Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Networking
Transféré par
Poorva KembhaviDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Networking
Transféré par
Poorva KembhaviDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NETWORKING
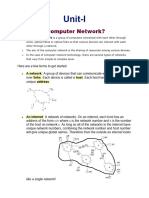
What is Networking? DefinitionDefinition- A Computer Network is a system that connects computers via communications media so that data can be transmitted among them.
Computer Networks are important to modern organization for many reasons: 1)Networks enable companies to share hardware, computer applications and data across the organization and among the organization. 2)Networks make it possible for geographically dispersed employees and work groups to share documents and ideas. 3)Thus Networked Computer systems enable organizations to be more flexible, so that they can adapt to the rapidly changing business conditions.
Benefits of Networks : 1)Sharing of peripheral devices - Peripheral devices such as printers, disk drives can be expensive. So, to justify their purchase, management wants to maximize their use. Usually best way to do this is to connect the peripheral device to a network serving several computer users. 2)Sharing of Programs In most organizations, people use the same software. It is less expensive for a company to buy one word processing program that serves many employees than to buy a separate word processing program for each employee.
3)Sharing of data In most organizations, people use the same information. Therefore if all employees have access to same data stored on a shared storage device, the organization can save money and serious problems. If each employee has a separate machine, some employees may update customer addresses, while others remain ignorant of the changes. Updating information on a shared server is much easier than updating every users individual system. 4) Better Communication With email, everyone on a network can easily keep others posted about important information.
5) Security of information Important data would be backed up or duplicated on a networked storage device shared by others. 6)Access to databases Networks enable users to tap into numerous databases, whether private company databases or public databases available online through the internet.
LAN (Local Area Network): A Local Area Network connects computers and devices in a limited geographic area, such as one office, one building, or a group of buildings close together (for instance a college campus).
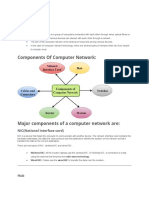
COMPONENTS OF LAN: A file server. A number of client machines called nodes. Wired or wireless communications media that connect devices on a network. Network interface cards (NIC), which are special adapters that link an individual device to the communications medium. NIC enable a computer to send and receive messages over a cable network.
Software to control LAN activities also called Network Operating System. NOS supports access by multiple users and provides recognition to users based on terminal identification and passwords. Depending on whether LAN is client/server or peer-to-peer, peer-tothe operating system may be stored on file server, on each of the microcomputer on the network or on a combination of both. Eg. Novell Netware, Microsoft Windows NT/2000, Unix and Linux.
ABOUT Server: The LAN file server is very crucial, for it stores various software and data files of the network. The server determines who gets access to which file and in which sequence. Servers can be powerful microcomputers, minicomputers or mainframes. The server houses the LANs NOS. Different servers may be used to manage various tasks: File Server : Stores files and programs shared by users on a LAN.
Database Server: Database server in a LAN stores data and not programs. A Print server controls one or more printers and stores print image output from all microcomputers on the system. Web Server stores web pages. Mail server manages email. TYPES OF LAN: 1. CLIENT/SERVER LAN : A client/server LAN consists of clients, which are microcomputers that request data and servers which are computers used to supply data.
PEER-TOPEER-TO-PEER LAN: In a peer-to-peer LAN, all microcomputers on peer-tothe network communicate directly with one another without relying on a server. Every computer can share files and peripherals with all other computers on the network. Peer-toPeer-topeer networks are less expensive than clientclientserver networks and work effectively upto 25 computers. Beyond that, they slow down.
OTHER COMPONENTS OF LAN : 1. ROUTER : Router is a special computer that directs messages when several networks are connected together. 2. BRIDGE : A bridge is a processor that connects same type of networks. eg. Two LANs can be connected to form a larger network. 3. GATEWAY : A gateway is a communication processor that connects dissimilar networks. Eg. Between a LAN and a WAN or between two LANs based on different NOS. 4. HUB : Hub is a place of convergence where data arrives from one or more directions and is forwarded out in one or more other directions. A hub contains multiple ports. When data arrives at a port it is copied to other ports so that all segments of the network can have all the data.
TOPOLOGY OF LAN : A logical layout or shape of network is called a topology. BUS NETWORK : In a bus network all the computers or nodes are connected to a single wire or cable which has two endpoints.Each communication device on the network transmits electronic messages to other devices. If some of those messages collide, the sending device waits and then tries to transmit again. Advantage: Can be organized as a client/server or peer-to-peer network. peer-to-
Disadvantages : An extra software is required to avoid collisions between data. If a connection in a BUS is broken the entire network may stop working. RING NETWORK: A ring network is one in which all microcomputers and other communication devices are connected in a continuous loop. There are no endpoints. There is no central server. The electronic messages are passed around the ring until they reach the right destination. Advantage: The messages flow in only one direction. Thus, there is no danger of collision. Disadvantage: If a connection is broken the entire network stops.
STAR NETWORK : A star network is one in which all microcomputers and other communication devices are directly connected to a central server. Electronic messages are routed through the central hub to their destination. Advantage: Hub prevents collision between messages. If a connection between any communication device and hub breaks, the rest of the devices on the network will continue operating. Disadvantage :If the hub stops the entire network stops
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lesson 1 Introduction To NetworkingDocument14 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To NetworkingKevin SambuPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Communication &network: 2.2. Data Topologies 2.3. Data Switching 2.4. Types of NetworkingDocument13 pagesData Communication &network: 2.2. Data Topologies 2.3. Data Switching 2.4. Types of NetworkingAbdiaziz QabilePas encore d'évaluation
- A Computer NetworkDocument12 pagesA Computer Networkosman100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document29 pagesChapter 2hariye2225Pas encore d'évaluation
- Data Communication: Introduction To Information TechnologyDocument11 pagesData Communication: Introduction To Information TechnologychloePas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Network?Document39 pagesWhat Is A Network?Manisundaram BalakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Everything You Need to Know About Computer NetworksDocument31 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Computer NetworksRoman clashPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Network & Data Communication f3Document16 pagesComputer Network & Data Communication f3ayissi jeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking ReviewerDocument69 pagesNetworking ReviewerBonbert LascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Selective CourseDocument51 pagesSelective CoursewilliamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Computer NetworkingDocument17 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Computer Networkingmufasahussein254Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computr NetworkingDocument204 pagesComputr Networkingbiswadeepbasak0212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 7 - Dela Cruz, Tehillah Mae ADocument17 pagesActivity 7 - Dela Cruz, Tehillah Mae ATehillah CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking Fundamentals: Selected ConceptsDocument48 pagesNetworking Fundamentals: Selected ConceptsRoy BernardPas encore d'évaluation
- CIT722 SUMMARY FROM NOUNGEEKS.COMDocument26 pagesCIT722 SUMMARY FROM NOUNGEEKS.COMBrian CopperPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.2 Computer Network & Data CommunicationDocument26 pages4.2 Computer Network & Data CommunicationMaxim TawoutiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 BBA VDocument56 pagesUnit 1 BBA Vaakanshatyagi030303Pas encore d'évaluation
- Networking EssentialsDocument16 pagesNetworking EssentialsSujin Sathianesan SPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesComputer NetworksFarai Willias MasochaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ambo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceDocument30 pagesAmbo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Introduction To Computer NetworkingDocument53 pages1 Introduction To Computer Networkingabel emmanuel100% (1)
- CN Unit 1Document28 pagesCN Unit 1Aman PathakPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER FOUR Networks and Cloud ComputingDocument24 pagesCHAPTER FOUR Networks and Cloud ComputingEndalkachew EmarePas encore d'évaluation
- LESSON 1 INTRODUCTION TO DATA COMM COMPUTER NETWORKsDocument17 pagesLESSON 1 INTRODUCTION TO DATA COMM COMPUTER NETWORKsteddykigiaPas encore d'évaluation
- NetworkingDocument16 pagesNetworkingAmit ThubePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 7A: NetworkDocument31 pagesChapter - 7A: NetworkRoman clashPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Networking NotesDocument28 pagesComputer Networking NotesAnujPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer 8T1 Tutorial 2021 2022Document21 pagesComputer 8T1 Tutorial 2021 2022FaheemPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking 1 ReviewerDocument46 pagesNetworking 1 ReviewerJoseph LapsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ict Cs1 Las q4 Week 1Document5 pagesIct Cs1 Las q4 Week 1Louise QuiazonPas encore d'évaluation
- DCN NOTES For COURSE FILEDocument13 pagesDCN NOTES For COURSE FILEÃmît TíwârìPas encore d'évaluation
- A Computer NetworkDocument11 pagesA Computer NetworkBridget DindiPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking Essentials PDFDocument16 pagesNetworking Essentials PDFfatospeci100% (5)
- PT Lesson1 CompNetworkDocument16 pagesPT Lesson1 CompNetworkbench SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Network: IBPS SO (IT) Exam 2017Document19 pagesComputer Network: IBPS SO (IT) Exam 2017Narsimha Charya ManthangodePas encore d'évaluation
- Components of Computer NetworkDocument4 pagesComponents of Computer NetworkRamanuj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Report (Networking)Document17 pagesSeminar Report (Networking)jbhamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Introduction Structure:: 1.0 ObjectivesDocument19 pagesUnit 1 Introduction Structure:: 1.0 ObjectivesMohamed HajiPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPUTER NETWORKING TOPICS</TITLEDocument46 pagesCOMPUTER NETWORKING TOPICS</TITLEColonelle CortezPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Comm N NTWRKDocument13 pagesData Comm N NTWRKBishakha SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Four Computer Networks and Internet: 4.1 Introduction To NetworkingDocument9 pagesChapter Four Computer Networks and Internet: 4.1 Introduction To NetworkingAsaye TesfaPas encore d'évaluation
- NETWORKINGDocument60 pagesNETWORKINGkurib38Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit1 (Chapter 2) INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKINGDocument17 pagesUnit1 (Chapter 2) INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKINGVinutha SanthoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Network & Data Communication Class NotesDocument24 pagesComputer Network & Data Communication Class NotesRonic DakPas encore d'évaluation
- Accowenting and FinanceDocument24 pagesAccowenting and FinanceSwete SelamPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer NetworkingDocument57 pagesComputer Networkingsomtechm100% (1)
- Lesson 25 Network FundamentalsDocument5 pagesLesson 25 Network FundamentalsAssumpta Minette BurgosPas encore d'évaluation
- CN Unit1Document33 pagesCN Unit1Gaytri HogalePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Computer Science & ProgrammingDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Computer Science & ProgrammingZaryab BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Communication and NetworkDocument11 pagesData Communication and NetworkvanditaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 13Document4 pagesLecture 13api-3723265Pas encore d'évaluation
- Determine Best Fit Information SheetDocument101 pagesDetermine Best Fit Information Sheetmuluken100% (2)
- Computer Network TutorialDocument33 pagesComputer Network TutorialAnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Fit TopologyDocument191 pagesBest Fit TopologyBikila SeketaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1D'EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Computer Networking Beginners Guide: An Introduction on Wireless Technology and Systems Security to Pass CCNA Exam, With a Hint of Linux Programming and Command LineD'EverandComputer Networking Beginners Guide: An Introduction on Wireless Technology and Systems Security to Pass CCNA Exam, With a Hint of Linux Programming and Command LinePas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Knowledge Guide For All Competitive ExamsD'EverandComputer Knowledge Guide For All Competitive ExamsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (4)
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyD'EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Quality and Its Importance: Marieke Guy Ukoln M.Guy@ukoln - Ac.ukDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Quality and Its Importance: Marieke Guy Ukoln M.Guy@ukoln - Ac.ukAbhishek DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Organisation Structure OverviewDocument24 pagesOrganisation Structure OverviewansmanstudiesgmailcoPas encore d'évaluation
- IT For CRMDocument62 pagesIT For CRMPoorva KembhaviPas encore d'évaluation
- PEST AnalysisDocument3 pagesPEST Analysisgekk0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To ManagementDocument27 pagesIntroduction To ManagementPoorva KembhaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Final PPT On Theory of Production IIIDocument22 pagesFinal PPT On Theory of Production IIIPoorva KembhaviPas encore d'évaluation
- 7b Terraform State LockingDocument2 pages7b Terraform State LockingTITAITOQQPas encore d'évaluation
- Rust cheat sheet basicsDocument2 pagesRust cheat sheet basicsfddf gfgfgPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple JavaDocument183 pagesSimple JavaNatalijaPas encore d'évaluation
- HIKVISION RAID ConfigurationDocument13 pagesHIKVISION RAID ConfigurationEmmanuel KAMANDAPas encore d'évaluation
- PX PX5 PX30 InstructionDocument10 pagesPX PX5 PX30 InstructionJake BloomPas encore d'évaluation
- Midteknologi Com Blog Mikrotik ScriptsDocument25 pagesMidteknologi Com Blog Mikrotik Scriptsakun youtubePas encore d'évaluation
- DRP TemplateDocument13 pagesDRP Templatemiloja99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 MCQDocument33 pagesChapter 4 MCQRoza MulukenPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Quick ConfigurationDocument102 pages04 Quick ConfigurationmarijuannePas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Hyperflex Hyperconverged Infrastructure All Flash Solution For Sap HanaDocument38 pagesCisco Hyperflex Hyperconverged Infrastructure All Flash Solution For Sap HanaUmAiR APas encore d'évaluation
- Auxillary Memory Organization by Sanjiv NambiarDocument26 pagesAuxillary Memory Organization by Sanjiv NambiaredaklavanPas encore d'évaluation
- (: 3.1 KHZ Channel) : NarrowbandDocument60 pages(: 3.1 KHZ Channel) : NarrowbandSaravanan PonnaiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structure by Naveen GargDocument584 pagesData Structure by Naveen GargBharat Arora100% (1)
- Netwrix Auditor For NetApp Quick Start GuideDocument31 pagesNetwrix Auditor For NetApp Quick Start GuidealimalraziPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating SystemDocument2 pagesOperating SystemDreamtech PressPas encore d'évaluation
- Coa Notes AktuDocument147 pagesCoa Notes AktuHappy KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 04 I CDocument93 pagesCH 04 I Cbalajinaik07Pas encore d'évaluation
- 0922 Phpmyadmin DocumentationDocument190 pages0922 Phpmyadmin DocumentationAli HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- LogDocument169 pagesLogMelPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Implementation of An AHB SRAM Memory Controller: ARM University ProgramDocument26 pagesDesign and Implementation of An AHB SRAM Memory Controller: ARM University ProgramVarshhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Run Java or .NET Apps on IaaS, PaaS or SaaSDocument174 pagesRun Java or .NET Apps on IaaS, PaaS or SaaSBaba RanchhordassPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structure Lab ManualDocument77 pagesData Structure Lab ManualkunalPas encore d'évaluation
- This Is A Bunch of KeysDocument5 pagesThis Is A Bunch of KeysJeffrey BarnesPas encore d'évaluation
- Client Chat LogDocument16 pagesClient Chat LogMateuszDrozdowskiDrozdośPas encore d'évaluation
- VTU Synopsis on QR CodeDocument2 pagesVTU Synopsis on QR CodeRajath KamathPas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle System Copy and Restoration in Less than 40 StepsDocument2 pagesOracle System Copy and Restoration in Less than 40 Stepsilyas2sapPas encore d'évaluation
- CCSZ r14.1 Administration GuideDocument359 pagesCCSZ r14.1 Administration Guideborisg3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures Questions For Class Test 2nd Semester BPUTDocument1 pageData Structures Questions For Class Test 2nd Semester BPUTBikash IndiaPas encore d'évaluation
- File AidDocument41 pagesFile Aidvijay reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Signal Modulation: Updated: 10/29/2014Document52 pagesSignal Modulation: Updated: 10/29/2014Jagat ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation