Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lung Infections - Jessica de Anda
Transféré par
MicroposterTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lung Infections - Jessica de Anda
Transféré par
MicroposterDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
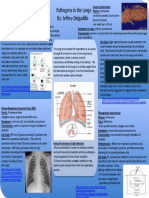
When Microorganisms Attack the Lungs
By: Jessica De Anda
Virus: Hanta Virus Parasite: Paragonimus westermani
Pathogenesis: Transmission: Santa Clara University
•Virus is normally carried by rodents, Lung Fluke Life Cycle: Epidemiology:
The disease caused by this virus is known as such as the deer mouse BIOL 116: Medical Microbiology •Most commonly encountered in:
Hantavirus Cardiopulmonary Syndrome(HPS). Hanta •HPS is a disease that comes from Paragonomiasis infection begins when a human ingests a •Africa, Asia, and South America
Virus is typically airborne and first infects the lung contact with infected rodents or their crustacean that has been infected with the mature form of the
fluke; a metacercaria. The metacercaria go through the stomach Morphology:
urine, droppings or saliva
parenchyma where it is phagocytized and
transported to draining lymph nodes. The virus then Symptoms: and once inside the small intestine they bore their way through •Reddish brown oval worm
•Adult: 4-6mm wide, 3-5mm thick,
disperses and targets vascular endothelial cells of •Early symptoms are similar to the the intestinal wall, through the diaphragm and into the lungs
flu
the lung; it can also attack the heart and lymphoid where it continues to form a capsule and develops into an adult. 7-12mm long
•After having the infection for a
tissue. couple of days the patient will start Symptoms:
to have: dry cough, headache,
•Dry cough
nausea and vomiting, shortness of
breath and shallow breathing •Blood stained rusty brown sputum
Treatment: •Chest pain- pleurisy may develop
•There is no specific treatment for
HPS Diagnosis:
•Early diagnosis and treatment in an •Sputum: look for fluke eggs
intensive care unit may improve a
person's chances of recovery
Adult •Feces examined
•X-rays and biopsies
Treatment:
Virus Background: •Drug: Praziquantel
•Negative sense RNA virus
Preventive measures:
•Zoonotic virus
•Make sure to cook seafood
•Member of the family
Bunyaviridae that are generally References: thoroughly
spherical in shape http://www2.bakersfieldcollege.edu/bio16/22_resppictures.htm •Improve sanitary conditions
•The lipid envelope contains 2 http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/236425-overview#showall Egg
major glycoproteins http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/imagepages/172.htm Reference: http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/parasitology/trematodes.htm
Fungus: Coccidioides immitis
Pathogenesis: Epidemiology: Pathogenesis: Bacterium: Bordetella pertussis
Structure:
• Infection is usually confined to •Gram-negative
Coccidioides immitis is a pathogenic fungus that causes the subjects in the endemic regions Bordetella pertussis causes whooping cough. At first •Aerobic coccobaccilli
lung infection Coccidioidomycosis The fungus resides in the of North and South America, with
most cases seen in the
symptoms are mild, and then develop into severe
Virulence factors:
soil and is dormant during dry weather. In moister weather southwestern United States coughing fights and when the patient takes a breath a
•Pertussis toxin
the fungus develops as a mold with long filaments that Transmission: deep “whooping” sound is produced. Transmission of B.
•Adenylate cyclase toxin
break off into airborne spores. The spores are known as •Coccidioidomycosis is not
pertussis is from an infected person by aerosolized
•Filamentous hemagglutinin
arthroconidia and can be swept into the air by strong winds transmitted from person to droplets. The bacteria colonizes ciliated cells of the
person •Hemolysin
or disruption of the soil in which the fungus is situated. respiratory mucosa and reproduce rapidly.
Inhalation of arthrospores is the portal of entry for the vast •Person becomes infected by
breathing in fungal particles from
majority of coccidioidal infections. Once in the respiratory soil. The infection starts in the
Symptoms:
lungs
tract, spherules proliferate, and host cell–mediated •Initial symptoms similar to common
immunity is crucial for controlling the infection. Symptoms: cold
•Chest pain, cough (possibly •Severe cough begins after 10 to 12
producing blood), body aches, days of infection- coughing ends with
loss of appetite, and many more “whoop” noise
Treatment: Diagnosis:
•There are 3 forms of
Virulence factors of B. pertussis Binding of pertussis toxin to host
•Can be cultured on modified Bordet-
coccidioidomycosis: acute, cell membranes Gengou medium, charcoal-horseblood
chronic, or disseminated agar (Regan-Lowe) or grown in
•Acute disease resolves on its supplement Stainer-Scholte broth
own •B. pertussis DNA can be detected by
•Disseminated or severe disease PCR
Spores of the fungus Coccidioides immitis should be treated with •Circulating antibodies appear in week 3
amphotericin B, ketoconazole, of illness and peak in the eighth to tenth
fluconazole, or itraconazole week
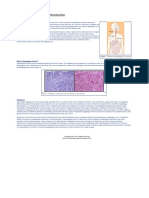
Chest x-ray showing the Gram stain of B. pertussis
affects of coccidioidomycosis. Treatment:
In the middle of the left lung
•Erythromycin- reduces infectious
(seen on the right side of the period
picture) there are multiple, thin- References:
References:
walled cavities (seen as light http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002299/figure/A001322.B1600/
?report=objectonly http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK7813/
areas) with a diameter of 2 to 4 http://www.textbookofbacteriology.net/pertussis.html
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/297976-overview#showall
centimeters
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002299/
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Developing A Telehealth Marketing Plan A Step by Step GuideDocument24 pagesDeveloping A Telehealth Marketing Plan A Step by Step GuidePham Kim Anh0% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken PoxDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Poxderic87% (62)
- Micp Midterms ReviewerDocument7 pagesMicp Midterms ReviewerReichelle Anne QuibinPas encore d'évaluation
- For EmailDocument1 pageFor EmailJonSabaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rabies ScribdDocument78 pagesRabies Scribdbryfar100% (1)
- Pneumonia Case PresentationDocument1 pagePneumonia Case PresentationFrancine kimberlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Measles (Case Presentation)Document19 pagesMeasles (Case Presentation)Zam Pamate100% (3)
- Class Nematoda - The Roundworms: Blood and Tissue-Dwelling NematodesDocument33 pagesClass Nematoda - The Roundworms: Blood and Tissue-Dwelling NematodesMayank TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Measles, Mumps, RubellaDocument5 pagesMeasles, Mumps, RubellaRohit KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Zoonotic and Vector Borne DiseasesDocument4 pagesZoonotic and Vector Borne DiseasesSupipi GamagePas encore d'évaluation
- Measles, Mumps, Rubella - MeaslesDocument5 pagesMeasles, Mumps, Rubella - MeaslesRohit KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Gauxy ) )Document54 pagesGauxy ) )Gauxy AromboPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 112 - Covid19Document2 pagesNCM 112 - Covid19Cailah Sofia SelausoPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal ClubDocument16 pagesJournal ClubArianna BetancourtPas encore d'évaluation
- (PARA) 2.05 - Lung Flukes - Dr. AlvaradoDocument4 pages(PARA) 2.05 - Lung Flukes - Dr. AlvaradoMarlon BauagPas encore d'évaluation
- MeaslesDocument58 pagesMeaslesDr.P.NatarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Geron-Ppt - 20231206 131738 0000Document29 pagesGeron-Ppt - 20231206 131738 0000Potato TomatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Positive Rod of Medical Imortance IIDocument36 pagesGram Positive Rod of Medical Imortance IIJoeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dengue PampletDocument2 pagesDengue Pampletemme77Pas encore d'évaluation
- MalariaDocument3 pagesMalariaAlexander ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- H1N1Document2 pagesH1N1shelayPas encore d'évaluation
- (16b) Togaviridae, FlaviviridaeDocument44 pages(16b) Togaviridae, FlaviviridaeFarrah BenoitPas encore d'évaluation
- Communicable DiseaseDocument32 pagesCommunicable Diseasekimberly shaynePas encore d'évaluation
- Rubella: Prepared and Presented by Ibrahim Ali Assiri 439106123Document21 pagesRubella: Prepared and Presented by Ibrahim Ali Assiri 439106123عادل حكميPas encore d'évaluation
- Paramyxovirus LecDocument25 pagesParamyxovirus Lecapi-19969058Pas encore d'évaluation
- BBB - Respi&gi ReportsDocument11 pagesBBB - Respi&gi ReportsshesahPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 109Document18 pagesNCM 109Grace Jane HannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Pox PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Pox PDFAkeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Com +Nursing+Care+Plan+Chicken+PoxDocument2 pagesCom +Nursing+Care+Plan+Chicken+PoxDahl Obañana Erojo100% (1)
- Micro Bio Disease ListDocument168 pagesMicro Bio Disease Listspiff spacemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 05 - 06Document68 pagesLecture 05 - 06Sami ArmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.4.1-Infectious and Non-Infectious DiseasesDocument2 pages2.4.1-Infectious and Non-Infectious DiseasesCHIA YIN MEIPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood and Tissue Protozoa (Con't) : DR - Mehru Nisha Mehrunisha@unikl - Edu.myDocument35 pagesBlood and Tissue Protozoa (Con't) : DR - Mehru Nisha Mehrunisha@unikl - Edu.myNida RidzuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Dr. Shahrul Rahman, SP - PD, FINASIMDocument46 pagesDr. Dr. Shahrul Rahman, SP - PD, FINASIMatikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Q3 HEALTH 8 WK1 LESSON 1 Disease Prevention and Control CommunicableDocument35 pagesQ3 HEALTH 8 WK1 LESSON 1 Disease Prevention and Control CommunicableJaeda EuclidPas encore d'évaluation
- Malaria 141112210953 Conversion Gate02Document33 pagesMalaria 141112210953 Conversion Gate02shubham vermaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCN Infectious Disorders PDFDocument14 pagesMCN Infectious Disorders PDFcalliemozartPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology MidtermDocument31 pagesPharmacology MidtermJohn MajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Arciaga, FG-ParaSGD 063021Document4 pagesArciaga, FG-ParaSGD 063021FG ArciagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Communicable DiseasesDocument32 pagesCommunicable DiseasesRobin Llemos100% (1)
- HASS BLK DeathDocument12 pagesHASS BLK Deathrn8cyjv4jhPas encore d'évaluation
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Measles: Department of Health & Human Services It's Not Just A Little Rash Find A VaccineDocument2 pagesMeasles: Department of Health & Human Services It's Not Just A Little Rash Find A VaccineFatmah Sarah CornellPas encore d'évaluation
- FINALS - Microbial Infections of The BloodDocument31 pagesFINALS - Microbial Infections of The BloodKate CortinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cause Agent Type of Agent MOT Signs and Symptoms Prevention and Control Treatment TuberculosisDocument6 pagesCause Agent Type of Agent MOT Signs and Symptoms Prevention and Control Treatment Tuberculosisvanessa patayonPas encore d'évaluation
- 005 Jennings Clinical DermDocument21 pages005 Jennings Clinical Dermshadhana sivakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument18 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumoniaمصطفى محمد جواد كاظمPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.chest and Lower Respiratory Tract DisordersDocument8 pages7.chest and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaePas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Viruses 2Document28 pagesDNA Viruses 2sairahhannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument6 pagesHuman Health and DiseaseSunil GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Viral Infec - Part 2Document13 pagesCommon Viral Infec - Part 2d99452727Pas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Medicine Table SummaryDocument31 pagesInternal Medicine Table SummaryShazaan Nadeem100% (1)
- RNA VirusesDocument143 pagesRNA VirusesCourtny Lenz Maygay GapaPas encore d'évaluation
- CD 1Document5 pagesCD 1Iriah Mara100% (1)
- Metazoa A ReviewerDocument4 pagesMetazoa A ReviewerMJ LomuntadPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Chapter 22 The Female Genital TractDocument59 pagesPDF Chapter 22 The Female Genital Tractsmian08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Paru Azham HandoutDocument11 pagesPathology Paru Azham HandoutKiky Martha A.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Demam Ruam: Della Rizki Anggilia 18105Document40 pagesDemam Ruam: Della Rizki Anggilia 18105Della Rizki AnggiliaPas encore d'évaluation
- So Much ItchingDocument14 pagesSo Much ItchingEmily EresumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Guide to Dysphonia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Dysphonia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Pathogens (Revised) - Courtney ChinnDocument1 pageSkin Pathogens (Revised) - Courtney ChinnMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionDocument1 pagePathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Jackie Tasarz-Liver Pathogens RevisedDocument1 pageJackie Tasarz-Liver Pathogens RevisedMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens of The Female Reproductice Site Erika HuertaDocument1 pagePathogens of The Female Reproductice Site Erika HuertaMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens of The Eye Revised - Jenna TuckerDocument1 pagePathogens of The Eye Revised - Jenna TuckerMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Infections of The Liver Revised - Nick GriffinDocument1 pageInfections of The Liver Revised - Nick GriffinMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Ear Infections - Fatima Khalid - Revised VersionDocument1 pageEar Infections - Fatima Khalid - Revised VersionMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- The Eye - Jenna TuckerDocument1 pageThe Eye - Jenna TuckerjktuckerPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens of The Vagina-CitationsDocument1 pagePathogens of The Vagina-CitationsMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Jesse Wackerbarth - CNS Pathogens RevisedDocument1 pageJesse Wackerbarth - CNS Pathogens RevisedMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens in The Lungs-Jeffrey DelgadilloDocument1 pagePathogens in The Lungs-Jeffrey DelgadilloMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Wylie, ClareDocument1 pageWylie, ClareMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Savannah Whitington: Your Brain On DrugsDocument1 pageSavannah Whitington: Your Brain On DrugsMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver PathogensDocument1 pageLiver PathogensMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Emily Scroggs Microorganisms Affecting The KidneyDocument1 pageEmily Scroggs Microorganisms Affecting The KidneyMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Eye Infections by Allison BakerDocument1 pageEye Infections by Allison BakerMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens of The Female Reproductive Site, Erika HuertaDocument1 pagePathogens of The Female Reproductive Site, Erika HuertaMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens of The Lungs - Michelle CumbaaDocument1 pagePathogens of The Lungs - Michelle CumbaaMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- The Urogenital Tract-Maija SwansonDocument1 pageThe Urogenital Tract-Maija Swansonmswanson5975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens in The Oral CavityDocument1 pagePathogens in The Oral CavityMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver PathogensDocument1 pageLiver PathogensMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowDocument1 pagePathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens of The Oral Cavity - Karisma ManciasDocument1 pagePathogens of The Oral Cavity - Karisma ManciasMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- CNS Pathogens-Jesse WackerbarthDocument1 pageCNS Pathogens-Jesse WackerbarthMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaby Saenz - The MeningesDocument1 pageGaby Saenz - The MeningesMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaby Saenz - Works Cited For Meninges PosterDocument2 pagesGaby Saenz - Works Cited For Meninges PosterMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie EspinosaDocument1 pagePathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosaannie_espinosa_2Pas encore d'évaluation
- EarInfections FatimaKhalidDocument1 pageEarInfections FatimaKhalidMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinDocument1 pagePathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinMicroposterPas encore d'évaluation
- Prevalence of Dengue Viral Infections Among Febrile Patients in Mombasa County, KenyaDocument95 pagesPrevalence of Dengue Viral Infections Among Febrile Patients in Mombasa County, KenyaMuhammad AyazPas encore d'évaluation
- Skill Checklist Removing Medication From An AmpuleDocument2 pagesSkill Checklist Removing Medication From An AmpuleAsep BageurPas encore d'évaluation
- Vitamin B 12 Fo Late DeficiencyDocument14 pagesVitamin B 12 Fo Late DeficiencyAnghelo Aldair Velásquez CarrilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Benefits of BreastfeedingDocument5 pagesBenefits of BreastfeedingAngelicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPauline AñesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrotic Syndrome - Nelson+JournalDocument11 pagesNephrotic Syndrome - Nelson+JournaljeanecalvoPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Health Promotion Throughout The Life Span 9th Edition by EdelmanDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Health Promotion Throughout The Life Span 9th Edition by EdelmanHeriberto Murray100% (32)
- DSDRelease Medical v1 EUDocument2 pagesDSDRelease Medical v1 EUTania FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Stages in Behavior ChangeDocument4 pagesStages in Behavior ChangeArbab Usman KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Headaches HomeopathyDocument30 pagesHeadaches HomeopathyRodica GheorghiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Profile: Doris A. MendozaDocument4 pagesProfile: Doris A. MendozaGerarld Immanuel KairupanPas encore d'évaluation
- Stroke 2Document8 pagesStroke 2Jarmy BjPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaastu and CancerDocument2 pagesVaastu and CancervivekpatelbiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Blood Picture: Master Degree in Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University DR - Enas AzzazyDocument2 pagesComplete Blood Picture: Master Degree in Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University DR - Enas AzzazyMohamed BadraPas encore d'évaluation
- Vibrio Cholerae PosterDocument1 pageVibrio Cholerae PosterStela MonkPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Background, Pathophysiology, EtiologyDocument5 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology'Riku' Pratiwie TunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Esophageal Cancer PDFDocument16 pagesEsophageal Cancer PDFAJ AYPas encore d'évaluation
- COPD2019Document9 pagesCOPD2019ClintonPas encore d'évaluation
- Brancati - The Art of Pimping and Other ArticlesDocument10 pagesBrancati - The Art of Pimping and Other ArticlesJavid MoslehiPas encore d'évaluation
- DR - Firas Mahmoud Abu Samra: Curriculum Vitae ofDocument16 pagesDR - Firas Mahmoud Abu Samra: Curriculum Vitae offerasallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthognathic SurgeryDocument72 pagesOrthognathic Surgeryrurinawangsari0% (1)
- Silicosis PublicationDocument12 pagesSilicosis PublicationRiddhi JhanwarPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Rebuildermedical.ca Manuals 2407 Instructions WetDocument7 pagesWWW - Rebuildermedical.ca Manuals 2407 Instructions WetGabriel MatthewsPas encore d'évaluation
- Alexandra Mcfall - Annotated BibliographyDocument6 pagesAlexandra Mcfall - Annotated Bibliographyapi-549246948Pas encore d'évaluation
- Florida Physician Database - Areas Includes Gainesville, Orlando and JacksonvilleDocument20 pagesFlorida Physician Database - Areas Includes Gainesville, Orlando and JacksonvilleBhuvana RajendranPas encore d'évaluation
- Vadim SentchoukDocument42 pagesVadim SentchoukAnil KapuPas encore d'évaluation
- J of Ultrasound Medicine 2022 Demi New International GuidelinesDocument36 pagesJ of Ultrasound Medicine 2022 Demi New International Guidelineslilo serranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec. Deep CariesDocument47 pagesLec. Deep CariesMaria EvergardenPas encore d'évaluation