Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
GEE 001 People and Earth's Ecosystem
Transféré par
Rex Martin Guce0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
49 vues38 pagesTitre original
GEE-001.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
49 vues38 pagesGEE 001 People and Earth's Ecosystem
Transféré par
Rex Martin GuceDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 38
GEE 001
People and Earth’s Ecosystem
Environment
• the natural world, as a whole or in a particular
geographical area, especially as affected by
human activity.
Environmental Science
• An interdiciplinary study of the relationships
of the natural world and the relationships
between organisms and their environments
Environmentalism
• Social movement to protect earth’s life
support systems
• Members Include- ecologists, conservationists,
preservationists, restorationists and
environmentalists
Sustainability
• Meets the basic needs of all people while not
affecting the future generations’ ability to do
so.
How unstable the world is?
• As the world population rises, the rate at
which we degrade the worlds natural capital is
constantly accelerating.
Resources
• Anything obtained from the environment to
meet our needs and wants.
– Example: water, food, shelter etc.
Classifications of resources
• Perpetual
• Renewable
• Nonrenewable
Perpetual resources
• resources that are renewed continuously on
the human timescale, such as the sun.
Renewable Resources
• resources that are refreshed fairly rapidly
(hours to several decades) through natural
processes, such as forests and freshwater
Non renewable Resources
• Exist in a fixed quantity or stock in the earth’s
crust. They can only be renewed after millions
or billions of years.
– Energy resources, metallic mineral resources and
nonmetallic mineral resources.
Population in the world
• Population in the world is currently (2018-
2019) growing at a rate of around 1.07% per
year (down from 1.09% in 2018, 1.12% in 2017
and 1.14% in 2016).
• The current average population increase is
estimated at 82 million people per year.
Economic Growth
• The increase in the capacity of a country to
provide people with goods and services.
– Measured by GDP (gross domestic product)
– Standard of living is measured by a change in per
capita GDP
Economic Development
• The improvement of living standards by
economic growth.
• Determines whether a country is developed or
not
• Based on degree of industrialization and per
capita GDP
– Developed nations have 1.2 billion people
– Undeveloped have about 5.2 billion people
Developed vs Underdeveloped nations
Globalization
• the process by which businesses or other
organizations develop international influence
or start operating on an international scale
Environmental problems
• The industrialization of society and explosion
of human population leads destruction to the
environment through indiscriminate discharge
of untreated industrial and domestic wastes.
Pollution
• the presence in or introduction into the
environment of a substance or thing that has
harmful or poisonous effects.
• Pollution can occur through natural processes
(volcanoes) or human or anthropogenic
actions (burning coal).
– Most comes from urban or industrialized areas
Pollutants
• a substance that pollutes something, especially
water or the atmosphere.
– Example
• Ground level ozone
• Carbon Monoxide
• Sulfur Dioxide
• Lead
• Nitrogen Oxides
• Particulate Matter
• Carbon Dioxide
• Methane
• Chlorofluorocarbons (CFS)
Types of Pollution
• Water pollution
• Thermal pollution
• Land pollution
• Radiation Pollution
• Noise pollution
• Air pollution
Water Pollution
• Degradation of the quality of water and
affects organisms living in it through :
– Chemical, physical or biological materials.
Thermal Pollution
• the harmful release of heated liquid into a
body of water or heat released into the air as
a waste product of a business
Land Pollution
• the deterioration (destruction) of the earth's
land surfaces, often directly or indirectly as a
result of man's activities and their misuse of
land resources
Major causes of Land Pollution
• Deforestation
• Agriculture
• Industry
• Mining
• Landfills and waste
• Urbanization
Radiation Pollution
• Caused by radioactive substances which emit
invisible radiation released in the environment
through human activities
Noise Pollution
• harmful or annoying levels of noise, as from
airplanes, industry, etc.
Air Pollution
• the presence in or introduction into the air of
a substance which has harmful or poisonous
effects.
Types of air pollution
• Primary pollutants
– Volcanic ash (natural occurrence)
– Gas emission from vehicles (man made pollutant)
• Secondary pollutants
– Nitrogen oxide from factory emission causes acid
rain
Global warming
• a gradual increase in the overall temperature
of the earth's atmosphere generally attributed
to the
Greenhouse Effect
• increased levels of carbon dioxide,
chlorofluorocarbons, and other pollutants
Effects of Global Warming
• Rising seas and increased coastal flooding
• More destructive hurricanes
• Longer and more damaging wildfire seasons
• More frequent and intense heat waves
• Costly and growing health impacts
• An increase in extreme weather events
• Destruction of marine ecosystems
Effects of Global Warming
• Widespread forest death in the Rocky
Mountains
• More severe droughts in some areas
• Growing risks to our electricity supply
• Changing seasons
• Disruptions to food supplies
• Melting ice
Solutions to Global warming
• Improvement of energy efficiency and vehicle
fuel economy
• Use of alternate natural powers
– Wind and solar power
– Biofuel (organic waste)
• Protection of forestry
• building better batteries to store renewable
energy
Solutions to Global warming
• building better batteries to store renewable
energy
• engineering a smarter electric grid
Overpopulation
• an undesirable condition where the number
of existing human population exceeds the
carrying capacity of Earth.
Causes of Overpopulation
• Decline in the Death Rate
• Better Medical Facilities
• More hands to overcome poverty
• technological Advancement in Fertility
Treatment
• Immigration
• Lack of Family Planning
Effects of Overpopulation
• Depletion of Natural Resources
• Degradation of Environment
• Conflicts and Wars
• Rise in Unemployment
• High Cost of living
Solutions to Overpopulation
• Better education
• Awareness on family planning
• Tax benefit (concessions)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Bernardino MODULE 6 EVALUATE 3 21JULY2020Document1 pageBernardino MODULE 6 EVALUATE 3 21JULY2020Erika BernardinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wolfgang MozartDocument13 pagesWolfgang MozartFaisal MGPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 07 - PEOPLE, GRASSLAND AND SCRUBDocument1 pageActivity 07 - PEOPLE, GRASSLAND AND SCRUBWilly WonkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 4: Biotic and Abiotic ComponentsDocument3 pagesActivity 4: Biotic and Abiotic ComponentsMica Angela Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Human CommunicationDocument26 pagesHuman CommunicationZuber Hashmi100% (1)
- Acids and Bases LabDocument2 pagesAcids and Bases Labtwisted-revelation100% (3)
- Love of Neighbor: Submitted To: Ms. Ladylyn Mabutol Submitted By: John Israel SiaronDocument6 pagesLove of Neighbor: Submitted To: Ms. Ladylyn Mabutol Submitted By: John Israel SiaronJohn Israel Siaron100% (1)
- Unit 1 Ecology and Ecosystem1Document22 pagesUnit 1 Ecology and Ecosystem1Riya ChandnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Popular Culture NotesDocument6 pagesPopular Culture NotesBianca Jane Asuncion100% (1)
- Rizal 3CDocument3 pagesRizal 3CshooestPas encore d'évaluation
- Es PrelimDocument108 pagesEs PrelimCrystal AlcantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- GEC: 106 Section: E329 DATE SUBMITTED: October 20, 2020 NAME: Kate B. Tacogue Course/Year Level: Baels-2 Year SCOREDocument2 pagesGEC: 106 Section: E329 DATE SUBMITTED: October 20, 2020 NAME: Kate B. Tacogue Course/Year Level: Baels-2 Year SCOREKate TacoguePas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Ethics: Between Anthropocentrism and EcocentrismDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Ethics: Between Anthropocentrism and EcocentrismbdalilePas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Solid Waste On Health and The EnvironmentDocument26 pagesImpact of Solid Waste On Health and The EnvironmentRavan ButtlerPas encore d'évaluation
- Hildegard E. Peplau - Psychiatric Nurse of The CenturyDocument9 pagesHildegard E. Peplau - Psychiatric Nurse of The CenturyLord Pozak Miller100% (1)
- 7 Environmental PrinciplesDocument26 pages7 Environmental PrinciplesDaxPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of EcologyDocument15 pagesBasics of Ecologychoudhary2k8100% (1)
- Student Worksheet - Planetary Boundaries and ResilienceDocument4 pagesStudent Worksheet - Planetary Boundaries and Resilienceapi-475438213100% (2)
- Lesson 1 - Rizal LawDocument17 pagesLesson 1 - Rizal LawJulyan Ira KabigtingPas encore d'évaluation
- Life and Works of Jose RizalDocument27 pagesLife and Works of Jose RizalSarah S FigueroaPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between Cold-Blooded and Warm-Blooded AnimalsDocument5 pagesDifference Between Cold-Blooded and Warm-Blooded AnimalsShakil AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 1 Report PDFDocument5 pagesGroup 1 Report PDFMark John TacangPas encore d'évaluation
- Freudian RevolutionDocument14 pagesFreudian RevolutionAngela PalmaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Geography of The PhilippinesDocument15 pagesGeography of The PhilippinesCyrus ResurrectedPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Population Growth PDFDocument21 pagesHuman Population Growth PDFnawaldabombPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus MATH 009Document2 pagesSyllabus MATH 009Pantalunan Garry100% (1)
- What Is Ozone LayerDocument4 pagesWhat Is Ozone LayerJoseph Gratil100% (1)
- David O. Norris, James A. Carr - Endocrine Disruption - Biological Bases For Health Effects in Wildlife and Humans-Oxford University Press, USA (2005) PDFDocument492 pagesDavid O. Norris, James A. Carr - Endocrine Disruption - Biological Bases For Health Effects in Wildlife and Humans-Oxford University Press, USA (2005) PDFlashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1987 Constitution After Matial LawDocument56 pages1987 Constitution After Matial LawUnibelle Joy LachicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science and Technology and Nation BuildingDocument3 pagesScience and Technology and Nation BuildingJasmine CarpioPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Prevent Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesHow To Prevent Climate ChangeJaGixPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental SanitationDocument3 pagesEnvironmental SanitationChristopher MaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Socratic Greek PhilosophyDocument11 pagesPre-Socratic Greek PhilosophyAdil IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Threats To Biodiversity Loss and Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesThreats To Biodiversity Loss and Climate ChangeEmma ElardePas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Solid WastesDocument18 pagesImpact of Solid WastesKarthik ManiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cultural DiversityDocument4 pagesCultural Diversitymina villamor100% (1)
- The Count of Montecisto ReactionDocument1 pageThe Count of Montecisto ReactionneilclaudioPas encore d'évaluation
- Population EcologyDocument3 pagesPopulation EcologyReefZPas encore d'évaluation
- People and ForestsDocument16 pagesPeople and ForestsdanieloshkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 7 NSTP 1Document55 pagesModule 7 NSTP 1PanJan BalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ra 1425Document1 pageRa 1425Rockinson TiangcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Meaning, Nature, and Importance of StratificationDocument10 pagesMeaning, Nature, and Importance of StratificationJoyce PalamaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study FionaDocument9 pagesCase Study FionaAnonymous PilotsPas encore d'évaluation
- STS Module 2 - Lesson 1Document2 pagesSTS Module 2 - Lesson 1jjjjjemPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 Handout 1Document2 pages08 Handout 1Rio Michelle Corrales100% (1)
- Rizal: Life, Work and Writing of RizalDocument11 pagesRizal: Life, Work and Writing of RizalAreej PalawPas encore d'évaluation
- On Philippine Revolts and RevolutionDocument32 pagesOn Philippine Revolts and RevolutionJr Ocampo100% (1)
- Lesson 1 - Human FlourishingDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - Human FlourishingKARYLLE MAE MIRAFUENTESPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Science Week No.1 2Document18 pagesEnvironmental Science Week No.1 2Mayla G. BalayonPas encore d'évaluation
- GlobalCity VColic Peisker2014 Ch26inSageHandbookofGlobalisationDocument18 pagesGlobalCity VColic Peisker2014 Ch26inSageHandbookofGlobalisationRosemae RoblePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Linroy ChristianDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology: Dr. Linroy ChristianBlake KamminPas encore d'évaluation
- The Human RaceDocument36 pagesThe Human RaceHazel HeramisPas encore d'évaluation
- Acids and BasesDocument4 pagesAcids and BasesSheryll Almira HilarioPas encore d'évaluation
- NSTP Citizenship Training: Robert Clarence Lee, CPA Roel V. RaferDocument78 pagesNSTP Citizenship Training: Robert Clarence Lee, CPA Roel V. RaferDjonraeNarioGalvezPas encore d'évaluation
- Strengthening The Philippine DRRM PDFDocument29 pagesStrengthening The Philippine DRRM PDFPatrick SoliguinPas encore d'évaluation
- Rizal Course Chapters 1-3Document4 pagesRizal Course Chapters 1-3Erika Soriano92% (12)
- Biochemical CycleDocument39 pagesBiochemical CycleShubhangi BPas encore d'évaluation
- International Environmental IssuesDocument5 pagesInternational Environmental IssuesSohel BangiPas encore d'évaluation
- Trends Q1 PPT 5 Planetary NetworksDocument15 pagesTrends Q1 PPT 5 Planetary NetworksJewel PascuaPas encore d'évaluation
- PollutionDocument19 pagesPollutionCrackshot 69Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bit 004 QuizDocument4 pagesBit 004 QuizRex Martin GucePas encore d'évaluation
- Quizzer Estate Tax PDFDocument58 pagesQuizzer Estate Tax PDFRex Martin GucePas encore d'évaluation
- Quizzer Estate TaxDocument58 pagesQuizzer Estate TaxRex Martin GucePas encore d'évaluation
- Bit 004 QuizDocument4 pagesBit 004 QuizRex Martin GucePas encore d'évaluation
- Bit 004 QuizDocument4 pagesBit 004 QuizRex Martin GucePas encore d'évaluation
- Technological Institute of The Philippines (Pre-Enrollment Form (2Nd Sem 2018-2019) )Document1 pageTechnological Institute of The Philippines (Pre-Enrollment Form (2Nd Sem 2018-2019) )Rex Martin GucePas encore d'évaluation
- EM MultiVIV OutdoorUnits PDFDocument152 pagesEM MultiVIV OutdoorUnits PDFPritam NatuskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Spark Decomposition Products of Sf6 Using MultivariateDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Spark Decomposition Products of Sf6 Using MultivariateMohd Nur Khaidir HusseinPas encore d'évaluation
- LIME - EthiopiaDocument18 pagesLIME - Ethiopiafayazca100% (1)
- Infection Prevention in ORDocument85 pagesInfection Prevention in ORAme MehadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Metaceram 25010: Aluminum Oxide PowderDocument2 pagesMetaceram 25010: Aluminum Oxide PowderTob NisapakulPas encore d'évaluation
- Damping Off DiseasesDocument4 pagesDamping Off DiseasesCharlesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Hyaluronic Acid Fillers Differences Between Monophasic and Biphasic FillersDocument4 pagesEx Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Hyaluronic Acid Fillers Differences Between Monophasic and Biphasic FillersImanuel CristiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- VSL Construction SystemsDocument32 pagesVSL Construction SystemsGiải Phóng Kết CấuPas encore d'évaluation
- Oven ManualDocument28 pagesOven ManualromwellPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study GuideDocument3 pagesDrug Study GuideNicole CardenasPas encore d'évaluation
- Atwood - 1984 - Molten Salt TechnologyDocument536 pagesAtwood - 1984 - Molten Salt TechnologyLanly Romuel100% (1)
- NQ 34746Document208 pagesNQ 34746bittu kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Neuroanatomical MethodsDocument11 pagesBasic Neuroanatomical Methods88jnfPas encore d'évaluation
- 225121000-05-902, Datasheet For Pressure Gauge RevDocument5 pages225121000-05-902, Datasheet For Pressure Gauge RevAlaa RamadanPas encore d'évaluation
- Metals and Metallurgy: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument43 pagesMetals and Metallurgy: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDheeraj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Integrated Pest Management (IPM) ?Document11 pagesWhat Is Integrated Pest Management (IPM) ?Kristine Joy Elizaga-CandelarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluor Daniel - GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS FOR SPACINGDocument7 pagesFluor Daniel - GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS FOR SPACINGharishcsharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Are One or Two Dangerous? Methyl Salicylate ExposureDocument7 pagesAre One or Two Dangerous? Methyl Salicylate ExposureAriPas encore d'évaluation
- Glucosamine Safety AssessmentDocument70 pagesGlucosamine Safety Assessmentk110235015Pas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of The Composition of Dry Gas According To GOST 14920, ASTM D1946, UOP 539, UOP 709. Overview of The Main Models PDFDocument2 pagesDetermination of The Composition of Dry Gas According To GOST 14920, ASTM D1946, UOP 539, UOP 709. Overview of The Main Models PDFSami AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Pxydiagram ThermoDocument23 pagesPxydiagram Thermoapi-285386989Pas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo CRC PDFDocument84 pagesCatalogo CRC PDFAlex CordovaPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry 2 Asynchronous Activity 1Document7 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Asynchronous Activity 1casinillojilianPas encore d'évaluation
- Rajesh DhukiaDocument48 pagesRajesh DhukiaSubham BhanotPas encore d'évaluation
- JCCO 2019 With AnswerDocument5 pagesJCCO 2019 With AnswerbellaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM111 Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument32 pagesCHEM111 Aromatic HydrocarbonsKharl Roei SalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
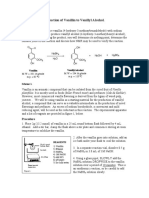
- Reduction of Vanillin To Vanillyl Alcohol.: BackgroundDocument2 pagesReduction of Vanillin To Vanillyl Alcohol.: BackgroundHawra JawadPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT IOG SAMPLE MATERIAL - Hydrocarbon Process Safety PDFDocument7 pagesUNIT IOG SAMPLE MATERIAL - Hydrocarbon Process Safety PDFBakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cracking Patterns and Ionisation EnergiesDocument2 pagesCracking Patterns and Ionisation EnergiesWilliamRiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pereaksi GrignardDocument8 pagesPereaksi Grignardisya_nurhidaPas encore d'évaluation