Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
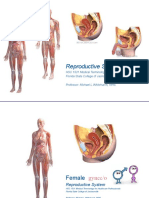
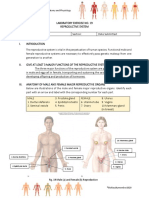
Human Reproductive System
Transféré par
Quennie Aceron0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
57 vues23 pagesThe female reproductive system produces eggs and secretes hormones, while the male reproductive system produces and stores sperm. The female system includes ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. An egg travels from the ovary through the fallopian tube to the uterus. The male system includes testes, epididymis, vas deferens, penis, prostate, and seminal vesicles. Sperm is produced in the testes and stored in the epididymis before ejaculation. Diseases of both systems include various cancers, infections, and disorders of the reproductive organs.
Description originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe female reproductive system produces eggs and secretes hormones, while the male reproductive system produces and stores sperm. The female system includes ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. An egg travels from the ovary through the fallopian tube to the uterus. The male system includes testes, epididymis, vas deferens, penis, prostate, and seminal vesicles. Sperm is produced in the testes and stored in the epididymis before ejaculation. Diseases of both systems include various cancers, infections, and disorders of the reproductive organs.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
57 vues23 pagesHuman Reproductive System
Transféré par
Quennie AceronThe female reproductive system produces eggs and secretes hormones, while the male reproductive system produces and stores sperm. The female system includes ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. An egg travels from the ovary through the fallopian tube to the uterus. The male system includes testes, epididymis, vas deferens, penis, prostate, and seminal vesicles. Sperm is produced in the testes and stored in the epididymis before ejaculation. Diseases of both systems include various cancers, infections, and disorders of the reproductive organs.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 23
WHAT IS REPRODUCTION?
Reproduction is the process by which organisms make more
organisms like themselves. But even though the reproductive
system is essential to keeping a species alive, unlike other body
systems, it's not essential to keeping an individual alive.
In the human reproductive process, two kinds of sex cells, or
gametes are involved. The male gamete, or sperm, and the
female gamete, the egg or ovum, meet in the female's
reproductive system. When sperm fertilizes an egg, this
fertilized egg is called a zygote.
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE
SYSTEM
The ovary is an organ found in the female
reproductive system that produces an ovum. When
released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the
uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm.
There is an ovary (from Latin ovarium, meaning
'egg, nut') found on each side of the body.
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in
the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum.
The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through
the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it
can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of
the uterus.
The Fallopian tubes, also known as uterine
tubes or salpinges (singular salpinx) are uterine
appendages. It also have small hair-like projections
called cilia on the cells of the lining.
One of the two Fallopian tubes that transport
the egg from the ovary to the uterus (the womb).
The cervix is the lower end of the womb (uterus).
It is at the top of the vagina. It is about 2.5 to 3.5 cm
long.
It allows blood from a menstrual period and a
baby (fetus) to pass from the womb into the vagina.
The cervical canal passes through the cervix.
The vagina is an elastic, muscular canal with a soft,
flexible lining that provides lubrication and
sensation.
The vagina connects the uterus to the outside
world. The vulva and labia form the entrance, and the
cervix of the uterus protrudes into the vagina,
forming the interior end.
HOW DOES THE FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM WORK?
The female reproductive system enables a
woman to:
1. produce eggs (ova)
2. have sexual intercourse
3. protect and nourish a fertilized egg until it is fully
developed
4. give birth
DISEASES OF THE FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
1. Menstrual cramping or dysmenorrheal is the most common
disease of the reproductive system occurs with a woman's monthly
menstrual period,
2. Vaginal yeast infection, which is caused by a yeast fungus in the
vagina. Most can be successfully treated with over-the-counter medications,
according to WebMD.
3. Endometriosis is a condition where that normally lines the inside of your
uterus — the endometrium — ends up outside of uterus, most commonly in
the ovaries, bowel or the tissue lining your pelvis. The endometrial tissue
becomes trapped, causing pain
4. Pelvic inflammatory disease can involve an infection of any of the
female reproductive organs, including the uterus and ovaries. Sexually
Scrotum, in the male reproductive system, a thin
external sac of skin that is divided into two
compartments; each compartment contains one of
the two testes, the glands that produce sperm, and
one of the epididymis, where the sperm is stored.
The testes (or testicles) are a pair of sperm-
producing organs that maintain the health of the male
reproductive system. The testes are known as gonads.
They produce gametes, or sperm, and
they secrete hormones, primarily
testosterone.
Epididymis is a highly convoluted duct behind
the testis, along which sperm passes to the vas
deferens.
It transports and stores sperm cells that
are produced in the testes.
The ductus deferens, also known as the vas
deferens, is a tiny muscular tube in the male
reproductive system that carries sperm from the
epididymis to the ejaculatory duct.
There is a pair of these ducts in the male
body, with one duct carrying sperm from
each testis to the left and right ejaculatory
ducts.
The human penis is an external male intromittent
organ that additionally serves as the urinal duct.
The penis is an external organ of the male reproductive
system. The root and body of the penis are spanned by
three masses of erectile tissue.
The prostate gland is a male reproductive organ
whose main function is to secrete prostate fluid, one
of the components of semen.
The muscles of the prostate gland also help propel
this seminal fluid into the urethra during ejaculation
The seminal vesicles (Latin: glandulae
vesiculosae), vesicular glands, or seminal glands, are
a pair of simple tubular glands posteroinferior to the
urinary bladder of some male mammals.
Seminal vesicles are located within the
pelvis. They secrete fluid that partly
composes the semen.
HOW DOES THE MALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
WORK?
The male sex organs work together to produce and release semen into
the reproductive system of the female during sexual intercourse. The
male reproductive system also produces sex hormones, which help a
boy develop into a sexually mature man during puberty.
1. During the first stage of male puberty, the scrotum and testes grow
larger.
2. Next, the penis becomes longer and the seminal vesicles and
prostate gland grow.
3. Hair begins to grow in the pubic area and later on the face and
underarms. During this time, a boy’s voice also deepens.
4. Boys also have a growth spurt during puberty as they reach their
DISEASES OF THE MALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
1. Prostate cancer is the most common, but men can also suffer from testicular and
penile cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. Treatment for prostate
cancer depends on the age, severity of the disease and other health conditions of the
patient. The usual treatments for prostate cancer are surgery, radiation therapy,
watchful waiting, and hormonal treatment, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
2. Erectile dysfunction is a common condition that affects about one in 10 males on
a long-term basis, the Cleveland Clinic noted. It can be linked to vascular disease,
neurological disorders such as Multiple Sclerosis, trauma and psychological episodes.
3. Prostatitis typically involves swelling or inflammation of the prostate gland,
according to the Mayo Clinic, and can cause painful or difficult urination and
ejaculation. Nearly half of all men experience symptoms of prostatitis at some point
during their lives.
ABAD, JOHN VINCENT
ABANIEL, HANS
ACERON, QUENNIE
ADOREMOS, RHAD YDNAR
AGUILLON, ALLYSA JANE
GROUP 1: REPRODUCTIVE
SYSTEM STEM 12 A
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Feedback Mechanism LabDocument5 pagesFeedback Mechanism LabBeverly Carballo - Moguel0% (1)
- Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemsMARIAM AVILAPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive System: Facts, Symptoms & TreatmentsDocument34 pagesReproductive System: Facts, Symptoms & TreatmentsJobelyn MalisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pagesCoordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsSarah CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive SystemDocument130 pagesReproductive SystemReymark NovecioPas encore d'évaluation
- Menstrual Cycle and Reproductive Health 4Document13 pagesMenstrual Cycle and Reproductive Health 4Beanna Pinard100% (1)
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument28 pagesMendelian GeneticsRea AnsusPas encore d'évaluation
- Feedback Mechanism of Endocrine System, Reproductive SystemDocument19 pagesFeedback Mechanism of Endocrine System, Reproductive Systemnhel gutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Mod 6 Day2-Dna ReplicationDocument17 pagesMod 6 Day2-Dna Replicationapi-293001217Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mentruation and It's CycleDocument35 pagesMentruation and It's CycleAshley SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument76 pagesCell Structure & FunctionMilka RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument26 pagesMendelian GeneticsLuisa SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductivesystem g10Document88 pagesReproductivesystem g10Mernie Grace DionesioPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Learning Objective:: /endocrine-System-Lesson-Plan-Final-Na-FinalDocument10 pagesI. Learning Objective:: /endocrine-System-Lesson-Plan-Final-Na-FinalGabilan Rose JeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Reproductive SystemMau Acusa100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/ies: CodeDocument14 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/ies: CodeMerce Tojino ManigosPas encore d'évaluation
- Suggested Timeframe: Science 10 ThirdDocument3 pagesSuggested Timeframe: Science 10 ThirdSaeRom dogguPas encore d'évaluation
- Sci q2 Wk3 Day 1-3Document40 pagesSci q2 Wk3 Day 1-3renato.minaPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Selection SlidesDocument34 pagesNatural Selection Slidesapi-283801432Pas encore d'évaluation
- Male Reproductive System FinalDocument5 pagesMale Reproductive System FinalJohn Dale Lulu CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Making A Poster Rubric 1Document1 pageMaking A Poster Rubric 1Shanna Basallo AlentonPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology: Third QuarterDocument63 pagesBiology: Third QuarterHill A. D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1st LESSON PLAN Earth ScienceDocument4 pages1st LESSON PLAN Earth ScienceLino Gayanilo100% (1)
- Gene Mutation Activity InstructionsDocument2 pagesGene Mutation Activity Instructionsapi-340677282Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number-1Document40 pagesAtoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number-1Khalid HdadPas encore d'évaluation
- Atp Adp CycleDocument18 pagesAtp Adp CycleLyn Dela Cruz Fontila100% (1)
- The Human Eye PowerpointDocument28 pagesThe Human Eye Powerpointapi-325864985Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - BIO-Explain The Effects of A Particular Hormone If It Is Not Properly RegulatedDocument2 pages2 - BIO-Explain The Effects of A Particular Hormone If It Is Not Properly RegulatedY Sa So RiPas encore d'évaluation
- How Protein Is Made Using Information From DNA BrentDocument18 pagesHow Protein Is Made Using Information From DNA BrentJed Sblz100% (1)
- Sci 10 Unit 3 Mod 1 (Lecture)Document41 pagesSci 10 Unit 3 Mod 1 (Lecture)Jonessa BenignosPas encore d'évaluation
- Darwin's Theory of EvolutionDocument53 pagesDarwin's Theory of EvolutionVincent BayawaPas encore d'évaluation
- CellsDocument18 pagesCellsapi-272901382Pas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Code: Learning Competency/iesDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Code: Learning Competency/iesMerce Tojino ManigosPas encore d'évaluation
- Menstrual Cycle: G10 BiologyDocument17 pagesMenstrual Cycle: G10 BiologyCharlize Andrea DiestaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water CycleDocument6 pagesWater CycleVal Daryl AnhaoPas encore d'évaluation
- MenstruationDocument6 pagesMenstruationOmhar CeresPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproduction of AnimalsDocument11 pagesReproduction of AnimalsNOVA LESLIE AGAPAYPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Exercise 19Document3 pagesLab Exercise 19Yeong-Ja KwonPas encore d'évaluation
- BilogyDocument3 pagesBilogyRome BillotePas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 ReproductiveSystemHormonesMenstrualCycleDocument37 pagesWeek 1 ReproductiveSystemHormonesMenstrualCycleAlice KrodePas encore d'évaluation
- Levels of Organization: LEVEL 1 - CellsDocument2 pagesLevels of Organization: LEVEL 1 - CellsYan Lean DollisonPas encore d'évaluation
- 4369232Document46 pages4369232Mahmuda LevinePas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Biological ScienceDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Biological Sciencejanelle belanoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Parts of The Human Reproductive System and Their FunctionsDocument13 pagesThe Parts of The Human Reproductive System and Their FunctionsRhodora Rendon OrizontePas encore d'évaluation
- I. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Are Able ToDocument6 pagesI. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Are Able ToC-nhaya Awing AlonzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Organismal BiologyDocument97 pagesOrganismal BiologyDaryl PansoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Endocrine SystemAzila JinPas encore d'évaluation
- Donor - Lesson 1.3 - Educ 103 (2590)Document5 pagesDonor - Lesson 1.3 - Educ 103 (2590)IAN JEM DONORPas encore d'évaluation
- DLP Mutation FinalDocument14 pagesDLP Mutation FinalJoeric Carinan100% (1)
- Q4 WK3 Weather PatternsDocument66 pagesQ4 WK3 Weather PatternsSherwin PhillipPas encore d'évaluation
- Fossils: Evidence For Evolution Worksheet: PaleontologyDocument3 pagesFossils: Evidence For Evolution Worksheet: PaleontologyJermaine Barnett-Weeks100% (1)
- Exemplar 3rdDocument5 pagesExemplar 3rdRAYMUND RODILLOPas encore d'évaluation
- Menstrual CycleDocument28 pagesMenstrual CycleNicole DanePas encore d'évaluation
- Patterns of Mendelian InheritanceDocument30 pagesPatterns of Mendelian InheritanceAngel Natty NewPas encore d'évaluation
- Roles of Hormones Involved in The Male ReproductiveDocument12 pagesRoles of Hormones Involved in The Male ReproductiveRaquel Bona ViñasPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th Class Computer Chapter No. 1Document4 pages9th Class Computer Chapter No. 1Muhammad AsifPas encore d'évaluation
- S5Q2MOD2 WK2 Menstrual CycleDocument18 pagesS5Q2MOD2 WK2 Menstrual CycleKring SandagonPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive System and Human Development 2018Document53 pagesReproductive System and Human Development 2018Kâmê KêlâhPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemJoseph CristianPas encore d'évaluation
- Fruit and Seed MorphologyDocument96 pagesFruit and Seed MorphologySleeping BeautyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Practical Term 1Document8 pagesBio Practical Term 1NiksPas encore d'évaluation
- Ascomycetes: Phylum AscomycotaDocument28 pagesAscomycetes: Phylum AscomycotaTayyaba QamarPas encore d'évaluation
- DR CasesDocument13 pagesDR CasesjaphethPas encore d'évaluation
- INBO 2023 Question-And-Answers 0Document40 pagesINBO 2023 Question-And-Answers 0vj jPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 1 Gametogenesis ReviewerDocument4 pagesExercise 1 Gametogenesis ReviewerJasper AdonisPas encore d'évaluation
- 2022 PT 2 Earthlifesci11Document3 pages2022 PT 2 Earthlifesci11JANET LAPITANPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Managing and Caring For The Self: at The End of This Module, The Student Is Expected ToDocument68 pages1 Managing and Caring For The Self: at The End of This Module, The Student Is Expected Tokhaila enriquez100% (1)
- Shiatsu For FertilityDocument3 pagesShiatsu For Fertilitysale18100% (2)
- Morphology of Flowering Plants - Chapter Notes - NotesDocument9 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants - Chapter Notes - NotesAAYUSH THAKURPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacterial ReproductionDocument12 pagesBacterial Reproductionchann.maahiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument39 pages2.sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsIshvaryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Study of Intrauterine Fetal Death Cases and Associated Maternal ConditionsDocument5 pagesAnalytical Study of Intrauterine Fetal Death Cases and Associated Maternal ConditionsNurvita WidyastutiPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of A Flower! Flower Dissection L. IntroductionDocument3 pagesParts of A Flower! Flower Dissection L. IntroductionDaryl Boldios LotertePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To BiologyDocument29 pagesIntroduction To BiologyRosalyn Marie SugayPas encore d'évaluation
- OpenSciEd High School Scope Sequence September 2021 PDFDocument22 pagesOpenSciEd High School Scope Sequence September 2021 PDFSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBPas encore d'évaluation
- Packet1 Reading Guide Juo1516 Answer KeyDocument3 pagesPacket1 Reading Guide Juo1516 Answer Keyapi-217623200Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assisted Reproduction Technology (ART)Document15 pagesAssisted Reproduction Technology (ART)RPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit100% (1)
- 2# Plant Cell and Tissue CultureDocument33 pages2# Plant Cell and Tissue CultureNuria Azmi Fadhila100% (1)
- Test Bank For Human Embryology and Developmental Biology 5th Edition Bruce M CarlsonDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Human Embryology and Developmental Biology 5th Edition Bruce M Carlsonjosephricejmkzxayows100% (40)
- Reproductive Parts of A Flower: © Windham Science 2019Document2 pagesReproductive Parts of A Flower: © Windham Science 2019api-524919792Pas encore d'évaluation
- Floral DevelopmentDocument49 pagesFloral DevelopmentLevi AckermanPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 5 LM Q1 Q4Document149 pagesScience 5 LM Q1 Q4Ludy Lyn100% (3)
- Scientists Ponder An Evolutionary Mystery - The Female Orgasm - The New York TimesDocument4 pagesScientists Ponder An Evolutionary Mystery - The Female Orgasm - The New York TimesMMVPas encore d'évaluation
- Making Sense of Sex - How Genes and Gender Influence Our Relationships (1997) by David P. Barash & Judith Eve LiptonDocument244 pagesMaking Sense of Sex - How Genes and Gender Influence Our Relationships (1997) by David P. Barash & Judith Eve LiptonGoosviePas encore d'évaluation
- Enumerate Advantages Disadvantages of Asexual ReproductionDocument2 pagesEnumerate Advantages Disadvantages of Asexual ReproductionRom RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment: Botany Class: Bs Zoology Submitted By: M Umair Submitted To: Mam FaizaDocument22 pagesAssignment: Botany Class: Bs Zoology Submitted By: M Umair Submitted To: Mam FaizaUmair DogarPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology 100%warantyDocument216 pagesHistology 100%warantyaqibhassan2022Pas encore d'évaluation
- UNPACKING THE SELF PhysicalDocument8 pagesUNPACKING THE SELF Physicalmary rose ombrogPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncma217 Lec PrelimDocument38 pagesNcma217 Lec PrelimIVY SUPNETPas encore d'évaluation