Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Phy Outline Ch17 STP
Transféré par
Mimi SuuDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Phy Outline Ch17 STP
Transféré par
Mimi SuuDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Preview
Multiple Choice Short Response Extended Response
Chapter 17 Multiple Choice
Standardized Test Prep
1. What changes would take place if the electron moved from point A to point B in the uniform electric field? A. The electrons electrical potential energy would increase; its electric potential would increase. B. The electrons electrical potential energy would increase; its electric potential would decrease. C. The electrons electrical potential energy would decrease; its electric potential would decrease. D. Neither the electrons electrical potential energy nor its electric potential would change.
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
1. What changes would take place if the electron moved from point A to point B in the uniform electric field? A. The electrons electrical potential energy would increase; its electric potential would increase. B. The electrons electrical potential energy would increase; its electric potential would decrease. C. The electrons electrical potential energy would decrease; its electric potential would decrease. D. Neither the electrons electrical potential energy nor its electric potential would change.
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
2. What changes would take place if the electron moved from point A to point C in the uniform electric field? F. The electrons electrical potential energy would increase; its electric potential would increase. G. The electrons electrical potential energy would increase; its electric potential would decrease. H. The electrons electrical potential energy would decrease; its electric potential would decrease. J. Neither the electrons electrical potential energy nor its electric potential would change.
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
2. What changes would take place if the electron moved from point A to point C in the uniform electric field? F. The electrons electrical potential energy would increase; its electric potential would increase. G. The electrons electrical potential energy would increase; its electric potential would decrease. H. The electrons electrical potential energy would decrease; its electric potential would decrease. J. Neither the electrons electrical potential energy nor its electric potential would change.
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
Use the following passage to answer questions 34. A proton (q = 1.6 1019 C) moves 2.0 106 m in the direction of an electric field that has a magnitude of 2.0 N/C. 3. What is the change in the electrical potential energy associated with the proton? A. 6.4 1025 J B. 4.0 106 V C. +6.4 1025 J D. +4.0 106 V
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
Use the following passage to answer questions 34. A proton (q = 1.6 1019 C) moves 2.0 106 m in the direction of an electric field that has a magnitude of 2.0 N/C. 3. What is the change in the electrical potential energy associated with the proton? A. 6.4 1025 J B. 4.0 106 V C. +6.4 1025 J D. +4.0 106 V
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
Use the following passage to answer questions 34. A proton (q = 1.6 1019 C) moves 2.0 106 m in the direction of an electric field that has a magnitude of 2.0 N/C. 4. What is the potential difference between the protons starting point and ending point? F. 6.4 1025 J G. 4.0 106 V H. +6.4 1025 J J. +4.0 106 V
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
Use the following passage to answer questions 34. A proton (q = 1.6 1019 C) moves 2.0 106 m in the direction of an electric field that has a magnitude of 2.0 N/C. 4. What is the potential difference between the protons starting point and ending point? F. 6.4 1025 J G. 4.0 106 V H. +6.4 1025 J J. +4.0 106 V
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
5. If the negative terminal of a 12 V battery is grounded, what is the potential of the positive terminal? A. 12 V B. +0 V C. +6 V D. +12 V
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
5. If the negative terminal of a 12 V battery is grounded, what is the potential of the positive terminal? A. 12 V B. +0 V C. +6 V D. +12 V
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
6. If the area of the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is doubled while the spacing between the plates is halved, how is the capacitance affected? F. C is doubled G. C is increased by four times H. C is decreased by 1/4 J. C does not change
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
6. If the area of the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is doubled while the spacing between the plates is halved, how is the capacitance affected? F. C is doubled G. C is increased by four times H. C is decreased by 1/4 J. C does not change
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
Use the following passage to answer questions 78. A potential difference of 10.0 V exists across the plates of a capacitor when the charge on each plate is 40.0 C. 7. What is the capacitance of the capacitor? A. 2.00 104 F B. 4.00 104 F C. 2.00 106 F D. 4.00 106 F
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
Use the following passage to answer questions 78. A potential difference of 10.0 V exists across the plates of a capacitor when the charge on each plate is 40.0 C. 7. What is the capacitance of the capacitor? A. 2.00 104 F B. 4.00 104 F C. 2.00 106 F D. 4.00 106 F
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
Use the following passage to answer questions 78. A potential difference of 10.0 V exists across the plates of a capacitor when the charge on each plate is 40.0 C. 8. How much electrical potential energy is stored in the capacitor? F. 2.00 104 J G. 4.00 104 J H. 2.00 106 J J. 4.00 106 J
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
Use the following passage to answer questions 78. A potential difference of 10.0 V exists across the plates of a capacitor when the charge on each plate is 40.0 C. 8. How much electrical potential energy is stored in the capacitor? F. 2.00 104 J G. 4.00 104 J H. 2.00 106 J J. 4.00 106 J
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
9. How long does it take 5.0 C of charge to pass through a given cross section of a copper wire if I = 5.0 A? A. 0.20 s B. 1.0 s C. 5.0 s D. 25 s
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
9. How long does it take 5.0 C of charge to pass through a given cross section of a copper wire if I = 5.0 A? A. 0.20 s B. 1.0 s C. 5.0 s D. 25 s
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
10. A potential difference of 12 V produces a current of 0.40 A in a piece of copper wire. What is the resistance of the wire? F. 4.8 G. 12 H. 30 J. 36
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
10. A potential difference of 12 V produces a current of 0.40 A in a piece of copper wire. What is the resistance of the wire? F. 4.8 G. 12 H. 30 J. 36
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
11. How many joules of energy are dissipated by a 50.0 W light bulb in 2.00 s? A. 25.0 J B. 50.0 J C. 100 J D. 200 J
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
11. How many joules of energy are dissipated by a 50.0 W light bulb in 2.00 s? A. 25.0 J B. 50.0 J C. 100 J D. 200 J
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
12. How much power is needed to operate a radio that draws 7.0 A of current when a potential difference of 115 V is applied across it? F. 6.1 102 W G. 2.3 100 W H. 1.6 101 W J. 8.0 102 W
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Multiple Choice, continued
12. How much power is needed to operate a radio that draws 7.0 A of current when a potential difference of 115 V is applied across it? F. 6.1 102 W G. 2.3 100 W H. 1.6 101 W J. 8.0 102 W
Chapter 17 Short Response
Standardized Test Prep
13. Electrons are moving from left to right in a wire. No other charged particles are moving in the wire. In what direction is the conventional current?
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Short Response, continued
13. Electrons are moving from left to right in a wire. No other charged particles are moving in the wire. In what direction is the conventional current?
Answer: right to left
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Short Response, continued
14. What is drift velocity, and how does it compare with the speed at which an electric field travels through a wire?
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Short Response, continued
14. What is drift velocity, and how does it compare with the speed at which an electric field travels through a wire?
Answer: Drift velocity is the net velocity of a charge carrier moving in an electric field. Drift velocities in a wire are typically much smaller than the speeds at which changes in the electric field propagate through the wire.
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Short Response, continued
15. List four factors that can affect the resistance of a wire.
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Short Response, continued
15. List four factors that can affect the resistance of a wire. Answer: length, cross-sectional area (thickness), temperature, and material
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Extended Response
16. A parallel-plate capacitor is made of two circular plates, each of which has a diameter of 2.50 103 m. The plates of the capacitor are separated by a space of 1.40 104 m. a. Assuming that the capacitor is operating in a vacuum and that the permittivity of a vacuum (e0 = 8.85 1012 C2/Nm2) can be used, determine the capacitance of the capacitor.
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Extended Response, continued
16. A parallel-plate capacitor is made of two circular plates, each of which has a diameter of 2.50 103 m. The plates of the capacitor are separated by a space of 1.40 104 m. a. Assuming that the capacitor is operating in a vacuum and that the permittivity of a vacuum (e0 = 8.85 1012 C2/Nm2) can be used, determine the capacitance of the capacitor. Answer: 3.10 1013 F
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Extended Response, continued
16. A parallel-plate capacitor is made of two circular plates, each of which has a diameter of 2.50 103 m. The plates of the capacitor are separated by a space of 1.40 104 m. b. How much charge will be stored on each plate of the capacitor when the capacitors plates are connected across a potential difference of 0.12 V?
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Extended Response, continued
16. A parallel-plate capacitor is made of two circular plates, each of which has a diameter of 2.50 103 m. The plates of the capacitor are separated by a space of 1.40 104 m. b. How much charge will be stored on each plate of the capacitor when the capacitors plates are connected across a potential difference of 0.12 V? Answer: 3.7 1014 C
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Extended Response, continued
16. A parallel-plate capacitor is made of two circular plates, each of which has a diameter of 2.50 103 m. The plates of the capacitor are separated by a space of 1.40 104 m. c. What is the electrical potential energy stored in the capacitor when fully charged by the potential difference of 0.12 V?
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Extended Response, continued
16. A parallel-plate capacitor is made of two circular plates, each of which has a diameter of 2.50 103 m. The plates of the capacitor are separated by a space of 1.40 104 m. c. What is the electrical potential energy stored in the capacitor when fully charged by the potential difference of 0.12 V? Answer: 2.2 1015 J
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Extended Response, continued
16. A parallel-plate capacitor is made of two circular plates, each of which has a diameter of 2.50 103 m. The plates of the capacitor are separated by a space of 1.40 104 m. d. What is the potential difference between a point midway between the plates and a point that is 1.10 104 m from one of the plates?
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Extended Response, continued
16. A parallel-plate capacitor is made of two circular plates, each of which has a diameter of 2.50 103 m. The plates of the capacitor are separated by a space of 1.40 104 m. d. What is the potential difference between a point midway between the plates and a point that is 1.10 104 m from one of the plates? Answer: 3.4 102 V
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Extended Response, continued
16. A parallel-plate capacitor is made of two circular plates, each of which has a diameter of 2.50 103 m. The plates of the capacitor are separated by a space of 1.40 104 m. e. If the potential difference of 0.12 V is removed from the circuit and the circuit is allowed to discharge until the charge on the plates has decreased to 70.7 percent of its fully charged value, what will the potential difference across the capacitor be?
Chapter 17
Standardized Test Prep
Extended Response, continued
16. A parallel-plate capacitor is made of two circular plates, each of which has a diameter of 2.50 103 m. The plates of the capacitor are separated by a space of 1.40 104 m. e. If the potential difference of 0.12 V is removed from the circuit and the circuit is allowed to discharge until the charge on the plates has decreased to 70.7 percent of its fully charged value, what will the potential difference across the capacitor be? Answer: 8.5 102 V
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CH 17 PPT QuestionsDocument41 pagesCH 17 PPT QuestionsSherline OliviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Xii PhysicsDocument9 pagesXii PhysicsLalu kuttyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ett Study GuideDocument8 pagesEtt Study Guidepatitay036817Pas encore d'évaluation
- Angel Education Half Yearly Exam Physics 2017-2018Document3 pagesAngel Education Half Yearly Exam Physics 2017-2018Atul Verma0% (1)
- Reduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Document15 pagesReduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Saher SaghirPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDocument128 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesraghudatheshPas encore d'évaluation
- D. The Field Strength Is Zero at All Points Where The Potential Is ZeroDocument3 pagesD. The Field Strength Is Zero at All Points Where The Potential Is ZeroKamran AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Electronics I Model KIoTDocument9 pagesApplied Electronics I Model KIoTERMIAS AmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Questions Set 4 (Physics Only)Document2 pagesMultiple Choice Questions Set 4 (Physics Only)librahimliPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase - 5Document54 pagesPhase - 5Sriram GangulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 - Physics - Semiconductor Electronic - Material, Devices and Simple CircuitsDocument14 pagesClass 12 - Physics - Semiconductor Electronic - Material, Devices and Simple CircuitsSOUMYA SHOUVIKPas encore d'évaluation
- SH 1Document9 pagesSH 1moh99eidPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric PotentialDocument4 pagesElectric PotentialEman AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ADS Past PaperDocument6 pagesPhysics ADS Past Paperkhanrameen747Pas encore d'évaluation
- HSSC 2 Phy Paper PreboardDocument4 pagesHSSC 2 Phy Paper PreboardEman AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Bank Soal Electric CircuitDocument25 pagesBank Soal Electric CircuitRudi BerlianPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper with SolutionsDocument20 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper with SolutionsANUP KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDocument128 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDilip TheLipPas encore d'évaluation
- Resources Chapter 32 StudentDocument3 pagesResources Chapter 32 StudentJA55EEPas encore d'évaluation
- XII Physics Q. Paper PB 1Document9 pagesXII Physics Q. Paper PB 1Gillu SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5-8Document10 pagesChapter 5-8Besu FikadPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 09 - GeneratorDocument5 pagesLab 09 - GeneratorChristopher SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics Engineering FundamentalsDocument77 pagesElectronics Engineering FundamentalsLeonard Jobet Villaflor PantonPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Energy and Capacitance ReviewDocument9 pagesElectrical Energy and Capacitance ReviewReymond CañoneroPas encore d'évaluation
- Apeejay School, Saket First Terminal Examination - 2016: Class Xii (Physics) General InstructionsDocument4 pagesApeejay School, Saket First Terminal Examination - 2016: Class Xii (Physics) General InstructionsabhilashagoelPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Circuits Part 9 REE Board ExamDocument23 pagesDC Circuits Part 9 REE Board ExamJay TabagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 12 Hot PhysicsDocument50 pagesPhysics 12 Hot PhysicsdhirendrasisodiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engineering Board Examination Review QuestionsDocument9 pagesElectrical Engineering Board Examination Review QuestionsHary Kriz100% (1)
- Physics (Electricity)Document46 pagesPhysics (Electricity)Ruchit YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- PINOYBIX3Document4 pagesPINOYBIX3andreareyesmalinao7Pas encore d'évaluation
- FT Gr-12 SET ADocument8 pagesFT Gr-12 SET ARAIRSPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ in Electricity and Magnetism Fundamentals Part 9 ECE Board ExamDocument18 pagesMCQ in Electricity and Magnetism Fundamentals Part 9 ECE Board ExamJirah GicangaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Board EeDocument119 pagesPre Board EeJohn Lloyd Santos75% (4)
- CBSE Physics Sample Paper TitleDocument11 pagesCBSE Physics Sample Paper TitleKOMAL NAVARIYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Adobe Scan 07 May 2021Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 07 May 2021Gautam ukeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24Document3 pagesClass 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24PrincePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 (Alternating Current) UnsolvedDocument7 pagesChapter 7 (Alternating Current) UnsolvedB. VivekPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Quiz Set 4 (Physics Only)Document14 pagesMultiple Choice Quiz Set 4 (Physics Only)librahimliPas encore d'évaluation
- Villamor Test - 2 PDFDocument18 pagesVillamor Test - 2 PDFLocrian IonianPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial QuestionsDocument20 pagesTutorial Questionsharshiika kathiravanPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Practical Viva 1 PDFDocument11 pagesPhysics Practical Viva 1 PDFJamuna BeheraPas encore d'évaluation
- ExtcDocument10 pagesExtcPrathamesh KeluskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse Class 12 Sample Paper 2017 18 Physics PDFDocument9 pagesCbse Class 12 Sample Paper 2017 18 Physics PDFIshika SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Re-Sendup Syllabus Part 12 23-24Document6 pagesRe-Sendup Syllabus Part 12 23-24azharhajana123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 Set 4Document34 pages2020 Set 4Giridhar MeruvalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Class XII - Sample Question Paper Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsDocument4 pagesPhysics Class XII - Sample Question Paper Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructionstreemango396Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cusat 2016Document37 pagesCusat 2016sreejitha KPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Lyp Physics s1Document7 pages12 Lyp Physics s1jashwanth kumar58Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics QDocument2 pagesPhysics QDhruv AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Ct2bDocument5 pagesElectronic Ct2bAtanazar YoldashovPas encore d'évaluation
- 12th Sept TestDocument4 pages12th Sept TestNouran ElrafiePas encore d'évaluation
- PRE BOARD EE (No Solutions)Document121 pagesPRE BOARD EE (No Solutions)John Lloyd Santos0% (1)
- Electronic DevicesDocument36 pagesElectronic DevicesGiridhar MeruvalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gibilisco: MCQ in Resistors - ECE Board ExamDocument4 pagesGibilisco: MCQ in Resistors - ECE Board Examandreareyesmalinao7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ece-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDocument238 pagesEce-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesShubhesh SwainPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics Solved Question BankDocument6 pagesBasic Electronics Solved Question BankosamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engineering Principles for Technicians: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionD'EverandElectrical Engineering Principles for Technicians: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (4)
- 85 Describing Motion OrganizerDocument10 pages85 Describing Motion OrganizerFernando Sorto50% (2)
- Testing of Rigid Plastic ContainersDocument22 pagesTesting of Rigid Plastic ContainersBhupendra Singh100% (12)
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University KakinadaDocument4 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University KakinadaVenkat ChadalavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Filter Vessel Calculations Per As Me Viii 1Document40 pagesFilter Vessel Calculations Per As Me Viii 1Anonymous J1vjrU2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solar System and Astronomy FactsDocument535 pagesSolar System and Astronomy FactsKavita KrishnamorthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Elders Ray SYstemsDocument7 pagesElders Ray SYstemssagarmkale4395Pas encore d'évaluation
- Partial Differential Equations Formula SheetDocument3 pagesPartial Differential Equations Formula SheetnewyorkstudyPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamic Study On Density and Viscosity of Binary Mixtures of Ethyl Acetoacetate With (C4-C9) Aliphatic Ketones at (303.15 and 308.15) KDocument17 pagesThermodynamic Study On Density and Viscosity of Binary Mixtures of Ethyl Acetoacetate With (C4-C9) Aliphatic Ketones at (303.15 and 308.15) KInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
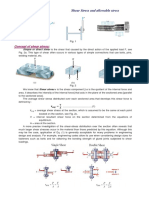
- LECTURE 3 - Shear Stress & Allowable StressDocument15 pagesLECTURE 3 - Shear Stress & Allowable StressIhab OmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Teacher Guide Activity 2 AccelerationDocument4 pagesTeacher Guide Activity 2 AccelerationCanada Railway TimesPas encore d'évaluation
- System Modelling and SimulationDocument260 pagesSystem Modelling and SimulationArvind Kumar100% (13)
- Parameter Estimation of Single Diode PV Module Based On GWO AlgorithmDocument12 pagesParameter Estimation of Single Diode PV Module Based On GWO AlgorithmFelicia Itusaca CcariPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 Energy 03 Complementary Strain Energy PDFDocument2 pages08 Energy 03 Complementary Strain Energy PDFjack_hero_56Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diketopiperazines RevDocument27 pagesDiketopiperazines RevIsaí MillánPas encore d'évaluation
- Mean Deviation - Wolfram MathWorldDocument4 pagesMean Deviation - Wolfram MathWorldbraulio.dantas-1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Composite Beams & Columns To Eurocode 4Document155 pagesComposite Beams & Columns To Eurocode 4dfdfdfasd324sad100% (2)
- Radar Systems Range Equation PDFDocument6 pagesRadar Systems Range Equation PDFSanjid ElahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of CT and CT TechnologyDocument15 pagesPrinciples of CT and CT TechnologyLida Velasquez SierraPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti Derivative Chain RuleDocument4 pagesAnti Derivative Chain Ruletutorciecle123Pas encore d'évaluation
- PEGN 419 / GPGN 419 Spring 2017: Manika Prasad Mansur Ermila Expert Resource: Robert LieberDocument30 pagesPEGN 419 / GPGN 419 Spring 2017: Manika Prasad Mansur Ermila Expert Resource: Robert LiebertahermohPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature SurveyDocument6 pagesLiterature SurveyAnonymous j0aO95fgPas encore d'évaluation
- Atlas TechNotes - Complete Set Rev Nov 2011Document50 pagesAtlas TechNotes - Complete Set Rev Nov 2011caod1712Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing Effective Surface Areas of Random PackingsDocument10 pagesComparing Effective Surface Areas of Random PackingsAntonio MezzopretePas encore d'évaluation
- Notesch # 18Document11 pagesNotesch # 18ZeeshanMahdiPas encore d'évaluation
- BS 476.6 PDFDocument10 pagesBS 476.6 PDFJmc NarelaPas encore d'évaluation
- GannZilla User GuideDocument20 pagesGannZilla User GuideNiladri Jana100% (26)
- SRS 413Document158 pagesSRS 413edderguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Approximations and Simplified Equations SPRING 2019Document12 pagesApproximations and Simplified Equations SPRING 2019Kula Segara PandiyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Judo Bio MechanicsDocument11 pagesJudo Bio MechanicsAttilio Sacripanti100% (6)
- Jar TestDocument1 pageJar TestEduardo Tonino Chavez GaytanPas encore d'évaluation