Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Prenatal Development
Transféré par
Karl Mesina0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
20 vues33 pagesTitre original
Prenatal Development.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
20 vues33 pagesPrenatal Development
Transféré par
Karl MesinaDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 33
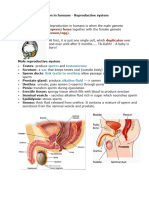
Prenatal Development
The Developing Baby
Conception
The process of the sperm fertilizing the o
vum.
◦ Sperm- male cell
◦ Ovum- women egg cell
Conception
Ovulation- Every 28 days an ovum is rel
eased by one of a woman’s two ovaries. (
Menstrual Cycle)
Hormones are released- prepares the ute
rus for the ovum to be fertilized.
◦ Uterus- the organ in a woman’s body in whic
h a baby develops during pregnancy.
Conception
During Ovulation, the inner lining of the u
terus grows and thickens.
◦ Ovum NOT Fertilized = menstrual period
◦ Fertilized Ovum = Baby
Conception
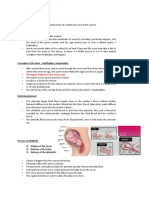
Journey of the Ovum (egg cell)
◦ Ovary Fallopian Tube Uterus
◦ Fallopian Tube- tube that connects the ovar
y to the uterus
◦ The Journey takes 2 to 3 days.
Conception
Ovum lives 12 to 24 hours
Sperm lives 48 to 72 hours
(fertilize the ovum in this time)
Sperm fallopian tube penetrate and
fertilize ovum.
3 to 4 day window where conception can
occur after intercourse
Conception
Conception
Pregnancy
Last about 9 months
Single cell grows and develops into a hum
an being
Ectopic Pregnancy- where the baby sta
rts to grow in the fallopian tubes rather t
han the uterus.
◦ Very dangerous, does not end in a live birth
3 Stages of Pregnancy
Prenatal Development- baby's develo
pment during pregnancy.
Grouped in 3 stages
The Germinal
Embryonic
Fetal
The Germinal Stage
1st stage in the baby's development
Formation of the zygote
The fertilized egg
Last about 2 weeks
Key steps in establishing pregnancy
The Germinal Stage
Cell Division- the cell begins to grow in
the fallopian tube.
In 4 days the zygote reaches the uterus.
Implantation- the lining of the uterus h
as now thicken enough for the zygote to
attach itself and grow.
Size of a pin head in 2 weeks
The Embryonic Stage
• 2nd Stage
• 3rd week to the 8th week
• Embryo grows rapidly
• Embryo- developing baby
• Face, eyes, ears, limbs, & bones
• Organs and Body Systems develop
• 6 weeks the brain and spinal cord connect
The Embryonic Stage
• Amniotic Sac- a sac filled with fluid (am
niotic fluid) that surrounds and protects t
he embryo in the uterus
• Placenta- tissue that connects the embr
yo to the uterus. Brings Oxygen and nou
rishment from the mother.
• Umbilical Cord- long tube that connect
s the baby to the placenta. Take waste aw
ay.
The Fetal Stage
• 3rd stage
• Longest stage: 8th or 9th week to birth
• Baby develops into a Fetus
• Vocal cords develop
• Digestive system and kidneys begin working
• 4th or 5th month kicks and other movements
• By the 7th month the baby can live outside of
the uterus with medical help.
• Common length of pregnancy is 40 weeks or
280 day
Changes that Occur in the Mother
Look at the chart
What changes occur during the first 2 mo
nths of pregnancy?
Lightening
Happens in the 9th month
1st child- days to weeks before birth
2nd + child- right before birth
Fetus drops into the pelvis
Pressure on upper abdomen is reduc
ed and breathing becomes easier
Genetics
Have you ever wondered…..
◦ Why do I have this hair color?
◦ Why do I have blue eyes life my mom instead
of brown eyes like my dad?
Heredity
Heredity- the passing on of characteristics
◦ Examples:
Physical Traits- hair, skin, eyes
Talents- musical, athletic ability
Medical Conditions
Genetics
At the moment of Conception
◦ Baby receives 46 chromosomes.
◦ Chromosome- a tiny threadlike structure in
the nucleus of every cell.
◦ Chromosomes come in 23 pairs
◦ Each chromosomes has 100s to 1,000s genes
Genetics
Chromosomes
◦ Chromosomes come in 23 pairs
◦ Each chromosomes has 100s to 1,000s genes
◦ Father’s sperm and mother’s ovum each contr
ibute one chromosome to each pair.
Genetics
Gene- a unit that determines a human’s i
nherited characteristics.
Genome- complete blueprint for the cre
ation of a person.
DNA- the complex molecules that make
up genes
Dominant vs. Recessive Gene
Inherited Characteristic
2 copies of a gene; 1 from mom, 1 fro
m dad
If both genes are the same, then the c
hild automatically has the characteristi
c.
Many cases this does not happen
Dominant Gene- a stronger gene, c
ontrols the characteristics
Recessive Gene- weaker gene, only
expressed if both parents give it.
Gender Determination
Sex Chromosomes X and Y
Women (ovum) carry only X
Male (sperm) carry X or Y
Children
Girl = XX
Boy = XY
Multiple Births
Most common is twins
2 types:
Identical- when the cell mass split in
half
Fraternal- 2 eggs fertilized by 2 sper
m
3 out of 100 births will be twins
Fraternal twins are more common
Multiple Births
Three or more babies
Very rare
Increase chances, if using treatment to
help with fertility.
More than one egg is released at a tim
e
Infertility
Inability to conceive a child
40% women infertility; 40% men infertility
; 20% unknown causes or linked to both
partners.
Example- A Woman's ovary does not
release an ovum each month.
Infertility Options
Medication- Fertility Drugs
Adoption- legally takes on all responsibil
ities and rights for raising, loving, and cari
ng for a child in need of a permanent ho
me.
Artificial Insemination- sperm injecte
d in uterus.
Infertility Options
In Vitro Fertilization- doctor combine
s sperm and ovum. If fertilized, then plac
ed in the uterus.
Ovum Transfer- similar to In Vitro. Ano
ther woman donates an ovum.
Surrogate Mother- a woman who beco
mes pregnant for another woman. (legal a
rrangements)
Not Using Infertility Options
Expensive
Controversial
Morals
New technology and knowledge
Reflection Journal
Why is it important to eat healthfully duri
ng all stages of life?
Why is exercise important to help keep a
body fit?
Where can you learn how to develop an
exercise routine that is right for you?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- How To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornD'EverandHow To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornPas encore d'évaluation
- 18 REPRODUCTION AnimalsDocument10 pages18 REPRODUCTION AnimalsSheniqua GreavesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 Prenatal DevelopmentDocument44 pagesLecture 7 Prenatal Developmentgasbag freePas encore d'évaluation
- Reproduction and HeredityDocument10 pagesReproduction and HeredityMonkey LoverPas encore d'évaluation
- Echidnas (/ɪ Kɪdnəz/), Sometimes Known As Spiny Anteaters. The FourDocument7 pagesEchidnas (/ɪ Kɪdnəz/), Sometimes Known As Spiny Anteaters. The FourHONLETH ROMBLONPas encore d'évaluation
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument30 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentAnu ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Class: THC Roll No.: 1Document43 pagesClass: THC Roll No.: 1Sajal RastogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexual Reproduction FullDocument46 pagesSexual Reproduction FullSharara YMPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Function - ReproductionDocument39 pagesBody Function - ReproductionAlistair FlemingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Basic Concepts of Human Reproduction and Biological / Developmental IssuesDocument52 pagesThe Basic Concepts of Human Reproduction and Biological / Developmental Issues-------Pas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics, Prenatal Development, and The Neonate: By: Geraldine P. GoDocument53 pagesGenetics, Prenatal Development, and The Neonate: By: Geraldine P. GoNorhana Taher BatunggaraPas encore d'évaluation
- PubertyDocument27 pagesPubertychristabelchen02Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Human Reproductive SystemDocument53 pagesThe Human Reproductive Systemapi-406307933Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prenatal Development (Child Psychology)Document37 pagesPrenatal Development (Child Psychology)Yel BaldemorPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexual Reproduction NotesDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction NotesZelPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic, Conception, and Fetal DevelopmentDocument54 pagesGenetic, Conception, and Fetal DevelopmentBiraito TakanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy PowerPointDocument59 pagesPregnancy PowerPointHervis FantiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3A - PRENATAL PERIOD-2Document27 pagesUnit 3A - PRENATAL PERIOD-2iamsathya2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fertilization To Conception: Maternal and Child Health Nursing PregnancyDocument8 pagesFertilization To Conception: Maternal and Child Health Nursing PregnancyNikki M. Arapol100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)Document40 pagesSexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)puspita8967628Pas encore d'évaluation
- Human ReproductionDocument3 pagesHuman ReproductionsamyukthaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocument13 pages8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument66 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentBlessie NgitngitPas encore d'évaluation
- The Process of ReproductionDocument4 pagesThe Process of ReproductionIvan BixenmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Reproduction 22-23 CorrectedDocument11 pagesHuman Reproduction 22-23 Correctedhi100% (1)
- Introduction To Embryology 1Document72 pagesIntroduction To Embryology 1Sam MumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy and Childbirth PowerpointDocument33 pagesPregnancy and Childbirth Powerpointmrey9839Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive SystemDocument23 pagesReproductive SystemJamis DelaraPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 Twins Birth DiagnosticDocument6 pages08 Twins Birth DiagnosticElliotPianoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Reproductive SystemDocument18 pagesThe Reproductive Systemcmillica1176Pas encore d'évaluation
- From Egg and Sperm To NewbornDocument63 pagesFrom Egg and Sperm To NewbornCristine Joy GuinoPas encore d'évaluation
- OvulationDocument4 pagesOvulationAshleyn Mary SandersPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Document15 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Halizah RamthanPas encore d'évaluation
- Stages of Human Development Before BirthDocument3 pagesStages of Human Development Before BirthAaronotix GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- NMD-4 Prenatal DevelopmentDocument49 pagesNMD-4 Prenatal DevelopmentYorgos TheodosiadisPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 101Document8 pagesNCM 101Bing58Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Reproductive SystemDocument23 pagesThe Reproductive SystemMERYL SALOMINA FRANCISCOPas encore d'évaluation
- Dev Psych CHAPTER3Document54 pagesDev Psych CHAPTER3Ezri Mariveles Coda Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Natal DevelopmentDocument13 pagesPre-Natal DevelopmentManilyn DominguezPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument21 pagesUntitledpearl arevaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio CH 4-Repdoduction NewDocument70 pagesBio CH 4-Repdoduction NewSanthiya MadhavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Twins and Multiple BabiesDocument6 pagesTwins and Multiple BabiespjcolitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio CH 4-Repdoduction NewDocument72 pagesBio CH 4-Repdoduction NewSiti Sarah Noor MeahPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Development: From Conception To BirthDocument55 pagesFetal Development: From Conception To BirthClyde R.OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal PregnancyDocument65 pagesNormal PregnancyRhesie Joyce AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument32 pagesPrenatal Developmentaspen8155Pas encore d'évaluation
- REPRODUCTION L2 (Prashant Kirad)Document32 pagesREPRODUCTION L2 (Prashant Kirad)superherosunny13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter#3 Developmental PsychologyDocument32 pagesChapter#3 Developmental Psychologyfatima bilalPas encore d'évaluation
- Fertilization and ImplantationDocument2 pagesFertilization and ImplantationAngelica AycardoPas encore d'évaluation
- MCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationDocument11 pagesMCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationJay EstrellaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Process of ConceptionDocument62 pagesThe Process of ConceptionKaren Ivy BacsainPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument51 pagesFetal DevelopmentLhiet Aguilar Hipolito50% (2)
- 2022 - 10 - 21 18 - 43 Office LensDocument30 pages2022 - 10 - 21 18 - 43 Office LensMaleesha PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- ReproductionDocument42 pagesReproductionValentina Bermudez CadavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Prenataldevelopment PDFDocument14 pagesPrenataldevelopment PDFAmber TajwerPas encore d'évaluation
- Caadlawon-Prenatal - Dev.and Infancy Nov.7Document36 pagesCaadlawon-Prenatal - Dev.and Infancy Nov.7Joan Rosanne CaadlawonPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument5 pagesReproduction in AnimalsOnlymexxPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio CH 4-Repdoduction NewDocument70 pagesBio CH 4-Repdoduction NewAzwan MohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine and Reproductive SystemsDocument53 pagesEndocrine and Reproductive Systemsapi-287032631Pas encore d'évaluation
- SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSCIENCEjoannalyn gregorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Analogies SynonymsDocument6 pagesAnalogies SynonymsKarl MesinaPas encore d'évaluation
- As St. Benedict's Academy Continually Envision Each Learner ToDocument1 pageAs St. Benedict's Academy Continually Envision Each Learner ToKarl MesinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Howdy!Document22 pagesHowdy!Karl MesinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Howdy!Document22 pagesHowdy!Karl MesinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Howdy!Document22 pagesHowdy!Karl MesinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Howdy!: It's Game TimeDocument22 pagesHowdy!: It's Game TimeKarl MesinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 Anoikos Wikis Industrial and Organizational Psychology PDFDocument296 pages2014 Anoikos Wikis Industrial and Organizational Psychology PDFKarl MesinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross-Cultural Activities: Ma. Claire B. MesinaDocument13 pagesCross-Cultural Activities: Ma. Claire B. MesinaKarl MesinaPas encore d'évaluation
- AnthropologicalDocument1 pageAnthropologicalKarl MesinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blocked Fallopian Tubes and Its Management With AyDocument2 pagesBlocked Fallopian Tubes and Its Management With AywinodhelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Investigatory Project Class 12 - EditedDocument17 pagesBiology Investigatory Project Class 12 - Editedharveylenseena2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Finals Hce Ivf DebateDocument7 pagesFinals Hce Ivf DebateBadilla, Farrah O.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Some Common Causes For Low Sperm CountDocument7 pagesSome Common Causes For Low Sperm Countjas899Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Cause of AutismDocument47 pagesThe Cause of Autismjoeimbriano100% (1)
- Menciano Vs San JoseDocument10 pagesMenciano Vs San JoseRonan MonzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ozan 2017 Effect of Nursing Care Based On Watson's TheoryDocument15 pagesOzan 2017 Effect of Nursing Care Based On Watson's TheoryGhea SulaemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Evidence Based Fertility Investigations Final 2018 2Document43 pagesEvidence Based Fertility Investigations Final 2018 2Sagie NaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 Article 233Document10 pages2016 Article 233Melanton Ifan Fernando RajagukgukPas encore d'évaluation
- Billings Method BrochureDocument2 pagesBillings Method BrochureJoanne Reandelar- BantangPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Increase Your Chances of Getting Pregnant FasterDocument16 pagesHow To Increase Your Chances of Getting Pregnant FasterHector Clandestino100% (1)
- Care of Male and Female Clients With General and Specific Problem in Reproduction and SexualityDocument7 pagesCare of Male and Female Clients With General and Specific Problem in Reproduction and SexualityAllaine Royce LibrandoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Economist UK Edition - July 22 2023Document94 pagesThe Economist UK Edition - July 22 2023ruoxuemiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Global Perspective On Infertility An Under Recognized Public Health Issue - OriginalDocument45 pagesA Global Perspective On Infertility An Under Recognized Public Health Issue - OriginalfezangauriPas encore d'évaluation
- SynopsisDocument17 pagesSynopsisPrashant Godase0% (1)
- CFE 102 Syallabus Midterm PDFDocument23 pagesCFE 102 Syallabus Midterm PDFAndi Te'a Mari SimbalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ats Menjawab Super Brankas Soal Unas 2020-2015Document424 pagesAts Menjawab Super Brankas Soal Unas 2020-2015anton suponoPas encore d'évaluation
- Vgo 411 QBDocument7 pagesVgo 411 QBSuryakantaRoulTuntunPas encore d'évaluation
- Letter Seeking Expert'S Opinion and Suggestion For The Content Validity of ToolDocument19 pagesLetter Seeking Expert'S Opinion and Suggestion For The Content Validity of ToolHimani PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- National Insurance ProspectusDocument8 pagesNational Insurance ProspectusSoumen PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Filipino ResearchDocument2 pagesFilipino ResearchKielene PalosPas encore d'évaluation
- Nihms 1804691Document25 pagesNihms 1804691Annisa Zaskia AlexandraPas encore d'évaluation
- LetrozoleDocument3 pagesLetrozoleSalima A. PundamdagPas encore d'évaluation
- Borders of Being - Citizenship, - Margaret JollyDocument335 pagesBorders of Being - Citizenship, - Margaret JollymajorbonoboPas encore d'évaluation
- The Acupuncture Treatment of Female Infertility With Particular Reference To Egg Quality and Endometrial ReceptivenessDocument9 pagesThe Acupuncture Treatment of Female Infertility With Particular Reference To Egg Quality and Endometrial ReceptivenesssillypoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Medicare Certificate of InsuranceDocument12 pagesGroup Medicare Certificate of InsuranceMallikarjunayya HiremathPas encore d'évaluation
- BioF5-4.4 Contribution of Science and Technology To Human ReproductionDocument24 pagesBioF5-4.4 Contribution of Science and Technology To Human ReproductionteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Dangerous Side Effects of Taking Unwanted 72 I-PillDocument7 pagesDangerous Side Effects of Taking Unwanted 72 I-PillVishu SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Merchant of Venice Essay QuestionsDocument7 pagesMerchant of Venice Essay Questionsd3gn731z100% (2)
- On The Origin of SpeciesDocument15 pagesOn The Origin of SpeciesDianne SagunPas encore d'évaluation