Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Design of Footings: Flores, Albert Andrew S. CE52FB1
Transféré par
Albert Andrew Flores0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
13 vues9 pagesTitre original
1.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
13 vues9 pagesDesign of Footings: Flores, Albert Andrew S. CE52FB1
Transféré par
Albert Andrew FloresDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 9
DESIGN OF FOOTINGS
FLORES, ALBERT ANDREW S.
CE52FB1
MAT (RAFT) FOUNDATION
If the loads transmitted by the columns in a structure are so
heavy or the allowable soil pressure so small that individual
footings would cover more than about one-half of the area, it
may be better to provide a continuous footing under all columns
and walls. Such a footing is called a raft or mat foundation
TYPES OF RAFT FOUNDATION
1. Flat slab types
2. Flat slab thickened under columns.
3. Flat slab thickened under columns with heavy loads.
4. Beam-slab type raft.
5. Box structures
USES OF RAFT FOUNDATIONS
1. Low soil bearing capacity
2. Spread footing cover about 70% of structure area
3. High structure loads
4. For structures like chimneys, silos, tanks, and large machines
5. Structures and equipment sensitive to differential settlement
6. Soft pockets or cavities of in the Soil to unknown extent raft
7. Watertight construction under basements below ground water
table
8. Highly compressible soil and extents to a great depth
DESIGN PROCEDURE (CONVENTIONAL METHOD)
1. Strips
2. Calculate eccentricity
3. Calculate pressure distribution on the soil at different locations under
the raft
4. Divide the raft into a series of continuous beams centered at column
rows .
5. Draw the bending moment, shear force diagrams for . Draw the bending
moment, shear force diagrams for each beam in x, y direction.
6. Depth of the beam raft, check the shear stress. Note that the Raft depth
should constant.
7. Design the raft in the other direction knowing the depth.
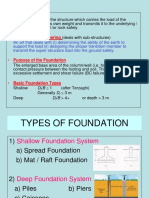
MAT (RAFT) FOUNDATION
If the loads transmitted by the columns in a structure are so
heavy or the allowable soil pressure so small that individual
footings would cover more than about one-half of the area, it
may be better to provide a continuous footing under all
columns and walls. Such a footing is called a raft or mat
foundation
MAT (RAFT) FOUNDATION
•Mat or raft foundation is a large concrete slab supporting several
columns in two or more rows.
• It is used where the supporting soil has low bearing capacity.
•The bearing capacity increased by combining all individual footings in to
one mat –since bearing capacity is proportional to width and depth of
foundations.
•In addition to increasing the bearing capacity, mat foundations tend to
bridge over irregularities of the soil and the average settlement does not
approach the extreme values of isolated footings.
•Thus mat foundations are often used for supporting structures that are
sensitive to differential settlement.
MAT (RAFT) FOUNDATION
Design Assumptions
- mat is indefinitely rigid
- planner soil pressure distribution under mat
Design Procedure
1. Determine the line of action of the resultant of all the loads acting on the mat
2. Determine the contact pressure distribution as under:
- If the resultant passes through the center of gravity of mat, . the contact pressure is given by
σ = Q/A
- If the resultant has an eccentricity of 𝑒𝑥 and 𝑒𝑦 in the x and y direction
X' = Pi xi /Ptot
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mat FoundationsDocument21 pagesMat FoundationsSangam AcharyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Footings by FloresDocument10 pagesDesign of Footings by FloresAlbert Andrew FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Foundations IntroductionDocument18 pagesSoil Foundations IntroductionrenrenzPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Piled - Raft Foundation PDFDocument48 pagesDesign of Piled - Raft Foundation PDFDrYoussefHammida100% (2)
- FoundationDocument28 pagesFoundationMerwin Andrew UyPas encore d'évaluation
- Q 1. When Is A Foundation Called Shallow Foundation ?Document13 pagesQ 1. When Is A Foundation Called Shallow Foundation ?Sanjit BadgujarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bearing Pressure Under A Base of FoundationDocument37 pagesBearing Pressure Under A Base of Foundationمحمد الذيبانيPas encore d'évaluation
- New Cel321 FootingDocument38 pagesNew Cel321 FootingArpit GunawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Procedure For Raft FoundationDocument5 pagesDesign Procedure For Raft FoundationOmkarnath YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Raft Foundation Analysis and Design ExampleDocument22 pagesRaft Foundation Analysis and Design ExampleEng Obadah Harastani91% (89)
- Handout-CE 415 RC FootingDocument82 pagesHandout-CE 415 RC FootingbilalPas encore d'évaluation
- Shallow Foundation - Week 3 - Lecture 1Document28 pagesShallow Foundation - Week 3 - Lecture 1Shivneel Karan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- FoundationsDocument36 pagesFoundationsnihaPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Mat Foundation - FullDocument34 pages7 Mat Foundation - FullRJ JordanPas encore d'évaluation
- BCM Model AnswersDocument5 pagesBCM Model AnswersMahesh RamtekePas encore d'évaluation
- RaftDocument16 pagesRaftpoojaPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation: Every Structure Consist of The Following Two Parts - Super Structure Foundation (Sub Structure)Document35 pagesFoundation: Every Structure Consist of The Following Two Parts - Super Structure Foundation (Sub Structure)Akanksha RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 2 Types of Foundations PDFDocument36 pagesLec 2 Types of Foundations PDFUsman AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Raft CWDocument5 pagesRaft CWEkky Cecil100% (1)
- Mat Foundations: Omitted PartsDocument55 pagesMat Foundations: Omitted PartsipmawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation Design To ES EN 1997Document24 pagesFoundation Design To ES EN 1997Abebe Wolde100% (1)
- Combined FootingsDocument8 pagesCombined FootingsJason Rodriguez100% (1)
- Raft Foundation - 37Document5 pagesRaft Foundation - 37ganesh patilPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Construction Lecture Note .2Document198 pagesBuilding Construction Lecture Note .2amu aytuPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture On Design of Shallow FoundationDocument60 pagesLecture On Design of Shallow Foundationdil afroza karim LinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation: Building Materials and ConstructionDocument59 pagesFoundation: Building Materials and Constructionbryan garciaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 BAA4513 Mat FoundationDocument41 pages6 BAA4513 Mat FoundationAizat HermanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 8&9Document35 pagesLecture 8&9TaukirPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - 2 Shallow Foundations - CF & RaftsDocument55 pages4 - 2 Shallow Foundations - CF & RaftsAnonymous Vx9KTkM8nPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 FoundationDocument11 pagesChapter 3 FoundationtofshomaPas encore d'évaluation
- Raft Foundation 1Document17 pagesRaft Foundation 1Sonali ChamadiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Selection of Foundation Type:-: PageDocument10 pagesSelection of Foundation Type:-: PageTaimoor azamPas encore d'évaluation
- Bearing CapacityDocument47 pagesBearing CapacityAlweendo MarthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Foundations and Its Uses Rahul Kumawat 08CE000137Document14 pagesTypes of Foundations and Its Uses Rahul Kumawat 08CE000137Rahul Kumawat100% (1)
- Building Constructure DesignDocument51 pagesBuilding Constructure DesignPiyush RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- CE-403 Bearing Capacity - Shallow FoundationDocument49 pagesCE-403 Bearing Capacity - Shallow Foundationlance carterPas encore d'évaluation
- Finite Element Analysis of Eccentric FootingDocument92 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Eccentric FootingJunaidAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Raft Foundation 2.0Document6 pagesRaft Foundation 2.0anuragPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Foundations PDFDocument30 pagesTypes of Foundations PDFHuzaifa TanzeelPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of FoundationsDocument30 pagesTypes of FoundationsFahad Areeb100% (1)
- Footing Analysis Nad DesignDocument50 pagesFooting Analysis Nad Designabdul haseebPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation Engineering I CE-325: Chapter 3: Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDocument17 pagesFoundation Engineering I CE-325: Chapter 3: Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsRobert Prince100% (1)
- 3 - Foundation TypesDocument27 pages3 - Foundation TypesimaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1a) Mat FoundationsDocument15 pagesChapter 1a) Mat FoundationsAngelaDeviPas encore d'évaluation
- Footings: General IntroductionDocument21 pagesFootings: General IntroductionMd Shafiul Alam FahadPas encore d'évaluation
- Pile FoundationDocument33 pagesPile FoundationAvantika DhimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 12 - Design Analysis of Mat - Raft FootingDocument19 pagesLecture 12 - Design Analysis of Mat - Raft FootingAsnil Prakash0% (1)
- Design of Footings: Foundation SystemDocument12 pagesDesign of Footings: Foundation SystemAbdirahman Ahmed IssePas encore d'évaluation
- FootingsDocument24 pagesFootingsLester Corvera OlaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation Seminar ReportDocument29 pagesFoundation Seminar ReportYash Boharupi0% (1)
- FootingsDocument10 pagesFootingsEleonor Pacomios-VirtudazoPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 LectureDocument37 pages4 LecturePranto KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Foundation Made by WeisiongDocument31 pagesTypes of Foundation Made by WeisiongSami ZamaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.construction of Sub Structure: By-Khan Nikhat NaazDocument77 pages2.construction of Sub Structure: By-Khan Nikhat NaazDharmesh MangratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fad MicroDocument4 pagesFad MicroT SuryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionD'EverandReinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910D'EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910Pas encore d'évaluation
- Turf Wall Architecture and Turf Furniture Assembly GuideD'EverandTurf Wall Architecture and Turf Furniture Assembly GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionD'EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (4)
- Design of Irrigation SystemDocument70 pagesDesign of Irrigation SystemAlbert Andrew FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Technological Institute of The Philippines Rubric For Engineering Projects (Engineering Programs)Document7 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines Rubric For Engineering Projects (Engineering Programs)Albert Andrew FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Design Project Assessment ToolDocument4 pagesEngineering Design Project Assessment ToolAlbert Andrew FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: 938 Aurora Boulevard, Cubao, Quezon CityDocument35 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines: 938 Aurora Boulevard, Cubao, Quezon CityAlbert Andrew FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Criterion's Importance (On A Scale of 0 To 10) Ability To Satisfy The Criterion (On A Scale From 0 To 10) (Final Estimate)Document9 pagesCriterion's Importance (On A Scale of 0 To 10) Ability To Satisfy The Criterion (On A Scale From 0 To 10) (Final Estimate)Albert Andrew FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Table D. 1 Detailed Estimate of Centrifugal Pump Monthly Inspection and Maintenance 10Document5 pagesTable D. 1 Detailed Estimate of Centrifugal Pump Monthly Inspection and Maintenance 10Albert Andrew FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Culvert RRLDocument5 pagesCulvert RRLAlbert Andrew FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised Cleaning and Painting Piece Rate Data 02-07-2021Document5 pagesRevised Cleaning and Painting Piece Rate Data 02-07-2021Corrosion FactoryPas encore d'évaluation
- SENR33120001 621E and 627E Tractor-Scraper Hydraulic System (SENR3312)Document2 pagesSENR33120001 621E and 627E Tractor-Scraper Hydraulic System (SENR3312)CEVegaOPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics: AllenDocument9 pagesThermodynamics: AllenronakPas encore d'évaluation
- Clack-commercial-WS1.5 2L 2 2QC Drawings and Service ManualDocument48 pagesClack-commercial-WS1.5 2L 2 2QC Drawings and Service ManualGreg ReynekePas encore d'évaluation
- Astm C12Document7 pagesAstm C12omarguillermogarzon100% (1)
- SWD Pipe Size Calculation For South CampusDocument4 pagesSWD Pipe Size Calculation For South Campussalmaan mastanPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 5 PDFDocument16 pagesTopic 5 PDFnrhdyaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Djj10022 Fitting ReportDocument7 pagesDjj10022 Fitting ReportTamil passang songPas encore d'évaluation
- SwissDocument8 pagesSwissRajaram RamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Agma 9112 - A04Document41 pagesAgma 9112 - A04FARIBA100% (2)
- Moment VectorDocument9 pagesMoment VectorGlen GulayPas encore d'évaluation
- Amit Goswami Quantum Mechanics, Second Edition 2003Document577 pagesAmit Goswami Quantum Mechanics, Second Edition 2003Solange Ev75% (4)
- D77003 enDocument57 pagesD77003 enzliangPas encore d'évaluation
- Type 1: Technical ParametersDocument7 pagesType 1: Technical ParametersMuhammad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Levers in Musculoskeletal SystemDocument22 pagesLevers in Musculoskeletal SystemGlenn JohnstonPas encore d'évaluation
- Propeller Shaft: Models FA and FBDocument15 pagesPropeller Shaft: Models FA and FBKomatsu Perkins HitachiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bixby MaxFire HighlightsDocument6 pagesBixby MaxFire HighlightsAl Malley100% (2)
- Parts Manual Yanmar VIO82Document187 pagesParts Manual Yanmar VIO82Stephen Rivett100% (1)
- Mi 9664 TDocument5 pagesMi 9664 Tamir barekatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Shridevi - Types of Machine FoundationDocument12 pagesShridevi - Types of Machine FoundationAshokan Keloth100% (1)
- 04 AdamsParts 71-98Document30 pages04 AdamsParts 71-98apuhapuh_153349Pas encore d'évaluation
- Plastic Injection Mold Maintenance Program LinkedInDocument11 pagesPlastic Injection Mold Maintenance Program LinkedInMBRPas encore d'évaluation
- CEN TOOL Standard Padeyes V4 Rollup Padeye SheaveDocument5 pagesCEN TOOL Standard Padeyes V4 Rollup Padeye SheaveMarvan100% (1)
- 02 110 BPS Foam Pump Skid With Foam Pump and RC ControllerDocument8 pages02 110 BPS Foam Pump Skid With Foam Pump and RC Controllerarachman297988Pas encore d'évaluation
- MG UniversityDocument2 pagesMG UniversityVaisakVenugopalPas encore d'évaluation
- Parallel & Series OperationDocument5 pagesParallel & Series OperationMayuresh MahajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Cun It PacketsDocument226 pagesPhysics Cun It PacketsRana MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring InstrumentsDocument10 pagesMeasuring Instrumentsmohsin931Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sae J500 EstriadosDocument2 pagesSae J500 EstriadosMarcel Dandaro100% (1)