Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Compressible Flow
Transféré par
crown2120 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
45 vues8 pagesCompressible Flow
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentCompressible Flow
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
45 vues8 pagesCompressible Flow
Transféré par
crown212Compressible Flow
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 8
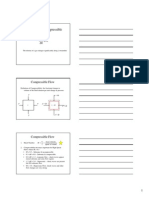
Compressible Flow
gas is so highly compressible that equations for
liquid flow cannot be used. Derivation of gas flow
rate for a linear horizontal system follows. Darcys
equation in differential form can be written as,
Eng. Haitem Ben-Massud
where q is the flow rate at reservoir
conditions, rcf/d.
Naturally, it is most desirable to determine gas
flow rate at surface, or standard conditions in
units of standard cubic feet per day (scf/d).
Beginning with Boyle's law for a re For steady-
state conditions, the flow rate in scf/d (qsc) is
constant everywhere in the system at any
pressure. al gas under isothermal conditions,
Eng. Haitem Ben-Massud
Eng. Haitem Ben-Massud
Substituting for reservoir flow rate and separating variables
Eng. Haitem Ben-Massud
Note that viscosity and z-factor are strong
functions of pressure; therefore to solve this
Eq. two approximations were developed.
In the low-pressure region (p < 2000 psi),
z = constant and can be evaluated at average
pressure (p1+p2)/2.
Eng. Haitem Ben-Massud
Eng. Haitem Ben-Massud
Eng. Haitem Ben-Massud
Eng. Haitem Ben-Massud
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Rig RepairDocument30 pagesRig Repaircrown212100% (1)
- Economic Pipe SizeDocument4 pagesEconomic Pipe SizeAndreamPas encore d'évaluation
- Flowing Material Balance (FMB) Analysis TheoryDocument14 pagesFlowing Material Balance (FMB) Analysis TheoryHậu DươngPas encore d'évaluation
- ENI - Casing Design ManualDocument134 pagesENI - Casing Design Manualwelltest2012100% (14)
- Mud ProgrammeDocument35 pagesMud Programmecrown212100% (1)
- CO2 Flooding PerformanceDocument8 pagesCO2 Flooding Performancecrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Deep Water Drilling Fluid Design ExampleDocument65 pagesDeep Water Drilling Fluid Design Examplecrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lean Six Sigma at A Material Recovery Facility - A Case StudyDocument16 pagesLean Six Sigma at A Material Recovery Facility - A Case Studycrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project Integration QuizDocument4 pagesProject Integration Quizcrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ipr ReservoirDocument40 pagesIpr ReservoirDr-Jitendra VaishPas encore d'évaluation
- Flowing Material Balance (FMB) TheoryDocument11 pagesFlowing Material Balance (FMB) Theorysaladinayubi1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Study Questions Solution ManualDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Study Questions Solution ManualSebastiàn Valle100% (3)
- ChaudhriDocument10 pagesChaudhriسحر سلامتیانPas encore d'évaluation
- Boundary Conditions Available in ANSYS FluentDocument3 pagesBoundary Conditions Available in ANSYS FluentAnonymous KVkTrZ7gzd100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Reservoir Oil Flows AnalysisDocument45 pagesFundamentals of Reservoir Oil Flows AnalysiszazoPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 Fundamental of Fluid Flow Part 4Document13 pages05 Fundamental of Fluid Flow Part 4FerdiNandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass BalanceDocument30 pagesMass BalanceThe PieonicBritzPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Well Deliverability TestDocument105 pagesGas Well Deliverability TestAlIbtidaSultanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Flow Equations (Pde)Document42 pagesFluid Flow Equations (Pde)Y'Dav IdPas encore d'évaluation
- DOCUMENTFUNDAMENTAL OF RESERVOIR FLUID FLOWDocument18 pagesDOCUMENTFUNDAMENTAL OF RESERVOIR FLUID FLOWFerdiNandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - Single Phase Fluid FlowDocument128 pagesChapter 3 - Single Phase Fluid FlowZulfikri ZulkifliPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Approximations SPRING 2005Document7 pagesCommon Approximations SPRING 2005Vinay GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Well Testing TechniquesDocument35 pagesGas Well Testing TechniquesFaraj NabiyevPas encore d'évaluation
- COW 2012 - Part 2: Inflow / OutflowDocument42 pagesCOW 2012 - Part 2: Inflow / OutflowShahinPas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir Engineering 1 (Week 1 & 2)Document35 pagesReservoir Engineering 1 (Week 1 & 2)Nasih AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Reservoir Oil Flows AnalysisDocument31 pagesFundamentals of Reservoir Oil Flows AnalysisMohamed AoudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipeline Engineering: Dept. ElectiveDocument19 pagesPipeline Engineering: Dept. ElectiveHarahwardhanamPas encore d'évaluation
- Petrophysics Application of Darcy's Law: DR - Falan SrisuriyachaiDocument20 pagesPetrophysics Application of Darcy's Law: DR - Falan SrisuriyachaiAnuchit ThanasrisurbwongPas encore d'évaluation
- Steady Periodic Gas Flow Around A Well of A CAES Plant: Roy Kushnir Amos Ullmann Abraham DayanDocument20 pagesSteady Periodic Gas Flow Around A Well of A CAES Plant: Roy Kushnir Amos Ullmann Abraham DayansasikalasivakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview of The Hydraulics of Water Distribution NetworksDocument35 pagesAn Overview of The Hydraulics of Water Distribution NetworksBoos yousufPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Flow Equations PDFDocument10 pagesFluid Flow Equations PDFahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Gas ProductionDocument32 pagesNatural Gas ProductionMalugu JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Derivation of Fluid Flow Equations Review of Basic StepsDocument9 pagesDerivation of Fluid Flow Equations Review of Basic StepsAaron LisandrioPas encore d'évaluation
- FME 432 - 532 Compressible Flow Theory 02-04-2024Document29 pagesFME 432 - 532 Compressible Flow Theory 02-04-2024Melody WachukaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Distribution in FluidsDocument28 pagesPressure Distribution in FluidsMuneeb RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Well PerformanceDocument36 pagesWell PerformanceKael SellsPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 9 FinalDocument26 pagesClass 9 FinalSagar DadhichPas encore d'évaluation
- General Features of Steady One Dimensional FlowDocument29 pagesGeneral Features of Steady One Dimensional FlowMSK65Pas encore d'évaluation
- Approximations and Simplified Equations SPRING 2019Document12 pagesApproximations and Simplified Equations SPRING 2019Kula Segara PandiyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Fluid Flow in Porous Media - 2Document72 pagesChapter 4 Fluid Flow in Porous Media - 2Hiếu Nguyễn TrungPas encore d'évaluation
- Air-Water Two Phase Flow Simulation UsingDocument6 pagesAir-Water Two Phase Flow Simulation Using박송환Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3-Natural Gas Production: 3-1 Darcy and Non-Darcy Flow in Porous MediaDocument25 pages3-Natural Gas Production: 3-1 Darcy and Non-Darcy Flow in Porous MediadfsdfsdPas encore d'évaluation
- GCU Thermo Fluid Science Module NotesDocument221 pagesGCU Thermo Fluid Science Module NotesBurner EmailPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Well Testing Methods and AnalysisDocument10 pagesGas Well Testing Methods and AnalysiskhushalPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Well Deliverability II 2018Document55 pagesGas Well Deliverability II 2018Johny ImitazPas encore d'évaluation
- Spring Semester in Water and Environmental Management: Surface and Groundwater ModellingDocument21 pagesSpring Semester in Water and Environmental Management: Surface and Groundwater ModellingjuanitaPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Fundamental of Fluid Flow Part 3Document21 pages04 Fundamental of Fluid Flow Part 3FerdiNandoPas encore d'évaluation
- PTA (Flow Regimes) DDFDocument4 pagesPTA (Flow Regimes) DDFahouaPas encore d'évaluation
- Compressible flow unit reviewDocument52 pagesCompressible flow unit reviewCorey ThomsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid C1 03 (1) StudentDocument24 pagesFluid C1 03 (1) Studenteric0910160212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter2 Well TestingDocument88 pagesChapter2 Well TestingSebastiánRodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- CHE 220 Flow of Compressible FluidsDocument53 pagesCHE 220 Flow of Compressible FluidsMay May MagluyanPas encore d'évaluation
- DF4 - Inflow Performance RelationshipDocument11 pagesDF4 - Inflow Performance Relationshipadnan0307Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Statics: Fluid Dynamics, Leon Liebenberg, 2019Document4 pagesFluid Statics: Fluid Dynamics, Leon Liebenberg, 2019wtkafePas encore d'évaluation
- SPE-172928-MS Analysis of Transient Linear Flow Associated With Hydraulically-Fractured Tight Oil Wells Exhibiting Multi-Phase FlowDocument18 pagesSPE-172928-MS Analysis of Transient Linear Flow Associated With Hydraulically-Fractured Tight Oil Wells Exhibiting Multi-Phase FlowhijoetigrePas encore d'évaluation
- Radial Flow Theory For Compressible Fluids: GasDocument3 pagesRadial Flow Theory For Compressible Fluids: Gasعلي التميميPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Seepage and Flow Net TheoryDocument56 pagesFinal Seepage and Flow Net TheoryAs MihPas encore d'évaluation
- Beggs, H. D. - Gas Production OperationsDocument302 pagesBeggs, H. D. - Gas Production OperationsArnandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simplified Model of Reynolds Equation With Linearized Ow Rate For Ultra-Thin Gas Film Lubrication in Hard Disk DrivesDocument9 pagesSimplified Model of Reynolds Equation With Linearized Ow Rate For Ultra-Thin Gas Film Lubrication in Hard Disk Drivesyousef mohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Multi-Phase Flow Measurment by Orifice MeterDocument8 pagesMulti-Phase Flow Measurment by Orifice MeterAbdeldjalil AchourPas encore d'évaluation
- Cve341lecturenotes1 220921133246 9aa9c294Document61 pagesCve341lecturenotes1 220921133246 9aa9c294Krishna P. YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - Effects of Reynolds NumberDocument4 pages5 - Effects of Reynolds NumberCharles PortnerPas encore d'évaluation
- ME2342 Sec4 CVAnalysisDocument93 pagesME2342 Sec4 CVAnalysisknowkenn3865Pas encore d'évaluation
- Well Test - Boundary - 2 Week 09Document47 pagesWell Test - Boundary - 2 Week 09robbi sobariPas encore d'évaluation
- Well-Test Pressure Data Using Duhameps Principle ,: Analysis of Variable-RateDocument17 pagesWell-Test Pressure Data Using Duhameps Principle ,: Analysis of Variable-RateJosue FishPas encore d'évaluation
- 04-Dynamique de L'eau Du SolDocument57 pages04-Dynamique de L'eau Du SolHocine HocinePas encore d'évaluation
- Intro Comp FlowDocument14 pagesIntro Comp FlowJoão HenriquesPas encore d'évaluation
- Inventory Record Accuracy: Methods and ImportanceDocument29 pagesInventory Record Accuracy: Methods and Importancecrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To Stochastic Modeling - Continuous Time Markov ChainsDocument1 pageAn Introduction To Stochastic Modeling - Continuous Time Markov Chainscrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Darcy LawDocument5 pagesDarcy Lawcrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inventory 0602Document8 pagesInventory 0602aryabhatmathsPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Download SASStudio PDFDocument9 pagesHow To Download SASStudio PDFcrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Supply and Demand Planning For Crude Oil Procurement - Theses - 2006 - Nnadili - ExecsummDocument8 pagesSupply and Demand Planning For Crude Oil Procurement - Theses - 2006 - Nnadili - Execsummcrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Production Productivity Using Overall Equipment EffectivenessDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Production Productivity Using Overall Equipment Effectivenesscrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Can Shippers and Carriers Benefit From More Robust PlanningDocument19 pagesCan Shippers and Carriers Benefit From More Robust Planningcrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Study of Inventory Systems Affected by Random Causes and OptimalDocument2 pagesA Study of Inventory Systems Affected by Random Causes and Optimalcrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Development of A Comprehensive Supply ChainDocument5 pagesDevelopment of A Comprehensive Supply Chaincrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abogrean and Bindra Developments in Sustainable Manufacturing and Environmental Protection in LibyaDocument11 pagesAbogrean and Bindra Developments in Sustainable Manufacturing and Environmental Protection in Libyacrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Operational Definitions of Inventory Record AccuracyDocument10 pagesOperational Definitions of Inventory Record Accuracycrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diseño de Casing 2.0Document16 pagesDiseño de Casing 2.0Miguel Angel SortizPas encore d'évaluation
- GF+ SIGNET Analytical Technical ReferenceDocument3 pagesGF+ SIGNET Analytical Technical Referencecrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- OIL, What Is ItDocument17 pagesOIL, What Is Itcrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management: Article InformationDocument18 pagesJournal of Manufacturing Technology Management: Article Informationcrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tech Drilling CasingDesign-Part01Document18 pagesTech Drilling CasingDesign-Part01Jinhichi Molero RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- AlmoalemDocument149 pagesAlmoalemcrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Petroleum IngineeringDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Petroleum Ingineeringcrown212Pas encore d'évaluation
- PMP GuideDocument12 pagesPMP Guidecrown212Pas encore d'évaluation