Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Innate and Acquired Immunity
Transféré par
makhan100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
34 vues22 pagesThis document summarizes innate and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity includes anatomic barriers like skin and mucous membranes, physiological barriers like temperature and pH, and phagocytic barriers like macrophages and neutrophils. It also includes inflammatory responses. Adaptive immunity is antigen specific, diverse, leads to immunological memory, and involves T and B lymphocytes that recognize self vs non-self. Effective immune responses require antigen presentation to T cells by antigen presenting cells and B cells that secrete antibodies.
Description originale:
Innate and Acquired Immunity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document summarizes innate and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity includes anatomic barriers like skin and mucous membranes, physiological barriers like temperature and pH, and phagocytic barriers like macrophages and neutrophils. It also includes inflammatory responses. Adaptive immunity is antigen specific, diverse, leads to immunological memory, and involves T and B lymphocytes that recognize self vs non-self. Effective immune responses require antigen presentation to T cells by antigen presenting cells and B cells that secrete antibodies.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
34 vues22 pagesInnate and Acquired Immunity
Transféré par
makhanThis document summarizes innate and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity includes anatomic barriers like skin and mucous membranes, physiological barriers like temperature and pH, and phagocytic barriers like macrophages and neutrophils. It also includes inflammatory responses. Adaptive immunity is antigen specific, diverse, leads to immunological memory, and involves T and B lymphocytes that recognize self vs non-self. Effective immune responses require antigen presentation to T cells by antigen presenting cells and B cells that secrete antibodies.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 22
CLASS PRESENTATION ON -: INNATE
AND ACQUIRED IMMUNITY
MAKHAN LAL PATEL
M.SC. 3RD SEM
GURU GHASIDAS VISHWAVIDYALAYA
BILASPUR ( C.G.)
ROLL NO. 16402217
IMMUNITY
• Immunis meaning “exempt”
• Immunity is state of protection from infectious
diseases
• phenomenon -: Thucydides ..plague..430 BC..
• Variolation… china and Turks.. 15th century
• Edward Jenner …small pox… 1798
• Louis pasteure…cholera..vaccine..in chickens,
anthrax in ship, 1885 rabbies vaccine..
Human..joshef meister.
INNATE IMMUNITY
4 types of defensive barriers -:
1. Anatomic
2. Physiologic
3. Phagocytic
4. Inflammatory
(1)Anatomic barriers -: (A) Skin
1.Epidermis -:contains several layers of Epithelial
cells, Dead cells, water proof protein keratin
2. Dermis -: composed of connective tissue, contain
blood vessels, hair follicle, sebaceous glands,
sweat glands.
sebum -: lactic acid, fatty acids … pH 3-5
-: Breaks in the skin - routes for infection.
also penetrated by biting insects…
eg. mosquito… malaria ..plasmodium parasite.
(B) mucous membrane
-: conjunctivae, alimentary, respiratory, and
urogenital tracts are lined by mucous memb.
consists outer epithelial and underlying layer of
connective tissue.
mucous – viscous fluid ..entraps mic.orgs.
some non pathogenic orgs colonized in
epithelial surface …they compete with
pathogens for…surface…nutrients
-: influenza virus..can attach…
(2) Physiologic barriers
Temperature, pH, various soluble factors, and
cell associated molecules…
pH -: e.g. - Gastric acidity…
Soluble factors -: soluble protein Lysozyme,
interferon's, complement
proteins, pattern recognition
molecules.
Complement proteins -: a group of serum
proteins normally in inactive state.. Activated by
immunologic mechanisms..
e.g. Collectins…surfactant..disrupts lipid memb.
Or alternate…to susceptible for
phagocytosis.
Pattern recognition molecules
have the ability to recognize a given class of
molecules..
they may be soluble or cell associated
receptors… e.g. TLRs
TLRs recognizes lipopolysaccharides
found on gm neg. bacteria.
(3) Phagocytic barriors
Blood monocytes, neutrophils, tissue
macrophages.
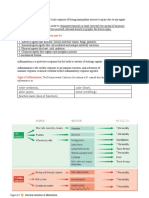
(4) Inflammatory barriers
Complex sequence of events.
Signs -: redness, swelling, heat, pain, loss of function.
Events -: 1.vasodilation, 2.increase in capillary permeability
3.influx of phagocytes into tissues
Chemical mediators -: acute phase proteins,
e.g.. c- reactive protein
histamine have role in vasodilation and increased
permeability of capillaries.
kinins present in blood plasma ..inactive form..
tissue injury – activation.
bradykinin stimulates pain receptors in skin
fibrin -: blood clotting
ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
Characteristics -:
1 antigenic specificity
2 diversity
3 immunologic memory
4 self/ non self recognition
Effective immune response -: involves 2 major
type of cells-: T lymphocytes and antigen
presenting cells
(1) B lymphocytes –: bone marrow.. They have Ab
in cell memb.
-: neive b cell encounters with Ag . Causes the
cell to divide rapidly to
-memory B cells and effector B cells
quick response to secretes Abs
next exposure Humoral immunity
(2) T lymphocytes -: arise in bone marrow .
Cell mediated immunity
Migrates to thymus to mature.. Have TCR
Ag binding molec.
TCR recognizes only those Ag. That is bound to
MHC molecule.
Types -: 1.THelper 2. TCytotoxic 3. TSuppressor.
Diversity in B and T cells Ag receptors -:
Specificity is created by-: random rearrangement of series
of gene segments that encodes Ab and TCR
MHC molecules-: class 1 and 2
distal region display wide variation in A.A. seq.
This region form cleft with Antigenic polypeptide..and
presented to T lymphocytes.
Ag processing and presentation.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Immunology - Chapter 1 OverviewDocument28 pagesImmunology - Chapter 1 OverviewJJHHJHi100% (1)
- Chapters 29 and 30, ImmunologyDocument28 pagesChapters 29 and 30, ImmunologyJuxhin XhahysaPas encore d'évaluation
- Immune SystemDocument21 pagesImmune SystemNarasimha MurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Immune SystemDocument145 pagesImmune SystemA. Pathak100% (9)
- Immune System DisorderDocument20 pagesImmune System Disorderkto12100% (1)
- Immuno BiologyDocument111 pagesImmuno BiologyAsyha KantifaPas encore d'évaluation
- Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images - H. Maitre (Wiley, 2008) WWDocument411 pagesProcessing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images - H. Maitre (Wiley, 2008) WWbehzad100% (4)
- Caterpillar Product Line 13Document7 pagesCaterpillar Product Line 13GenneraalPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ImmunologyDocument108 pagesBasic Immunologyw5waPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of ImmunityDocument13 pagesDiseases of ImmunityRose AnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Immunologykaiyeol exoPas encore d'évaluation
- Start Up and Commissioning of Chilled Water PumpsDocument6 pagesStart Up and Commissioning of Chilled Water PumpsAlaa AnwerPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology 1.1 Immunology - Dr. FontanillaDocument115 pagesMicrobiology 1.1 Immunology - Dr. FontanillaRyn ShadowPas encore d'évaluation
- The Immune System: Back To The BasicsDocument37 pagesThe Immune System: Back To The BasicsHani GowaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Organization of Immune SystemDocument44 pagesOrganization of Immune SystemSaubie AslamiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunology and SerologyDocument225 pagesImmunology and SerologyialegnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ImmunologyDocument41 pagesBasic ImmunologyFebri Yudha Adhi Kurniawan100% (1)
- Bodybuilder Guidelines: Update: 2011-22Document438 pagesBodybuilder Guidelines: Update: 2011-22thkimzone73100% (12)
- Basic Immunology From The Dermatologicpointofviewbasicimmunology From The Dermatologic Point of ViewDocument84 pagesBasic Immunology From The Dermatologicpointofviewbasicimmunology From The Dermatologic Point of ViewHendAbdelazizPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 112: Care of Client With Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseDocument10 pagesNCM 112: Care of Client With Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseNikitaCaitlynLeyaleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Immune System Has Two Lines of Defense:: A. Innate (Non Specific) ImmunityDocument105 pagesImmune System Has Two Lines of Defense:: A. Innate (Non Specific) ImmunityHåíthãm KhãtïßPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunology OverviewDocument83 pagesImmunology OverviewHARIS KKPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - OverviewDocument47 pagesChapter 1 - OverviewZea Mae AgirPas encore d'évaluation
- ImmunologyDocument11 pagesImmunologyBiology BảoPas encore d'évaluation
- Immuno Topics AnsweredDocument20 pagesImmuno Topics AnsweredAlesiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010Document85 pagesChapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010TofikPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecturer One Introduction To General Principles of ImmunologyDocument6 pagesLecturer One Introduction To General Principles of ImmunologyKevin KipropPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Imunologi Dasar Fast TrackDocument23 pagesTugas Imunologi Dasar Fast TrackAnditri WeningtyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1,2,3 y 4Document15 pagesTopic 1,2,3 y 4Olaya De Dios HuertaPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunology NotesDocument4 pagesImmunology NotesDavinci LegaspiPas encore d'évaluation
- A.Ince - Lab 3 (Immunology Review Quiz)Document8 pagesA.Ince - Lab 3 (Immunology Review Quiz)ameeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 16 Reading WorksheetDocument9 pagesChap 16 Reading WorksheetSarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Immuno PathologyDocument28 pagesImmuno PathologyIdrissa John Sebeh ContehPas encore d'évaluation
- Sarcoptes Scabiei: Mites Modulate Gene Expression in Human Skin EquivalentsDocument11 pagesSarcoptes Scabiei: Mites Modulate Gene Expression in Human Skin EquivalentsNailahRahmahPas encore d'évaluation
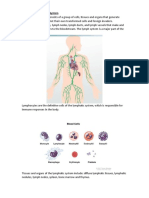
- The Lymphatic System HandoutDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic System HandoutLleana TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunity: Innate Defenses Specific Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Self RecognitionDocument56 pagesImmunity: Innate Defenses Specific Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Self RecognitionMiranda sekar arumPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Immunology IDocument57 pagesBasic Immunology Idevika priyavathi0% (1)
- Immunology and Serology SolutionDocument17 pagesImmunology and Serology Solutionzakaria hossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityDocument53 pagesCells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityfrenchaticiPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 3 Study Guide INNATE DEFENSES A&P2Document13 pagesTest 3 Study Guide INNATE DEFENSES A&P2Sarah C. SnooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14 Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 14 Lymphatic SystemDivinefavourPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesDocument2 pagesChapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesChryza Faith QuicoyPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Form 6Document5 pagesSTPM Form 6d_caasi100% (2)
- 02 - 24092018 - Basic ImmunologyDocument35 pages02 - 24092018 - Basic ImmunologyleonPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are The Main Cells of The Immune System?Document5 pagesWhat Are The Main Cells of The Immune System?Idrissa John Sebeh ContehPas encore d'évaluation
- III. Immunology Review: M L A B 2 4 3 1 1 7Document13 pagesIII. Immunology Review: M L A B 2 4 3 1 1 7Gianna SablanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1Document24 pagesLec 1Ab AbPas encore d'évaluation
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesdicePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Vocabulary Review (Fox)Document270 pagesPathology Vocabulary Review (Fox)DianaNitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Specific and Non Specifc Defense of The BodyDocument38 pagesSpecific and Non Specifc Defense of The BodycedrickjamesarestaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Immunology From The Dermatologic Point of ViewDocument87 pagesBasic Immunology From The Dermatologic Point of ViewnovelraaaPas encore d'évaluation
- M2 Lecture 8 Immune ResponseDocument23 pagesM2 Lecture 8 Immune ResponseChing CHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTDocument18 pagesLymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTJezreel OrquinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphatics - Immunity Lec Notes - With PicsDocument14 pagesLymphatics - Immunity Lec Notes - With PicsEdgar MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- Innate and Acquired ImmunityDocument17 pagesInnate and Acquired ImmunityPiyush KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument9 pagesDiseases of The Immune SystemVenzPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunity (Lecture Notes)Document5 pagesImmunity (Lecture Notes)Anisha NishanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 21 - ImmunityDocument77 pagesChapter 21 - ImmunityAk62442100% (1)
- 1.notes PowerpointDocument27 pages1.notes Powerpointt4ths999Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Agents Causing Inflammation May BeDocument3 pagesThe Agents Causing Inflammation May BemidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument26 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune SystemMithila BanikPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Physiology and ImmunologyDocument12 pagesHuman Physiology and ImmunologyYash BansodPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityD'EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityPas encore d'évaluation
- Transfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsD'EverandTransfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Baulkham Hills 2012 2U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument11 pagesBaulkham Hills 2012 2U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsYe ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Code of Practice For Selection, Laying of Moist Fuel Gas Lines IPSS:1-06-014-17Document11 pagesCode of Practice For Selection, Laying of Moist Fuel Gas Lines IPSS:1-06-014-17Sarbendu PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To DatabasesDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Databases米皮皮Pas encore d'évaluation
- Asme Ix Test 1Document8 pagesAsme Ix Test 1RedzuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming For Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesProgramming For Problem SolvingAPOLLO Sem 4 I.T.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Valence Bond Theory VBTDocument32 pagesValence Bond Theory VBTAsif AhnafPas encore d'évaluation
- Mohamad Fakhari Mehrjardi - 1Document18 pagesMohamad Fakhari Mehrjardi - 1Hilmi SanusiPas encore d'évaluation
- Signal Integrity Modeling and Measurement of TSV in 3D ICDocument4 pagesSignal Integrity Modeling and Measurement of TSV in 3D IC張志榮Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solution of Linear System Theory and Design 3ed For Chi Tsong ChenDocument106 pagesSolution of Linear System Theory and Design 3ed For Chi Tsong ChensepehrPas encore d'évaluation
- Script Track IP TermuxDocument5 pagesScript Track IP TermuxAsepPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Coil PWM Drivers PDFDocument4 pages8 Coil PWM Drivers PDFDuzng Hoang TriPas encore d'évaluation
- Kids Curriculum BreakdownDocument6 pagesKids Curriculum BreakdownSuniel ChhetriPas encore d'évaluation
- 86-Article Text-596-1-10-20211030Document7 pages86-Article Text-596-1-10-20211030adel bbPas encore d'évaluation
- 20CB PDFDocument59 pages20CB PDFChidiebere Samuel OkogwuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ant CabDocument93 pagesAnt CabZubair MinhasPas encore d'évaluation
- Geared Motors Power Distribution: V V V VDocument2 pagesGeared Motors Power Distribution: V V V VShamim Ahsan ParvezPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation: Isa Test Sets Training Course - 2014Document5 pagesPresentation: Isa Test Sets Training Course - 2014Sultan Uddin KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- AtomDocument15 pagesAtomdewi murtasimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mackie USB Driver InstructionsDocument4 pagesMackie USB Driver InstructionsSamuel CotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Dictionary PDFDocument95 pagesComputer Dictionary PDFMarjenneilPas encore d'évaluation
- FlopX NT5.1 Patch V1aDocument5 pagesFlopX NT5.1 Patch V1aAmilcar AndradePas encore d'évaluation
- Typical Detailing of Reinforcements in Beams and SlabsDocument2 pagesTypical Detailing of Reinforcements in Beams and SlabsNaveen BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- MA201 Mechanical Vertical Machining Center 133-134Document2 pagesMA201 Mechanical Vertical Machining Center 133-134Ali HashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Spesiikasi PerallatanDocument10 pagesSpesiikasi PerallatanRafi RaziqPas encore d'évaluation
- IFoA Directory of Actuarial Employers 2016-17-14102016Document22 pagesIFoA Directory of Actuarial Employers 2016-17-14102016Mian BialPas encore d'évaluation