Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Database Environment
Transféré par
Wahab Mansoor0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
6 vues16 pagesThe document discusses database environments and their components. It defines key concepts like data, databases, metadata and information. It compares file processing systems to database approaches, outlining advantages like reduced redundancy and improved data sharing in databases. The document also describes database management systems, applications of databases at different levels from personal to enterprise, and the typical components of a database environment including tools, repositories, databases and users.
Description originale:
Titre original
DBMS
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe document discusses database environments and their components. It defines key concepts like data, databases, metadata and information. It compares file processing systems to database approaches, outlining advantages like reduced redundancy and improved data sharing in databases. The document also describes database management systems, applications of databases at different levels from personal to enterprise, and the typical components of a database environment including tools, repositories, databases and users.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
6 vues16 pagesThe Database Environment
Transféré par
Wahab MansoorThe document discusses database environments and their components. It defines key concepts like data, databases, metadata and information. It compares file processing systems to database approaches, outlining advantages like reduced redundancy and improved data sharing in databases. The document also describes database management systems, applications of databases at different levels from personal to enterprise, and the typical components of a database environment including tools, repositories, databases and users.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 16
The Database Environment
The database environment
• To be able to function, an organisation needs information, e.g.
list of books in a library, customer details in a retail business,
specifications of cars and their components for a car
manufacturer
• Information may be defined as data represented in a
meaningful form. Same data shown in different ways will
provide different information to different viewers
• A major requirement of any computer system is to store and
retrieve data in a way that is meaningful to the end user – so
the core of any Information System is data, which is to be
transformed into information through data modelling
Definitions
• Data: Meaningful facts, text, graphics, images, sound,
video segments.
• Database: An organized collection of logically related
data.
• Information: Data processed to be useful in decision
making.
• Metadata: Data that describes data.
Summarized data
Disadvantages of file processing
systems
Still widely used today (e.g. for backup) but have the following problems:
• Program-Data Dependence (see Fig.) – file descriptions are stored
within each application that accesses file, so change to file structure
requires changes to all file descriptions in all programs.
• Data Redundancy (Duplication of data) – wasteful, inconsistent, loss
of metadata integrity (same data has different names in different files,
or same name may be used for different data in different files).
• Limited Data Sharing – users have little opportunity to share data
outside their own applications.
• Lengthy Development Times – little opportunity to re-use previous
development efforts.
• Excessive Program Maintenance – factors above combine to create
heavy maintenance load
Three file processing systems
Advantages of the
database approach
• Minimal Data Redundancy/Improved Consistency
• Data Integration
• Multiple Relationships
Database management system
• A DBMS is a data storage and retrieval system which
permits data to be stored non-redundantly while making it
appear to the user as if the data is well-integrated.
Advantages of the
database approach
• Data Independence/Reduced Maintenance
• Improved Data Sharing
• Increased Application Development Productivity
• Enforcement of Standards
• Improved Data Quality (Constraints)
• Better Data Accessibility/ Responsiveness
• Security, Backup/Recovery, Concurrency
Costs and risks of the
database approach (Disadvantages of DB)
• New, Specialized Personnel required
• Installation Management Cost and Complexity
• Conversion Costs
• Need for Explicit Backup and Recovery
• Organizational Conflict
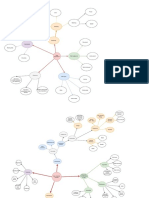
Segment from enterprise data model
Figure 3
The range of
database applications
• Personal Database PCs/PDAs, Cellphones – OK in special situations
where need to share data amongst users is unlikely to arise
• Workgroup Database. Designed to support collaboration in a small
team (less than 25 people)
• Department Database typically larger than a workgroup (25-100
people) and more diverse range of functions – e.g. personnel database
• Enterprise Database – scope of the whole organisation. May be more
than one, as a single database for a large organisation may be
impractical due to performance difficulties for large databases, diverse
needs of user groups, and difficulty of achieving common definition of
data (metadata) for all users.
An enterprise
data
warehouse
Components of the
database environment
• CASE Tools – automated tools used to design databases and applications
• Repository – generalised knowledge for all data definitions, relationships,
screen/report formats – an extended set of metadata for managing databases
and other components of the information system
• Database Management System (DBMS) – software (sometimes specialised
hardware) used to define, create, maintain and provide controlled access to the
database and the repository.
• Database(DB) – an organised collection of logically related data occurrences
• Application Program
• User interface
• End User
• System Developer
• DBA
Components of the database
environment
• Application Programs – software used to create and
maintain the database and provide information to users.
• User Interface – languages, menus etc by which users
interact with other system components
• Data Administrators – people responsible for overall
information resources of an organisation.
• Systems analysts/programmers and end Users – people
who add, delete and modify the database and who get
information from it.
Components
of the
database
environment
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Azure Data Factory Data Flows: Luke Newport Technical Specialist - Data & AIDocument30 pagesAzure Data Factory Data Flows: Luke Newport Technical Specialist - Data & AIBabu Shaikh100% (1)
- Database Systems: by Neil A. BasabeDocument33 pagesDatabase Systems: by Neil A. BasabeNeil Basabe100% (1)
- Oracle 11g RAC Student Guide Volume 2Document364 pagesOracle 11g RAC Student Guide Volume 2shklifoPas encore d'évaluation
- Packt - Hands On - Deep.learning - With.apache - Spark.2019Document363 pagesPackt - Hands On - Deep.learning - With.apache - Spark.2019yohoyonPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Systems IntroductionDocument40 pagesDatabase Systems IntroductionJustin JJPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit I - Introduction To DatabaseDocument31 pagesUnit I - Introduction To DatabaseGaurav Patni100% (1)
- Apps DBA Interview QuestionDocument12 pagesApps DBA Interview QuestionRamesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Thank You For Your Purchase: Ibm C1000-074 Exam Question & Answers Ibm Filenet P8 V5.5.3 Deployment Professional ExamDocument21 pagesThank You For Your Purchase: Ibm C1000-074 Exam Question & Answers Ibm Filenet P8 V5.5.3 Deployment Professional ExamKaran GowdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Employee Management System: CS8582-Object Oriented Analysis and Design LabDocument19 pagesEmployee Management System: CS8582-Object Oriented Analysis and Design LabGANESHKARTHIKEYAN VPas encore d'évaluation
- ER and NormalizationDocument158 pagesER and NormalizationTulipPas encore d'évaluation
- Task 1nayoDocument35 pagesTask 1nayoNimal JayasundaraPas encore d'évaluation
- DatabaseDocument45 pagesDatabasewaqas08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Design & ManagementDocument45 pagesDatabase Design & ManagementyohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ConceptsDocument9 pagesBasic Conceptsuseless0151Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Systems MISDocument22 pagesDatabase Systems MISYonse Epic StoriesPas encore d'évaluation
- 02.advantages of Database ApproachDocument14 pages02.advantages of Database ApproachMadhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management System: Dr. G. Jasmine Beulah, Dept. Computer Science Kristu Jayanti College, BengaluruDocument49 pagesDatabase Management System: Dr. G. Jasmine Beulah, Dept. Computer Science Kristu Jayanti College, BengaluruRaj KundraPas encore d'évaluation
- EDIT 3101 - Database Management System - Lecture 1Document29 pagesEDIT 3101 - Database Management System - Lecture 1sichingadavies84Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document39 pagesChapter 1YasukePas encore d'évaluation
- File Systems Introduction To DatabasesDocument37 pagesFile Systems Introduction To DatabasesbijjarPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - The Database EnvironmentDocument25 pagesModule 1 - The Database EnvironmentPatrick RomanPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation1 DatabaseDocument49 pagesPresentation1 DatabaseSameedPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 SudhaDocument129 pagesModule 1 SudhaRupith Kumar .NPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMSDocument70 pagesDBMSGitte DnyaneshwarPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS Chapter 1Document23 pagesDBMS Chapter 1ShutDownPas encore d'évaluation
- W1. Introduction To DatabaseDocument26 pagesW1. Introduction To DatabaseSABOOR UR RAHMANPas encore d'évaluation
- Database SystemsDocument104 pagesDatabase SystemsLanreFalolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management Systems (DBMS) Course-KCS-501: Lec 1 - R. S. KohliDocument13 pagesDatabase Management Systems (DBMS) Course-KCS-501: Lec 1 - R. S. KohliRS kohliPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMSDocument373 pagesDBMSTushar PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1: Databases and Database UsersDocument25 pagesUnit 1: Databases and Database UsersVarun RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 - The Database Environment and Development ProcessDocument47 pagesLesson 1 - The Database Environment and Development ProcessGintoki Sakata0% (1)
- Midterm Exam FDS PDFDocument35 pagesMidterm Exam FDS PDFAlthea ManlapazPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of Dbms in SportsorganizationDocument12 pagesUse of Dbms in SportsorganizationPrateek ChaturvediPas encore d'évaluation
- DB 1Document29 pagesDB 1aishaPas encore d'évaluation
- File Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramDocument35 pagesFile Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramJan Reinhart PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Mis - Data Files and DatabasesDocument40 pagesMis - Data Files and DatabasesSaikatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To DatabasesDocument47 pagesGuide To DatabasesAnne RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Database and DBMS IntroductionDocument31 pagesDatabase and DBMS IntroductionJoseph MungaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To DatabaseDocument28 pagesIntroduction To DatabaseAdnan SohailPas encore d'évaluation
- WINSEM2023-24 BCSE302L TH CH2023240502444 Reference Material I 08-01-2024 MODULE 1Document165 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BCSE302L TH CH2023240502444 Reference Material I 08-01-2024 MODULE 1sarvesh.vitchennaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture - 1: The Database EnvironmentDocument22 pagesLecture - 1: The Database EnvironmentEsraa SamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Dbms Basic ConceptsDocument47 pagesDbms Basic ConceptsSâürãbh KùmårPas encore d'évaluation
- 214 Lecture 1Document57 pages214 Lecture 1Eniola Joyce AdedejiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - 2Document26 pagesUnit - 2kalik goyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 DBMSDocument96 pagesModule 1 DBMSreddytejaswini0431Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Systems-Introduction: Bayu Adhi TamaDocument32 pagesDatabase Systems-Introduction: Bayu Adhi TamaHimani RathorePas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument21 pagesIntroductionMarkapuri Santhoash kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To DB: Introduction and Conceptual ModelingDocument25 pagesIntroduction To DB: Introduction and Conceptual Modelinghaya ansariPas encore d'évaluation
- Guru Nanak College BudhladaDocument6 pagesGuru Nanak College BudhladaRohit MahajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Database and Data ModelingDocument31 pagesDatabase and Data ModelingKudakwashe MotsiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2-Introduction To DBMS - Need - Characteristics - Advantages - Applications-28!04!2023Document19 pages2-Introduction To DBMS - Need - Characteristics - Advantages - Applications-28!04!2023konkimalla ganeshPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS Basic ConceptsDocument52 pagesDBMS Basic ConceptsPuru RajPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMSDocument52 pagesDBMSjjs17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To DatabasesDocument16 pagesIntroduction To DatabasesJoseph KimaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 - MDocument40 pagesUnit 4 - Mriyan hussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Part 2Document31 pagesUnit 1 Part 2Shreyansh 1485Pas encore d'évaluation
- Information Technology: Chapter TwoDocument56 pagesInformation Technology: Chapter TwoĒrmias ÁlemayehuPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Introduction To DataBase SystemsDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To DataBase Systemsprathameshm.cs21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution of Database Management SystemDocument12 pagesEvolution of Database Management SystemsambashivaraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ConceptsDocument33 pagesBasic Conceptskiller GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To: Database ProgrammingDocument60 pagesIntroduction To: Database ProgrammingJlin Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Access Week 1Document15 pagesAccess Week 1Daisy Mangahas BaleritePas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Introduction To DatabaseDocument28 pages1-Introduction To DatabaseJoseph CrossPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS1 7Document531 pagesDBMS1 7savoir001Pas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS SlidesDocument127 pagesDBMS SlidesAmit KushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 6 PPT Data Table IntroductionDocument13 pagesYear 6 PPT Data Table Introductionاحمد ابراهيمPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Programming With PL/SQL 9-5: Practice Activities: Review of Object PrivilegesDocument3 pagesDatabase Programming With PL/SQL 9-5: Practice Activities: Review of Object PrivilegesMiroslava Melgares0% (1)
- Converting Email From .Eml To .CSV Files.Document8 pagesConverting Email From .Eml To .CSV Files.EncryptomaticPas encore d'évaluation
- INT306 ManishDocument37 pagesINT306 ManishManish ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Big Data To Improve Customer Experience and Business PerformanceDocument15 pagesUsing Big Data To Improve Customer Experience and Business PerformanceAngel AngelPas encore d'évaluation
- Vtu 7TH Sem Cse/ise Data Warehousing & Data Mining Notes 10cs755/10is74Document70 pagesVtu 7TH Sem Cse/ise Data Warehousing & Data Mining Notes 10cs755/10is74EKTHATIGER63359094% (18)
- Qlik Associative Big Data Index Setup Configuration and DeploymentDocument30 pagesQlik Associative Big Data Index Setup Configuration and DeploymentManuel SosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Dissertation: Master of Computer Applications Mca-Vi - SemesterDocument22 pagesGuidelines For Dissertation: Master of Computer Applications Mca-Vi - SemesterRabin KoiralaPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume Tata Consultancy ServicesDocument14 pagesResume Tata Consultancy ServicesSanjayPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume Tata Consultancy ServicesDocument4 pagesResume Tata Consultancy Servicesrishabh aroraPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS-Wee3 - Lecture MaterialDocument164 pagesDBMS-Wee3 - Lecture MaterialmanaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Contemporary Computing TechnologiesDocument25 pagesContemporary Computing TechnologiesIgwe VictorPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3 Informix Database Administration LabDocument57 pages1.3 Informix Database Administration LabLuis Zepeda HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 11 - Tables and Clusters Full NotesDocument44 pagesModule 11 - Tables and Clusters Full NotesGautam TrivediPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 - Logical Database DesignDocument33 pagesChapter 16 - Logical Database Designkibet calebPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS Question Bank StudentDocument10 pagesDBMS Question Bank Student187Sayan BhattacharjeePas encore d'évaluation
- User Manual in EnglishDocument169 pagesUser Manual in Englishalan.mruiz4985Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mindmap Business Intelligence (BI)Document2 pagesMindmap Business Intelligence (BI)Tran Chi TinhPas encore d'évaluation
- GIS Data Management: Ge 118: Introduction To Gis Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State UniversityDocument47 pagesGIS Data Management: Ge 118: Introduction To Gis Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State UniversityKrystel Joy Matilde NOblePas encore d'évaluation
- 05uapterminalsystemissue1 141112121228 Conversion Gate02Document56 pages05uapterminalsystemissue1 141112121228 Conversion Gate02mhammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Siska2 SQLDocument73 pagesSiska2 SQLJodiGinandraPaksiPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study - J. J. Keller & Associates, Inc. Is A ...Document3 pagesCase Study - J. J. Keller & Associates, Inc. Is A ...Hamza ShafiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Mining and Ware HousingDocument130 pagesData Mining and Ware Housingvjkarthika45Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concepts of Database Management 8th Edition Pratt Test Bank 1Document10 pagesConcepts of Database Management 8th Edition Pratt Test Bank 1roy100% (33)