Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Volcanic Eruption Hazards
Transféré par
Adrian Carl Bronola0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
80 vues13 pagesImportance of Knowing Volcanic Eruption Hazard
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentImportance of Knowing Volcanic Eruption Hazard
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
80 vues13 pagesVolcanic Eruption Hazards
Transféré par
Adrian Carl BronolaImportance of Knowing Volcanic Eruption Hazard
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 13
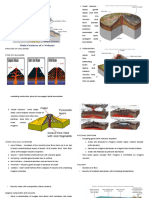
Lava flow is a mass of magma that flows
down the slope of the volcano at a rate of 3
kilometers per day or 45 kilometers per hour.
The speed of a lava flow depends on the local
topography; steep slopes encourage faster
and longer flows than gentle slopes or
terrain. Lava flows can cause injuries and
burn structures and vegetation.
Pyroclastic flow refers to hot dry masses of
fragmented volcanic materials that move along
the slope and in contact with ground surface at a
speed greater than 60 kilometers per hour. This
flows from a collapsed eruption column or lava
dome. On the other hand, pyroclastic surges are
turbulent low concentration density currents of
gases, rock debris and in some cases, water, that
move above the ground surface at high
velocities.
Tephra falls are showers or fine to coarse-
grained volcanic eruption. The diameter of the
particles can be less than 2 millimeters, 2 to 64
millimeters, or greater than 64 millimeters. The
ash can be reach distant places since it is carried
by the wind. The ash form the Mt. Pinatubo
eruption reached as far as Vietnam. Tephra falls
can cause pollution, health problems, poor
visibility, and disruption of electricity and
communication lines.
Ballistic projectiles are rocks that are released
into the air by an erupting volcano. These
land within 2 kilometers of the vent but can
travel as far as 5 kilometers or further if the
eruption is very explosive.
Volcanic gas is one of the basic components of
magma or lava. Active and inactive volcanoes
may release gases to the atmosphere in the
form of water vapor, hydrogen sulfide, sulfur
dioxide, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide,
hydrogen chloride, and hydrogen fluoride.
Hydrogen chloride and hydrogen fluoride are
released by volcanic activity and dissolved in
water vapor droplets in steam clouds. This
creates acid rains that can harm plants, marine
life, and infrastructures.
Lahar is flowing mixture of volcanic debris and water. It is
classified into two: the primary or hot lahar that is
associated directly with volcanic eruption and the
secondary or cold lahar caused by heavy rainfall. Lahar
can destroy and bury structures and communities, just like
what happened after the eruption of Mt. Pinatubo. On
October 1, 1995, typhoon rains cause lahar that was
formed from 50 million cubic meters of volcanic debris.
These buried Cabalantian, one of the barangays in
Pampanga which had initially escaped lahar that had
affected other areas since the eruption. In six hours, 2,300
houses, 500 vehicles, and countless people were buried.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Development of An AtomDocument61 pagesDevelopment of An AtomPhil GainPas encore d'évaluation
- Revolution/Rotation Day/Night Phases of The Moon SeasonsDocument41 pagesRevolution/Rotation Day/Night Phases of The Moon SeasonsNiña Socorro Macasil PedrosaPas encore d'évaluation
- DRRR Notes DiscussionDocument31 pagesDRRR Notes DiscussionCharline A. RadislaoPas encore d'évaluation
- History of AstronomyDocument731 pagesHistory of Astronomyioli99Pas encore d'évaluation
- ElectricityDocument30 pagesElectricityJopie ArandaPas encore d'évaluation
- LightDocument56 pagesLightnabeeha malhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Virtual Stomata LabDocument4 pagesVirtual Stomata Labapi-522847737Pas encore d'évaluation
- (Edward Lee Thorndike) : Prepared By: Ma. Cesarmela DomingoDocument7 pages(Edward Lee Thorndike) : Prepared By: Ma. Cesarmela DomingoEdralinePas encore d'évaluation
- HazardsDocument97 pagesHazardsJoana Jean SuymanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 17 - Special RelativityDocument37 pagesChapter 17 - Special Relativityascd_msvuPas encore d'évaluation
- Metacognitive Analogy IntructionDocument21 pagesMetacognitive Analogy IntructionPat BitaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity MagnestismDocument51 pagesElectricity MagnestismMiranti UrbaningrumPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys1 Ch3 Workenergy NewDocument58 pagesPhys1 Ch3 Workenergy NewDuy ĐỗPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Volume Profit Analysis ReportDocument52 pagesCost Volume Profit Analysis ReportCharly Mint Atamosa IsraelPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Rocks PowerpointDocument18 pagesTypes of Rocks PowerpointEjurango JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal ConductivityDocument21 pagesThermal ConductivityVincent ManganaanPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 16 Financing Current AssetsDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 16 Financing Current AssetsAhsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Adjusting Entries KaroleDocument89 pagesAdjusting Entries Karole이시연Pas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Materials and Resources - RocksDocument30 pagesEarth Materials and Resources - RocksKen AguilaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Basics of Capital Budgeting: Should We Build This Plant?Document24 pagesThe Basics of Capital Budgeting: Should We Build This Plant?remus007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Carbon CompoundsDocument21 pagesChemistry of Carbon Compoundsdela2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transfer of LearningDocument30 pagesTransfer of LearningMei JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Origin of Life On EarthDocument36 pagesOrigin of Life On EarthGuiana Kaila Capito Ibanez100% (1)
- Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionDocument67 pagesDisaster Readiness and Risk ReductionZergaia WPPas encore d'évaluation
- The Earth - S Water BudgetDocument33 pagesThe Earth - S Water BudgetKeysi02Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Solar SystemDocument10 pagesThe Solar Systemrosana f.rodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Momentum Final 1 EditedDocument51 pagesLinear Momentum Final 1 EditedRyry LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics: College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument7 pagesFluid Mechanics: College of Engineering and Technologycharmaine fos100% (1)
- Combined Gas Law & Dalton's Law (G4)Document37 pagesCombined Gas Law & Dalton's Law (G4)Kesziah CalambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitutions of The Republic of The Philippines ConstitutionDocument18 pagesConstitutions of The Republic of The Philippines ConstitutionJoan Mila CoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physci Lesson 1 Lighter ElementsDocument24 pagesPhysci Lesson 1 Lighter Elementsjo_aligoraPas encore d'évaluation
- People V Mahinay (A.e.nuyda)Document1 pagePeople V Mahinay (A.e.nuyda)Alvin Earl NuydaPas encore d'évaluation
- Temperature and HeatDocument26 pagesTemperature and HeatAlessandro YumangPas encore d'évaluation
- Hand-Out For VolcanoesDocument4 pagesHand-Out For VolcanoesalyssaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements of Weather Climate Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1-Day 41Document89 pagesElements of Weather Climate Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1-Day 41BENJ AMINPas encore d'évaluation
- Ambrosio Stars of Philippine Skies InquirerDocument11 pagesAmbrosio Stars of Philippine Skies InquirerLeogiver MañoscaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hurricane Vs TornadoesDocument11 pagesHurricane Vs TornadoesMelanie Valladares RPas encore d'évaluation
- Continenetal Drift TheoryDocument31 pagesContinenetal Drift TheoryFarzanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biogeochemical Cycle: Environmental CyclesDocument21 pagesBiogeochemical Cycle: Environmental CyclesAhmad Sharief Bin JaylaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Naming and Writing Ionic FormulasDocument24 pagesNaming and Writing Ionic FormulasCristina Nicomedes AguinaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Practice For First ExamDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanics Practice For First ExamKyle WhitesidePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 in Hydrology QuizDocument4 pagesChapter 1 in Hydrology QuizG-ann DatarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Climate ChangeDocument5 pagesClimate ChangeJhecyl Ann BasagrePas encore d'évaluation
- Lithosphere and GeomorphologyDocument41 pagesLithosphere and GeomorphologycristitamasPas encore d'évaluation
- Light ColorsDocument34 pagesLight ColorsROSIEL MANDRIQUEPas encore d'évaluation
- Note Chapter1 SF017Document67 pagesNote Chapter1 SF017Anonymous Kx8TAybnXQPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment On Sources of EnergyDocument2 pagesAssignment On Sources of EnergyMukulika ChatterjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Solid Waste HandoutsDocument10 pagesSolid Waste HandoutsTheo Jhullian CabasalPas encore d'évaluation
- Volcanoes PDFDocument74 pagesVolcanoes PDFLawrence CezarPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth and The Early Atmosphere TimelineDocument1 pageEarth and The Early Atmosphere Timelinemaddy kreiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Biogeochemical Cycle: Prepared By: Maria Florida Mariano Bsed Iv Biosci EcologyDocument55 pagesBiogeochemical Cycle: Prepared By: Maria Florida Mariano Bsed Iv Biosci EcologyYona makaneryPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotation and Revolution: What Causes Night and Day? What Causes The Seasons To Change?Document5 pagesRotation and Revolution: What Causes Night and Day? What Causes The Seasons To Change?ajay_competitionPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling DistributionDocument102 pagesSampling DistributionMark B. BarrogaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4q Elements of Weather Climate Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1-Day 4Document89 pages4q Elements of Weather Climate Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1-Day 4Winlyn B. Malazarte0% (1)
- 13 Intro To WavesDocument29 pages13 Intro To WavesEdna OsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 1-Traditional LiteraciesDocument41 pagesMODULE 1-Traditional LiteraciesKristine OgatisPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5 Energy ResourcesDocument22 pagesModule 5 Energy ResourcesCarlos TuazonPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 4 Intro Grade 8 Atomic Theory NotesDocument45 pagesWeek 4 Intro Grade 8 Atomic Theory Notesmkraemer50% (2)
- Hazardous Volcanic EventsDocument18 pagesHazardous Volcanic EventsMatt ValenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- FSC 3 Episode 4Document11 pagesFSC 3 Episode 4Jopie Aranda77% (22)
- Ash Flow Tuffs Origin IdentificationDocument90 pagesAsh Flow Tuffs Origin IdentificationBaculitesPas encore d'évaluation
- Greeenstone Belts of South IndiaDocument27 pagesGreeenstone Belts of South IndiasojaPas encore d'évaluation
- T He 706 Volcanoes True or False Sorting Activity Sheet English - Ver - 4Document3 pagesT He 706 Volcanoes True or False Sorting Activity Sheet English - Ver - 4Lily Anne CerilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Volcanic Texture McPhie 1 50Document50 pagesVolcanic Texture McPhie 1 50tina nur puspitasariPas encore d'évaluation
- DRRR-Grade 11/12: I. Introductory ConceptDocument15 pagesDRRR-Grade 11/12: I. Introductory ConceptCK BernalPas encore d'évaluation
- Sandwich-Style Au Mineralization 2020 3-4Document44 pagesSandwich-Style Au Mineralization 2020 3-4Alberto Lobo-GuerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- Sci9 Q3 Module2Document26 pagesSci9 Q3 Module2Sherwin Lee PascualPas encore d'évaluation
- Geology and Mineralization of The Eocene Tuscarora Volcanic Field, Elko County, NevadaDocument12 pagesGeology and Mineralization of The Eocene Tuscarora Volcanic Field, Elko County, NevadaJulio Miranda AlarconPas encore d'évaluation
- Fdsci201 Document w05VolcanoesRev330UpdatedVersionDocument11 pagesFdsci201 Document w05VolcanoesRev330UpdatedVersionFerdy Cipriano0% (1)
- Flood of AssamDocument1 pageFlood of AssamTTM LEGENDPas encore d'évaluation
- Mayon VolcanoDocument12 pagesMayon VolcanoJuan UnoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cataclysmic 1991 Eruption of Mount Pinatubo, PhilippinesDocument2 pagesThe Cataclysmic 1991 Eruption of Mount Pinatubo, PhilippinesWong Jhfunnyfunny100% (1)
- Active and Inactive List of VolcanoesDocument5 pagesActive and Inactive List of VolcanoesGRascia Ona100% (2)
- Bahasa Inggris Volcanic EruptionDocument10 pagesBahasa Inggris Volcanic Eruptionendah100% (1)
- VolcanoesDocument6 pagesVolcanoesRoger Corre RivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mars Atlas MOM 26 32Document7 pagesMars Atlas MOM 26 32aldert_pathPas encore d'évaluation
- VolcanoesDocument7 pagesVolcanoesMarilyn LaquindanumPas encore d'évaluation
- Volcano Project GuidelinesDocument7 pagesVolcano Project GuidelinesWelfredo Jr YuPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 5 Science Lesson 14 Natural DisastersDocument3 pagesClass 5 Science Lesson 14 Natural Disastersrashi baksh100% (2)
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Geology VolcanoesDocument4 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Geology VolcanoesElle RamiloPas encore d'évaluation
- VolcanoDocument84 pagesVolcanoJM LomoljoPas encore d'évaluation
- Volcano Case StudyDocument3 pagesVolcano Case StudyJosephat MugumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Geological Map of LomblenDocument8 pagesGeological Map of LomblenginanjarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 - VolcanoesDocument45 pagesLesson 1 - VolcanoesTeacher DennisPas encore d'évaluation
- Disasters and Disaster Risk: Prepared By: Ms. Charisse Joy B. ArcaDocument66 pagesDisasters and Disaster Risk: Prepared By: Ms. Charisse Joy B. ArcaCj NacarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Storyworks: "The Eruption of Mt. Vesuvius": Text. Common Core Anchor Standards: R.1, R.2, R.3, R.4., W.1, SL.1, L, 5, L.6Document11 pagesStoryworks: "The Eruption of Mt. Vesuvius": Text. Common Core Anchor Standards: R.1, R.2, R.3, R.4., W.1, SL.1, L, 5, L.6arkadiy samoylovPas encore d'évaluation
- Gabriella Pedranti Mount STDocument7 pagesGabriella Pedranti Mount STapi-412649056Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 6 DLL Science 6 q3 Week 2Document5 pagesGrade 6 DLL Science 6 q3 Week 2Trisha ManaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Dacite Rock (Igneous Rock) ExtrusiveDocument6 pagesDacite Rock (Igneous Rock) ExtrusiveDewanshu VikramPas encore d'évaluation