Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Tanawala Chirag (123) Rinkal Patadia
Transféré par
kg101981Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Tanawala Chirag (123) Rinkal Patadia
Transféré par
kg101981Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Tanawala Chirag(123) Rinkal Patadia(81)
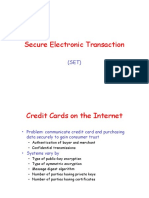
Problem: communicate credit card and purchasing data securely to gain consumer trust Authentication of buyer and merchant Confidential transmissions Systems vary by Type of public-key encryption Type of symmetric encryption Message digest algorithm Number of parties having private keys Number of parties having certificates
SSL 1 or 2 parties have private keys TLS (Transport Layer Security) IETF version of SSL
i KP (IBM) SEPP (Secure Encryption Payment Protocol) MasterCard, IBM, Netscape STT (Secure Transaction Technology) VISA, Microsoft
OBSOLETE
SET (Secure Electronic Transactions) MasterCard, VISA all parties have certificates
VERY SLOW ACCEPTANCE
is a standard protocol for securing credit card transactions over insecure networks, specifically, the Internet Developed by SETco, led by Visa and MasterCard (involving other companies such as IBM, Microsoft, Netscape, Safelayer- formerly SET Projects/ VeriSign) Starting in 1996
Designed to protect credit card transactions Confidentiality: all messages encrypted Trust: all parties must have digital certificates Privacy: information made available only when and where necessary
Participants in the SET System
Provide confidentiality information (payment) Ensure the integrity of all transmitted data Provide authentication that a cardholder is a legitimate user of a credit card account Provide authentication that a merchant can accept credit card transactions through its relationship with a financial institution
SET Transactions
The customer opens an account with a card issuer. MasterCard, Visa, etc.
The customer receives a X.509 V3 certificate signed by a bank. X.509 V3
A merchant who accepts a certain brand of card must possess two X.509 V3 certificates. One for signing & one for key exchange The customer places an order for a product or service with a merchant. The merchant sends a copy of its certificate for verification.
The customer obtains a credit card account with a bank that supports electronic payment and SET Merchants have their own certificates The customer places an order The order and payment are sent The merchant requests payment authorization The merchant confirms the order The merchant ships the goods or provides the service to the customer The merchant requests payment
Concept: Link Two Messages Intended for Two Different Receivers: Order Information (OI): Customer to Merchant Payment Information (PI): Customer to Bank Goal: Limit Information to A Need-to-Know Basis: Merchant does not need credit card number. Bank does not need details of customer order. Afford the customer extra protection in terms of privacy by keeping these items separate. This link is needed to prove that payment is intended for this order and not some other one.
Suppose that customers send the merchant two messages: The signed order information (OI). The signed payment information (PI). In addition, the merchant passes the payment information (PI) to the bank. If the merchant can capture another order information (OI) from this customer, the merchant could claim this order goes with the payment information (PI) rather than the original.
The operation for dual signature is as follows: Take the hash (SHA-1) of the payment and order information. These two hash values are concatenated [H(PI) || H(OI)] and then the result is hashed. Customer encrypts the final hash with a private key creating the dual signature. DS = EKRC [ H(H(PI) || H(OI)) ]
The merchant has the public key of the customer obtained from the customers certificate. Now, the merchant can compute two values: H(PIMD || H(OI)) DKUC[DS] Should be equal!
The bank is in possession of DS, PI, the message digest for OI (OIMD), and the customers public key, then the bank can compute the following: H(H(PI) || OIMD) DKUC [ DS ]
The merchant has received OI and verified the signature. The bank has received PI and verified the signature. The customer has linked the OI and PI and can prove the linkage.
card holder registration merchant registration purchase request
purchase notification sale transaction authorization reversal capture reversal credit reversal
payment authorization
payment capture certificate query purchase inquiry
Simple purchase transaction: Four messages between merchant and customer Two messages between merchant and payment gateway 6 digital signatures 9 RSA encryption/decryption cycles 4 DES encryption/decryption cycles 4 certificate verifications Scaling: Multiple servers need copies of all certificates
CSE 5349/7349
SMU
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Review of Some Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersD'EverandReview of Some Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Electronic TransactionDocument33 pagesSecure Electronic TransactionSnehal SolankePas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To Crypto: The Ultimate Beginners Guide To Cryptocurrency and Its TechnologiesD'EverandIntro To Crypto: The Ultimate Beginners Guide To Cryptocurrency and Its TechnologiesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 (SET)Document20 pagesLecture 5 (SET)kwaheedPas encore d'évaluation
- NSM Lab (Set)Document6 pagesNSM Lab (Set)omkar omiPas encore d'évaluation
- L30 - Secure Electronic TransactionDocument19 pagesL30 - Secure Electronic TransactionShivam KushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Electronic Transactions-SET: January 2017Document23 pagesSecure Electronic Transactions-SET: January 2017Vikas SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) : E-CommerceDocument12 pagesSecure Electronic Transaction (SET) : E-CommercePraveen BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- Nad Ns Unit 4 Part 3Document12 pagesNad Ns Unit 4 Part 3Akshay UtanePas encore d'évaluation
- Credit Card Protocols/ Web Security: SSL, SetDocument20 pagesCredit Card Protocols/ Web Security: SSL, SetAmogh S MirashiPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Electronic TransactionDocument6 pagesSecure Electronic TransactionKirupakaran HarikrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Electronic Transaction: SMU CSE 5349/7349Document33 pagesSecure Electronic Transaction: SMU CSE 5349/7349Sankar RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Electronic Transaction: SMU CSE 5349/7349Document33 pagesSecure Electronic Transaction: SMU CSE 5349/7349DuttaUdayaVenkataChegondiPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Electronic TransactionDocument22 pagesSecure Electronic TransactionRiddhi DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment GatewayDocument25 pagesElectronic Payment GatewayAnvar Vh V HPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Electronic TransactionDocument2 pagesSecure Electronic TransactionAashish SutarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd (Abhis Part) AssignmentDocument3 pages2nd (Abhis Part) AssignmentAbrahmi SelvarajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment On Secure Electronic TransactionDocument10 pagesAssignment On Secure Electronic TransactionSubhash SagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Kuldeep Kumawat: Secure Electronic TransactionDocument10 pagesKuldeep Kumawat: Secure Electronic TransactionKuldeep KumawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - 4 - Internet Payment SystemsDocument49 pagesUnit - 4 - Internet Payment Systemsaruna2707Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment Systems and Security: © Prentice Hall, 2000Document35 pagesElectronic Payment Systems and Security: © Prentice Hall, 2000John MuketsiPas encore d'évaluation
- E - Payment and Security System MbaDocument5 pagesE - Payment and Security System MbaShwetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Electronic Transaction (Set Protocol) : Yang Li & Yun WangDocument16 pagesSecure Electronic Transaction (Set Protocol) : Yang Li & Yun Wangsharma@delhiPas encore d'évaluation
- EypaymentDocument76 pagesEypaymentaxn8inPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport Layer Security (TLS)Document14 pagesTransport Layer Security (TLS)svmc bcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Web Security: Secure Socket Layer (SSL)Document6 pagesWeb Security: Secure Socket Layer (SSL)Lokesh Sai Kumar DasariPas encore d'évaluation
- E Commerce 6Document15 pagesE Commerce 6premaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport Layer Security (TLS)Document14 pagesTransport Layer Security (TLS)svmc bcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment SystemDocument23 pagesElectronic Payment System741Mohd Saif AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment Systems-FinalDocument105 pagesElectronic Payment Systems-Finaldileepvk1978Pas encore d'évaluation
- Web Security: Course: Network Security by DR Adnan NadeemDocument37 pagesWeb Security: Course: Network Security by DR Adnan NadeemKatherine GenailPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment System: Presented byDocument43 pagesElectronic Payment System: Presented bysheetal28svPas encore d'évaluation
- Trends in Information Technology Infrastructure: DR Ritu YadavDocument16 pagesTrends in Information Technology Infrastructure: DR Ritu YadavsudhanshuPas encore d'évaluation
- E CommerceDocument7 pagesE CommerceNimya RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment Systems-FinalDocument105 pagesElectronic Payment Systems-FinalDileep VkPas encore d'évaluation
- E COMMERCE FINAL COVERAGE MODULE 1 and 2Document9 pagesE COMMERCE FINAL COVERAGE MODULE 1 and 2BRIAN CORPUZ INCOGNITOPas encore d'évaluation
- 1256450638lesson 3 - E-Commerce Payment SystemsDocument16 pages1256450638lesson 3 - E-Commerce Payment SystemsAvinash ShelkePas encore d'évaluation
- PIS Module 6Document42 pagesPIS Module 6Zayn TawfikPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment Systems: MBA EX 9607 - Managing E-BusinessDocument32 pagesElectronic Payment Systems: MBA EX 9607 - Managing E-BusinessAshutosh SinghalPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment SystemDocument23 pagesElectronic Payment SystemSongs Punjabi SharePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit II PDFDocument11 pagesUnit II PDFPrameela KPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecommerce E Payments - Payment Gateway - Ebusiness Transaction ProcessingDocument19 pagesEcommerce E Payments - Payment Gateway - Ebusiness Transaction ProcessingJyotindra Zaveri E-Library100% (3)
- Unit-V: Electronic Payment SystemsDocument28 pagesUnit-V: Electronic Payment SystemsimmadhiPas encore d'évaluation
- ECommerce Unit 2Document21 pagesECommerce Unit 2Prabakaran VPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment Systems and SecurityDocument36 pagesElectronic Payment Systems and SecurityPaksmilerPas encore d'évaluation
- E-Business For Hospitality 5Document20 pagesE-Business For Hospitality 5Tsea CaronPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment Systems: Bachu Vinay Chaithanya (1421408)Document12 pagesElectronic Payment Systems: Bachu Vinay Chaithanya (1421408)Utkaljyoti JenasamantPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecom 3Document10 pagesEcom 3Rachit SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment Mechanisms:: Submitted by Group 5Document24 pagesElectronic Payment Mechanisms:: Submitted by Group 5Pinak MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment SystemDocument21 pagesElectronic Payment SystemHaidarPas encore d'évaluation
- E Commerce Notes Chapter 5-10Document5 pagesE Commerce Notes Chapter 5-10Taniya Bhalla100% (1)
- Secure E-Cheque Clearance Between Financial InstitutionsDocument18 pagesSecure E-Cheque Clearance Between Financial InstitutionsAmith Ram ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- E-Commerce - BUS426 - Topic 3Document44 pagesE-Commerce - BUS426 - Topic 3Atease ProductionPas encore d'évaluation
- SwiftDocument96 pagesSwiftVenkat Baliga86% (7)
- Web Security: Prepared By, R.S.Rampriya/CseDocument46 pagesWeb Security: Prepared By, R.S.Rampriya/CseVishalini ChinnathuraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Payment SystemDocument33 pagesElectronic Payment SystemGunjan JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Traditional and Electronic Payment MethodsDocument35 pagesTraditional and Electronic Payment Methodsarshiyashah50% (2)
- Web SecurityDocument23 pagesWeb SecurityBruno BlayPas encore d'évaluation
- Cryptography and Network Security: Fourth Edition by William StallingsDocument24 pagesCryptography and Network Security: Fourth Edition by William Stallingskstu1112Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-4 E-Commerce (PDF - Io) - 1Document6 pagesUnit-4 E-Commerce (PDF - Io) - 1rahuldodiyat001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bank Locker Security System Based On Two-Factor AuthenticationDocument8 pagesBank Locker Security System Based On Two-Factor AuthenticationBELLA JACOBPas encore d'évaluation
- Form LRA 87Document2 pagesForm LRA 87Godfrey ochieng modi67% (3)
- PKI SecurityDocument64 pagesPKI SecurityVivien Di100% (1)
- Register: Welcome To NBI CLEARANCE ONLINE SERVICES You Can Now Apply Online. Anytime. AnywhereDocument1 pageRegister: Welcome To NBI CLEARANCE ONLINE SERVICES You Can Now Apply Online. Anytime. AnywhereNOELGREGORIOPas encore d'évaluation
- Bitcoin NSADocument5 pagesBitcoin NSAbimbaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Alarme Password WcdmaDocument2 pagesAlarme Password WcdmaJoaquim PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- April Bs and CashbookDocument797 pagesApril Bs and CashbookBoyi Enebinelson0% (1)
- Thor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 5Document18 pagesThor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 5babyPas encore d'évaluation
- Doge Chain WPDocument21 pagesDoge Chain WPEthan GooberPas encore d'évaluation
- Hybrid Approach To Minimize 51 Attack in CryptocurrenciesDocument4 pagesHybrid Approach To Minimize 51 Attack in CryptocurrenciesArun SPas encore d'évaluation
- Credenatials UpdatedDocument10 pagesCredenatials UpdatedVPLAN INFOTECHPas encore d'évaluation
- EUR Statement: Halvard SolbergDocument11 pagesEUR Statement: Halvard Solbergtomasvetlana31Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aneka Soal Ujian Sistem Operasi: Security, Protection, Privacy & CDocument5 pagesAneka Soal Ujian Sistem Operasi: Security, Protection, Privacy & CRahmat M. Samik-IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Key ProcedureDocument7 pagesDigital Key Procedureavsrao123Pas encore d'évaluation
- CV 1Document5 pagesCV 1Mirza Muhammad BaigPas encore d'évaluation
- Coinmarketcap Com Currencies SolanaDocument7 pagesCoinmarketcap Com Currencies SolanaAaatv AaabbbPas encore d'évaluation
- Parcial Resuelto Ingles Tecnico 1 Adm. Emp. Preguntas 1-2-3Document4 pagesParcial Resuelto Ingles Tecnico 1 Adm. Emp. Preguntas 1-2-3Valentin MacagnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gauripur: Dhubri District (Assam E-District Project)Document1 pageGauripur: Dhubri District (Assam E-District Project)vishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Web3 and DeFi ApplicationsDocument59 pagesWeb3 and DeFi ApplicationsalabbbPas encore d'évaluation
- Crypto Theft Incidents Timeline, Kyle S Gibson - Draft 2 Mar 19, 2019Document38 pagesCrypto Theft Incidents Timeline, Kyle S Gibson - Draft 2 Mar 19, 2019Kyle GibsonPas encore d'évaluation
- PCI DSS Gap Analysis Checklist Ver 1.0Document31 pagesPCI DSS Gap Analysis Checklist Ver 1.0Horace Paredes NavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Booking ProcessDocument10 pagesPre Booking ProcessRajat AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Omnibus Certification of Authenticity and Veracity of Documents v3Document1 pageOmnibus Certification of Authenticity and Veracity of Documents v3TV - Project 26Pas encore d'évaluation
- WebTicket Indemnity FormDocument1 pageWebTicket Indemnity FormTaif KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- T24 BiDocument2 pagesT24 BiSyed Muhammad Ali SadiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Modelo Carta ConviteDocument3 pagesModelo Carta ConviteVeronica CappaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Romney Ais13 PPT 06 UIC CustomDocument9 pagesRomney Ais13 PPT 06 UIC Customtarawneh92Pas encore d'évaluation
- VAHAN 4.0 (Citizen Services) SP-MORTH-WS03 175 8015Document1 pageVAHAN 4.0 (Citizen Services) SP-MORTH-WS03 175 8015krishna salesPas encore d'évaluation
- Correction Application in Birth Teor+certificateDocument3 pagesCorrection Application in Birth Teor+certificateParesh NaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Crypto Chart PatternsDocument5 pagesCrypto Chart PatternsYeshab BhattiPas encore d'évaluation