Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Renal Function Tests CSF
Transféré par
SajjadAhmad_QMC0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
23 vues22 pagesRenal Function test
Titre original
46521285 Renal Function Tests CSF
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentRenal Function test
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
23 vues22 pagesRenal Function Tests CSF
Transféré par
SajjadAhmad_QMCRenal Function test
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 22
Renal Function Tests
Functions of the Kidneys.
1. Formation of urine.
a. Excretion of water soluble waste products of
metabolism, mainly the nitrogenous waste
products.
b. Excretion of toxic substances.
c. Control of blood volume and extra-cellular fluid volume
by regulating the re-absorption of water and electrolytes.
d. Re-absorption of essential metabolites filtered in the
glomerular filtrate.
2. Endocrine functions.
a. Secretion of erythropoietin and control of red blood cell
production.
b. Secretion of renin and maintenance of blood pressure.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 1
Renal Function Tests
1. Urine routine examination: appearance, volume, sp
gravity, pH, glucose, protein and sediment.
2. Blood urea conc.
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN).
3. Serum creatinine conc..
4. Clearance tests to measure the GFR.
a. Inulin clearance test.
b. Creatinine clearance test.
c. Urea clearance test.
5. Serum electrolytes (Na, K, Cl, HCO).
6. Urinary total protein, Microalbumin.
7. Other Investigations.
USG of kidneys.
X-ray KUB, IVU, CT Scan.
Renal biopsy (FNAC).
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 2
Blood Urea
• Urea in blood is mostly derived from catabolism of
protein.
• It is freely filtered through glomeruli.
• It is passively reabsorbed from the filtrate.
• Its blood conc. may rise due to increased production,
decreased filtration or increased reabsorption.
• Normal blood conc. is 15 – 50 mg/dl of blood.
• BUN is the nitrogen derived from protein breakdown
only. It is calculated as:
Urea X 28/60 = BUN
BUN X 60/28 = Urea
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 3
Serum Creatinine
• Creatinine is derived from creatine.
• Its blood conc. depends on total muscle mass.
• It is filtered freely through glomeruli.
• It is not reabsorbed from the filtrate.
• Small amount of it is secreted by the tubules.
• Its blood conc. rises due to decreased filtration and
increased production.
• Normal blood conc 0.6-1.2 mg/dl of blood.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 4
Clearance tests
• Clearance test measures the volume of plasma
completely cleared of a substance per minute. It
is a measure of GFR.
• Inulin clearance test is the most ideal but a little
difficult to perform. Most convenient and useful
is the creatinine clearance test.
• Clearance of a substance (GFR) is calculated
using the following formula:
Clearance (GFR) = Conc. in urine X 24 hrs urine
volume/ Conc. in blood X Collecting time in min.
• Normal creatinine clearance is:
Adults < 55 yrs: 95– 145 ml/min.
Clearance decreases progressively with age.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 5
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 6
CSF
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 7
Examination of CSF
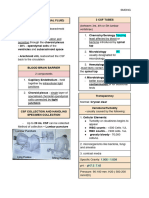
Introduction: Cerebrospinal fluid is formed
from plasma by the filtering & secretory activities
of the choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles. It
passes through the third & fourth ventricles into
the subarachnoid space between the pia mater
& arachnoid mater, & completely surrounds the
brain & spinal cord. CSF is reabsorbed into the
blood stream by the arachnoid villi which project
into the subarachnoid space.
In the adult the total volume of CSF is about 140
ml.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 8
CSF STYDY
Functions of CSF:
The CSF supports the brain &
protects it against injury. It also has a
similar function to lymph & remove waste
products of metabolism.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 9
Laboratory Examination Of CSF
It includes the following examination:
*A. Physical Examination
*B. Chemical Exam.
*C. M/E
*D. Bacteriological Examination.
*E. Other tests.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 10
Physical Examination
* Appearance: Normal CSF is clear.
* Colour: Colourless.
* Clot: Normal CSF does not clot.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 11
Cell Count
Normal: 0-5 lymphocytes/cmm.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 12
Chemical Examination
1. Protein: Normal: 15- 45mg/dl.
2. Glucose: Normal: 50-70mg/dl.
3. Chloride: Normal: 710-750mg/dl.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 13
Bacteriological Examination
Normal CSF is sterile.
1. Smear of centrifused deposit.
2. Culture.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 14
Other tests
1. VDRL
2.Antigen detection
3.Immunologial tests &
Electrophoresis.
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 15
Meningitis
• Bacterial
1. 1st 06 wks
• Enteric gram neg
• Group B strept
• Meningococci
• Staph
• Pneumococci
• L.monocytogens
• Group A strept
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 16
Meningitis
2. Six wks to six yrs
• H. influnzae
• Meningococci
• Pneumococci
3. Over six yrs
Pneumococci
Meningococci
4. All ages: Tuberculosis
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 17
Meningitis
• Viral causes
1. Neurotropic viruses
Polio viruses
LCM
Arbo.encephalitis
2. Non-neurotropic viruses
Enteroviruses,Mumps,Herpes simplex,Infectios
mononucleosis,Varicela-zoster,measles
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 18
CSF
• 3.Fungal causes
Cryptococcosis
Aspergillosis
Histoplasmosis
Mucormycosis
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 19
CSF in normal health & common disorders
Normal Pyogeni Tubercul Viral Subarac Tumour
c ous Meningit hnoid
Meningit Meningit is Haemorr
is is hage
1.Press 60-100 Normal/i Normal/i Normal Increase Increase
ure(mm ncrease ncrease d d
H20) d d
2.Color Crystal Cloudy, Clear/Cl Clear Blood- Clear
Clear purulent oudy mixed/x
anthocro
mic
3.Cell Lympho Neutrop Mostly Lympho RBCs Normal
count/m cytes 0- hils Lympho cytes mostly
m3 5 often cytes upto 200
more upto 500
than
1000-
QMC BAHAWALPUR 5000 SAJJAD AHMAD 20
CSF in normal health & common disorders
4.Protein( 15-45 Increased Increased Increased Normal Increased
mg/dl) 500-2000 500-3000 500-2000 500-2000
5.Glucos 50-70 May Decrease Normal Normal Normal
e(mg/dl) disappear d 20-30
6.Chlorid 710-750 Normal <600 Normal Normal Normal
e(mg/dl)
7.Other Culture- Organism Tubercle Stain & Centrifug
bacilli in
Changes Sterile s on Culture- ed-
fibrin clot
Deposit gram and deposit No supernat
stain & on ZN stain organism ant is
culture & yellow
culture:PCR
may identify
the
organism
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 21
CSF
• Indication of CSF study
Meningitis
Subarachnoid haemorrhage
Malignancy
Demyelinating disease
QMC BAHAWALPUR SAJJAD AHMAD 22
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- clinical pathology ( body fluids) 4 semesterDocument12 pagesclinical pathology ( body fluids) 4 semesterSiddhi KaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. MowafyDocument64 pagesNephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafyrazan moneerPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. MowafyDocument64 pagesNephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. MowafyMohammed Risq100% (1)
- Blood Investigations: Dr. Maulika PatelDocument21 pagesBlood Investigations: Dr. Maulika Patelpatrikmodi100% (1)
- CSF Analysis Presentation 3Document24 pagesCSF Analysis Presentation 3Suresh Kumar RamanathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Aubf Lec Reviewer MidtermDocument129 pagesAubf Lec Reviewer MidtermTrangia, SharmainePas encore d'évaluation
- 20 CSFDocument53 pages20 CSFnivetha26082000Pas encore d'évaluation
- CSF & Body FluidDocument42 pagesCSF & Body FluidlopaPas encore d'évaluation
- CSF LectureDocument58 pagesCSF Lectureshweta yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Count the sperm in the central grid and multiply by 10,000 to obtain the sperm concentration per mLDocument81 pagesCount the sperm in the central grid and multiply by 10,000 to obtain the sperm concentration per mLAris ResurreccionPas encore d'évaluation
- Meningitis MicrobiologyDocument74 pagesMeningitis MicrobiologyJyoti YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- CSF PDFDocument58 pagesCSF PDFVas KannanPas encore d'évaluation
- CSFDocument37 pagesCSFMujtaba IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrospinal Fluid CSFDocument60 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid CSFpikachuPas encore d'évaluation
- Other Body Fluid Cerebrospinal FluidDocument16 pagesOther Body Fluid Cerebrospinal Fluidrona hilarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Kapil GargDocument21 pagesKapil GargTanya ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BLOODDocument30 pagesHUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BLOODNishchal KutarekarPas encore d'évaluation
- SEMEN ANALYSIS GUIDEDocument31 pagesSEMEN ANALYSIS GUIDEVinodkhanna Kairamkonda100% (1)
- CSF Examination.Document31 pagesCSF Examination.kamalPas encore d'évaluation
- BloodDocument9 pagesBloodPrashant PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- LECTURE NOTES ON HAEMATOLOGYDocument94 pagesLECTURE NOTES ON HAEMATOLOGYAnmar ZawahraPas encore d'évaluation
- CSF Formation and Analysis GuideDocument5 pagesCSF Formation and Analysis GuideKLIPPPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Composition - KnoxDocument34 pagesBlood Composition - KnoxMehedi HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Print Notes Analysis of The Urine and Other Body FluidsDocument11 pagesPrint Notes Analysis of The Urine and Other Body FluidsVenice Natasha B. GalgalaPas encore d'évaluation
- AUBFDocument10 pagesAUBFnillascadivinevan.rPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology PreliminariesDocument7 pagesHematology PreliminariesRomie SolacitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Serous Fluid AnalysisDocument23 pagesSerous Fluid AnalysisMarl EstradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology lab: Faculty of Medical laboratory since Patch 7 ليعامسإ دمحم اللهدبع مكوخأ صيخلتDocument32 pagesPhysiology lab: Faculty of Medical laboratory since Patch 7 ليعامسإ دمحم اللهدبع مكوخأ صيخلتmohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Haematology Lab. 1: Practical PhysiologyDocument31 pagesClinical Haematology Lab. 1: Practical PhysiologyHameed SabahPas encore d'évaluation
- CSF and Other Body FluidsDocument9 pagesCSF and Other Body FluidsJobelle0% (1)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid: Gonzalo B. Roman JR.,MD.,FPSPDocument19 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid: Gonzalo B. Roman JR.,MD.,FPSPBenjamin PrabhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Kuliah Ginjal 2017 Blok 18Document78 pagesKuliah Ginjal 2017 Blok 18Kookie RookiePas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia, Tic, DLC MbbsDocument50 pagesAnemia, Tic, DLC Mbbssharads221004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Microscopy - Other Body FluidsDocument93 pagesClinical Microscopy - Other Body FluidsTherese Ann Eve FlorenososPas encore d'évaluation
- Examination of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSFDocument3 pagesExamination of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSFMoon YoungheePas encore d'évaluation
- Body Fluids Tsilioni SlidesDocument31 pagesBody Fluids Tsilioni SlidesShaira Jane AlcantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CSF Exam Guide: Tests, Findings & AbnormalitiesDocument14 pagesCSF Exam Guide: Tests, Findings & AbnormalitiesMalliga SundareshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Body FluidsDocument24 pagesBody FluidsMohamed MidoPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 FT CSFDocument37 pages10 FT CSFClarence SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrospinal Fluid: Practice Test SheetDocument7 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid: Practice Test SheetJoey MagnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrospinal FluidDocument43 pagesCerebrospinal FluidBrylle UgayPas encore d'évaluation
- CSF WithnotesDocument43 pagesCSF WithnotesanggaririnPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology 1 (Laboratory) - Week 10-11 ModuleDocument8 pagesHematology 1 (Laboratory) - Week 10-11 ModuleJam RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- CSF Analysis Reveals Clues to Neurological ConditionsDocument22 pagesCSF Analysis Reveals Clues to Neurological ConditionsSathish RamrajaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Microscopic Examination of UrineDocument116 pages6 Microscopic Examination of Urineaddine061421Pas encore d'évaluation
- Congenital Hemolytic Anemia GuideDocument37 pagesCongenital Hemolytic Anemia GuideSomendra Mohan ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Final Exam ReviewDocument59 pagesLab Final Exam ReviewManju ShreePas encore d'évaluation
- International Clinical LaboratoriesDocument23 pagesInternational Clinical Laboratoriesmihret genenePas encore d'évaluation
- HL and NHL: Case PresentationDocument26 pagesHL and NHL: Case PresentationFrankenstein MelancholyPas encore d'évaluation
- Body FluidsDocument52 pagesBody Fluidskwon hoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrospinal Fluid: Prepared By: Fe P. Lleno, MSMTDocument39 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid: Prepared By: Fe P. Lleno, MSMTthe songwriterPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Hemorrhage & Hemorrhagic Shock (Handout)Document10 pagesClassification of Hemorrhage & Hemorrhagic Shock (Handout)Ayuub AbdirizakPas encore d'évaluation
- 231 Path - CBC Report - 10Document21 pages231 Path - CBC Report - 10442800520Pas encore d'évaluation
- Examination of CSF: Dr. Md. Razib HasanDocument33 pagesExamination of CSF: Dr. Md. Razib HasanRazib HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- CSF Analysis GuideDocument248 pagesCSF Analysis GuideGennelyn Ross Delos Reyes0% (1)
- 3.5 - 5.5 X 10 Cells/mm 7.4-9.9 Mmol/l HCT: Normal For Female Patients 33% - 45%Document2 pages3.5 - 5.5 X 10 Cells/mm 7.4-9.9 Mmol/l HCT: Normal For Female Patients 33% - 45%Jeann CaldereroPas encore d'évaluation
- Hookworm Infection in A Puppy CaseDocument19 pagesHookworm Infection in A Puppy Caseapi-345675212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Specimen Collection in Body Fluids AnalysisDocument22 pagesSpecimen Collection in Body Fluids AnalysisShafira AzzahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Hema Mod 4Document17 pagesHema Mod 4Moon KillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Alert Medical Series: Internal Medicine Alert I, II, IIID'EverandAlert Medical Series: Internal Medicine Alert I, II, IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Attitudes in AuDocument2 pagesAttitudes in AuSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolism of CopperDocument1 pageMetabolism of CopperSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Biostatistics MCQDocument5 pagesBiostatistics MCQSajjadAhmad_QMC82% (72)
- Causes of Hearing LossDocument11 pagesCauses of Hearing LossSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Hla Tissue TypingDocument10 pagesHla Tissue TypingSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Behaviour in Children With Hearing LossDocument1 pageCommon Behaviour in Children With Hearing LossSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Cad TestDocument8 pagesCad TestSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages and Limitations of Various Business Legal StructuresDocument7 pagesAdvantages and Limitations of Various Business Legal StructuresSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Causes of Hearing LossDocument11 pagesCauses of Hearing LossSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- VDRL TestDocument2 pagesVDRL TestSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- CryoglobulinsDocument39 pagesCryoglobulinsanamariavPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy Test in Urine: Uroscopy, A Nonscientific Method To Evaluate UrineDocument4 pagesPregnancy Test in Urine: Uroscopy, A Nonscientific Method To Evaluate UrineSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Ateneo Parmense Acta BiomedDocument5 pagesAteneo Parmense Acta BiomedSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Ateneo Parmense Acta BiomedDocument5 pagesAteneo Parmense Acta BiomedSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Ateneo Parmense Acta BiomedDocument5 pagesAteneo Parmense Acta BiomedSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Widal TestDocument57 pagesWidal TestSajjadAhmad_QMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - DNADocument8 pagesChapter 5 - DNAzsuzanna100% (1)
- Effects of Ethanol and Caffeine on Crayfish Heart RateDocument1 pageEffects of Ethanol and Caffeine on Crayfish Heart Ratebroddy1Pas encore d'évaluation
- MANUAL For Wheat Flour Fortification - Technical GuidelinesDocument46 pagesMANUAL For Wheat Flour Fortification - Technical GuidelinesRahul JuwarePas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Stress Fact SheetDocument3 pagesHeat Stress Fact SheetjacquestsPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis and Characterization of EDTA ComplexesDocument7 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of EDTA ComplexesLucas PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- (Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemDocument18 pages(Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemTrúc Linh NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- TissuesDocument23 pagesTissuesWubalem DestaPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Air Pollutants On Mediterranean and Temperate Forest EcosystemsDocument263 pagesEffects of Air Pollutants On Mediterranean and Temperate Forest EcosystemsPACIFIC SOUTHWEST RESEARCH STATION REPORTPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide Lecture Exam 1 Use This Handout With Your Video Review Possible Essay QuestionsDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Lecture Exam 1 Use This Handout With Your Video Review Possible Essay QuestionsBrandice BradleyPas encore d'évaluation
- DocumentDocument7 pagesDocumentDébàshis Dash50% (2)
- Journal of Theoretical Biology: Qihua Huang, Hao Wang, Mark A. LewisDocument19 pagesJournal of Theoretical Biology: Qihua Huang, Hao Wang, Mark A. Lewisyuukanishi6881Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz - Mosndarja e Kromozomeve Gjate MejozwsDocument5 pagesQuiz - Mosndarja e Kromozomeve Gjate MejozwsleartaPas encore d'évaluation
- Allplex SARS-CoV-2 Variant I AssaysDocument1 pageAllplex SARS-CoV-2 Variant I AssaysadibyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion - The Expulsion of A Fetus From The Uterus Before It Has Reached TheDocument2 pagesAbortion - The Expulsion of A Fetus From The Uterus Before It Has Reached TheRomelyn AngelPas encore d'évaluation
- Organizational Behavior Field Map and Perception FactorsDocument32 pagesOrganizational Behavior Field Map and Perception FactorsPratik TagwalePas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Gender On Short Term Memory FinishedDocument27 pagesEffect of Gender On Short Term Memory Finishedhafsah286Pas encore d'évaluation
- Salt IodateDocument2 pagesSalt IodateRKMPas encore d'évaluation
- Fermentation Variables: Important Physical and Chemical Variables For Alcoholic FermentationDocument15 pagesFermentation Variables: Important Physical and Chemical Variables For Alcoholic FermentationRemus GheorghițăPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Docking: in Computer Aided Drug DesignDocument26 pagesMolecular Docking: in Computer Aided Drug DesignGravelandPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysioEx Exercise 1 Activity 2Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 1 Activity 2CLAUDIA ELISABET BECERRA GONZALESPas encore d'évaluation
- Extraocular Muscles Anatomy PDFDocument2 pagesExtraocular Muscles Anatomy PDFCherylPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.3 Gene Pools and SpeciationstudentnotesDocument4 pages10.3 Gene Pools and SpeciationstudentnotesMoahmed Mahmoud IB15A 363KAGYPas encore d'évaluation
- Adam Moser and Darrin M. York - 2008 - 基因的改变NIH Public AccessDocument19 pagesAdam Moser and Darrin M. York - 2008 - 基因的改变NIH Public AccessAlexandre Campos Moraes AmatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Eosinophilic GastroenteritisDocument7 pagesEosinophilic GastroenteritisSotir LakoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Expression Profiling Using MicroarraysDocument23 pagesGene Expression Profiling Using MicroarraysNiloy KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Individual Differences and Emotional IntelligenceDocument91 pagesIndividual Differences and Emotional IntelligenceSREEKUTTY K MPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 9 14 Answers PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz 9 14 Answers PDFюрий локтионовPas encore d'évaluation
- REVIEW OF MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY-Twelfth Edition PDFDocument2 pagesREVIEW OF MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY-Twelfth Edition PDFSai Venkata Suresh VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- TATIANADocument8 pagesTATIANAKaizer NdoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Sigma Services, Equipment, Instruments and Media Services overviewDocument87 pagesSigma Services, Equipment, Instruments and Media Services overviewPreeti JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation