Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Photoelectric Effect
Transféré par
A.Sheikh0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
347 vues1 pageThe photoelectric effect occurs when light ejects electrons from the surface of a metal. Each metal requires a different minimum amount of energy from each photon to eject an electron, which is known as the work function. A graph of the kinetic energy of ejected electrons versus frequency can be used to determine the threshold frequency and work function of different metals. Above the threshold frequency, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons increases linearly with increasing frequency.
Description originale:
AQA AS Level Physics
Scientific Poster on Photoelectric Effect
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe photoelectric effect occurs when light ejects electrons from the surface of a metal. Each metal requires a different minimum amount of energy from each photon to eject an electron, which is known as the work function. A graph of the kinetic energy of ejected electrons versus frequency can be used to determine the threshold frequency and work function of different metals. Above the threshold frequency, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons increases linearly with increasing frequency.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
347 vues1 pagePhotoelectric Effect
Transféré par
A.SheikhThe photoelectric effect occurs when light ejects electrons from the surface of a metal. Each metal requires a different minimum amount of energy from each photon to eject an electron, which is known as the work function. A graph of the kinetic energy of ejected electrons versus frequency can be used to determine the threshold frequency and work function of different metals. Above the threshold frequency, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons increases linearly with increasing frequency.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
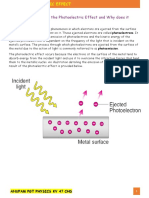
PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT The Photoelectric effect occurs
when light knocks electrons out
h= Plancks Constant (6.63x10-34) E= Energy of a Photon of the surface of a metal.
f= Frequency (Measured in Hertz) However each metal requires a
= Work Function (Minimum energy needed to different amount of energy (per
free an electron from the surface of a metal) photon) to be able to free the
EK= The maximum kinetic energy of a photon (measured in Joules) electron, this is what is known as
c= Speed of light (3x108) the work function ().
= Wavelength (Measured in metres)
So where some metals easily
Above is the most important equation you need to know for the Threshold Frequency = the
loose their electrons with a
photoelectric effect, however there are a couple more which can minimum frequency of
green light, others need
make the calculations easier to work out. radiation that will free one
ultraviolet or gamma rays to be
electron. (One photon can
able to free an electron.
In the diagram below, it shows Only if the work function only free one electron)
the photoelectric effect in of this metal is lower
action. There is a photon than the energy of the What this graph shows, is that Na
coming into contact with the photon being emitted. electrons requires less energy to This is known as the threshold
metal surface and the energy is be freed from the metals surface,
absorbed by an electron. IF the e- whereas the Zn electrons need
frequency and can be shown on
a graph and represented by = f0
energy of the photon is greater slightly more energy, which is why
than the work function of the Na has a lower threshold
metal an electron will be given frequency.
off. But if the energy of the EK
photon is lower than the work e- e- e- e- e- e- e- e- Also, I have identified the Gradient= h
function no electrons will be Metal Surface gradient to be; h (Planck's
given off. constant). The gradient for any f0 f0
metal on this graph will always be Frequency
the same.
RADIOWAVES INFRARED ULTRAVIOLET GAMMA RAYS
R O Y G B I V
Longest Wavelengths Wavelength = 700nm Wavelength = 550nm Wavelength = 450nm Shortest Wavelengths
Lowest Frequency Long Wavelengths Short Wavelengths Highest Frequency
Lowest Energy Photons Low Frequency High Frequency Highest Energy Photons
Low Energy Photons High Energy Photons
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 03 Modern Photoelectric Effect LabDocument3 pages03 Modern Photoelectric Effect LabMeagan TamplinPas encore d'évaluation
- Photo Electric Effect NotesDocument11 pagesPhoto Electric Effect NotesChitransh AwasthiPas encore d'évaluation
- (MIT) The Photoelectric EffectDocument4 pages(MIT) The Photoelectric EffectTVFionnaXQPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Physics - 104: Photoelectric Effect & Postulates of Quantum MechanicsDocument22 pagesEngineering Physics - 104: Photoelectric Effect & Postulates of Quantum MechanicsSalaar Khan100% (1)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument13 pagesPhotoelectric EffectEr Purushottam PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Projectaneezabdul2003100% (1)
- Photoelectric Effect Lecture NotesDocument33 pagesPhotoelectric Effect Lecture NotesSebastian Quiceno100% (1)
- 6 Intrinsic Semiconductor-1Document12 pages6 Intrinsic Semiconductor-1api-462620165Pas encore d'évaluation
- Photoelectric EffectDocument7 pagesPhotoelectric EffectAnushka Jaiswal100% (1)
- Chapter No 4Document27 pagesChapter No 4Moin KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nano SuperconductivityDocument26 pagesNano Superconductivity2018 01403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of RelativityDocument51 pagesTheory of RelativityZiaTurk0% (1)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument10 pagesPhotoelectric EffectSouvik BaruaPas encore d'évaluation
- Photoelectric EffectDocument19 pagesPhotoelectric EffectSonu SinghalPas encore d'évaluation
- Photoelectric Effect PDFDocument7 pagesPhotoelectric Effect PDFVenu GopalPas encore d'évaluation
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation-1Document10 pagesDual Nature of Matter and Radiation-1Aaditya Divyam100% (1)
- Topic 3 Electric Field & Electric ChargeDocument73 pagesTopic 3 Electric Field & Electric ChargesarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Photoelectric Effect PresentationDocument13 pagesPhotoelectric Effect PresentationXofoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaya Coulomb IIDocument126 pagesGaya Coulomb IIElang TimurPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Charge and Field ForcesDocument3 pagesElectric Charge and Field ForcesAhmet UlusoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Particle DualityDocument32 pagesWave Particle DualityDavid ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Charge and Forces: Key Concepts and FormulasDocument4 pagesElectric Charge and Forces: Key Concepts and FormulasSyed Raheel AdeelPas encore d'évaluation
- The Special Theory of Relativity: Chapter - 47Document6 pagesThe Special Theory of Relativity: Chapter - 47charmilft9100% (1)
- Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences Physics II Lecture NotesDocument35 pagesFaculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences Physics II Lecture NotesYuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic field and applicationsDocument4 pagesMagnetic field and applicationsKay RPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrostatics CH2 Part - 2Document24 pagesElectrostatics CH2 Part - 2Rishab SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Photoelectric EffectDocument15 pagesPhotoelectric EffectMichael LeungPas encore d'évaluation
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation MainsDocument14 pagesDual Nature of Matter and Radiation MainsVigneshRamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Static Electric FieldsDocument175 pagesStatic Electric FieldsAli Ahmad100% (1)
- Standing WavesDocument5 pagesStanding WavesCristi IugaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation PDFDocument49 pagesDual Nature of Matter and Radiation PDFabhishekPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic StructureDocument30 pagesAtomic StructureCM PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz (Lecture 5) : Date: 14/3/2018 (Wednesday) Time: 2.15 PM VenueDocument50 pagesQuiz (Lecture 5) : Date: 14/3/2018 (Wednesday) Time: 2.15 PM VenueKoh Jiun AnPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Absorption in SemiconductorsDocument13 pagesUnit 2 Absorption in SemiconductorsKapilkoundinya NidumoluPas encore d'évaluation
- Photoelectric EffectDocument3 pagesPhotoelectric EffectFilip Leonard100% (1)
- N P Fermi-Gas ModelDocument8 pagesN P Fermi-Gas ModelabdulbaseerPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromanetic InductionDocument53 pagesElectromanetic InductionNor RazmanPas encore d'évaluation
- General Physics 2 (Electric Charge and Electric Field)Document53 pagesGeneral Physics 2 (Electric Charge and Electric Field)Ronnel MacadangdangPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar CellDocument24 pagesSolar CellanupamanupamPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric FieldDocument42 pagesElectric FieldMuhammad Kashif IshaquePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8: Band Theory of Solids Concept of Free Electron Theory: Hour 1Document25 pagesChapter 8: Band Theory of Solids Concept of Free Electron Theory: Hour 1Vivek kapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Cahpter 16 Wave MotionDocument71 pagesCahpter 16 Wave MotionAliPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic Field LabDocument5 pagesMagnetic Field LabEamon BarkhordarianPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Field AND GAUSS LAWDocument15 pagesElectric Field AND GAUSS LAWLexis Music labPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic Field Basics: Magnetic Fields Are Different From ElectricDocument2 pagesMagnetic Field Basics: Magnetic Fields Are Different From ElectricJudelin Da FrogmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric FieldsDocument19 pagesElectric Fieldsmostafa_m_ibrahim2444Pas encore d'évaluation
- Franck Hertz ExperimentDocument15 pagesFranck Hertz Experimentlalal345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument98 pagesElectronic Structure of AtomsDexter EnthusiastsPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Questions: (CHAPTER 19) Dawn of Modern PhysicsDocument17 pagesShort Questions: (CHAPTER 19) Dawn of Modern PhysicsEhtesham Ali KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Physics Semiconductor FundamentalsDocument12 pagesEngineering Physics Semiconductor FundamentalsWallabh UmrekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Physics NotesDocument157 pagesModern Physics NotesGregory HillhousePas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrostaticsDocument9 pagesElectrostaticstechzonesPas encore d'évaluation
- SemiconductorsDocument37 pagesSemiconductorsANSHU RAJPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1 Behavior of Electric DipolesDocument12 pages8.1 Behavior of Electric DipolesKamalKiran Tata100% (1)
- 11 QuantumDocument54 pages11 QuantumVinod RajPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - Atoms and Nuclei PDFDocument25 pages8 - Atoms and Nuclei PDFthinkiit67% (3)
- (#3) Direct, Indirect, Ek Diagram, Effective Mass-1Document6 pages(#3) Direct, Indirect, Ek Diagram, Effective Mass-1zubairPas encore d'évaluation
- Referat Closed Globe InjuryDocument1 pageReferat Closed Globe InjuryromiamryPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Pomr Interna - CompressDocument1 pagePDF Pomr Interna - Compressbyeongari oppaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 29 Particles and Waves: Photon Nature of Light and Photoelectric EffectDocument14 pagesChapter 29 Particles and Waves: Photon Nature of Light and Photoelectric EffectMikaela Rome BigayPas encore d'évaluation
- Question BankDocument125 pagesQuestion BankChaitanya KapilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shivani Laser PDFDocument23 pagesShivani Laser PDFShalini Mahajan100% (1)
- Solid State Lighting and ControlsDocument4 pagesSolid State Lighting and ControlsRakshitAnandPas encore d'évaluation
- VerTera Flyer enDocument2 pagesVerTera Flyer enErcx Hijo de AlgoPas encore d'évaluation
- It4 - Xy-1Document1 pageIt4 - Xy-1Helio JustinianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec-PH301 7-8 Lens 09-11.08.2023Document30 pagesLec-PH301 7-8 Lens 09-11.08.2023Latu BharaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Rr410404 Optical CommunicationDocument8 pagesRr410404 Optical CommunicationSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- Outdoor Workplace Lighting StandardsDocument17 pagesOutdoor Workplace Lighting StandardsRoberto MiletPas encore d'évaluation
- The Quantum-Mechanical Model of The Atom: Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 1Document77 pagesThe Quantum-Mechanical Model of The Atom: Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 1ynottripPas encore d'évaluation
- Color FilterDocument1 pageColor FilterFunkozor ShiftPas encore d'évaluation
- MEASUREMENT DEVICES: PMMC & AC METER PRINCIPLESDocument24 pagesMEASUREMENT DEVICES: PMMC & AC METER PRINCIPLESBryan MatthiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-41 Electromagnetic WavesDocument17 pagesChapter-41 Electromagnetic Wavesökkeş kurtPas encore d'évaluation
- NPL Flatness InterferometerDocument6 pagesNPL Flatness InterferometerMoula Moulali100% (1)
- Emf Equation of A DC Generator (Page No: 2.9)Document11 pagesEmf Equation of A DC Generator (Page No: 2.9)Poornima SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Dwnload Full Microbiology An Introduction 10th Edition Tortora Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Microbiology An Introduction 10th Edition Tortora Test Bank PDFgambolrapinous.ggqcdr100% (7)
- All About Aspheric LensesDocument4 pagesAll About Aspheric LensesAnonymous 9oYiZMPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Things Have Color: The Electromagnetic Spectrum ExplainedDocument5 pagesWhy Things Have Color: The Electromagnetic Spectrum Explainedbinyang lalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fd-Uv, Fd-Uvir, Fd-Uv2Ir: Product DescriptionDocument15 pagesFd-Uv, Fd-Uvir, Fd-Uv2Ir: Product DescriptionMostafa SayedPas encore d'évaluation
- Measure Coil Resistance and Impedance of TransformerDocument8 pagesMeasure Coil Resistance and Impedance of TransformerFarizal JaafarPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation Control For Implementing The Single Dielectric Resonator Based Tunable THZ Mimo Antenna and FilterDocument14 pagesIsolation Control For Implementing The Single Dielectric Resonator Based Tunable THZ Mimo Antenna and Filteryoussef.amraoui2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ferrite DevicesDocument19 pagesFerrite DevicesSumangil, Maria Margarita P.Pas encore d'évaluation
- How Transformers Work: A Guide to Their Basic Principles and ApplicationsDocument15 pagesHow Transformers Work: A Guide to Their Basic Principles and Applicationstim schroderPas encore d'évaluation
- 010 Modern Color Theory (Concepts)Document7 pages010 Modern Color Theory (Concepts)john rockwellPas encore d'évaluation
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and Refractiondjshlok359Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abhishek GuptaDocument15 pagesAbhishek GuptasinjiniwasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment - 06 To Study Magnetisation Characteristics of DC Shunt Generator.Document9 pagesExperiment - 06 To Study Magnetisation Characteristics of DC Shunt Generator.charanrck10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fiber optics and waveguides exercises: modes, NA, and propagationDocument4 pagesFiber optics and waveguides exercises: modes, NA, and propagationmokhaladPas encore d'évaluation
- Exploring Pulsars An Introduction by ARNABDocument11 pagesExploring Pulsars An Introduction by ARNABARNAB HALDERPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - Data Communication and Transmission MediaDocument29 pagesChapter 2 - Data Communication and Transmission MediaMichael WorkinehPas encore d'évaluation
- Hunter Color Lab UltraScan - PRO - ProspektusDocument4 pagesHunter Color Lab UltraScan - PRO - ProspektusSumeet KaurPas encore d'évaluation