Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Day 4
Transféré par
api-37596460 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
112 vues23 pagesPlants may be classified according to the presence or absence of a part. Flowers contains pollen and tiny egg called the ovules and serve as the reproductive part of most plants. Flowering plants form seeds which are pollinated by wind, water, animals, birds, insects and even man.
Description originale:
Titre original
day4
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentPlants may be classified according to the presence or absence of a part. Flowers contains pollen and tiny egg called the ovules and serve as the reproductive part of most plants. Flowering plants form seeds which are pollinated by wind, water, animals, birds, insects and even man.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
112 vues23 pagesDay 4
Transféré par
api-3759646Plants may be classified according to the presence or absence of a part. Flowers contains pollen and tiny egg called the ovules and serve as the reproductive part of most plants. Flowering plants form seeds which are pollinated by wind, water, animals, birds, insects and even man.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 23
At the end of the lesson,
the pupils are expected to:
1. classify plants
2. describe plants with each
characteristic.
3. differentiate flowering from
non-flowering plants.
Observe the pictures below…
Grass
Gumamela Bougainvill
ea
Club Moss Pine Tree
Fern
-Do these plants have similar
characteristics?
-How do they differ?
-Which plants bear flowers?
-Which plants do not bear flower?
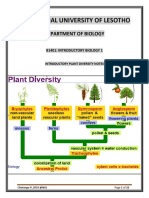
Plants may be classified
according to the presence or
absence of a part. For
example, plants may be
flowering or non- flowering.
There flowers contains pollen
and tiny egg called the ovules and
serve as the reproductive part of
most plants.
These plants may bear brightly
colored flowers to attract insects
and may also release pleasant
odors.
Gumamela,
bougainvillea,and grass have
similar parts. They have roots,
stems, leaves and flowers. They
are called flowering plants.
Flowering plants form
seeds which come from
flowers. Seeds are pollinated
by wind, water, animals,
birds, insects and even man.
Gumamela and
bougainvillea are pollinated by
insects such as butterflies and
bees. They have bright-colored
petals to attract these insects.
Grass on the other hand,
bears flowers, too. However ,
they produce dull colored
flowers that lack scent. Their
seeds are carried by the wind.
Flowering plants
(Angiosperms) develop
roots, stems, and leaves.
They have an efficient
vascular or transport
system for carrying food
and water.
The vascular system is
composed of tiny tubes that run
through the plant. These tubes
carry nutrients and water to the
plant.
Flowering plants produce
seeds. These seed- producing
plants are further divided
into:
1. monocotyledon
(monocot) or
2. dicotyledon (dicot)
This division is based on the
number of seeds cotyledon.
A corn plant The avocado
is a plant is a dicot.
monocot.
There are simple green
plants on Earth. They do not
have any vascular tissues.
They usually attach
themselves to rocks. These
plants reproduce through
spores that are dispersed in
the wind.
Ferns have roots, leaves and
stems. Their leaves are popularly
known as fronds. On the underside
of each frond, dark cases called
sori are found. Sori contains many
tiny spores. These are usually
blown away by the wind when
they mature.
Pine trees belong to
the cone-bearing plants
because they produce
cones. Cones carry the
male and the female
spores. When these two
sex cells unite, they form
new plants. They have
well developed roots,
stems and needle-shaped
leaves. These plants do
Why is there a
need to group
plants?
Grouping plants according
to their common characteristics
make studies on them easier. In
our lesson, we have classified
some common characteristics
by which plants may be
grouped.
Plants may be grouped
according to the presence or
formation of flowers, seed, true
roots, and stems.
Flowering plants usually bear
flowers, seeds and in most cases
fruits. Some non-flowering
plants produce cones that carry
spores.
Scientist classify or group
plants so that there is a
systematic way of identifying
them. This is important in
research and in their continuous
search for new plants. Anybody
who possesses the basic
knowledge of how plants are
grouped would find it easy to
classify a new found plant.
Classification of Plants. Available:
http://www.theseedsite.co.uk/class.html
lesson plan in how to classify plants. Available:
http://www.thesolutionsite.com/lpnew/lesson/100
1/classifyingplants.html
Non-flowering Seed Plant.
Available:http://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/hall_tour/sp
ectrum/8. html
Llarinas Jose F. and Pelobello Emily M., (1999). Into
the Future: Science and Health, Textbook for
Science and Health for Grade V. Diwa
Scholastic Press Inc.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksD'EverandThe Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Flowering Plants: Life-Cycle of A Flowering PlantDocument5 pagesFlowering Plants: Life-Cycle of A Flowering Plantraunak sarafPas encore d'évaluation
- Flowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants : Knowing the Difference - Biology 3rd Grade | Children's Biology BooksD'EverandFlowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants : Knowing the Difference - Biology 3rd Grade | Children's Biology BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Q2 - W6 Science 5Document45 pagesQ2 - W6 Science 5Mac RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics of Plants: Sixth Grade Science ExperimentsD'EverandCharacteristics of Plants: Sixth Grade Science ExperimentsPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Flowers and Pine Trees Are Both Seed-Producing Plants.: How Does The Plant Reproduce and Make New Plants?Document4 pagesFlowers and Pine Trees Are Both Seed-Producing Plants.: How Does The Plant Reproduce and Make New Plants?Anchal ChadhaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th Grading Classification of PlantsDocument57 pages4th Grading Classification of PlantsAlea DuquePas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesNon-Flowering PlantsJimmy SerendipPas encore d'évaluation
- B5-Plant & Animal ClassificationDocument11 pagesB5-Plant & Animal ClassificationHarshaWakodkar100% (1)
- Plant ReproductionDocument62 pagesPlant ReproductionAdonis BesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Organoleptic Evaluation of The Different Parts of Plant (Flower, Fruits, and Seeds)Document13 pagesOrganoleptic Evaluation of The Different Parts of Plant (Flower, Fruits, and Seeds)Joanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Botany 2Document92 pagesBasic Botany 2Michael OduorPas encore d'évaluation
- Biji (Morfologi Tumbuhan)Document34 pagesBiji (Morfologi Tumbuhan)Nur Hasnah PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary PlantsDocument6 pagesSummary Plantsvictor fdezPas encore d'évaluation
- SN Chapter 3Document90 pagesSN Chapter 3Mohd Razin F2025Pas encore d'évaluation
- First Look Background InformationDocument6 pagesFirst Look Background Informationahuddle1Pas encore d'évaluation
- PteridophytesDocument5 pagesPteridophytesAsif SultanPas encore d'évaluation
- Q2 - W5 Science 5Document48 pagesQ2 - W5 Science 5Mac RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument13 pagesNotes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsAdnan SathikPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Types of PlantsDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of PlantsKen ZiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Sem 3Document13 pagesBiology Sem 3yondaimeredzuan0% (1)
- Tips To Help Kids Learn The Parts of PlantsDocument2 pagesTips To Help Kids Learn The Parts of PlantsMiraflor VirayPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument9 pagesReproduction in Plantsmr. unknownPas encore d'évaluation
- SCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 4Document16 pagesSCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 4Mary Ann Gabion100% (11)
- Science B. G8 3rdDocument16 pagesScience B. G8 3rdBen sik ali mohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument8 pagesIntroductionBanana LattePas encore d'évaluation
- Subject-Biology Chapter - 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument35 pagesSubject-Biology Chapter - 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsNikunj kumar chaurasiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plants ClassificationDocument11 pagesPlants ClassificationLeslie GandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Herbal and Complementary Medicine Dr. Denise K. DaleyDocument92 pagesHerbal and Complementary Medicine Dr. Denise K. DaleyMarquel CulmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Flower Background InfoDocument5 pagesFlower Background Infoahuddle1Pas encore d'évaluation
- About PlantsDocument8 pagesAbout PlantsOana100% (1)
- Activity 7 Angiosperm Plant BodyDocument13 pagesActivity 7 Angiosperm Plant BodyHerlyn SabulaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Plants & Seeds: Prior KnowledgeDocument60 pagesPlants & Seeds: Prior KnowledgeGurpreet Bedi0% (1)
- Classification of PlantsDocument2 pagesClassification of PlantsNhecel PascuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 5 LPDocument7 pagesGrade 5 LPJuhanna Lizl GustiloPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)Document10 pagesReproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)richelyn navalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1&2 ReportDocument28 pagesLesson 1&2 Reportmaria olivia mercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- LP in Science VIDocument5 pagesLP in Science VIJudy C. BelardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproduction in Non Flowering PlantsDocument14 pagesReproduction in Non Flowering Plantsbalderramajoshua10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reproduction of PlantsDocument19 pagesReproduction of PlantsYash Vardhan MundhraPas encore d'évaluation
- A. Abstraction: Sexual ReproductionDocument5 pagesA. Abstraction: Sexual ReproductionJoy MagbutongPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedDocument18 pagesBIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedChristine angel mae BalsomoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Leaf: Short Notes Class 6 ScienceDocument4 pagesThe Leaf: Short Notes Class 6 ScienceParimala DhanasekaranPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationDocument7 pagesI. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationBethymay EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 12 NotesDocument21 pagesCH 12 Noteseepai80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Orca Share Media1645490440596 6901687136957622992Document6 pagesOrca Share Media1645490440596 6901687136957622992Kelly CasterPas encore d'évaluation
- Botany Handbook For Florida PDFDocument23 pagesBotany Handbook For Florida PDFBá Tùng Phan100% (2)
- Agronomy Assignment 3Document3 pagesAgronomy Assignment 3Nguyễn Minh ThànhPas encore d'évaluation
- PLANT BIOLOGY Plant Form and FunctionDocument12 pagesPLANT BIOLOGY Plant Form and FunctionNis DancelPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of A FlowerDocument10 pagesParts of A FlowerAnaly CPas encore d'évaluation
- Alberto P. Navarette Jr. Earth and Life Gas 11 Boyle Mrs. CruzDocument4 pagesAlberto P. Navarette Jr. Earth and Life Gas 11 Boyle Mrs. CruzJobadzPas encore d'évaluation
- PollinationDocument17 pagesPollinationSoumik MahapatroPas encore d'évaluation
- Examining Fruits and FlowersDocument45 pagesExamining Fruits and Flowerscarlos monteaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plants Around YouDocument6 pagesPlants Around YouJovilyn JardielPas encore d'évaluation
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsATHIRA PPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsDocument22 pagesPlant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsLebohang MakhanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- K 2 Fun With FlowersDocument2 pagesK 2 Fun With FlowersMiriam MilaneloPas encore d'évaluation
- Plants WorksheetDocument5 pagesPlants WorksheetRachel LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeDocument9 pagesPlant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeYan DechosPas encore d'évaluation
- Letter 2Document1 pageLetter 2api-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Why The Sky Is BlueDocument1 pageWhy The Sky Is Blueapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trick QuestionDocument1 pageTrick Questionapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- ElectddrolyDocument5 pagesElectddrolyapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- CompareDocument2 pagesCompareapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- LetterDocument1 pageLetterapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- BlogDocument1 pageBlogapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Perception QuestionnaireDocument1 pagePerception Questionnaireapi-3759646100% (1)
- Day 1Document10 pagesDay 1api-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- ANNEDocument5 pagesANNEapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Table of SpecificationDocument3 pagesTable of Specificationapi-375964683% (6)
- PretestQuest 1Document3 pagesPretestQuest 1api-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Conductivity ApparatusDocument4 pagesElectric Conductivity Apparatusapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Conductivity 2Document3 pagesElectrical Conductivity 2api-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation RubricDocument2 pagesPresentation Rubricapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Appedix C Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade V About Plants Day1Document6 pagesAppedix C Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade V About Plants Day1api-375964681% (16)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade V About Plants Day1Document6 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade V About Plants Day1api-3759646100% (7)
- Review of RelDocument4 pagesReview of Relapi-3759646100% (1)
- AppendixDocument2 pagesAppendixapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter IDocument5 pagesChapter Iapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Day 3Document16 pagesDay 3api-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Title PageDocument4 pagesTitle Pageapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter VDocument3 pagesChapter Vapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- ABSTRACTDocument6 pagesABSTRACTapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Third RevisionDocument22 pagesThird Revisionapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4api-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- BibliographyDocument3 pagesBibliographyapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 NajudDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Najudapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Math IV I. ObjectiveDocument8 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Math IV I. Objectiveapi-3759646Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rabbit Meat NutrientsDocument49 pagesRabbit Meat NutrientsAndrea LagdameoPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 6 Chapter 2 History On The Trail of The Earliest PeopleDocument2 pagesGrade 6 Chapter 2 History On The Trail of The Earliest PeopleShambavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Item Promo LocknLock 2022Document3 pagesItem Promo LocknLock 2022Akunting MekarsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Test - LOOK 1Document4 pagesFinal Test - LOOK 1achochiquePas encore d'évaluation
- Stefs ResumeDocument4 pagesStefs Resumeapi-285699130Pas encore d'évaluation
- NG T Đi V I Gi I T - Phrasal VerbsDocument13 pagesNG T Đi V I Gi I T - Phrasal VerbsĐỗ Thị Hồng NguyênPas encore d'évaluation
- Dairy Technology 9002 01 07 2008 GBDocument110 pagesDairy Technology 9002 01 07 2008 GBThaVinci100% (1)
- Powtorki - Gramatyczne - B1 B2 - Pytania I ZaimkiDocument2 pagesPowtorki - Gramatyczne - B1 B2 - Pytania I ZaimkiBeata KucPas encore d'évaluation
- Why It Is Important To Take Care Our HairDocument3 pagesWhy It Is Important To Take Care Our HairKennedy KenPas encore d'évaluation
- Read The Following Texts and Answer Questions Following. Text 1 Is For Questions No 1 - 4Document9 pagesRead The Following Texts and Answer Questions Following. Text 1 Is For Questions No 1 - 4SadirinIrinPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal Pat Bahasa Inggris Kelas XiDocument7 pagesSoal Pat Bahasa Inggris Kelas XiIca KhaefiatunnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Economy in BriefDocument77 pagesAP Economy in Briefdarimadugu100% (1)
- Latihan Soal Procedure TextDocument3 pagesLatihan Soal Procedure Textrais akbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastronomic Tourism, A New Trend For Contemporary Tourism??: Georgică Gheorghe, Petronela Tudorache, Puiu NistoreanuDocument10 pagesGastronomic Tourism, A New Trend For Contemporary Tourism??: Georgică Gheorghe, Petronela Tudorache, Puiu NistoreanuMuhammad RojaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Pricelist Sourire 2023Document26 pagesPricelist Sourire 2023Joysan RLPas encore d'évaluation
- Ficus Carica PDFDocument2 pagesFicus Carica PDFPierrePas encore d'évaluation
- Rejuvenating & Detox Mineral Mask - 1152 Ingredient Function Percent WGT (G) WGT (Oz) Vol (TSP.) Phase ADocument1 pageRejuvenating & Detox Mineral Mask - 1152 Ingredient Function Percent WGT (G) WGT (Oz) Vol (TSP.) Phase AWangari Lothaire RachealPas encore d'évaluation
- Scope and Sequence All Levels Bebop and FriendsDocument24 pagesScope and Sequence All Levels Bebop and FriendsPerla AntiqueraPas encore d'évaluation
- FageDocument8 pagesFageapi-282903171Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses KelompokDocument5 pagesTenses KelompokricodaPas encore d'évaluation
- Canvas Monthly Magazine - February IssueDocument32 pagesCanvas Monthly Magazine - February IssuegoodproducePas encore d'évaluation
- Activities: Quitor, Marjorie M. BSHM 2C HPC 4Document25 pagesActivities: Quitor, Marjorie M. BSHM 2C HPC 4Math TangikPas encore d'évaluation
- Pony Club D Test - Basic Needs of PonyDocument5 pagesPony Club D Test - Basic Needs of Ponyapi-306398192Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cultured Make Healthy Fermented Foods at Home EBook PDFDocument182 pagesCultured Make Healthy Fermented Foods at Home EBook PDFAles Sandra100% (14)
- FST 7 BlueprintDocument15 pagesFST 7 BlueprintArup Roy78% (9)
- Bok:978 81 322 0958 4 PDFDocument304 pagesBok:978 81 322 0958 4 PDFSamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Marc Lobliner - Fat Loss Factor BookDocument77 pagesMarc Lobliner - Fat Loss Factor Bookcleudimartins100% (2)
- Banquet ProtocolDocument11 pagesBanquet ProtocolARUN JOSEPas encore d'évaluation
- Things To Do in LagunaDocument4 pagesThings To Do in LagunaThess Tecla Zerauc AzodnemPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise On Simple PresentDocument5 pagesExercise On Simple PresentTeodor MățăuPas encore d'évaluation