Patching of Pot holes
2.3 Treatment of Areas with Wide
Cracks
Figure 5
Figure 6
2.4 Treatment of bituminous surface
with fine cracks
Liquid seal
Fog seal
Slurry seal
Seal coat
Premix patching
2.5 Profile correction
Depression filling
Correction of cross slope
2.6 Resurfacing (after steps 2.1 to
2.5)
Thin bituminous surfacings
S.D.
PC with Type A or B seal coat
MSS
SDBC
Figure 7
3 Strengthening by overlay
Pavement evaluation
Overlay design
Steps 2.1 to 2.5
Selection of overlaying materials &
thickness
BM+PC/MSS/SDBC/BC
BM+DBM+BC
DBM+PC
BC
4 Rehabilitation of old damaged
surface and strengthening /
resurfacing
4.1 Removal of damaged bituminous
layer
Methods for this surfacing
Method for removal of one of the thick
bituminous layers
4.2 Profile correction -material
4.3 Scope of re-using of removed
5.Upgradation of Road Geometrics
5.1 Cross Sectional Elements
- Cross Slope
- Width of Carriageway / Roadway
- Medians / Kerbs
5.2 Sight Distance
- Stopping Sight Distance
- Overtaking Sight Distance
- Intermediate Sight Distance
Geometric Design
5.3 Horizontal Alignment
- Superelevation
- Horizontal Curves
radius, widening at curves
- Transition Curves
5.4 Vertical Alignment
- Gradient
- Vertical Curves ..summit curves, valley
curves
6. Upgradation - Widening of
single carriage-way
6.1 Requirements of widening
Formation and shoulders
Single / Intermediate lane to 2 lanes
2 lanes to 2 lanes with paved
shoulders
6.2 Types of widening of pavement
Direct widening (See figure 8)
Removal of part of pavement and
widening (See figure 9)
Figure 8
Figure 9
6.3 Steps for widening with
conventional drainage layer
6.4 Steps for widening with alternate
method of sub-surface drainage
Figure 10
Figure 11
7 Upgradation -Raising of
formation and re-construction
7.1 Objects
7.2 Method (Figure 13)
7.3 Steps
7.4
Figure 12
8 Upgradation - Widening of 2
lane road to divided carriage-
way
8.1 Symmetrical widening -Alternative-1
Method (Figure 13)
Advantages
Limitations
Figure 13
8.2 One side widening by new
carriage-way and raised central
median (Alternative-2)
Method
Advantages
Limitations
Figure 14
8.3 One side widening by new
carriage-way and depressed central
median
Method
Advantages
Limitations
Figure 15
Any Questions?
Thank You
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Certificate-12-"Hydrological Studies of Chandrabhaga River'Document3 pagesCertificate-12-"Hydrological Studies of Chandrabhaga River'ashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- A Seminar Report On Self Sustainable BuildingDocument32 pagesA Seminar Report On Self Sustainable BuildingashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Mini Proj Sample Report BPPDocument50 pagesMini Proj Sample Report BPPashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate-10-"Hydrological Studies of Kishna RiverDocument26 pagesCertificate-10-"Hydrological Studies of Kishna RiverashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate-9-"SUITABLE CONDITIONS FOR ROOTZONE-UbaleDocument3 pagesCertificate-9-"SUITABLE CONDITIONS FOR ROOTZONE-UbaleashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomediacal Waste Project FinalDocument43 pagesBiomediacal Waste Project Finalashoknr100% (1)
- Certificate-11-"Hydrological Studies of Panchaganga River'Document3 pagesCertificate-11-"Hydrological Studies of Panchaganga River'ashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Po 1Document1 pagePo 1ashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Road Note No. 4 Method/DOE MethodDocument11 pagesRoad Note No. 4 Method/DOE MethodashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate 1 Biomedical Waste Management PVDDocument3 pagesCertificate 1 Biomedical Waste Management PVDashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate 1 Biomedical Waste Management PVDDocument3 pagesCertificate 1 Biomedical Waste Management PVDashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate 1 Biomedical Waste Management PVDDocument3 pagesCertificate 1 Biomedical Waste Management PVDashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- PROJECT REPORT (ITS) - Mini Project-Bipin PatilDocument51 pagesPROJECT REPORT (ITS) - Mini Project-Bipin PatilashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Justifications 17.9.18Document23 pagesJustifications 17.9.18ashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- S. Y. B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) - I, Semester-III: Course ContentDocument5 pagesS. Y. B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) - I, Semester-III: Course ContentashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- S. Y. B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) - I, Semester-III: Course ContentDocument5 pagesS. Y. B. Tech. (Civil Engineering) - I, Semester-III: Course ContentashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- NHAI LetterDocument1 pageNHAI LetterashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Po 1Document1 pagePo 1ashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Justifications 17.9.18Document23 pagesJustifications 17.9.18ashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
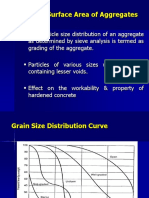
- Unit-I-Aggregate GradingDocument22 pagesUnit-I-Aggregate GradingashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Raw Materials of Portland: - Lime - Silica - Alumina - Iron OxideDocument10 pagesRaw Materials of Portland: - Lime - Silica - Alumina - Iron OxideashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- NHAI LetterDocument1 pageNHAI LetterashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Presented BY: Ashok KumarDocument50 pagesPresented BY: Ashok KumarashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Walchand Institute of Technology, Solapur B.E. Part-II 2018-19 (CBCS Pattern) In-Sem. Examination - IIIDocument2 pagesWalchand Institute of Technology, Solapur B.E. Part-II 2018-19 (CBCS Pattern) In-Sem. Examination - IIIashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Name-Airport Obstructions Add Sections: 1) Imaginary Surfaces: A) Add Video B) Quiz C) Lecture Notes In-Video QuizDocument1 pageChapter Name-Airport Obstructions Add Sections: 1) Imaginary Surfaces: A) Add Video B) Quiz C) Lecture Notes In-Video QuizashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Proposals For IIC in WIT SolapurDocument1 pageProposals For IIC in WIT SolapurashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- ACI MethodDocument57 pagesACI MethodashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual of Concrete Technology: Chetan S. PatilDocument76 pagesLab Manual of Concrete Technology: Chetan S. PatilashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- External Audit Format - 25022021Document17 pagesExternal Audit Format - 25022021ashoknrPas encore d'évaluation
- Live Interactions Via Google Meet: Kameswari Chebrolu Department of CSE, IIT BombayDocument5 pagesLive Interactions Via Google Meet: Kameswari Chebrolu Department of CSE, IIT BombayAshok Kumar RajanavarPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- PGT Computer Science Kendriya Vidyalaya Entrance Exam Question PapersDocument117 pagesPGT Computer Science Kendriya Vidyalaya Entrance Exam Question PapersimshwezPas encore d'évaluation
- Boonton Radio Corporation - The Notebook 12Document8 pagesBoonton Radio Corporation - The Notebook 12Luiz Roberto PascottePas encore d'évaluation
- Artikel 8 - (CURRICULUM EVALUATION)Document12 pagesArtikel 8 - (CURRICULUM EVALUATION)Kikit8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Utah Vaccine AdministrationDocument1 pageUtah Vaccine AdministrationOffice of Utah Gov. Spencer J. CoxPas encore d'évaluation
- Performace Task 2 Electric Field LinesDocument31 pagesPerformace Task 2 Electric Field LinesStephanie Nichole Ian CasemPas encore d'évaluation
- The Future of Comparative Literary StudiesDocument14 pagesThe Future of Comparative Literary StudiesNabeesath ArifaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure Delegation Training For LeadersDocument6 pagesBrochure Delegation Training For LeadersSupport ALProgramsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cracking Passwords GuideDocument45 pagesCracking Passwords GuideKorben100% (6)
- Hatchery Practice: InternationalDocument40 pagesHatchery Practice: Internationalabhe prasetyaPas encore d'évaluation
- D1 001 Prof Rudi STAR - DM in Indonesia - From Theory To The Real WorldDocument37 pagesD1 001 Prof Rudi STAR - DM in Indonesia - From Theory To The Real WorldNovietha Lia FarizymelinPas encore d'évaluation
- Historic Trial of Ali Brothers and Shankaracharya-1921Document276 pagesHistoric Trial of Ali Brothers and Shankaracharya-1921Sampath Bulusu100% (3)
- Assessment 3 Comparative Analysis Primary Vs Secondary SourcesDocument5 pagesAssessment 3 Comparative Analysis Primary Vs Secondary SourcesMATOZA, YLJOE V.Pas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - Packed Tower Design-1Document65 pages8 - Packed Tower Design-1M.H vafaeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation Manual of FirmwareDocument6 pagesInstallation Manual of FirmwareOmar Stalin Lucio RonPas encore d'évaluation
- Task 4 - Illustrating Psychoanalytic CriticismDocument9 pagesTask 4 - Illustrating Psychoanalytic CriticismTroJaf OfficialPas encore d'évaluation
- Grief and BereavementDocument4 pagesGrief and BereavementhaminpocketPas encore d'évaluation
- Thetford c250 InstallationDocument19 pagesThetford c250 InstallationCatalin Bejan100% (1)
- Unit 8 Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry PDFDocument23 pagesUnit 8 Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry PDFCh AswadPas encore d'évaluation
- Jim 1000 RC 3Document33 pagesJim 1000 RC 3singingblueePas encore d'évaluation
- Somanabolic+Muscle+Maximizer+PDF+ +eBook+Free+Download+Kyle+LeonDocument34 pagesSomanabolic+Muscle+Maximizer+PDF+ +eBook+Free+Download+Kyle+LeonAaron BarclayPas encore d'évaluation
- FPI - Study Permit Application GuideDocument9 pagesFPI - Study Permit Application GuideKian Mark DarioPas encore d'évaluation
- A320 Abnormal Notes: Last UpdatedDocument13 pagesA320 Abnormal Notes: Last UpdatedDevdatt SondePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2: TransducerDocument24 pagesUnit 2: TransducerROYAL GAMER YTPas encore d'évaluation
- Sector San Juan Guidance For RepoweringDocument12 pagesSector San Juan Guidance For RepoweringTroy IveyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan - Organization and ManagementDocument5 pagesLesson Plan - Organization and ManagementBilly Joe80% (15)
- 13-Mike Engelbrecht - Methods of Maintenance On High Voltage Fluid FilledDocument5 pages13-Mike Engelbrecht - Methods of Maintenance On High Voltage Fluid FilledRomany AllamPas encore d'évaluation
- Obat Keras N0vember 2021Document137 pagesObat Keras N0vember 2021antonPas encore d'évaluation
- N Mon Visualizer OverviewDocument27 pagesN Mon Visualizer OverviewClaudioQuinterosCarreñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Archaeology - October 2016 PDFDocument72 pagesArchaeology - October 2016 PDFOmer CetinkayaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104Document57 pages1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104f.kpobi1473Pas encore d'évaluation