Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Steam Power Plant
Transféré par
ajeet kumar0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
73 vues33 pagesTitre original
SteamPowerPlant.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
73 vues33 pagesSteam Power Plant
Transféré par
ajeet kumarDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 33
Lesson 7
mechanical power is produced by a heat
engine that transforms thermal energy (from
combustion of a fuel) into rotational energy
heat (generated in the furnace) is transmitted
to the boiler where water forced into the
boiler by the feed pump is converted into
steam
steam drives turbine blades shaft
the efficiency of a steam turbine is limited by
the maximum temperature of the steam
produced and is not directly a function of the
fuel used (for the same steam conditions,
coal, nuclear and gas power plants all have
the same theoretical efficiency)
Operating pressure
Boiler efficiency
Steaming hours
Heating surface
Generating surface
Superheated steam
Operating pressure the pressure at which
the boiler is operated in service
Boiler efficiency -the ratio between the
thermal energy actually absorbed by water
and the thermal energy available in fuel (80
90 %)
Steaming hours -the time during which the
boiler generates steam
Heating surface -the total surface of all parts
exposed to combustion gases (tubes,
superheater, economiser)
Generating surface - a part of the surface in
which water is heated and steam is generated
(tubes, drum)
Superheated steam = saturated steam +
more heat at constant pressure > dry steam
(to avoid damage to tubine blades)
FURNACE
BOILER
SUPERHEATER
TURBINE
CONDENSER
a chamber in which heat is produced
combustion of fuel & generation of hot gases
burners break oil into fine particles to
ensure efficient combustion
steam generator saturated & superheated
steam
steam drum - a reservoir of water/steam at
the top end of the water tubes, it stores the
steam generated in the water tubes and acts
as a separator for the steam/water mixture
(difference in densities)
water circulation natural or forced
watertube boiler
firetube boiler
hot gases pass through the tubes, feed water
surrounds them
steam and water circulate through drums and
small diameter tubes, gases of combustion
pass around them
more commonly used, lighter, occupies less
space and has increased efficiency (higher
pressure and temperature)
main boiler
donkey (auxiliary) boiler
low, intermediate, high pressure b.
single-drum b., two-drum b., three-drum b.
vertical b., horizontal b.
single-flow b., double-flow b.
consists of headers and superheater tubes
converts saturated steam into dry steam
steam is admitted to the turbine
heat energy is converted into mechanical
energy useful work
high pressure turbine
low pressure turbine
heat exchanger
tubes sea water
steam water (condensate)
vacuum is created due to steam / condensate
volume difference
vacuum is maintained by constant cool water
circulation through the tubes
CONDENSATE COLLECTING TANK
(HOTWELL)
MAIN CONDENSATE PUMP
AIR EJECTOR
DEAERATING FEED TANK
MAKE UP TANK (EMERGENCY FEED TANK)
FEED PUMP
FEED HEATER
ECONOMISER
condensate collecting tank (hotwell)
Main Condensate Pump
to pump water from the hotwell through the
main air ejector to the deaerating feed tank
no moving parts
jet pump
Bernoullis principle
to remove air and gases from the condensate
to remove the oxygen from the system
to heat the condensate
to be used as storage tank for heated feed
water
Form: cylindrical tank in three sections
First section (the lowest) storage space =
beginning of the feed phase
Middle section: atomizing valve assembly to
release entrapped air from the water
Upper section: preheater compartment
losses in cycle
when the feed water level in the deaerating
tank drops to a minimum, make-up feed
water enters the system
pump that forces feed water into the boiler
preheats the feed water before it enters the
boiler
to improve the efficiency of the steam plant
by using thermal energy, i.e. preheating the
feedwater before it passes into the boiler
water is heated under pressure to remove
dissolved air and vapour to minimize internal
boiler corrosion
double-bottom tank -> transfer pump ->
settling tank -> daily (service) tank -> fuel oil
pressure pump -> strainer -> heater -> fine
mesh -> burner (recirculating connection)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- BoilerDocument45 pagesBoilerEr Prem PrincepsPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Power Plant PDFDocument20 pagesSteam Power Plant PDFarchitPas encore d'évaluation
- PT KOWEPO SUMSEL O & M SERVICES BAYUNG LENCIR AUXILIARY BOILER START-UPDocument2 pagesPT KOWEPO SUMSEL O & M SERVICES BAYUNG LENCIR AUXILIARY BOILER START-UPMuhammad Fauzan0% (1)
- Power PlantDocument24 pagesPower PlantARUNGREESMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Rankine Cycles: IIT BombayDocument19 pagesOrganic Rankine Cycles: IIT BombayShubham PunjabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Boiler ControlDocument23 pagesAutomatic Boiler ControlKishore KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- SOP Simulator BoilerDocument10 pagesSOP Simulator BoilerBambang SetiajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rankine Cycle Efficiency Improvement TechniquesDocument7 pagesRankine Cycle Efficiency Improvement TechniquesJhomz MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Conversion Engineering: Steam Power PlantsDocument73 pagesEnergy Conversion Engineering: Steam Power Plantsanuragburman17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Siklus RankineDocument26 pagesSiklus RankineArialdi Almonda0% (1)
- StartupDocument28 pagesStartupAjay Chauhan100% (1)
- Vapor and Combined Power Cycles: TopicsDocument52 pagesVapor and Combined Power Cycles: TopicsAshlin Augusty100% (1)
- Pulveriser-Power PlantDocument67 pagesPulveriser-Power PlantARUNGREESMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Condensate Extraction Pump: GeneralDocument5 pagesCondensate Extraction Pump: GeneralAnonymous DKv8vpPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Device and Accessories p1Document60 pagesBoiler Device and Accessories p1OsamaEhmaid100% (2)
- Producing Power from Heat: The Rankine CycleDocument55 pagesProducing Power from Heat: The Rankine CyclemjunaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Test for Half of Condenser Operation冷凝器半面运行试验Document2 pagesTest for Half of Condenser Operation冷凝器半面运行试验erwin5sambas5aryanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Logsheet Turbin DeskDocument7 pages02 Logsheet Turbin DeskKeniBataraPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler EfficiencyDocument28 pagesBoiler EfficiencyRintu BiswasPas encore d'évaluation
- Report #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantDocument41 pagesReport #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantKian TecsonPas encore d'évaluation
- System Automatic Control Level Dan Temperature Dearator: Pt. Multi Ganda ScoteknikDocument18 pagesSystem Automatic Control Level Dan Temperature Dearator: Pt. Multi Ganda ScoteknikichsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tata Chemicals Limited Mithapur 1 x 200 TPH CFBC Boiler Logic SystemDocument26 pagesTata Chemicals Limited Mithapur 1 x 200 TPH CFBC Boiler Logic Systemraveekas6148Pas encore d'évaluation
- What is a Superheater and how does it workDocument2 pagesWhat is a Superheater and how does it workPangestu Try WibowoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ennore Thermal Power StationDocument14 pagesEnnore Thermal Power StationRajesh Kumar100% (2)
- BDA30403 Steam Power Plant - Rankine CycleDocument43 pagesBDA30403 Steam Power Plant - Rankine CycleShishajimoo100% (1)
- Boiler Flow DiagramDocument1 pageBoiler Flow Diagramshobhan1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- BOILER EFFICIENCYDocument11 pagesBOILER EFFICIENCYWisnu Jati NugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation: Feasibility Study of Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) in Terms of The Following Parameters: Technology, Reliability and Economy For High High-Ash Content Indian Coal.Document14 pagesPresentation: Feasibility Study of Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) in Terms of The Following Parameters: Technology, Reliability and Economy For High High-Ash Content Indian Coal.Prithvi JawaharPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine Power Plant: By: Ms. Monika DeshwalDocument19 pagesGas Turbine Power Plant: By: Ms. Monika DeshwalKeshantSharma100% (1)
- 3.boiler OperationDocument167 pages3.boiler OperationMa Vũng ÁngPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of NTPC PDFDocument40 pagesOverview of NTPC PDFRahul KediaPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Turbine Fundamentals: Definition, Operation, Types & ClassificationDocument9 pagesSteam Turbine Fundamentals: Definition, Operation, Types & ClassificationJaviStg1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Super Critical Power PlantDocument27 pagesSuper Critical Power PlantPrabir Kumar PatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluidized Bed BoilerDocument4 pagesFluidized Bed BoilerbobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 - Coal Power PlantsaDocument48 pagesLecture 3 - Coal Power PlantsaGomolemo BaarxxPas encore d'évaluation
- Boilers and Thermic Fluid HeatersDocument54 pagesBoilers and Thermic Fluid HeatersAmit ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Power Cycles Sivakumar.E VITDocument47 pagesGas Power Cycles Sivakumar.E VITmohan govindasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Study The Efficiency of Air PeheaterDocument3 pagesStudy The Efficiency of Air PeheaterManoj PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 212 Air PreheaterDocument5 pages1 212 Air Preheaterhanafy_arnandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Soot BlowerDocument8 pagesSoot BlowerArun YogaPas encore d'évaluation
- System DescriptionDocument28 pagesSystem DescriptionGloria HamiltonPas encore d'évaluation
- APH Brochure PDFDocument10 pagesAPH Brochure PDFdillipsh123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dead Weight Safety Valve and Fusible Plug Function in BoilersDocument4 pagesDead Weight Safety Valve and Fusible Plug Function in BoilersAsif Saleem0% (1)
- Boiler ParameterDocument2 pagesBoiler ParameterFiePas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler MaintenanceDocument29 pagesBoiler MaintenanceNeng Sri Widianti100% (1)
- Vacuum - Condenser Presentasi 2Document17 pagesVacuum - Condenser Presentasi 2Neon PhoerbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Boiler SystemDocument45 pagesChapter 2 Boiler SystemSurendra Louis Dupuis NaikerPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Coal Based Thermal Power Plants - NotesDocument13 pages1-Coal Based Thermal Power Plants - NotesPradeepkumar SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- De Super HeaterDocument27 pagesDe Super HeaterShivam Mannan MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Performance Assessment of Boiler at P.S.S.K. LTDDocument12 pagesEnergy Performance Assessment of Boiler at P.S.S.K. LTDPajooheshPas encore d'évaluation
- Training ReportPDF PDFDocument42 pagesTraining ReportPDF PDFAman RajPas encore d'évaluation
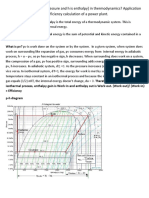
- Pressure Vs Enthalpy in Thermodynamics - Bell CurvesDocument3 pagesPressure Vs Enthalpy in Thermodynamics - Bell CurvesMahe MahendiranPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Presisi UniflairDocument32 pagesAC Presisi UniflairBayu Hermawan0% (1)
- Super Critical Salient FeaturesDocument16 pagesSuper Critical Salient Featureshanumehrotra100% (1)
- Unit Hot Start Up Check List: For 5 MinutesDocument7 pagesUnit Hot Start Up Check List: For 5 MinutesShift Incharge BrbclPas encore d'évaluation
- Essentials of Steam Power Plant EquipmentDocument102 pagesEssentials of Steam Power Plant EquipmentPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plants: Key Components and Working PrincipleDocument157 pagesThermal Power Plants: Key Components and Working Principlegteklay100% (1)
- Unit - I Steam Power PlantsDocument32 pagesUnit - I Steam Power Plantsrsankarganesh MECH-HICET100% (1)
- Engineering Lesson Guide 5: Main Steam CycleDocument17 pagesEngineering Lesson Guide 5: Main Steam CycleNader Ragab AmmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Power Plant Components & ProcessesDocument37 pagesSteam Power Plant Components & ProcessessureshlalPas encore d'évaluation
- 374 - COVID Advisory 13.3.2020Document1 page374 - COVID Advisory 13.3.2020ajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil 5thDocument8 pagesCivil 5thajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3Document21 pages3ajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Water PollutionDocument18 pagesWater PollutionСаманати СоринPas encore d'évaluation
- Does Marriage, Not Money, Lead to HappinessDocument8 pagesDoes Marriage, Not Money, Lead to Happinessajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 RDocument10 pages1 Rajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 10 Solutions Mode Mean Midrange Dispersion PlotsDocument2 pagesQuiz 10 Solutions Mode Mean Midrange Dispersion Plotsajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Does Marriage, Not Money, Lead to HappinessDocument8 pagesDoes Marriage, Not Money, Lead to Happinessajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric 2 Marks With Answers PDFDocument11 pagesElectric 2 Marks With Answers PDFajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- FrictionDocument4 pagesFrictionM.Saravana Kumar..M.EPas encore d'évaluation
- Time TableDocument1 pageTime Tableajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- How Facebook Creates Social ImpactDocument15 pagesHow Facebook Creates Social Impactajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- IES Syllabus For 2015Document10 pagesIES Syllabus For 2015rehenaparbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pin diagrams for common logic ICs: 7408, 7432, 7404, 7400, 7402, 7486Document1 pagePin diagrams for common logic ICs: 7408, 7432, 7404, 7400, 7402, 7486ajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of Media on Children's DevelopmentDocument56 pagesThe Impact of Media on Children's Developmentajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Merge From OfoctDocument9 pagesMerge From Ofoctajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- IES Syllabus For 2015Document10 pagesIES Syllabus For 2015rehenaparbinPas encore d'évaluation
- NIT-RAIPUR-BEE-SYLLABUSDocument1 pageNIT-RAIPUR-BEE-SYLLABUSVijendra Kumar DubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Differential Equations and Applications No. 2 2015, 65-79Document16 pagesInternational Journal of Differential Equations and Applications No. 2 2015, 65-79ajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Merge From OfoctDocument2 pagesMerge From Ofoctajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- MachinesDocument32 pagesMachinesajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Merge From OfoctDocument8 pagesMerge From Ofoctajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Electri Sem 3Document6 pagesElectri Sem 3Ajeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Differential Equations and Applications No. 2 2015, 65-79Document16 pagesInternational Journal of Differential Equations and Applications No. 2 2015, 65-79ajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- SSD JfetDocument36 pagesSSD Jfetajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- GEE NotesDocument23 pagesGEE Notesajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Info Security BasicsDocument3 pagesInfo Security Basicsmamdouh2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Merge From OfoctDocument9 pagesMerge From Ofoctajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nacp Lab ManualDocument18 pagesNacp Lab Manualajeet kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Midea CAC Aqua Tempo Super II Series (DC Inverter Air-Cooled Chiller)Document5 pagesMidea CAC Aqua Tempo Super II Series (DC Inverter Air-Cooled Chiller)ikac3Pas encore d'évaluation
- LincolnDocument4 pagesLincolnJuan CaceresPas encore d'évaluation
- Geothermal Energy NCESDocument71 pagesGeothermal Energy NCESAdarsh ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gissa Navira SevieDocument31 pagesGissa Navira SevieGissa SeviePas encore d'évaluation
- Machinery Breakdown InsuranceDocument20 pagesMachinery Breakdown InsuranceRumman Arshad DarPas encore d'évaluation
- CH24Document8 pagesCH24Jenny ChoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Marathon Voltage Regulator DVR2000EPlus - IOM - GPN046Document92 pagesMarathon Voltage Regulator DVR2000EPlus - IOM - GPN046Khaled KamelPas encore d'évaluation
- JAC 4DA1 Series Diesel Engine PDFDocument12 pagesJAC 4DA1 Series Diesel Engine PDFFerran Alfonso80% (5)
- Type Tests Report: #REF! #REF!Document2 pagesType Tests Report: #REF! #REF!DIPAKPas encore d'évaluation
- Review On A Protective Scheme For Wind Power Plant Using Co-Ordination of Overcurrent Relay-NOTA TECNICADocument5 pagesReview On A Protective Scheme For Wind Power Plant Using Co-Ordination of Overcurrent Relay-NOTA TECNICAEdgardo Kat ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Select An Air Handling UnitDocument12 pagesHow To Select An Air Handling UnitKumudu PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ten KasiDocument152 pagesTen KasiR AbishekPas encore d'évaluation
- ct-2000 Viscometer BathDocument2 pagesct-2000 Viscometer BathJessePas encore d'évaluation
- Downhole Tools HDD Brochure ENDocument2 pagesDownhole Tools HDD Brochure ENuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing Joints and Pressure VesselsDocument2 pagesDesigning Joints and Pressure Vesselssutha_me200982820% (1)
- 03 VESPR and PolarityDocument5 pages03 VESPR and PolarityNursalfarinah BasirPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 11.1 - Electromagnetic Induction - AHLDocument40 pagesTopic 11.1 - Electromagnetic Induction - AHLPaul Amezquita0% (1)
- Aero Indoor and Weathertight Outdoor Air Handlers: Product DataDocument172 pagesAero Indoor and Weathertight Outdoor Air Handlers: Product DataANGEL MURILLOPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC Air Filters Catalogue Provides Clean Air SolutionsDocument6 pagesHVAC Air Filters Catalogue Provides Clean Air SolutionssemoyapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Especificaciones MAGNUM MMG55Document5 pagesEspecificaciones MAGNUM MMG55DAVNIALPas encore d'évaluation
- A LVRT Control Strategy Based On DC-link VoltageDocument4 pagesA LVRT Control Strategy Based On DC-link VoltageFatih BurakPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Concept DesignDocument8 pagesStructural Concept DesignaahtagoPas encore d'évaluation
- CDM835E - Manual de Partes PDFDocument155 pagesCDM835E - Manual de Partes PDFhumberto67% (6)
- Indoor Air Quality in HospitalsDocument8 pagesIndoor Air Quality in HospitalsSamiYousifPas encore d'évaluation
- Craftsman Trimmer ManualDocument32 pagesCraftsman Trimmer ManualNaomi CuevasPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument2 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsKing AshokPas encore d'évaluation
- MARKS N Manual Instrucciones (35451180 07-02)Document84 pagesMARKS N Manual Instrucciones (35451180 07-02)Juan Francisco García GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mansoor Ali Khan: Summary of QualificationsDocument6 pagesMansoor Ali Khan: Summary of QualificationsMansoor Khanali100% (1)
- Mathcad - Q5Document2 pagesMathcad - Q5Desejo SozinandoPas encore d'évaluation
- TI - 20191218 - SG5000UD & SG5000UD-20 Series P-Q Diagram - V20 - ENDocument4 pagesTI - 20191218 - SG5000UD & SG5000UD-20 Series P-Q Diagram - V20 - ENSAEL SOLARPas encore d'évaluation