Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
5.fistula 29.7.19
Transféré par
HEZIL0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
11 vues19 pagesThis document discusses vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) and rectovaginal fistula (RVF). VVF is an abnormal connection between the bladder and vagina that causes continuous involuntary discharge of urine. It is often caused by prolonged obstructed labor or trauma during delivery. RVF is a fistula between the rectum and vagina that allows passage of gas, stool and pus through the vagina. Both conditions are typically treated first through medical management like antibiotics and drainage, and then surgically to repair the fistula. Post-operative care involves bladder or bowel drainage, infection prevention and pelvic rest.
Description originale:
Titre original
5.fistula 29.7.19.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document discusses vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) and rectovaginal fistula (RVF). VVF is an abnormal connection between the bladder and vagina that causes continuous involuntary discharge of urine. It is often caused by prolonged obstructed labor or trauma during delivery. RVF is a fistula between the rectum and vagina that allows passage of gas, stool and pus through the vagina. Both conditions are typically treated first through medical management like antibiotics and drainage, and then surgically to repair the fistula. Post-operative care involves bladder or bowel drainage, infection prevention and pelvic rest.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
11 vues19 pages5.fistula 29.7.19
Transféré par
HEZILThis document discusses vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) and rectovaginal fistula (RVF). VVF is an abnormal connection between the bladder and vagina that causes continuous involuntary discharge of urine. It is often caused by prolonged obstructed labor or trauma during delivery. RVF is a fistula between the rectum and vagina that allows passage of gas, stool and pus through the vagina. Both conditions are typically treated first through medical management like antibiotics and drainage, and then surgically to repair the fistula. Post-operative care involves bladder or bowel drainage, infection prevention and pelvic rest.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 19
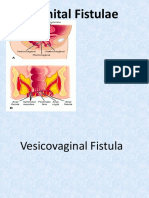
RVF and VVF
VESICOVAGINAL FISTULA
• Is an abnormal communication between urinary
bladder and the vagina results in continous
involuntary discharge of urine into the vaginal
vault
Etiology:
1. Ischemia – due to prolong compression of
bladder in obstructed labour
2. Trauma-instrumental delivery, abdominal
hysterectomy
3. gynaecological: malignancy, radiation, trauma,
infective diseases
Risk factors
• Prior pelvic or vaginal delivery
• Previous pelvic inflammatoty disease
• Ischemia
• Diabetis
• Arterioscerosis
• Carcinoma
• infection
Signs and symptoms
1. Constant urinary drainage per vagina
2. Recurrent cystitis, perineal skin irritation,
vaginal fungal infection, rarely pelvic pain
3. In large vvf, pt may not void at all
diagnosis
Speculum examination
History
Intravenous pylogram
management
• Prevention:
Adequate antenatal care
Emtying bladder frequently before and after
delivery
Avoid bladder injury
• Medical:
Transurethral or supra pubic cathter is placed
Infection control
Surgical:
1. Fistula repair; transabdominal, transvaginal,
transvesical approach is used
2.Laparoscopic fistula repair
3. Electrocautery and endoscopic closure using
fibrin glue
4. Laser welding
Post op care
Bladder dainage using cathter
Acidification of urine using vit c 500mg orally tid
estrogen replacement therapy
Antibiotic therapy:
Administer stool softner
fibre rich diet
Avoid pelvic and speculum examinations during
1st few weeks
Pelvic rest for 3 months: prohibit coitus , tampoon
use
RECTO VAGINAL
FISTULA
RVF
• RVF is a medical condition where there is a
fistula or abnormal connection between rectum
and vagina
• Etiology:
1. Congenital
2. Acquired- obstructed labour, instrumental
injury,trauma, malignancy of vagina, radiation,
diverticulitis, crohn s disease
symptoms
• Passage of gas stool and pus from the vagina
• A foul smelling vaginal discharge
• Recurrent vaginal tract infection
• Recurrent UTI
• Irritation or pain on the vulva, vagina, anus
• Pain during sexual activity
• Urgent bowel movements
• Inability to control bowel movements
diagnosis
• History
• Physical examination
• Vaginal and rectal examination
• Vaginogram
• barium enema
• anorectal ultrasound
• MRI, CT
MANAGEMENT
• MEDICAL:
Antibiotic therapy
Drainage of abscess
Dietary modification and suppementary fibre
Perform biopsy for neoplasm, treat neoplasm
surgical
Perineal or trans abdominal appraoch for repair
Transanal advancement flap repair
Transvaginal inversion repair
Bioprosthetic repair
Simple fistulotomy
Post op care
Note vaginal discharge
Bed rest
Perineal cleaning atleast twice daily and after
each voiding and defecation
Local application of ice pack for comfort
Use of laxatives
Thank you
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Genital Tract InjuriesDocument74 pagesGenital Tract InjuriesDevuchandana RPas encore d'évaluation
- 10-Advance Nursing Management of Reproductive DiseasesDocument87 pages10-Advance Nursing Management of Reproductive Diseasesabdul satar100% (1)
- Puerperal Infections: Mrs - Jagadeeswari. J M.SC (N)Document43 pagesPuerperal Infections: Mrs - Jagadeeswari. J M.SC (N)Vincent Maralit MaterialPas encore d'évaluation
- Puerperal Infections: Mrs - Jagadeeswari.J M.SC (N)Document43 pagesPuerperal Infections: Mrs - Jagadeeswari.J M.SC (N)Vincent Maralit MaterialPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstetric FistulaDocument52 pagesObstetric FistulaAdaiah Priscillia SoibiharryPas encore d'évaluation
- Rinary Ract Nfections: Classification Pathophysiology Risk Factors Clinical Manifestation DiagnosticsDocument27 pagesRinary Ract Nfections: Classification Pathophysiology Risk Factors Clinical Manifestation DiagnosticsDARYmagpantayPas encore d'évaluation
- Genital Injury, VVF, RVFDocument65 pagesGenital Injury, VVF, RVFDevuchandana RPas encore d'évaluation
- Canuuc - Uti May 2017Document31 pagesCanuuc - Uti May 2017Praluki HerliawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaginal FistulaDocument14 pagesVaginal FistulaNainesh RavaliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genitourinary Fistula (VVF) 18066Document32 pagesGenitourinary Fistula (VVF) 18066Sarvagya ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Pemicu 4 GIT DevinDocument94 pagesPemicu 4 GIT DevinDevin AlexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Genitourinary Infections For ClassDocument74 pagesGenitourinary Infections For ClassKashif BurkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormal PuerperiumDocument21 pagesAbnormal PuerperiumNatukunda DianahPas encore d'évaluation
- Dilatation & Curettage: DR Ayswarya NarayanDocument19 pagesDilatation & Curettage: DR Ayswarya NarayanPrajwal Kp0% (1)
- Repro Female Repro DisordersDocument11 pagesRepro Female Repro Disordersloli popPas encore d'évaluation
- Diverticulitis 100401121737 Phpapp02Document17 pagesDiverticulitis 100401121737 Phpapp02farhan adiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bladder Atony/Urinary RetentionDocument11 pagesBladder Atony/Urinary RetentionAngela CaguitlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Infeksi Sal KemihDocument41 pagesInfeksi Sal Kemihnovida situmorangPas encore d'évaluation
- K-25 Acute AppendicitisDocument23 pagesK-25 Acute AppendicitiscarinasheliapPas encore d'évaluation
- Cesarean Section: Associate Professor Ph.D. E.A. EinyshDocument33 pagesCesarean Section: Associate Professor Ph.D. E.A. EinyshPrerit Aggarwal100% (1)
- Urinary Tract Infection-AnthieDocument25 pagesUrinary Tract Infection-AnthieGumarbio Setiadi ZakariaPas encore d'évaluation
- FistulaDocument29 pagesFistulaluttomiayvonnePas encore d'évaluation
- Hysterectomy 160819044047Document36 pagesHysterectomy 160819044047Baljeet KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument27 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionNaseem Bin Yoosaf100% (1)
- VVF Clinical Presentation 1Document24 pagesVVF Clinical Presentation 1api-370504683% (6)
- Appendicitis: DR - Sigid Djuniawan, SPBDocument50 pagesAppendicitis: DR - Sigid Djuniawan, SPBWinda AlpiniawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Alterations in Fluid and Electrolyte and AcidDocument11 pagesAlterations in Fluid and Electrolyte and Acidlaurie.charlynjanePas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Urological FistulaeDocument31 pagesManagement of Urological FistulaeBrendan DiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Fistula GenitaliaDocument35 pagesFistula GenitaliaFifi FruitasariPas encore d'évaluation
- UTI On A Background of Obstructive NephropathyDocument26 pagesUTI On A Background of Obstructive NephropathyAminath MeesanPas encore d'évaluation
- VVF Clinical Presentation 1Document24 pagesVVF Clinical Presentation 1georgeloto12Pas encore d'évaluation
- CystitisDocument13 pagesCystitisCHRISTIAN RAY ALPAS PASILIAOPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract Infection: DR Badriya Al-Mahrouqi 12/11/2017Document51 pagesUrinary Tract Infection: DR Badriya Al-Mahrouqi 12/11/2017NinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Puerperium: Bahaa MaliDocument34 pagesPuerperium: Bahaa Mali'محمد علي' محمد لافيPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract Infection: Medical Student Case-Based LearningDocument22 pagesUrinary Tract Infection: Medical Student Case-Based LearningEben Leonel Albano MaiopuePas encore d'évaluation
- Referat - Syifa Firza UtiDocument28 pagesReferat - Syifa Firza Utimiir ikbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orLorebellPas encore d'évaluation
- Peritonitis and AppendicitisDocument35 pagesPeritonitis and AppendicitisRose Anne AbivaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5-Pelvic Imflamatory DiseasesDocument10 pages5-Pelvic Imflamatory DiseasesTouseeq ManzoorPas encore d'évaluation
- UTIDocument57 pagesUTIGireesh NagaruruPas encore d'évaluation
- Vesicovaginal Fistula: Urology DepartmentDocument24 pagesVesicovaginal Fistula: Urology DepartmentHardiTariqHamma100% (1)
- Gynaecological Diseases in PregnancyDocument76 pagesGynaecological Diseases in PregnancyKarishma Shroff67% (9)
- Utis in Pregnancy: Rachael Mweigwa NakimuliDocument55 pagesUtis in Pregnancy: Rachael Mweigwa NakimuliRuva Oscass JimmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Infection of The Cervics 1Document23 pagesInfection of The Cervics 1PreciousMpachikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genital FistulaeDocument15 pagesGenital Fistulaesangeetha francisPas encore d'évaluation
- Genital FistulaeDocument27 pagesGenital Fistulaeapi-3705046100% (1)
- Chapter 36 The Urinary System in GynaecologyDocument19 pagesChapter 36 The Urinary System in Gynaecologypmj050gpPas encore d'évaluation
- UTIDocument46 pagesUTIGlorya Benthamy SiamiloyPas encore d'évaluation
- UTI in PregnancyDocument33 pagesUTI in Pregnancyyusufkiduchu8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Third Stage Complication of LabourDocument56 pagesThird Stage Complication of LabourshravaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Document23 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Diana Rashid100% (1)
- Reproductive Tract FistulaeDocument16 pagesReproductive Tract FistulaeKiprotich Titus NgetichPas encore d'évaluation
- Analrectal Conditions and Managements: Presenter Dr. Gilbert SangaDocument63 pagesAnalrectal Conditions and Managements: Presenter Dr. Gilbert SangaSamar AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- MALE REPRODUCTIVE PROBLEMS 2021 With NotesDocument35 pagesMALE REPRODUCTIVE PROBLEMS 2021 With NotesNikky SilvestrePas encore d'évaluation
- PeritonitisDocument20 pagesPeritonitisYasirPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract Infection: Tbilisi Referral Hospital, Tbilisi, Georgia Nephrologist Nino MaglakelidzeDocument50 pagesUrinary Tract Infection: Tbilisi Referral Hospital, Tbilisi, Georgia Nephrologist Nino MaglakelidzePayal bhagatPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary EliminationDocument71 pagesUrinary EliminationFrances LiquePas encore d'évaluation
- Hydronephrosis & Vesicoureteral Reflux: Dr. Farhanul Huda Associate Professor Dept. of Surgery Aiims RishikeshDocument33 pagesHydronephrosis & Vesicoureteral Reflux: Dr. Farhanul Huda Associate Professor Dept. of Surgery Aiims Rishikeshanjusb712Pas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument46 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionShubham GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Constipation: Stools ExplainedDocument4 pagesConstipation: Stools ExplainedArun MuralidharanPas encore d'évaluation
- LoperamidaDocument19 pagesLoperamidaGlo RyndaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rectal Irrigation Range: Product Choice GuideDocument7 pagesRectal Irrigation Range: Product Choice GuideKidz to Adultz ExhibitionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemorrhoids and Anal ProblemsDocument64 pagesHemorrhoids and Anal ProblemsAhmed Noureldin Ahmed100% (3)
- Fecal-Elimination QuizDocument4 pagesFecal-Elimination QuizAlyssa Jade GolezPas encore d'évaluation
- Fistulotomy or Fistulectomy and Primary Sphincteroplasty For Anal Fistula (FIPS) : A Systematic ReviewDocument11 pagesFistulotomy or Fistulectomy and Primary Sphincteroplasty For Anal Fistula (FIPS) : A Systematic ReviewmiguelPas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions, Pathophysiology, and Evaluation of Chronic DiarrhoeaDocument12 pagesDefinitions, Pathophysiology, and Evaluation of Chronic Diarrhoeamariana gamboa zapataPas encore d'évaluation
- RektokelDocument13 pagesRektokelIntan PermataPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument18 pagesFundamentals of NursingRommel IsraelPas encore d'évaluation
- Defecography: Technique, Interpretation, and Current Use: Arden M. Morris and Susan C. ParkerDocument14 pagesDefecography: Technique, Interpretation, and Current Use: Arden M. Morris and Susan C. ParkerSuraj KurmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Slow Transit Constipation A Review of A Colonic FuDocument8 pagesSlow Transit Constipation A Review of A Colonic FuErin Bleza FaylonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 6 Powerpoint PresentationDocument47 pagesGroup 6 Powerpoint PresentationHafsah S. MarohomPas encore d'évaluation
- Fecal IncontinenceDocument5 pagesFecal IncontinenceDaniel Galindo SotomayorPas encore d'évaluation
- Rectal Computer 2Document5 pagesRectal Computer 2Su-sake KonichiwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medscape Imperforate AnusDocument22 pagesMedscape Imperforate AnusVonny RiskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundam Nursing Skill Lab ManualDocument97 pagesFundam Nursing Skill Lab ManualBirhanu AyenewPas encore d'évaluation
- Akp Important Guidelines 22 Guidlines Brief FinalDocument55 pagesAkp Important Guidelines 22 Guidlines Brief FinalRaheelPas encore d'évaluation
- Perineal RuptureDocument24 pagesPerineal RuptureIzz ShuhaimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Constipation in Infants and Children - Evaluation - UpToDateDocument25 pagesConstipation in Infants and Children - Evaluation - UpToDatemonalisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alterations in Elimination: GI Elimination Urinary EliminationDocument27 pagesAlterations in Elimination: GI Elimination Urinary EliminationMarion Liana DayritPas encore d'évaluation
- Fecal IncontinenceDocument57 pagesFecal Incontinenceiqiqiqiqiq100% (1)
- Chronic Constipation: Guest Editor: Bhim S. PandhiDocument5 pagesChronic Constipation: Guest Editor: Bhim S. PandhiAndreea PopescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plankristel_nicole18yaho100% (4)
- Pgi Hemorrhoids PresentationDocument41 pagesPgi Hemorrhoids PresentationIkea BalhonPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormal PuerperiumDocument21 pagesAbnormal PuerperiumNatukunda DianahPas encore d'évaluation
- Anorectal Manometry Patient Information 8-5-2005Document2 pagesAnorectal Manometry Patient Information 8-5-2005fifahcantikPas encore d'évaluation
- Anal FissureDocument2 pagesAnal FissureRae02Pas encore d'évaluation
- AbstractDocument23 pagesAbstractaashish21081986Pas encore d'évaluation
- DRUGS Affecting Gastrointestinal Motility: BisacodylDocument3 pagesDRUGS Affecting Gastrointestinal Motility: BisacodylLara TechiesPas encore d'évaluation
- Fistula in AnoDocument4 pagesFistula in AnoosamabinziaPas encore d'évaluation