Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Foreign Direct Investment
Transféré par
si ran0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues7 pagesFDI
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentFDI
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues7 pagesForeign Direct Investment
Transféré par
si ranFDI
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 7
FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT
Foreign direct investment refers to the net inflow of
investment to acquire a lasting management interests in an
enterprise operating in an economy other than that of investor
FDI is an investment to acquire long term interest operating
outside of the economy of the investor
FDI is a source of external finance which mean that countries
with limited amount of capital can receive finance beyond the
national border from wealthier countries
FDI is consider as an ingredient in economic growth
WHY FDI????
• No debt creation on the part of the government.
• Triggers technology transfer.
• Assists capital formation.
• Contributes to international integration by
promoting exports.
• Increases productivity and competitiveness.
Improves efficiency of resources.
• Promotes innovation.
FDI IN INDIA
Currently FDI is permitted in India;
• Through financial collaborations.
• Through joint ventures and technical collaborations. Through capital
markets via Euro issues.
• Through private placements or preferential allotments
Major Sector for FDI in India are:
• Infrastructure
• Automotive
• Pharmaceuticals
• Defense
• Retails
• Railways Infrastructure
• Chemicals
• Textiles
• Airlines
FDI RELATED INSTITUTION IN INDIA
• Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB)
• Foreign Investment Promotion Council (FIPC)
• Foreign Investment Implementation Authority
(FIIA)
• Secretariat for Industrial Assistance (SIA)
FDI IN MULTIBRAND RETAIL TRADING
• Marketing of similar and competing products
by the same firm under different and
unrelated brands. For example: walmart, big
bazar, tesco
• FDI in multi brand retail was not permitted in
India. however, the Government of India
proposed some policy changes in late 2011.
they are as follows..
• A decision has been taken by the Government to permit FDI in
all products, in a calibrated manner, subject to the following
conditions:
• FDI in Multi Brand Retail Trade (MBRT) may be permitted up
to 51%, with Government approval;
• Fresh agricultural produce, including fruits, vegetables,
flowers, grains, pulses, fresh poultry, fishery and meat
products, may be unbranded.
• Minimum amount to be brought in, as FDI, by the foreign
investor, would be US $ 100 million.
• At least 50% of total FDI brought in shall be invested in 'back-
end infrastructure‟. Back-end infrastructure will include
investment made towards processing, manufacturing,
distribution, design improvement, quality control, packaging,
logistics, storage, ware-house, agriculture market produce
infrastructure etc.
• At least 30% of the procurement of manufactured/ processed
products shall be sourced from Indian 'small industries' which have
a total investment in plant & machinery not exceeding US $ 1.00
million. Further, if at any point in time, this valuation is exceeded,
the industry shall not qualify as a 'small industry' for this purpose.
• Retail sales locations may be set up only in cities with a population
of more than 10 lakh as per 2011 Census and may also cover an
area of 10 kms around the municipal/urban limits of such cities;
retail locations will be restricted to conforming areas as per the
Master/Zonal Plans of the concerned cities and provision will be
made for requisite facilities such as transport connectivity and
parking;
• Government will have the first right to procurement of agricultural
products
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Submitted To: Prof. Kalyan AggarwalDocument8 pagesSubmitted To: Prof. Kalyan Aggarwalsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Law Case Presentation: Cantonment Board, Dinapore & Others Versus Taramani Devi & AnotherDocument9 pagesBusiness Law Case Presentation: Cantonment Board, Dinapore & Others Versus Taramani Devi & Anothersi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- XX/XX/XXXX Sir / Ma'am, XXXX:, As - I Believe I Meet All The Essential Criteria For The PositionDocument1 pageXX/XX/XXXX Sir / Ma'am, XXXX:, As - I Believe I Meet All The Essential Criteria For The Positionsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- XX/XX/XXXX Sir / Ma'am, XXXX:, As - I Believe I Meet All The Essential Criteria For The PositionDocument1 pageXX/XX/XXXX Sir / Ma'am, XXXX:, As - I Believe I Meet All The Essential Criteria For The Positionsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Loan Amortization Schedule: Enter Values Loan SummaryDocument1 pageLoan Amortization Schedule: Enter Values Loan Summarysi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- BIHAR Lockdown Guidelines APRIL 2021Document1 pageBIHAR Lockdown Guidelines APRIL 2021si ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Assets: - Assets Are Economic Resources or Properties Owned by The Firm. - There Are Two Types of AssetsDocument6 pagesAssets: - Assets Are Economic Resources or Properties Owned by The Firm. - There Are Two Types of Assetssi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Plan Report of PurefirstDocument12 pagesMarketing Plan Report of Purefirstsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovation Management: Applied Research Technology IncDocument14 pagesInnovation Management: Applied Research Technology Incsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- SCM Group 05Document21 pagesSCM Group 05si ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Public Policy Group 05 (A)Document16 pagesPublic Policy Group 05 (A)si ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Pure FirstDocument41 pagesPure Firstsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Marketing Communication: Team Name: Locomotors Team MembersDocument8 pagesIntegrated Marketing Communication: Team Name: Locomotors Team Memberssi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- J&B Case SolutionDocument11 pagesJ&B Case Solutionsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- BEP Presentation: Course Instructor: Prof. Sibananda SenapatiDocument93 pagesBEP Presentation: Course Instructor: Prof. Sibananda Senapatisi ranPas encore d'évaluation
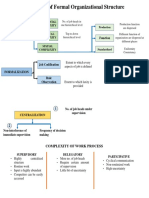
- Dimension of Formal Organizational Structure: Complexity FunctionDocument2 pagesDimension of Formal Organizational Structure: Complexity Functionsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Golden Rules of AccountingDocument1 pageGolden Rules of Accountingsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- POM Group 05Document25 pagesPOM Group 05si ran100% (1)
- Case Solution: Presented By: Group No.:-05 Group MembersDocument24 pagesCase Solution: Presented By: Group No.:-05 Group Memberssi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- CmaDocument6 pagesCmasi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- POM Group 05Document25 pagesPOM Group 05si ran100% (1)
- Chandragupt Institute of Management Patna: Information Technology For Managers (Individual Assignment)Document9 pagesChandragupt Institute of Management Patna: Information Technology For Managers (Individual Assignment)si ranPas encore d'évaluation
- CmaDocument6 pagesCmasi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Butler Lumber Company: An Analysis On Estimating Funds RequirementsDocument17 pagesButler Lumber Company: An Analysis On Estimating Funds Requirementssi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Dream CreamDocument37 pagesDream Creamsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- Conflict and Negotiation: Presented By: Group No.:-06 Group MembersDocument19 pagesConflict and Negotiation: Presented By: Group No.:-06 Group Memberssi ran100% (1)
- MC Group 05Document14 pagesMC Group 05si ranPas encore d'évaluation
- MC Group 05Document14 pagesMC Group 05si ranPas encore d'évaluation
- MCDocument25 pagesMCsi ranPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Mutual FundDocument75 pagesMutual FundpopPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper - Iv - Economy and Development of India and Andhra PradeshDocument3 pagesPaper - Iv - Economy and Development of India and Andhra PradeshlavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Statements: Reference Books: Accountancy by D. K. Goel Rajesh Goel OR Double Entry Book Keeping by T. S. GrewalDocument21 pagesFinancial Statements: Reference Books: Accountancy by D. K. Goel Rajesh Goel OR Double Entry Book Keeping by T. S. GrewalNischay GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 11 PLAN OF REORGANIZATION Easkman Kodak PDFDocument817 pagesCHAPTER 11 PLAN OF REORGANIZATION Easkman Kodak PDFscottleeyPas encore d'évaluation
- 62 US Soft Drink MarketDocument20 pages62 US Soft Drink MarketViktoria BerezhetskayaPas encore d'évaluation
- FIN320 Tutorial W2Document4 pagesFIN320 Tutorial W2Sally OngPas encore d'évaluation
- T. Oetting CV International 21.05.2017.doc-2Document4 pagesT. Oetting CV International 21.05.2017.doc-2Marcel RiedelPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Elasticity: Q Q Q Q P P P PDocument6 pagesI. Elasticity: Q Q Q Q P P P PAIREEN DEIPARINEPas encore d'évaluation
- Arabtec HoldingDocument4 pagesArabtec HoldingArkar SoePas encore d'évaluation
- The Real Power of Real OptionsDocument12 pagesThe Real Power of Real OptionsgoogkitePas encore d'évaluation
- Comperative Study On Performance of Public & Private Sector BanksDocument96 pagesComperative Study On Performance of Public & Private Sector BanksJaimit Shah Raja100% (2)
- Alfalah Education Consultant (AEC)Document32 pagesAlfalah Education Consultant (AEC)Kim NisarPas encore d'évaluation
- Taxation 101: Basic Rules and Principles in Philippine TaxationDocument8 pagesTaxation 101: Basic Rules and Principles in Philippine TaxationZamZamiePas encore d'évaluation
- Company DetailsDocument30 pagesCompany DetailssudehelyRPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching The Art of Market Making With A Game SimulationDocument4 pagesTeaching The Art of Market Making With A Game SimulationRamkrishna LanjewarPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting PrinciplesDocument8 pagesAccounting PrinciplesNitish BatraPas encore d'évaluation
- ACCA F7int ATC Study Text 2012Document562 pagesACCA F7int ATC Study Text 2012hamid2k30100% (4)
- Value Relevance of Accounting Information and Firm ValueDocument19 pagesValue Relevance of Accounting Information and Firm ValueRosedian AndrianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Stock MarketDocument3 pagesStock MarketUPPULAPas encore d'évaluation
- Minor Project Report On Bajaj Automobiles IndiaDocument55 pagesMinor Project Report On Bajaj Automobiles IndiaAmit Jain71% (7)
- Macy's Store Closings News ReleaseDocument6 pagesMacy's Store Closings News ReleaseJim KinneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Business AnalystDocument17 pagesBusiness Analystaabid_chem3363Pas encore d'évaluation
- Relative Valuation JaiDocument29 pagesRelative Valuation JaiGarima SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- House Designs, QHC, 1950Document50 pagesHouse Designs, QHC, 1950House Histories100% (8)
- Joel Greenblatt - Special Situations (John Chew)Document312 pagesJoel Greenblatt - Special Situations (John Chew)Luke Constable100% (6)
- Notice: Rail Carriers: Control Exemption— Moscow, Camden & San Augustine RailroadDocument1 pageNotice: Rail Carriers: Control Exemption— Moscow, Camden & San Augustine RailroadJustia.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Vinacafe Bien Hoa Final ReportDocument24 pagesVinacafe Bien Hoa Final ReportQuang NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Key On Comprehensive ExerciseDocument13 pagesAnswer Key On Comprehensive ExerciseErickaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009-SEC Form ExA-001-Initia External AuditorlDocument3 pages2009-SEC Form ExA-001-Initia External Auditorlalfx216Pas encore d'évaluation
- Resulting & Contructive TrustsDocument16 pagesResulting & Contructive TrustsMuhammad Amir HannifPas encore d'évaluation