Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Early History of Wireless Communication
Transféré par
Praveen Yadav0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
15 vues7 pagesEarly wireless communication methods included smoke signals, heliographs, and optical telegraphs. In the late 19th century, scientists like Faraday, Maxwell, and Hertz discovered and experimented with electromagnetic waves, paving the way for wireless communication. In the 20th century, pioneers like Marconi demonstrated wireless telegraphy and helped develop radio communication technologies. Standards and networks then evolved, including wireless local and cellular networks, leading to today's digital cellular standards like GSM and 4G networks.
Description originale:
Titre original
Lec-2.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentEarly wireless communication methods included smoke signals, heliographs, and optical telegraphs. In the late 19th century, scientists like Faraday, Maxwell, and Hertz discovered and experimented with electromagnetic waves, paving the way for wireless communication. In the 20th century, pioneers like Marconi demonstrated wireless telegraphy and helped develop radio communication technologies. Standards and networks then evolved, including wireless local and cellular networks, leading to today's digital cellular standards like GSM and 4G networks.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
15 vues7 pagesEarly History of Wireless Communication
Transféré par
Praveen YadavEarly wireless communication methods included smoke signals, heliographs, and optical telegraphs. In the late 19th century, scientists like Faraday, Maxwell, and Hertz discovered and experimented with electromagnetic waves, paving the way for wireless communication. In the 20th century, pioneers like Marconi demonstrated wireless telegraphy and helped develop radio communication technologies. Standards and networks then evolved, including wireless local and cellular networks, leading to today's digital cellular standards like GSM and 4G networks.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 7
Early history of wireless communication
• Many people in history used light for communication
– heliographs, flags („semaphore“), ...
– 150 BC smoke signals for communication;
(Polybius, Greece)
– 1794, optical telegraph, Claude Chappe
• Here electromagnetic waves are
of special importance:
– 1831 Faraday demonstrates electromagnetic induction
– J. Maxwell (1831-79): theory of electromagnetic Fields, wave
equations (1864)
– H. Hertz (1857-94): demonstrates
with an experiment the wave character
of electrical transmission through space
(1888, in Karlsruhe, Germany, at the
location of today’s University of Karlsruhe)
History of wireless communication I
• 1896Guglielmo Marconi
– first demonstration of wireless
telegraphy (digital!)
– long wave transmission, high
transmission power necessary (> 200kw)
• 1907Commercial transatlantic connections
– huge base stations
(30 100m high antennas)
• 1915Wireless voice transmission New York - San Francisco
• 1920Discovery of short waves by Marconi
– reflection at the ionosphere
– smaller sender and receiver, possible due to the invention of the
vacuum tube (1906, Lee DeForest and Robert von Lieben)
• 1926Train-phone on the line Hamburg - Berlin
– wires parallel to the railroad track
History of wireless communication II
• 1928 many TV broadcast trials (across Atlantic, color TV, TV
news)
• 1933 Frequency modulation (E. H. Armstrong)
• 1958A-Netz in Germany
– analog, 160MHz, connection setup only from the mobile station,
no handover, 80% coverage, 1971 11000 customers
• 1972B-Netz in Germany
– analog, 160MHz, connection setup from the fixed network too
(but location of the mobile station has to be known)
– available also in A, NL and LUX, 1979 13000 customer in D
• 1979NMT at 450MHz (Scandinavian countries)
• 1982Start of GSM-specification
– goal: pan-European digital mobile phone system with roaming
• 1983Start of the American AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone
System, analog)
• 1984CT-1 standard (Europe) for cordless telephones
History of wireless communication III
• 1986C-Netz in Germany
– analog voice transmission, 450MHz, hand-over possible,
digital signaling, automatic location of mobile device
– Was in use until 2000, services: FAX, modem, X.25, e-mail,
98% coverage
• 1991Specification of DECT
– Digital European Cordless Telephone (today: Digital
Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications)
– 1880-1900MHz, ~100-500m range, 120 duplex channels,
1.2Mbit/s data transmission, voice encryption,
authentication, up to several 10000 user/km2, used in more
than 50 countries
• 1992Start of GSM
– in D as D1 and D2, fully digital, 900MHz, 124 channels
– automatic location, hand-over, cellular
– roaming in Europe - now worldwide in more than 200
countries
– services: data with 9.6kbit/s, FAX, voice, ...
History of wireless communication IV
• 1994E-Netz in Germany
– GSM with 1800MHz, smaller cells
– As Eplus in D (1997 98% coverage of the population)
• 1996HiperLAN (High Performance Radio Local Area Network)
– ETSI, standardization of type 1: 5.15 - 5.30GHz, 23.5Mbit/s
– recommendations for type 2 and 3 (both 5GHz) and 4 (17GHz)
as wireless ATM-networks (up to 155Mbit/s)
• 1997Wireless LAN - IEEE802.11
– IEEE standard, 2.4 - 2.5GHz and infrared, 2Mbit/s
– already many (proprietary) products available in the beginning
• 1998Specification of GSM successors
– for UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunication System) as
European proposals for IMT-2000
• Iridium
– 66 satellites (+6 spare), 1.6GHz to the mobile phone
History of wireless communication V
• 1999 Standardization of additional wireless LANs
– IEEE standard 802.11b, 2.4-2.5GHz, 11Mbit/s
– Bluetooth for piconets, 2.4Ghz, <1Mbit/s
• Decision about IMT-2000
– Several “members” of a “family”: UMTS, cdma2000, DECT, …
• Start of WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) and i-mode
– First step towards a unified Internet/mobile communicaiton
system
– Access to many services via the mobile phone
• 2000 GSM with higher data rates
– HSCSD offers up to 57,6kbit/s
– First GPRS trials with up to 50 kbit/s (packet oriented!)
• UMTS auctions/beauty contests
– Hype followed by disillusionment (50 B$ payed in Germany for 6
licenses!)
• 2001 Start of 3G systems
– Cdma2000 in Korea, UMTS tests in Europe, Foma (almost
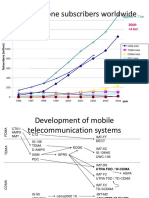
Wireless systems: overview of the
development
cordless wireless LAN
cellular phones satellites
phones
1980:
1981: CT0
NMT 450 1982:
1983: Inmarsat-A
AMPS 1984:
CT1
1986:
NMT 900 1987:
1988: CT1+
Inmarsat-C
1989:
CT 2
1991: 1991: 1991:
1992: CDMA D-AMPS 1992: DECT 199x:
GSM Inmarsat-B proprietary
1993:
Inmarsat-M
PDC
1994: 1997:
DCS 1800 IEEE 802.11
1998:
Iridium 1999:
802.11b, Bluetooth
2000: 2000:
analogue GPRS IEEE 802.11a
2001:
IMT-2000
digital
200?:
Fourth Generation
(Internet based)
4G – fourth generation: when and how?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Satellite Television: Analogue and Digital Reception TechniquesD'EverandSatellite Television: Analogue and Digital Reception TechniquesÉvaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- Pirate Radio and Video: Experimental Transmitter ProjectsD'EverandPirate Radio and Video: Experimental Transmitter ProjectsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayD'EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)
- Mobile Network Evolution To 5gDocument57 pagesMobile Network Evolution To 5gAqib EhsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Brough's 2G 3G 4G Wireless Tutorial Oct2008Document123 pagesBrough's 2G 3G 4G Wireless Tutorial Oct2008Brough TurnerPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQs Wireless and Wire Communications SystemsDocument115 pagesMCQs Wireless and Wire Communications SystemsMitzOsorioPas encore d'évaluation
- 3G TutorialDocument126 pages3G Tutorialanon-721936100% (1)
- Manual Alcatel Oxo Expert 8.1Document1 046 pagesManual Alcatel Oxo Expert 8.131ksouzaPas encore d'évaluation
- DCN M5 S1 Wireless IntroDocument36 pagesDCN M5 S1 Wireless Introsocialsync2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elective II-Mobile Computing: History of Wireless Communication A Simplified Reference Model Session (2019-2020)Document45 pagesElective II-Mobile Computing: History of Wireless Communication A Simplified Reference Model Session (2019-2020)Chetan GaurkarPas encore d'évaluation
- C11 OutlookDocument17 pagesC11 OutlookIHABALYPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless ATM Handover Issues: Mobile CommunicationsDocument48 pagesWireless ATM Handover Issues: Mobile Communicationsworldno1thiruPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 03813xyDocument25 pages01 03813xyHedayatullah NiaziPas encore d'évaluation
- CMMT423 - Mobile Computing Lecture 2.1Document34 pagesCMMT423 - Mobile Computing Lecture 2.1Dennis JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM BianchiDocument159 pagesGSM BianchimihaisanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abhay Technical Introduction To IdeaDocument73 pagesAbhay Technical Introduction To IdeaShivam BaslasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDocument77 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsBenin06Pas encore d'évaluation
- 200318A GoodDocument12 pages200318A Goodmymobilej71402Pas encore d'évaluation
- History of Mobile Communication EvolutionDocument4 pagesHistory of Mobile Communication Evolutiongaurav tiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDocument91 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsgskaswinthPas encore d'évaluation
- EEE 264-5: 3G Wireless NetworksDocument102 pagesEEE 264-5: 3G Wireless NetworksSundus AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Communications: Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDocument108 pagesMobile Communications: Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systemsradislamy-1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Wireless Communication Sy StemsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Wireless Communication Sy StemsRutuja VartalePas encore d'évaluation
- C04-Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDocument98 pagesC04-Wireless Telecommunication SystemssalsonPas encore d'évaluation
- 3G Tutorial: History and Evolution of Mobile RadioDocument126 pages3G Tutorial: History and Evolution of Mobile RadioAnang PrasetyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mohamed Mokdad Ecole D'ingénieurs de BienneDocument25 pagesMohamed Mokdad Ecole D'ingénieurs de BienneIman El HilahPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Connection Speeds OverviewDocument7 pagesStandard Connection Speeds OverviewVince CentenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile phone subscribers worldwide development and GSM overviewDocument13 pagesMobile phone subscribers worldwide development and GSM overviewYugandhara RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- EPL476 Mobile Networks Fall 2009: Cellular Telephony Architectures Instructor: Dr. Vasos VassiliouDocument71 pagesEPL476 Mobile Networks Fall 2009: Cellular Telephony Architectures Instructor: Dr. Vasos Vassiliourtamrakar53Pas encore d'évaluation
- UMTS Basic PrinciplesDocument64 pagesUMTS Basic Principlesmazagngi2010100% (3)
- W (Level1) - General Description of 3G-20051115-A-1 (1) .1Document51 pagesW (Level1) - General Description of 3G-20051115-A-1 (1) .1gargmanishgargPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.wpo-01 Wcdma Radio Theory-53Document53 pages1.wpo-01 Wcdma Radio Theory-53sabirelnaraPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Pengantar Komunikasi WirelessDocument51 pages1-Pengantar Komunikasi WirelessBloko BudiPas encore d'évaluation
- MOBILE TELECOM SYSTEMDocument76 pagesMOBILE TELECOM SYSTEMRethina Sabapathi PandiyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless CourseDocument9 pagesWireless CourseFadi ShaterPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Communications Systems OverviewDocument101 pagesWireless Communications Systems OverviewAnushka PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Soft Handover For 3G WCMDA NetworksDocument53 pagesSoft Handover For 3G WCMDA NetworksNoilalam100% (2)
- Wcdma For Umts: Eng/Ahmed HamedDocument20 pagesWcdma For Umts: Eng/Ahmed Hamedanon-305811Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Tm2201eu04tm 0002 Third Generation 3gDocument18 pages02 Tm2201eu04tm 0002 Third Generation 3gBassem AbouamerPas encore d'évaluation
- ELEC 6040 Mobile Radio Communications: Lecturers: Dr. S. D. Ma and Dr. T. I. YukDocument53 pagesELEC 6040 Mobile Radio Communications: Lecturers: Dr. S. D. Ma and Dr. T. I. YukTugas UtomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Networking: Prof. Jean-Pierre HubauxDocument20 pagesMobile Networking: Prof. Jean-Pierre HubauxpanakantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Communications and NetworksDocument201 pagesWireless Communications and Networksrasool5711Pas encore d'évaluation
- C04-Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDocument98 pagesC04-Wireless Telecommunication SystemsGrace KaslanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDocument74 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsRAJESHPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDocument74 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsUma TamilPas encore d'évaluation
- 3G TutorialDocument126 pages3G TutorialRajaRajan ManickamPas encore d'évaluation
- 3G Tutorial: Brough Turner & Marc OrangeDocument125 pages3G Tutorial: Brough Turner & Marc OrangeAshishch67Pas encore d'évaluation
- TotalDocument215 pagesTotalDeepakGuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2. WCDMA System OverviewDocument49 pagesChapter 2. WCDMA System OverviewrajwarangPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 WN - BT1001 - E01 - 1 CS Principle Overview-56Document56 pages01 WN - BT1001 - E01 - 1 CS Principle Overview-56IyesusgetanewPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 1-Introduction 2Document26 pagesPart 1-Introduction 2Tugas UtomoPas encore d'évaluation
- PropagationModelingforUMTS PDFDocument19 pagesPropagationModelingforUMTS PDFLê Quang VũPas encore d'évaluation
- FHSS FundamentalsDocument10 pagesFHSS FundamentalsPraveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 8Document8 pagesLec 8Praveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Slotted Aloha and DAMA access methodsDocument15 pagesSlotted Aloha and DAMA access methodsPraveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Antennas: Isotropic RadiatorDocument4 pagesAntennas: Isotropic RadiatorPraveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- MAC Layer Access MethodsDocument7 pagesMAC Layer Access MethodsPraveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 3Document14 pagesLec 3Praveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Signal propagation ranges and effectsDocument5 pagesSignal propagation ranges and effectsPraveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile and satellite communication frequenciesDocument6 pagesMobile and satellite communication frequenciesPraveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1Document9 pagesLec 1Praveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- QB EEE-5th Communication Theory RAVEEN YADAVDocument6 pagesQB EEE-5th Communication Theory RAVEEN YADAVPraveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Spread Spectrum Technology: Interference Spread Signal Signal Spread Interference Power PowerDocument5 pagesSpread Spectrum Technology: Interference Spread Signal Signal Spread Interference Power PowerPraveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 7Document5 pagesLec 7Praveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- 7720 06 IP Office LicensingDocument17 pages7720 06 IP Office LicensingLeonar Dosis temaPas encore d'évaluation
- C01 IntroductionDocument28 pagesC01 IntroductionAnushka PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Yealink W56P VoIP DECT Cordless Phone DatasheetDocument2 pagesYealink W56P VoIP DECT Cordless Phone DatasheetWebAntics.com Online Shopping StorePas encore d'évaluation
- AEI Hospitality Product Guide 2021Document43 pagesAEI Hospitality Product Guide 2021fahimyaseen8175Pas encore d'évaluation
- 15 Phase in Opentouchsuite MLE EF C134 enDocument10 pages15 Phase in Opentouchsuite MLE EF C134 enblackmamba etti jeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile GlossaryDocument9 pagesMobile GlossaryDavid SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Start of Chapter: CH 4 Multiple Access Techniques For Wireless CommunicationDocument22 pagesStart of Chapter: CH 4 Multiple Access Techniques For Wireless CommunicationDineshsingh ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Wiley WiMAX Technology For Broadband Wireless Access Mar 2007Document353 pagesWiley WiMAX Technology For Broadband Wireless Access Mar 2007Christian TipantuñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tc1380-Ed.01 Installation Procedure For V - enDocument44 pagesTc1380-Ed.01 Installation Procedure For V - enDiogo VillodrePas encore d'évaluation
- Global IP Office Tech Bulletin Number 80Document78 pagesGlobal IP Office Tech Bulletin Number 80GroWBusiness SMDPas encore d'évaluation
- Aeg Voxtel d100 v3 Uk GRDocument38 pagesAeg Voxtel d100 v3 Uk GRMarvinFrost VaitsoudisPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 3Document28 pagesPart 3michaelliu123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Telematrix 9600 Series User GuideDocument8 pagesTelematrix 9600 Series User Guideabcde12345678326Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ascom d83 DECT Handset: Configuration ManualDocument80 pagesAscom d83 DECT Handset: Configuration ManualDavid DecerfPas encore d'évaluation
- Um9802 Dect Module v2.1Document12 pagesUm9802 Dect Module v2.1Josue ZunigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 CellDocument24 pagesUnit 2 CellK Sasi RekhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fitre SptsDocument37 pagesFitre SptsTarek KhafagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Of00te600us 03Document600 pagesOf00te600us 03emelchor57100% (1)
- NBN_guideDocument14 pagesNBN_guidekaitlinpoli21Pas encore d'évaluation
- AA7Document156 pagesAA7progressksbPas encore d'évaluation
- IQxel M 8port Brochure 030117Document7 pagesIQxel M 8port Brochure 030117kkovuruPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Communication 7th Semester ECE - AlkaDocument2 pagesWireless Communication 7th Semester ECE - AlkaMukti Nath GogoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Frame Comunication ArhitectureDocument84 pagesFrame Comunication ArhitectureNedim SpahicPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxo Connect SMB Datasheet enDocument7 pagesOxo Connect SMB Datasheet enJohnny_BesugoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ackermann Clino System99Document121 pagesAckermann Clino System99Syed Rahmath AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Panasonic KX-TG9581 - TG9582 2lineDocument100 pagesPanasonic KX-TG9581 - TG9582 2lineelpirata666Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sekotech CatalogDocument48 pagesSekotech CatalogIonut PopescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Portfolio - Grandstream All Product BrochureDocument4 pagesComplete Portfolio - Grandstream All Product BrochureDenis RangelPas encore d'évaluation