Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Remote Sensing
Transféré par
api-3705107100%(2)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (2 votes)
655 vues23 pagesEM radiation is energy capable of transmission through empty space in a plane harmonic wave pattern at the velocity (c) of light. EM occurs as a continuum of wavelengths and frequencies from short wavelength, high-frequency cosmic waves to longwavelength, low-frequency radio waves. A spectral scanner Can capture EM radiation outside of visible light.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentEM radiation is energy capable of transmission through empty space in a plane harmonic wave pattern at the velocity (c) of light. EM occurs as a continuum of wavelengths and frequencies from short wavelength, high-frequency cosmic waves to longwavelength, low-frequency radio waves. A spectral scanner Can capture EM radiation outside of visible light.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(2)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (2 votes)
655 vues23 pagesRemote Sensing
Transféré par
api-3705107EM radiation is energy capable of transmission through empty space in a plane harmonic wave pattern at the velocity (c) of light. EM occurs as a continuum of wavelengths and frequencies from short wavelength, high-frequency cosmic waves to longwavelength, low-frequency radio waves. A spectral scanner Can capture EM radiation outside of visible light.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 23
Chapter 8-
Remote Sensing and GIS
Integration
Concepts and Techniques of
Geographic Information Systems,
2e
by C.P Lo and Albert K.W. Yeung
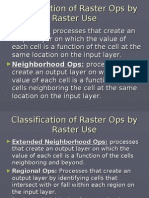
Definition
► Theacquisition of information about
an object without physical contact.
► Includesgathering and processing of
information about the Earth’s
environment through the use of
photographs and related data acquired
from an aircraft or satellite.
Remote Sensing
► Can be digital or analog
► Theterm “photograph” usually associated
with analog, while imagery from a spectral
scanner.
► Spectralscanners usually operate with EM
radiation outside of visible light.
► Easyto use with and update raster GIS
layers.
What type of data do you
get?
► Synoptic maps
► Land cover
► Planimetric location
► Elevation
► Spectral Signature
► Chlorophyll absorption characteristics
► Biomass
► Moisture content
► Temperature
► Roughness
Principles of Electromagnetic
Remote Sensing
► Record data of reflected or emitted electromagnetic energy.
► EM radiation is energy capable of transmission through empty
space in a plane harmonic wave pattern at the velocity (C) of
light.
► The frequency of oscillation (f) is related to wavelength (λ) by
c = λf
► EM occurs as a continuum of wavelengths and frequencies
from short wavelength, high-frequency cosmic waves to long-
wavelength, low-frequency radio waves (aka
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM)
Figure 8.1
Figure 8.3
Principles of Electromagnetic Remote
Sensing
► EM from the sun is seriously attenuated by
passage through the atmosphere, which
particles scatter or absorb certain
wavelengths.
► Scattering
decreases with increase in
wavelength.
► Wavelengths shorter than 0.3 micrometers
are completely absorbed by ozone.
► Thereexists “transmission windows,”
which are exploited for imagery remote
sensing.
Figure 8.4
► Once EM energy reaches the surface, it is further
modified through interacting with features on the
Earth’s surface (reflected, refracted, transmitted,
or absorbed).
► Absorbed energy will usually be emitted in a
different form.
► Reflection depends on surface material and
roughness.
► A rougher surface will give rise to more diffused
and brighter reflection.
► Smooth surfaces look dark because they reflect
away from sensor.
► Hot objects emit more IR than cool, through the
“windows”
► All surface objects have their own spectral
signature-allowing it to be characterized and
mapped.
Remote Sensing System
Classifications
► Passive and active.
► Passive = analog or digital
► Active = Synthetic Aperture radar and
others
► Can also be based on aerial or space
based systems
Imaging Characteristics
► Remote sensing imaging systems
possess four major resolution
characteristics that determine the type
of geographic data that can be
detected.
► Spatial resolution
► Spectral resolution
► Radiometric resolution
► Temporal resolution
Plate 8.1
Plate 8.2
Figure 8.6
Imaging Characteristics
► Remote sensing imaging systems
possess four major resolution
characteristics that determine the
type of geographic data that can be
detected.
► Spatial resolution
► Spectral resolution
► Radiometric resolution
► Temporal resolution
Spatial Resolution
► Most important
► Ability of system to record detail.
► Analog = photograph sharpness; up to 60
lp/mm.
► The number of line pairs per millimeter does
not take into account the scale of the aerial
photo, GR combines scale and resolution
GR = W*SF
1:10,000 scale photo at 60 lp/mm =0.17 m
Spatial Resolution for
Scanners
► Measured in instantaneous field of
view (IFOV) or the angle through which
the detector is sensitive to energy.
► D = H*B; D = ground dimension
(resolution); H = height of platform; B
= IFOV in milliradians.
► SPOT = 10 m resolution
► IKONOS-2 = 1 m resolution
► Landsat = 15 m.
Spectral Resolution
► Two things considered here.
► Number of Wavelength Bands
► Wavelength of Bands
► More bans with smaller wavelengths
means higher resolution.
Radiometric Resolution
► The smallest difference in radiant
energy that can be detected by a
sensor.
► Inversely proportional to contrast of
film=film can pick up more subtle
changes
► For digital images, number of discrete
levels into which a signal may be
divided, 6 bit vs. 8 bit, etc.
Temporal Resolution
► Frequency data is collected.
► Clouds play a role usually.
► Landsats 1-3 capture the Earth every
18 days
► Landsats 4-7 capture the Earth every
16 days = better temporal resolution
► Import for many studies like
vegetation growth.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Swine Odor FinDocument7 pagesSwine Odor Finapi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9bDocument15 pagesChapter 9bapi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9CDocument11 pagesChapter 9Capi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arc SceneDocument8 pagesArc Sceneapi-3705107100% (2)
- Projection QuirksDocument15 pagesProjection Quirksapi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6aDocument9 pagesChapter 6aapi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9aDocument12 pagesChapter 9aapi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5bDocument39 pagesChapter 5bapi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Meteorite ExerciseDocument9 pagesMeteorite Exerciseapi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Mosaic DEMs in ArcGISDocument2 pagesHow To Mosaic DEMs in ArcGISapi-3705107100% (1)
- Intro Chapter 5 ADocument18 pagesIntro Chapter 5 Aapi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3bDocument50 pagesChapter 3bapi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- First DayDocument14 pagesFirst Dayapi-3705107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Foundations of Spectroscopy 11Document1 pageFoundations of Spectroscopy 11PhiPhiPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM C597 (Velocidad Del Pulso Atraves Del Concreto)Document2 pagesASTM C597 (Velocidad Del Pulso Atraves Del Concreto)legna92Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Solid State PhysicsDocument80 pagesIntroduction To Solid State Physics林忠佑Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 25.9 - Doppler EffectDocument21 pagesCh. 25.9 - Doppler EffectNaveed AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocument10 pagesSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Speaker Lab Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSpeaker Lab Lesson PlanKayla RhodesPas encore d'évaluation
- 0625 w14 QP 31Document20 pages0625 w14 QP 31Haider AliPas encore d'évaluation
- WS - Igcse 9 - (Physics 9) - 2021 - 22Document9 pagesWS - Igcse 9 - (Physics 9) - 2021 - 22Karan PuriPas encore d'évaluation
- STE Electronics10 Q3 Mod2 Lesson1-SignalControl, ComponentsandApplicationsofRadioDocument16 pagesSTE Electronics10 Q3 Mod2 Lesson1-SignalControl, ComponentsandApplicationsofRadioMenchu CanlasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ripple TankDocument3 pagesRipple Tankphydotsi100% (1)
- Physics - Exam Preparation Guide - K.A. Tsokos - First Edition - Cambridge 2012Document226 pagesPhysics - Exam Preparation Guide - K.A. Tsokos - First Edition - Cambridge 2012anannyaa100% (3)
- Commercial Pilot Entrance Syllabus: IGRUA CPL Test Syllabus For MathematicsDocument3 pagesCommercial Pilot Entrance Syllabus: IGRUA CPL Test Syllabus For MathematicsAbhishek Bera100% (1)
- Wave Tranquility On The Breakwater Design Consideration in The Pangandaran PortDocument10 pagesWave Tranquility On The Breakwater Design Consideration in The Pangandaran PortEka Oktariyanto NugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Transmission and Wave Induced Currents Around A Reef BreakwaterDocument14 pagesWave Transmission and Wave Induced Currents Around A Reef BreakwaterpsuvarnasPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4.5 Formative Answer KeyDocument1 pageTopic 4.5 Formative Answer Key이수연Pas encore d'évaluation
- Btech Computer SC Engg 19 20Document138 pagesBtech Computer SC Engg 19 20Divyanshu GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 7 TG SCIENCE 3rd Quarter PDFDocument54 pagesGrade 7 TG SCIENCE 3rd Quarter PDFValkyrie delos Santos0% (2)
- Exam UniselDocument10 pagesExam Uniselnadiajky2686Pas encore d'évaluation
- General Physics SHS Quarter 2 Module 5Document28 pagesGeneral Physics SHS Quarter 2 Module 5Sofia PerniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 2 Wave On A StringDocument7 pagesLab 2 Wave On A StringMavy KylinePas encore d'évaluation
- Rheed & Leed: Presented By-Mohammad Rameez Devika LaishramDocument42 pagesRheed & Leed: Presented By-Mohammad Rameez Devika LaishramMohammad RameezPas encore d'évaluation
- Antennas and Wave PropagationDocument3 pagesAntennas and Wave PropagationArockia RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tibebu Hunegn Birhane - Blast Analysis of Railway Masonry BridgesDocument134 pagesTibebu Hunegn Birhane - Blast Analysis of Railway Masonry BridgesFraosmPas encore d'évaluation
- CIE IGCSE Physics 3rd Edition Chapter 1Document27 pagesCIE IGCSE Physics 3rd Edition Chapter 1MELODY CHEN100% (1)
- Sound Waves: By: British Bunnies/Group 3Document7 pagesSound Waves: By: British Bunnies/Group 3milesPas encore d'évaluation
- U4AOS1 - How Can Waves Explain The Behaviour of LightDocument55 pagesU4AOS1 - How Can Waves Explain The Behaviour of LightPraveen RavichandranPas encore d'évaluation
- NONWOVEN - Vinay Kumar MidhaDocument11 pagesNONWOVEN - Vinay Kumar Midhaglobal-marketin8184Pas encore d'évaluation
- BS en 10205-2016Document30 pagesBS en 10205-2016Sainath Amuda100% (1)
- Design of An Inexpensive PVC Shock Tube For Educational UseDocument118 pagesDesign of An Inexpensive PVC Shock Tube For Educational Useji.lang.vuPas encore d'évaluation