Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Personality Self Concept
Transféré par
Vinlax Arguilles0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
10 vues18 pagesTitre original
19974746-Personality-Self-Concept.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
10 vues18 pagesPersonality Self Concept
Transféré par
Vinlax ArguillesDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 18
In the past, the field of psychology
was always classified under
philosophy. Psychology was
considered more of an art rather
than a science. Sigmund Freud was
able to charge people’s perception
of psychology with his revolutionary
theory of psychoanalysis.
Psychoanalysis is the study that
explains human behavior. In his
theory, Freud explained that there
are many conscious and
unconscious factors that can
influence behavior and emotions.
Despite criticisms, Freud still
continued to work on refining his
theory and in fact tried to explain
how psychoanalysis can be a
clinical method in treating some
mental disorders.
Soon enough, people were able to
understand the concepts of
psychoanalysis, which eventually
resulted in classifying psychology as
a science.
Personality
Some theorists prefer to view personality
as a unified whole.
Others focus on specific traits.
Definition
“Those inner psychological
characteristics that both determine and
reflects how a person responds to his or
her environment”.
Nature Of Personality
Personality reflects individual differences
Unique combination of inner
characteristics –
No two individuals are exactly alike
Nature Of Personality
Personality is Consistent & Enduring
Mother – “child has been impulsive from
the day he was born” – enduring &
consistent.
But understanding which specific
characteristics bring in required
responses, can help marketers to appeal to
these traits in their target audience.
Nature Of Personality
Personality Can Change
May be altered by major life events – birth
of a child, death of a loved one, personal
tragedies – accident, health problem,
divorce, significant career promotion.
Personality changes can also be part of
maturing process.
Theories of Personality
Freudian Theory
Neo – Freudian Theory
Trait Theory
Freudian Theory
Personality consists of three interacting
systems.
Id – related to physiological or impulsive needs
to which one seeks immediate satisfaction.
Ego – The individuals conscious control.
Functions as an internal monitor that attempts
to balance the impulsive needs and socio
cultural constraints.
Super Ego – individuals internal expression of
moral / ethical codes of conduct; socio–cultural
forces.
Although Ego is capable of resolving
many of the conflicts that arise between
the personality components, -- there are
certain occasions when no solutions
could be achieved, leading to tensions
within
Defense mechanisms are unconsciously
determined techniques for avoiding or
escaping from such high levels of tension.
Defense Mechanisms
Repression: resolving conflict by
minimizing aspects of the conflicting
situation.
Projection: feelings generated by
individual’s id or super ego is ascribed
to another person or group;
Identification: the individual
unconsciously imitates the behavior of
another person who has successfully
handled a similar conflict.
Reaction Formation: unconscious feelings
held toward others are consciously
expressed as opposites. …
a partner who is unloyal might actually
purchase many gifts for that person.
Neo Freudian Personality Theory
Social relationships are
fundamental to formation of
personality (Freud - impulsive and
sexual in nature)
Three personality Groups
1. Compliant Individuals – those who
move towards others (desire to be loved,
wanted and appreciated).
2. Aggressive Individuals – those who
move against others (desire to excel / win
admiration).
3. Detached Individuals- those who move
away from others (desire independence,
self reliance, self sufficiency - freedom
from obligation)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- 3rd Quarterly Exam in Cesc (Exam Edited)Document7 pages3rd Quarterly Exam in Cesc (Exam Edited)Vinlax Arguilles80% (5)
- Parties To A Civil Suit: (Nigeria) by Christian NwachukwuDocument2 pagesParties To A Civil Suit: (Nigeria) by Christian NwachukwuChristian NwachukwuPas encore d'évaluation
- Face Reading Lesson1Document10 pagesFace Reading Lesson1tushar100% (2)
- Time As An Essence of ContractsDocument20 pagesTime As An Essence of ContractsAyushi Agrawal100% (1)
- Form No. 212 Revised Personal Data Sheet - NewDocument14 pagesForm No. 212 Revised Personal Data Sheet - NewGisselle PauloPas encore d'évaluation
- To Printfollow Traffic RulesDocument1 pageTo Printfollow Traffic RulesVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Balancing Hard To Balance Equations PDFDocument2 pagesBalancing Hard To Balance Equations PDFVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Natscie Sts MidtermDocument3 pagesNatscie Sts MidtermVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd QUARTERLY EXAM IN CESC (Exam Edited)Document8 pages3rd QUARTERLY EXAM IN CESC (Exam Edited)Vinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Gene Interaction:: ContentsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Gene Interaction:: ContentsVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Omnibus Certification of Authenticity and Veracity of DocumentsDocument1 pageOmnibus Certification of Authenticity and Veracity of DocumentsVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- ResDocument27 pagesResVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Quarterly Exam in General BioDocument6 pages1st Quarterly Exam in General BioVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Colonization of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesColonization of The PhilippinesVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Enrolment List: Office of The RegistrarDocument1 pageEnrolment List: Office of The RegistrarVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Local CommunityDocument17 pagesLocal CommunityVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
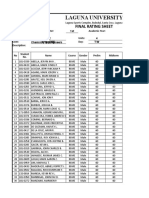
- Laguna University: Final Rating SheetDocument13 pagesLaguna University: Final Rating SheetVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Senior High School Student Permanent Record: Laguna UniversityDocument9 pagesSenior High School Student Permanent Record: Laguna UniversityVinlax ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)Document9 pagesBusiness Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)nethsaraPas encore d'évaluation
- LEVINE Dl-Schweinfurt Talk FinalDocument12 pagesLEVINE Dl-Schweinfurt Talk FinalKezoPas encore d'évaluation
- Valeriano vs. ECC and GSIS, June 8, 2000 GR 136200Document2 pagesValeriano vs. ECC and GSIS, June 8, 2000 GR 136200Lex DgtPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Types of EssayDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of EssayBambi Pajaro75% (4)
- Conflict Resolution 2Document238 pagesConflict Resolution 2jaseme7579100% (3)
- Removal of Judges of The Supreme Court by The Parliament Under 16Th Amendment of The Constitution of Bangladesh: A Tension Between Judicial Independence and AccountabilityDocument12 pagesRemoval of Judges of The Supreme Court by The Parliament Under 16Th Amendment of The Constitution of Bangladesh: A Tension Between Judicial Independence and AccountabilitysabitavabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 18Document18 pagesUnit 18Sai Anil SPas encore d'évaluation
- Bay Al InahDocument12 pagesBay Al InahAyu SetzianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rizal Activity 1Document2 pagesRizal Activity 1Mesael S. Mateo Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCTV PolicyDocument8 pagesCCTV PolicyRamesh SwaminathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gendron 2005Document38 pagesGendron 2005Daniel WambuaPas encore d'évaluation
- GSIS Vs - COADocument1 pageGSIS Vs - COAXander 4thPas encore d'évaluation
- Vanshika Gupta - Professional EthicsDocument16 pagesVanshika Gupta - Professional EthicsVanshika GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Level 5 LeadershipDocument13 pagesLevel 5 LeadershipSuvi PawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Define Moral PhilosophyDocument4 pagesDefine Moral PhilosophyjeganrajrajPas encore d'évaluation
- Lacan - Mirror Stage - Sheridan PDFDocument5 pagesLacan - Mirror Stage - Sheridan PDFsantanu6Pas encore d'évaluation
- LeadershipDocument34 pagesLeadershipErika BernardinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Corridor AgreementDocument6 pagesSuper Corridor AgreementSandeep ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Kingdom Loyalty of MatthewDocument7 pagesThe Kingdom Loyalty of MatthewrealmenministryPas encore d'évaluation
- To The Philosophy of A Human PersonDocument20 pagesTo The Philosophy of A Human PersonRiza AmoresPas encore d'évaluation
- Narrative Report MCLEDocument1 pageNarrative Report MCLEMayer BaladbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Déclaration Du Candidat Malheureux Joseph BoakaiDocument3 pagesDéclaration Du Candidat Malheureux Joseph BoakaijeuneafriquePas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar On Refinery Maintenance Management and TPM Held at Saudi Aramcos Ras Tanura RefineryDocument4 pagesSeminar On Refinery Maintenance Management and TPM Held at Saudi Aramcos Ras Tanura Refinerychaitanya_kumar_13Pas encore d'évaluation
- SGND Khalsa College: MR Samarpit Kalra Iiird Year (B) Roll No.-028Document46 pagesSGND Khalsa College: MR Samarpit Kalra Iiird Year (B) Roll No.-028Sagar Kapoor100% (3)
- The Role of The Academe in The CJSDocument16 pagesThe Role of The Academe in The CJSMelcon S. Lapina100% (1)
- Art 171-172PRCDocument2 pagesArt 171-172PRCDan SilPas encore d'évaluation
- Legal Profession Reviewer MidtermsDocument9 pagesLegal Profession Reviewer MidtermsShasharu Fei-fei LimPas encore d'évaluation