Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Refrigeration
Transféré par
Ishg0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
21 vues22 pagesppt on refrigeration
Titre original
Refrigeration[1]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentppt on refrigeration
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
21 vues22 pagesRefrigeration
Transféré par
Ishgppt on refrigeration
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 22
Refrigeration
INTRODUCTION
1 The mechanism used for lowering or producing low temp
in a body or a space whose temp is already below the
temp of its surroundings is called the REFRIGERATION
SYSTEM
2 Here the heat is being generally pumped from low level
to the higher one and is rejected at high temp
Refrigeration
• The term refrigeration may be defined as the process of removing
heat from a substance under controlled conditions.
• It also includes the process of reducing heat & maintaining the temp.
of a body below the general temp. of its surroundings.
• In other words the refrigeration means a continued extraction of heat
from a body whose temp is already below the temp. of its
surroundings.
. CAPACITY OF REFRIGERATION UNIT IS EXPRESSED IN TONNE
1 TONNE OF REFRIGERATION [ TR] =14000 KJ/H
Refrigerator & Refrigerant
• A refrigerator is a reversed heat engine or a heat
pump which takes out heat from a cold body &
delivers it to a hot body.
• The refrigerant is a heat carrying medium which
during their cycle in a refrigeration system
absorbs heat from a low temp. system & delivers
it to a higher temp. system
Refrigeration Systems
•Vapour compression refrigeration
system
•Vapour absorption refrigeration
Vapour Compression Refrigeration
• This is the most important system from the point of commercial &
domestic utility & most practical form of refrigeration.
• The working fluid refrigerant used in this refrigeration system readily
evaporates & condenses or changes alternatively between the vapour
& liquid phases without leaving the refrigerating plant
• During evaporation it absorbs heat from the cold
body or in condensing or cooling it rejects heat
to the external hot body .
• The heat absorbed from cold body during
evaporation is used as its latent heat for
converting it from liquid to vapour.
• Thus a cooling effect is created in working fluid.
• This system of refrigeration thus act as latent heat pump since its
pump its latent heat from the cold body or brine & rejects it or deliver
it to the external hot body or the cooling medium.
• According to the law of thermodynamics , this can be done only on
the expenditure of energy which is supplied to the system in the form
of electrical energy driving the compressor.
• The vapour compression cycle is used in most of the
modern refrigeration systems in large industrial
plants.
• The vapour in this cycle is circulated through the
various components of the system, where it
undergoes a number of changes in its state or
condition.
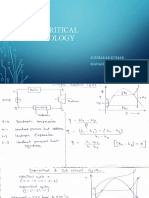
REFRIGERATOR COMPONENTS
• Each cycle of operation consists of the four fundamental
changes of state or processes:-
Expansion
Vaporisation
Compression
Condensation
Compressor
The low pressure & temp. refrigerant from evaporator is
drawn into the compressor through the inlet or suction valve
, where it is compressed to a high pressure & temp.
The high pressure & temp vapour refrigerant is discharged
into the condenser through the delivery or discharge valve.
Condenser
The condenser or the cooler consists of coils of pipe in which the high
pressure & temp. vapour refrigerant is cooled & condensed.
The refrigerant while passing through the condenser, rejects its
latent heat to surrounding condensing medium which is normally air
or water.
Thus hot refrigerant vapour received from compressor is converted
into liquid form in condenser.
Receiver
• The condensed liquid refrigerant from the condenser is stored in a
vessel, known as receiver, from where it is supplied to the expansion
valve or refrigerant control valve.
Expansion Valve
The function of this valve is to allow the liquid refrigerant under high
pressure & temp. to pass at a controlled rate after reducing its
pressure & temp.
some of liquid refrigerant evaporates as it passes through the
expansion valve, but the greater portion is vaporised in the
evaporator at the low pressure & temp.
Evaporator
An evaporator consists of coils of pipes in which the liquid vapour
refrigerant at low pressure & temp. is evaporated & changed into
vapour refrigerant at low pressure & temp.
During evaporation process, the liquid vapour refrigerant absorbs its
latent heat of vaporization from the medium which is to be cooled.
VAPOUR COMPRESSION CYCLE ON T/S DIAGRAM
Advantages
• Smaller size for a given refrigerating capacity
• Higher coeff. of performance
• Lower power requirements for a given capacity
• Less complexity in both design & operation
• It can be used over large of temp.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Air Cooled and Water Cooled ChillerDocument17 pagesAir Cooled and Water Cooled ChillerAbdelhameed NadyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- En Manual City 1.24-2.24 FFDocument44 pagesEn Manual City 1.24-2.24 FFduma262005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- MHI Brochure (2019) PDFDocument132 pagesMHI Brochure (2019) PDFlechepinitoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Clivet-2003-1C Air Cooled Module Chiller and Mini Chiller-H3326 - WCAN WGANDocument23 pagesClivet-2003-1C Air Cooled Module Chiller and Mini Chiller-H3326 - WCAN WGANremigius yudhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Sipercritical Technology: Sudhakar Kumar Manager (Operation)Document23 pagesSipercritical Technology: Sudhakar Kumar Manager (Operation)Gargi PatnaikPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- DehumidificationDocument9 pagesDehumidificationRafael Echano AcederaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Specification Sheet: Split System Air ConditionerDocument6 pagesSpecification Sheet: Split System Air ConditionerByronPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Dilution VentilationDocument4 pagesDilution VentilationUthman OpeyemiPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Supplemental Instructions: ModelsDocument13 pagesSupplemental Instructions: ModelsAbdiel MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- GHP 2 Way TD7110003 - 00Document139 pagesGHP 2 Way TD7110003 - 00alexandrePas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Twa TweDocument60 pagesTwa Tweanon_568723957100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Carrier: Psychrometric ChartDocument1 pageCarrier: Psychrometric ChartAhmed SabryPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Ideal Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument9 pagesIdeal Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleStephanie ParkPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Contoh WATER COOLED MAGNETIC BEARING CHILLERDocument1 pageContoh WATER COOLED MAGNETIC BEARING CHILLERsitiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Optimal Charge Amount For Different Refrigerants in Air-to-Water Heat PumpsDocument11 pagesOptimal Charge Amount For Different Refrigerants in Air-to-Water Heat Pumpsparth bhalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cop and EerDocument3 pagesCop and Eerطاہر رضاPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Habor enDocument28 pagesHabor enEmerson TerrelPas encore d'évaluation
- Compress Air Golden RulesDocument1 pageCompress Air Golden Rulesmymail0808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration Process in Oil and Gas IndustryDocument20 pagesRefrigeration Process in Oil and Gas IndustrysanjayPas encore d'évaluation
- (Colored) Psychrometric Chart (Si Units)Document1 page(Colored) Psychrometric Chart (Si Units)Mc Jason Laurete0% (1)
- HVAC Visual Guide-20120113Document15 pagesHVAC Visual Guide-20120113deville305Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parts Catalogue Puhz p100-140v y Ka Ocb670Document8 pagesParts Catalogue Puhz p100-140v y Ka Ocb670Book LebanonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pan Humidifier Load Calculation: Air Conditioning SystemDocument1 pagePan Humidifier Load Calculation: Air Conditioning SystemRamachandran Venkatesh100% (1)
- The Wall-Mount™ Air Conditioners - 9.0 Eer, (60Hz) : G R R-410aDocument16 pagesThe Wall-Mount™ Air Conditioners - 9.0 Eer, (60Hz) : G R R-410aYhonny OviedoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- TraneDocument12 pagesTranebehnam197100% (2)
- Rguidelines For Air Conditioning in Operation TheatresDocument6 pagesRguidelines For Air Conditioning in Operation TheatresNaqqash Sajid100% (1)
- Compresores Mabe - PDF-2Document1 pageCompresores Mabe - PDF-2Liseth MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Broad Xii Non-Electric Chiller: Model Selection & Design ManualDocument50 pagesBroad Xii Non-Electric Chiller: Model Selection & Design ManualUmar MajeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Aire Acondicionado CARRIER 24ABB3 - Product - DataDocument88 pagesAire Acondicionado CARRIER 24ABB3 - Product - DataOPER123Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- H-10 PRO: Refrigerant Leak DetectorDocument2 pagesH-10 PRO: Refrigerant Leak DetectoriwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)