Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Agar
Transféré par
RamuCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Blood Agar
Transféré par
RamuDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Blood Agar
• Used for cultivation of fastidious organisms and
studying haemolytic reactions.
• It provides improved and enhanced haemolysis.
• Addition of blood makes the medium more nutritious
by providing additional growth factors required by
fastidious organisms.
• Haemolytic reactions depend on the animal blood
used
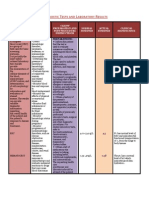
Composition
Ingredients Grams/Litre
Casein enzymic hydrolysate 14.000
Peptic digest of animal tissue 4.500
Yeast extract 4.500
Sodium chloride 5.000
Agar 12.500
Sheep Blood 5.000
Final pH [at 25° C ] 7.3±2
• Casein enzymic hydrolysate and yeast extract provide nitrogen, carbon, amino
acids and vitamins.
• Peptic digest of animal tissue is the nitrogen source.
• Sodium chloride maintains the osmotic balance.
Principle
Haemolysins are exotoxins produced by bacteria that lyse red blood
cells.
The haemolytic reaction can be visualized on blood agar plates.
On blood agar plates colonies of haemolytic bacteria may be
surrounded by clear, colourless zone where the red blood cells have
been lysed and the haemoglobin destroyed to a colourless compound.
There are three types of hemolysis, designated alpha, beta and gamma
Alpha hemolysis is a greenish
discoloration that surrounds a
bacterial colony growing on the
agar.
This type of hemolysis
represents a partial
decomposition of the
hemoglobin of the red blood
cells.
Alpha hemolysis is characteristic
of Streptococcus pneumonia.
Beta hemolysis represents
a complete breakdown of the
hemoglobin of the red blood
cells in the vicinity of a
bacterial colony.
There is a clearing of the
agar around a colony.
Beta hemolysis is
characteristic of
Streptococcus pyogenes and
some strains of
Staphylococcus aureus.
Gamma hemolysis is a lack
of hemolysis in the area
around a bacterial colony.
A blood agar plate
displaying gamma
hemolysis actually appears
brownish.
This is a normal reaction
of the blood to the growth
conditions used (37° C in
the presence of carbon
dioxide).
Gamma hemolysis is a
characteristic
of Enterococcus faecalis.
Limitations
Sheep blood gives best results for Group A Streptococci.
But sheep blood fails to support growth of Haemophilus
haemolyticus since sheep blood is deficient in pyridine
nucleotides.
However when horse blood is used H. haemolyticus
colonies produce haemolysis and mimic Streptococcus
pyogenes .
References
Hi Media Labs
https://www.encyclopedia.com/science/encyclopedi
as-almanacs-transcripts-and-maps/blood-agar-
hemolysis-and-hemolytic-reactions
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Triple Sugar Iron Agar (TSI) and Blood Agar Tests ExplainedDocument9 pagesTriple Sugar Iron Agar (TSI) and Blood Agar Tests ExplainedSt HadijahPas encore d'évaluation
- Other Body Fluid Cerebrospinal FluidDocument16 pagesOther Body Fluid Cerebrospinal Fluidrona hilarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Culture MediaDocument9 pagesMicrobial Culture Mediaማላያላም ማላያላም100% (2)
- Et Al. Immunology, 6th Ed., pp7, 132-134 Et Al. Medical Microbiology, 4th Ed., PP 102-103Document7 pagesEt Al. Immunology, 6th Ed., pp7, 132-134 Et Al. Medical Microbiology, 4th Ed., PP 102-103Cristina Georgiana100% (1)
- Cultivation of MicroorganismsDocument27 pagesCultivation of MicroorganismsLyndz Lee92% (13)
- Hematology 2 TEST QUESTIONSDocument4 pagesHematology 2 TEST QUESTIONSa a r o n b a u t i s t aPas encore d'évaluation
- ConnectivetissuepptDocument20 pagesConnectivetissuepptChicco De AngelisPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood AgarDocument4 pagesBlood Agarsyafa latifahPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Science Education Resources PowerPointsDocument20 pagesOnline Science Education Resources PowerPointsMarina DintiuPas encore d'évaluation
- DHA General MLS ExamDocument4 pagesDHA General MLS ExamIRSHADBHAI BAHELIMPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Urine Reveals E. coli InfectionDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Urine Reveals E. coli InfectionHaridha ChandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Stain and Culture Approach in Microbiology LabDocument8 pagesGram Stain and Culture Approach in Microbiology LabOscar Moisés López SanabioPas encore d'évaluation
- Mycobacteria: Nocardia, Rhodococcus, Tsukamurella and GordoniaDocument7 pagesMycobacteria: Nocardia, Rhodococcus, Tsukamurella and Gordonia20C – Gorospe, Rhai Chezka V.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Clinical Chemistry TestsDocument49 pagesBasic Clinical Chemistry TestsMegbaru100% (1)
- (MT6317) Unit 6.1 Introduction To Carbohydrates and Glucose DeterminationDocument12 pages(MT6317) Unit 6.1 Introduction To Carbohydrates and Glucose DeterminationJC DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Eprubete. Culori. UtilizareDocument3 pagesEprubete. Culori. UtilizareCuCUPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinial MicrosDocument53 pagesClinial MicrosDreyden HaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Corynebacterium and other non-spore-forming Gram-positive rodsDocument3 pagesCorynebacterium and other non-spore-forming Gram-positive rodsYelai CarveroPas encore d'évaluation
- Routine UrinalysisDocument4 pagesRoutine UrinalysisDanica Joy Christelle L. PilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Platelet CountDocument14 pagesManual Platelet CountMiyo SobremisanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacte Day 2Document24 pagesBacte Day 2Jadey InfantePas encore d'évaluation
- Atlas Medical BacteriologyDocument104 pagesAtlas Medical BacteriologyradulusPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemolytic AnemiaDocument99 pagesHemolytic AnemiaSagar Chandrakant Mhetre100% (3)
- BLOOD PresentationDocument33 pagesBLOOD PresentationLezlie Jane SahaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Enterobacteriaceae ChartDocument1 pageEnterobacteriaceae ChartNisha Hernandez100% (1)
- Microanatomy pt1Document27 pagesMicroanatomy pt1poopziPas encore d'évaluation
- A. B. C. A. B. C. D.: Clinical Chemistry II - Prelims (Bandala)Document19 pagesA. B. C. A. B. C. D.: Clinical Chemistry II - Prelims (Bandala)IcePas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To ImmunohematoDocument48 pagesIntro To Immunohematojong188Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hemoglo-: (Cyanmethemoglobin Method)Document2 pagesHemoglo-: (Cyanmethemoglobin Method)sharik masoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Final DX ResultsDocument9 pagesFinal DX ResultszysheaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Capillary Fragility/ Resistance Test: Tourniquet or Rumpel-Leede or Hess TestDocument4 pagesCapillary Fragility/ Resistance Test: Tourniquet or Rumpel-Leede or Hess TestGerly MaglangitPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteriology Laboratory OrganizationDocument65 pagesBacteriology Laboratory Organizationtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Microbiology CaseDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Caseclower112100% (2)
- Gram Positive CocciDocument34 pagesGram Positive CocciMaria Cecilia Flores50% (2)
- Swu Phinma, College of Pharmacy 2020: Wr/Urinalysis - Html#Ixzz6Zxlj RQKH /Product-Manual/3008 - 3B - UrinalysisDocument7 pagesSwu Phinma, College of Pharmacy 2020: Wr/Urinalysis - Html#Ixzz6Zxlj RQKH /Product-Manual/3008 - 3B - UrinalysisTrex MarciiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Urinalysis and Urine Test-2Document34 pagesComplete Urinalysis and Urine Test-2azuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Red Blood Cell Anomalies: Elliptocytes & Oval MacrocyteDocument12 pagesRed Blood Cell Anomalies: Elliptocytes & Oval MacrocyteSHUPATUSSAI100% (1)
- 6 - HemoglobinopathiesDocument55 pages6 - HemoglobinopathiesSara BakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Clearance and GFR: Major DR Arabinda Mohan Bhattarai Lecturer (Biochemistry), NAIHSDocument25 pagesClearance and GFR: Major DR Arabinda Mohan Bhattarai Lecturer (Biochemistry), NAIHSChandan SahPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 02 Urinalysis I Review of Ana and Phy of KidneysDocument6 pagesTopic 02 Urinalysis I Review of Ana and Phy of KidneysNatasha MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- LJ MediaDocument3 pagesLJ MediaJerry ThompsonPas encore d'évaluation
- CSF LectureDocument58 pagesCSF Lectureshweta yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- La2 Structure and Function With Growth of BacteriaDocument10 pagesLa2 Structure and Function With Growth of BacteriaRihan RihanPas encore d'évaluation
- RBC and WBC Abnormalities in Blood SmearsDocument38 pagesRBC and WBC Abnormalities in Blood SmearsTorillo KimPas encore d'évaluation
- HAEMOPOIESISDocument6 pagesHAEMOPOIESISDiyana ZahariPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Protein CompoundsDocument64 pagesNon Protein CompoundsAbigail Mayled LausPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Grouping ReagentsDocument7 pagesBlood Grouping ReagentsDominic EmerencianaPas encore d'évaluation
- URIC ACID LyphoDocument2 pagesURIC ACID LyphoDharmesh Patel50% (2)
- Estimation of Blood Glucose by Glucometer andDocument15 pagesEstimation of Blood Glucose by Glucometer andmaya hawani100% (1)
- 3.2 Acid Fast StainingDocument26 pages3.2 Acid Fast StainingMiguel CuevasPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Chemistry Lecture: Exercise, Training EffectsDocument3 pagesClinical Chemistry Lecture: Exercise, Training EffectsHenry QuimbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacillus History, Morphology, Growth RequirementsDocument5 pagesBacillus History, Morphology, Growth RequirementsNeha SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1 - IntroductionDocument3 pagesLec 1 - IntroductionHaendra Mae DapilagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelainan Morfologi EritrositDocument19 pagesKelainan Morfologi EritrositAdel shbelPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report Blood SugarDocument3 pagesLab Report Blood Sugarapi-341316130Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Lipemia Ind Blood ProductsDocument1 pageWhat Is Lipemia Ind Blood ProductsWardatun ZuhraPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Technologies History of Medtech in United StatesDocument1 pageMedical Technologies History of Medtech in United StatesAthaliah Del MontePas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Concentration Techniques SedimentationDocument18 pages3 Concentration Techniques SedimentationFatihah JahsmiPas encore d'évaluation
- At HemoglobinDocument2 pagesAt HemoglobinzulfiPas encore d'évaluation
- HematocritDocument3 pagesHematocritMaybelle Acap PatnubayPas encore d'évaluation
- LABORATORY MEASUREMENTS OF PLATELET ACTIVITIESDocument73 pagesLABORATORY MEASUREMENTS OF PLATELET ACTIVITIESMary Lyka ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Examination of BloodDocument6 pagesBasic Examination of BloodMadeleinePriscillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide Hematologic AssessmentDocument5 pagesStudy Guide Hematologic AssessmentNancy LemusPas encore d'évaluation
- Antigenandantibodyreaction 120515041533 Phpapp01Document44 pagesAntigenandantibodyreaction 120515041533 Phpapp01Azhar Clinical Laboratory TubePas encore d'évaluation
- HaematologyDocument68 pagesHaematologytapoolnoPas encore d'évaluation
- STAINS TABLE ArcDocument4 pagesSTAINS TABLE ArcBenson PaglinawanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyD'EverandThe Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyLawrence ChakrinPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyD'EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Amylase: Frazer Silvera Malika Teli Gayatri VolvoikarDocument27 pagesAmylase: Frazer Silvera Malika Teli Gayatri VolvoikarRamuPas encore d'évaluation
- Kombucha: Rameshwar Singh RathoreDocument11 pagesKombucha: Rameshwar Singh RathoreRamuPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes & Their Application in Food IndustryDocument14 pagesEnzymes & Their Application in Food IndustryRamuPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellulases: MBT Part IiDocument29 pagesCellulases: MBT Part IiRamuPas encore d'évaluation
- Abzymes/ Catalytic AntibodiesDocument24 pagesAbzymes/ Catalytic AntibodiesRamuPas encore d'évaluation
- Agar Manufacturing MethodsDocument5 pagesAgar Manufacturing MethodsSanjay GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Streptococci and Enterococci and OthersDocument11 pagesStreptococci and Enterococci and OthersthedarkwingPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - StreptocociDocument30 pages2 - StreptocociAndrew Sig100% (1)
- Corynebacterium - Listeria - Bacteriology Lab - Angeles, Q.PDocument2 pagesCorynebacterium - Listeria - Bacteriology Lab - Angeles, Q.PLiterally NoOnePas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 6. Microbial Nutrition & GrowthDocument35 pagesCh. 6. Microbial Nutrition & Growthminy1229Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11-11 Dm-AssesmentDocument102 pages11-11 Dm-Assesments.zainabtanweerPas encore d'évaluation
- MOLB 2210 Microbiology Lab Biochemical TestsDocument17 pagesMOLB 2210 Microbiology Lab Biochemical TestsOsama BakheetPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology Practical Exam NotesDocument14 pagesMicrobiology Practical Exam NotesTovin Nguyen100% (1)
- 02.culture Media Infection Control 26Document26 pages02.culture Media Infection Control 26Hosam GomaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Agar Base (Infusion Agar)Document4 pagesBlood Agar Base (Infusion Agar)Kunal VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of HemolysisDocument17 pagesTypes of HemolysisThe tooth fairyPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology Lab Diagnosis by ARC PDFDocument21 pagesMicrobiology Lab Diagnosis by ARC PDFZahid iqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Use colony morphology for presumptive IDDocument12 pagesUse colony morphology for presumptive IDsgd2josPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 7 Streptococcus and EnterococcusDocument7 pagesLesson 7 Streptococcus and EnterococcusRazmine RicardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology 1Document35 pagesMicrobiology 1pikachuPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacte Sample QuestionDocument45 pagesBacte Sample QuestionpikachuPas encore d'évaluation
- Fdocuments - in General Microbiology Spotters by DR Sudheer Kher MD Hod MicrobiologyDocument32 pagesFdocuments - in General Microbiology Spotters by DR Sudheer Kher MD Hod MicrobiologyOppo VivoPas encore d'évaluation
- StreptococcusDocument12 pagesStreptococcusSahyudi Darma AseptiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 13 Diagnosing Infectious DiseasesDocument47 pagesChapter 13 Diagnosing Infectious DiseasesSherinne Jane CariazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Training and Procedures: Bacteriological TechniquesDocument8 pagesLaboratory Training and Procedures: Bacteriological TechniquesMarco cenabrePas encore d'évaluation
- Penjelasan Praktikum KardiovaskulerDocument54 pagesPenjelasan Praktikum KardiovaskulerQuswah MaharaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteriology and Microbiology Safety NotesDocument35 pagesBacteriology and Microbiology Safety NotesAngelo Jude CobachaPas encore d'évaluation